The hard drive should eventually be divided into two drives C and D:
- C - for DOS (file system FAT16);
- D - for Win XP (FAT32 or NTFS it all depends on whether you need to see it from under DOS or not).
Laptop with floppy drive, you will need:
- Boot files (system files command. com);
- fdisk;
- Format.
Laptop without floppy drive, you will need:
- Boot disk (WinXP or Win98);
- Program partitionmagic;
- Norton or Volkov commander.
As practice has shown, it is not possible to boot from new ZVER DVD boot disks
Stage 1 (disk cleaning)
Cleaning options are:
- Win XP installation disk;
- partition magic program.
We clean the hard drive through the installation of win XP
In fact, we won’t install anything, we’ll just get to the stage when we are given a choice of found OSes and found disks, where we will delete them all.
We boot from the XP disk, start the installation, as soon as we find the installed OS on our hard drive, delete all the partitions that are (as well as all the marked areas, they are not needed)
The drive must remain unpartitioned without any C or D drives (blank, empty, unformatted)
Formatting through this disk will not work, since it only formats at least underFAT32, and we have currentFAT16 will do.
We start it, we begin to divide the hard disk, well, the most important thing here is to create the main Active section for DOS (only 1-2 Gb can be allocated for it)
The rest of the space can not be split or divided, it will be occupied by Win XP
We clean the hard drive through the partition magic program
After installation Microsoft programs Undelete, Microsoft Anti-Virus and Microsoft Backup, a "Microsoft Tools" group containing their icons is added to the main Program Manager window. The "Tools" menu is added to the main Program Manager menu.
- new version of EMM386.EXE driver;
The new version of the EMM386.EXE driver provides access to more upper memory blocks. This frees up more main memory for MS-DOS programs.
- new versions of LOADHIGH and DEVICEHIGH commands;
Newer versions of the LOADHIGH and DEVICEHIGH commands allow you to specify the location in memory where programs and drivers are loaded.
- usage optimizer random access memory computer - program MemMaker;
MS-DOS version 6.0 includes the MemMaker program, which allows computers with 80386 and higher processors to optimize the use of RAM. MemMaker adjusts the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files so that drivers and resident programs are loaded into extended memory whenever possible. This increases the amount of main RAM available to MS-DOS programs.
- the possibility of step-by-step execution of commands in the CONFIG.SYS file.
If you press a key when the operating system is booting, when the screen displays the inscription "Starting MS-DOS ...", then in this case the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT configuration files will not be executed and the MS-DOS prompt will immediately appear.
You can also step through the commands in the CONFIG.SYS file, confirming that each command has been executed. To do this, at the time of loading MS-DOS, you need to press a key.
The next command will be displayed on the screen followed by the menu "?". If you now press the key, the command will be executed, and if you press the command, the command will be skipped. After executing all the commands of the CONFIG.SYS file, the message "Process AUTOEXEC.BAT ?" will appear on the screen. To switch to executing the commands of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, press the key. If you do not wish to execute AUTOEXEC.BAT, press the key.
9.7. How to create a menu in CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT
menuitem=Windows, Windows Configuration menuitem=Lexicon, Lexicon Configuration menuitem=Standart, Standard Configuration device=c:\dos\himem.sys dos=high buffers=15 device=c:dos\emm386 NOEMS dos=high,umb devicehigh =c:\dos\SMARTDRV.EXE 2048 1024 device=c:\dos\SMARTDRV.EXE 2048 device=c:\dos\setver.sys device=c:dos\emm386 NOEMS dos=high,umb devicehigh=c:\ dos\SMARTDRV.EXE 2048 devicehigh=c:\dos\setver.sys files=40This CONFIG.SYS file contains descriptions of three different configurations - configuration for working in the environment of the Windows operating system, configuration for working with word processor Lexicon and configurations for working in the MS-DOS operating system.
For all three configurations, the commands in the block are executed. There are two commands there: DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS and DOS=HIGH. These commands load the extended memory manager HIMEM.SYS, and enable MS-DOS to use the high memory area (HMA).
After executing these two commands, the main menu appears on the screen, defined in the block:
_ Configuration for Windows Configuration for Lexicon Standard configurationWhen you have selected the configuration you wish to download, press the key. After that, the commands from the block corresponding to the selected menu item - , or will be executed.
Finally, the files=40 command located in the last block is executed. This completes the interpretation of the CONFIG.SYS file and MS-DOS starts executing the batch file AUTOEXEC.BAT.
You can optionally branch within the AUTOEXEC.BAT file based on the configuration selected from the CONFIG.SYS file menu. The special environment variable CONFIG is intended for this purpose. When executing commands in the CONFIG.SYS file, the CONFIG variable is set to the name of the selected configuration block.
In the batch file AUTOEXEC.BAT you can check the value of the CONFIG variable and execute various commands depending on its value. You can use the and commands to check the status of the CONFIG environment variable.
Let's take AUTOEXEC.BAT as an example for the previous example.
set temp=c:\temp c:\dos\mode >nul CON CP PREP=((866) c:\dos\ega.cpi) c:\dos\mode >nul CON CP SEL=866 loadhigh c:\ut \swakeyb.com rem !!! Let's move on to the label corresponding to the value of rem !!! environment variable CONFIG goto %config% :Windows path c:\win;c:\dos;e:\nc;c:\ut;d:\nu7;e:\bc\bin;d:\winword; loadhigh c:\win\SMARTDRV.EXE 2048 1024 loadhigh c:\win\mouse.com win goto end_ :Lexicon path c:\lex;c:\dos;e:\nc;c:\ut;d:\nu7 ;e:\bc\bin; c:\dos\SMARTDRV.EXE 2048 c:\mouse\mouse.com lex goto end:Standart path c:\dos;e:\nc;c:\ut;d:\nu7;e:\bc\bin; loadhigh c:\dos\SMARTDRV.EXE 2048 loadhigh c:\mouse\mouse.com nc goto end:endWhen MS-DOS starts executing commands from the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, the TEMP environment variable is set first, then fonts containing Cyrillic characters are loaded.
Then, with the GOTO %CONFIG% command, control is transferred to the label corresponding to the name of the selected configuration block. The configuration block names are listed in the menu description block in the CONFIG.SYS file.
Thus, depending on which configuration is selected in the menu, control will be transferred to one of three labels - Windows, Lexicon or Standard. In this case, only its own commands are executed for each configuration. After executing the commands following the labels, control passes to the END label and the execution of the batch file AUTOEXEC.BAT ends.
For example, if, when interpreting the CONFIG.SYS file, you select the main menu item labeled "Configuration for Windows", then the CONFIG environment variable will be set to Windows and control will go to the label:Windows.
Here the PATH environment variable is set, the disk cache driver and the mouse driver are loaded. Then the Windows operating system is loaded.
9.8. Why are there no Russian characters in MS-DOS?
The set of characters that can be displayed on your computers screen in MS-DOS text and graphics modes is located on the read-only memory (ROM) chip on the video adapter.
The Windows operating system, unlike MS-DOS, does not use characters from the video adapter's ROM. To display characters, Windows uses font sets stored in special files.
Usually, the so-called standard extended set of ASCII characters is stored in the ROM of the video adapter. This set does not contain Cyrillic characters and therefore the computer cannot display them on the display screen.
To "russify" video adapters, you can either reprogram the adapter's ROM, or use special resident programs that replace the video adapter character set with your own.
"Russification" of video adapters at the ROM level allows you to save a few kilobytes of computer RAM in the future, since there is no need to use special resident programs. In addition, if you are unlucky and have a CGA or Hercules video adapter installed on your computer, then flashing the ROM is the only possibility (except, of course, replacing the video adapter, which, by the way, is preferable in this case) to display Cyrillic characters in text modes.
However, flashing the video adapter's ROM requires special hardware and information about the location of the font set in the ROM. Thus, flashing a ROM is a very difficult task and can only be performed by highly qualified specialists.
When "russifying" the video adapter with the help of special programs, it is necessary to load a small resident module into the computer's RAM. This resident module will replace the character set stored in the video adapter's ROM.
In the "How to Russify MS-DOS" section, the process of Russifying a video adapter will be described in more detail.
In addition to Russification of the video adapter, it is necessary to "Russify" the computer keyboard. Usually keyboards do not contain special keys for entering Russian characters. Special resident programs are designed to "russify" the keyboard. Once loaded, they remain in RAM and track the user pressing a specific key combination, such as the right key and the left key. After the user presses this key combination, the characters corresponding to the keyboard keys are redefined.
Now pressing the keyboard keys will cause the input of not Latin, but Russian characters. Usually, the keys are reassigned in accordance with the domestic standard for typewriters ("YTSUKEN"). Next to the Latin characters located on the keyboard keys, we recommend placing stickers with Cyrillic characters. It is convenient if Latin characters are black and Cyrillic characters are red.
More detailed information about the Russification of the keyboard is presented in the section "How to Russify MS-DOS".
9.9. How to Russify MS-DOS
The MS-DOS version 6.0 operating system contains commands and programs for international support.
For Russification, after installing MS-DOS version 6.0, we suggest that you replace the files of commands and international support programs with the corresponding files from the Russian version of MS-DOS. Russian versions of MS-DOS 4.01, 5.0 and 6.0 are currently released.
If you do not have the Russian version of MS-DOS, copy from the Russian version 4.0 or 5.0 of the MS-DOS operating system the following files: COUNTRY.SYS, DISPLAY.SYS, KEYBOARD.SYS, KEYB.COM, as well as files with the CPI extension. Replace these files with the appropriate files in the MS-DOS directory.
Since the DISPLAY.SYS driver and the KEYB.COM program check the version of the operating system, they must be "fooled". To do this, run the following commands:
C:\DOS\SETVER KEYB.COM 4.01 C:\DOS\SETVER DISPLAY.SYS 4.01Then, using any text editor, you need to add international support commands to the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files. In the CONFIG.SYS file, you must load the SETVER.EXE driver, add a call to the COUNTRY command, and load the DISPLAY.SYS driver:
DEVICE=C:\DOS\SETVER.EXE COUNTRY=7,C:\DOS\COUNTRY.SYS DEVICE=C:\DOS\DISPLAY.SYS CON=(EGA,437,1)In the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, you need to add a call to two MODE commands and load the KEYB resident program:
c:\dos\mode CON CP PREP=((866) C:\DOS\EGA.CPI) c:\dos\mode CON CP SEL=866 D:\DOS\keyb RU,D:\DOS\KEYBOARD.SYS /ID:093After making all the changes to the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files, restart your computer. When the computer is restarted, the resident modules of the Russification programs are loaded into the RAM.
Do not use word processors to edit CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files that save edited files in special formats. When you save editable text in a file that has a special format, other control information will be written to it, in addition to the text. As a result, MS-DOS will not be able to interpret these files, and the computer will not boot properly.
Now you can view and edit documents written in Russian, in addition, you will have all the benefits of MS-DOS version 6.0.
When editing texts in Russian, switch the keyboard to the Cyrillic character input mode. To do this, press the right key. By pressing the right key a second time, you will switch the keyboard back to entering Latin characters.
9.10. What are viruses and trojans
The most general definition of a virus can be given as a program code that self-propagates in the information environment of computers. According to the way viruses spread, they can be divided into the following main groups:
- programs embedded in executable files - files with COM and EXE extensions;
- spreading through boot sectors diskettes and hard drives, as well as through the boot sector of hard drives;
- infecting driver files - files with SYS and EXE extensions;
- propagated through translator object library files.
In addition to the above groups, there are others, such as viruses that infect batch files - files with the BAT extension. "Progress" in the world of viruses does not stand still and we can expect the emergence of new groups of viruses.
The action of most viruses, unfortunately, is not limited to reproduction and spread. They can cause relatively harmless or devastating effects.
Outwardly, the action of viruses can be expressed in the fact that periodically, for example, after reaching a certain time, the virus is activated and performs some operations. In particular, viruses can: display extraneous inscriptions and symbols on the screen, "shower" symbols already displayed on the screen, restart the computer, slow down the computer, play all kinds of melodies, delete files and directories, erase randomly selected sectors of hard and floppy disks.
In principle, viruses can perform any action. They are limited only by the imagination of the author of the virus and the capabilities of the computer.
Trojans are much less common than viruses. Trojans are programs that perform some useful functions, but at some point they can additionally perform some malicious actions, such as formatting HDD.
Currently, the spread of viruses has reached truly gigantic proportions and threatens users with irretrievable loss of data stored on a computer.
To increase the security of data on your computer, it is necessary to limit the exchange of executable program modules, as well as periodically carry out preventive work to detect viruses. For more information on how to deal with viruses, see the "How to deal with viruses" section.
9.11. How to deal with viruses
If you do not periodically carry out work to prevent and treat computers from viruses, the possibility of losing stored information and destroying the operating environment becomes more than real.
The negative consequences of your negligence may be different, depending on which virus gets into your computer. You can lose either part of the information from the files stored on the computer, or entire files, or even all the files on the disk.
Work on the prevention and treatment of computers from viruses may include the following actions:
- limit the exchange of programs and diskettes, scan such programs and diskettes for viruses;
- periodically check the computer's RAM and disks for viruses using special antivirus programs, for example, the AIDSTEST.EXE program;
- use special protector programs that, after being launched, remain resident in the computer's memory and monitor all suspicious actions of programs (for example, writing to a program file or system disk areas).
Currently, there are thousands of different viruses and hundreds of programs to combat them. The most famous anti-virus programs for MS-DOS are: AIDSTEST, SCAN, ANTI4US, VAKCINA, ADINF.
The problem of fighting viruses has become so serious that Microsoft included in version 6.0 of the MS-DOS operating system its own software tools: Microsoft Anti-Virus for MS-DOS and for Windows.
There are even special programs for fighting viruses in networks. For example, NetShield is loaded on a Nowell NetWare 3.11 server as an NLM process. It can scan server disks for viruses once a day. If a virus is detected, a corresponding warning message will be sent to all network users. You can also set the mode in which NLM Anti-Virus will scan all files written to or read from the server for virus infection.
Consider the most common software tools designed to detect and remove viruses - AIDSTEST.EXE and Microsoft Anti-Virus.
AIDSTEST.EXE
The author of the AIDSTEST.EXE anti-virus program is Lozinsky Dmitry Nikolaevich. AIDSTEST can detect a wide variety of viruses and can also remove detected viruses.
A description of the AIDSTEST options can be obtained by running AIDSTEST with the /h option. We will allow ourselves to give only the most important parameters of this program. The format of the AIDSTEST call is as follows:
AIDSTEST path [options]The first, mandatory, path parameter must specify the directory in which the virus scan will be performed. This automatically checks all subdirectories. If you specify only the drive name as the first parameter (eg AIDSTEST C:), then the entire drive will be checked.
If you don't give the AIDSTEST program any additional parameters, it will only scan for viruses. In the event that you want to remove the found viruses, you need to specify an additional parameter /F. AIDSTEST will fix virus-infected programs and erase those that cannot be repaired. In order for AIDSTEST to ask for permission to remove corrupted program files, you must additionally specify the /Q option.
Below is an example of using the AIDSTEST antivirus to detect and treat viruses on the C: drive.
AIDSTEST C: /F /Q
Usage antivirus programs cannot guarantee that your computer will be fully protected from viruses. The fact is that antiviruses like AIDSTEST are configured to detect already known viruses and their clones. New viruses may not be known to AIDSTEST and may not be able to detect them. We emphasize once again that, in our opinion, the most reliable way to protect your computer from attack by viruses is to install software tools only from distributions and limited use of floppy disks for program exchange.
Microsoft AntiVirus
Microsoft Anti-Virus is included with the MS-DOS version 6.0 distribution. At the same time, Microsoft Anti-Virus is presented in two versions - for MS-DOS and for Windows.
The detailed procedure for installing these anti-virus programs is described in the "How to install MS-DOS" section. Here we will only note that Microsoft Anti-Virus for Windows requires Windows to be installed on the computer's hard drive.
My article will be somewhat unusual, because in it I will tell you how to install an old OS on a new computer DOS.
Why dos? Because it's a great operating system. My article is addressed to her lovers.
If you are a visitor to such sites as www.386.by.ru, www.dos-systems.narod.ru and the like, then you already know about the advantages of this wonderful system.
Publications about installing on a computer above 433 megahertz Windows 95 I met. Also about installation Windows 3.11 to a new car.
But what if a person cannot reboot in mode MS-DOS due to ATX motherboard form factor? And work with dos I want to. This is where the logical solution comes in - we put dos! About Compatibility MS-DOS and other operating systems on new machines, I'll tell you. Also about the problems associated with the installation.
Let's start with a story that happened to me. My friend had a COMPAQ PENTIUM-100 laptop. And suddenly ... Windows ordered to live long. Since all devices are built-in in the laptop, and the CD-ROM uses the PCMCIA bus (and only one drive can be connected), it ran into a problem - you need to boot and install the system, but from where? It didn't have a bootable CD-ROM.
That is, it is impossible to rewrite anything from CD-Rom to the hard drive, and the DOS driver MSCDEX won't help here. Later I learned that the driver PCMCIA for the drive is in the very BIOS, or rather its full support. This architecture is found only in the company COMPAQ. At least I haven't heard of others. Of course, it was possible to download a special boot disk from www.compaq.com, but we didn't know about that at the time.
This is where the boot floppy from the kit came in handy. Windows 98! The fact is that other boot floppy disks do not allow the sys command to be done on a non-empty hard drive, an error “it is impossible to specify a disk” is issued. And in Win98, the FORMAT utility supports the format c: /b switch.
This means that the disk will be formatted with forced transfer to it system files. After this operation, I managed to boot from the hard drive, access the CD-ROM and install the system.
So, to install MS-DOS we will need:
Win98 boot floppy, boot floppy and distribution MS-DOS.
First of all, of course, let's decide on the place of the disk: its layout should look something like this:
Partition C with file FAT system or FAT 16 up to about 2 gigabytes in size ( MS-DOS 6.22 larger partitions are not supported). It will be installed on it. dos, because it can only boot from the primary partition. The rest is up to the user. So, change the size C to acceptable for dos. I would recommend changing the partition structure not with the FDISK utility, but with PARTITION MAGIC for dos, since it does everything much faster, and it does not require you to format partitions after they are created or reorganized. We need to format the C partition using the FORMAT C: /B key. This is done after booting from a Win98 floppy disk. Then convert this partition to FAT using PARTITION MAGIC (just FAT, not FAT32).
Now you can boot from floppy dos and give the command sys a: c:. This means that we are moving the system from A to C. Other sections dos will not see it, because they have a different file system.
After that, we boot again from the Win98 floppy disk and copy the distribution kit from another partition dos to disk C.
Then we boot from the hard drive and issue the setup / G command from the distribution kit
The G key means that the installer dos will not create backup floppies.
All! dos installed. Now you need to install another operating system, already modern.
Let's make a choice. You can put any on another section, but I want to tell you in more detail.
WITH Windows XP And 2000 there will be no problems, their built-in loader will see dos and will ask when loading which one to run.
Windows ME do not support REAL-TIME DOS, its autoexec.bat and config.sys boot files are only needed for compatibility with older DOS applications(to define an environment variable TEMP etc.) Therefore, there will be no conflict. But you will need to implant a third-party bootloader in the MBR (master boot record), again, I recommend the company's product POWER QUEST - BOOT MAGIC. Any version.
And here WIN98 will have to be changed so that autoexec.bat And config.sys there were different configurations - for dos and actually WIN 98. Such a change will perform the multi-boot function.
And the last: Windows it is advisable to install not from under a freshly installed DOS, but from the “native” boot floppy.
File Manager
Text editor
Convenient graphical shell
Programs to maintain the health of the computer
Various viewers
It's time to start choosing a shell, because everyone needs to copy, delete and run programs, I would choose between Norton Commander`om () and Dos Navigator`om (http://www.ritlabs.com/download/files3/dn/dn151.zip), the first is easier to use - suitable for beginners, respectively, the second has more features (LFN support, flexible settings, two built-in games, built-in terminal, CD player, calculator, notebook, understands 22 types of archives...) and is suitable for both beginners and advanced users. Well, if you're used to Windows, and do not want to wean from the window interface, I can offer GVFM (http://homepage.ntlworld.com/gvision/gv/gvfm.zip)
Well, the file manager seems to have been sorted out, now it’s up to the functional text editor, of course, there are people for whom ncview`a is enough, but most, I think, don’t think so, so I suggest such an alternative as: Breeze (http:/ /www.theabsolute.net/sware/files/breeze56.zip), Aurora (http://www-personal.umich.edu/~knassen/aurora/auror30c.zip) (syntax highlighting, HEX editor), Lexicon, Work&Deed (http://winwd.narod.ru/DosWD.exe). In short, all these editors are good, you just need to choose the most suitable and convenient for you. I would recommend Auror or Work&Deed. And finally, for win-dependent comrades, I offer a beautiful text editor with a window interface GVEdit (http://homepage.ntlworld.com/gvision/gv/gvedit.zip)
Naturally, any business user needs to communicate through world wide web. The great and mighty Arachne browser will help us in this seemingly impossible task. Here you have a graphics viewer, and a desktop, and a file manager, and an email client, and, finally, the browser itself. The program itself is easy to set up, has a convenient setup wizard, has its own built-in ppp-packet driver, but you can also connect an external one, the program's capabilities are expandable using plug-ins that can be downloaded from the manufacturer's website http://www.glennmcc.org/ and not only from him...
In principle, if you are not satisfied with Arachne's built-in pop client, you can use third-party utilities such as NetMail, Pegasus Mail, Mutt, POPMail (), Pine. I chose Pegasus Mail as it is the most functional, but for normal operation POPMail is enough with mail, but it requires an external batch driver, and it has practically no minuses, and it will suit a user with any level of knowledge.
LADSoft has released a plug-in for the Arachne browser (http://web.archive.org/web/20010312183617/http://ladsoft.tripod.com/lsicq/download.htm) especially for online communication maniacs, which allows you to work with the console ICQ version. If, again, for some reason you need a separate program, then I can offer dosmicq(http://dosinet.chat.ru/ICQ/dosmicq.exe), the program has a built-in dialer...
For creative individuals, I can offer NeoPaint programs - creating, editing images using various filters and the ability to change the format, and NeoBook is a kind of FrontPage program, although the program is intended to create e-books with illustrations and more... (Get both programs from http://www.neosoftware.com)
For complete comfort, it’s also good to listen to music, you say. No problem, there are two of the best programs: MPXPlay and DSS, both programs are very solid, with a large set of functions, and MPXPlay () is almost an exact copy of WinAMP - it understands playlists from it, it can adjust the sound volume itself, the processor load indicator ...
For cinephiles, there is a rather versatile Quick View utility (www.multimediaware.com), besides the fact that the program can watch videos, it also plays music and shows pictures ...
Well, that's all, now you have a computer on which you can perform your usual tasks and at the same time do without Windows:)))
That's all, thanks for your attention. I hope the article will help you avoid some problems and enjoy dos!
It's not a fairy tale, Dos is with you...
Let's remember the past, how it looked!
For this experiment, a VirtualBox virtual machine and, of course, floppy disk images with a packaged distribution were used. To start the installation, let's create a virtual machine, I think many people know how to do this! Having created virtual machine we must add a system image to boot the primary device later.
You can add a floppy disk image as follows: select the created virtual machine, go to "settings", then to the section "carriers", then add "Floppy controller" and specify our image, as shown in the figure below.
If you do everything right, then you can safely proceed to start the virtual machine using the key "Run", after pressing for a moment, the inscription will be displayed Starting MS-DOS.
Then we'll see a familiar blue screen setup, which for many editions of Windows has been a prime representation of the Windows operating system setup wizard. To continue installation, click "ENTER".


At the next stage, the installation wizard will format the disk, which will be almost instantaneous and reboot the system.

After the installer will offer to install the system settings, check for correctness and confirm by selecting the item "The settings are correct".

Specify the directory for unpacking and installing operating system files.

Since we mounted the first floppy in the form of an image, at this stage the installation of the system begins. After a while, a message will appear indicating that the 2nd system image needs to be mounted.

In order to mount the following operating system image, you need to go to the menu in the virtual machine "Devices", then select "floppy drives", and then specify the desired system image. Try!

If you succeed, then you will see a message about the need to mount the 3rd image. Do the same again!

The installation is nearing completion and the installation wizard warns the user to unmount all images mounted as a primary device and press the "ENTER" button when finished.

The next window displays positive information about the successful installation and notifies us to reboot the system in order to correctly complete the installation process.

And here is the "black screen" - the same legendary MICROSOFT MS-DOS 6.22!!!

The operating system is installed, use it!!!
So that MS DOS 6.22 can recognize Russian characters.
You can download Oracle VM VirtualBox from this link (http://www.virtualbox.org/).
Install and run the VirtualBox program.
Click the item Create, the Wizard for creating a new virtual machine will open, click Next.
Fill in the machine name and operating system type.
We set the amount of RAM that will be available to the OS, usually it is determined automatically, you add it at your discretion, you can usually just click Next.

Next, we indicate the maximum size of the virtual hard disk, usually determined automatically, if you need more space you can add.
But first we need to create a new hard drive, for this we click Next, we select the type at our discretion, but I recommend choosing VHD, since it is most compatible with other OS virtualization systems.
Hard disk attributes I recommend installing a virtual dynamic disk, since it takes up less space during transfer and grows as it is filled with information.
Next, you need to specify the location of the virtual disk on our computer, by default it is located in the user folder, the VirtualBox VMs folder.
In the same place, we indicate the size by moving the label or manually enter the size of the disk in MB in the field.

Finally, click the Create button.
Extract the floppy disk images from the archive that we downloaded to a temporary folder.

Add a floppy and select an image, specifying the path to the first floppy image.

We switch to the System item and check whether the download from the floppy is located, waiting for this it should be placed at the very top.
If this is not the case, select our device and click on the arrows on the right to move it up or down. We can also edit other settings.
After finishing the system setup, click ok.
Next, in the list of programs, select our virtual machine, click the Start item.

After that, the MS DOS 6.22 installation window will open.

To continue the installation, press Enter, for help, press F1, to install on a floppy disk, press F7. Following the instructions of the master.
Select Configure unallocfted disk space and Enter.
After that, a window will appear with a warning that you need to restart the computer and insert the first floppy disk, but we don’t need this, since we have already configured (inserted), just press Enter.

We are waiting for the preparation to be completed and a window with parameter settings will appear in front of us, all that can be set so far is the date and it will be determined automatically, therefore we select The setting are correct and press Enter.
Next, you need to specify the disk where the OS will be installed. By default in VirtualBox it will be C:\DOS, all that remains is to press Enter, but if you need to install DOS in another place, just write where, for example D:\DOS.

Next, we need to insert floppy disk number 2 and press Enter.
To do this, at the bottom of the window on the right, right-click on the floppy icon and select floppy disk image number 2.

We continue the installation, install the following image, similarly to the previous method.
Finally, at the bottom of the window on the right, right-click on the floppy icon and select Eject disk from drive. Press Enter.
Here is the window that announces that our MS DOS 6.22 has been successfully installed, we reboot.

Now it remains for us to Russify our MS DOS 6.22.
To do this, we need to copy the files from the second archive along the C:\DOS path.
All this can be done using the command line, but it is not given to everyone to understand and it is not so easy to implement if we first encountered it.
I will describe later how to do it using the command line, but now we will do it more cunningly.
But for this we need additional manipulations.
So we need to install in VirtualBox - Windows XP, here I will not describe the installation process for now, but if necessary I will definitely write.
Let's assume that you have successfully installed Windows XP. Let's get down to business, select Windows XP from the list and click Properties - Media.
Click add a new hard drive - select an existing drive, specify the path to the drive with our MS DOS 6.22

Loading Windows XP. Using the file manager, we load files along the path D: \ DOS - where D: is a disk with MS DOS 6.22. I also recommend copying some file manager DOS - Volkov Commander or Norton Commander.
Next, you need to edit the AUTOEXEC.BAT, CONFIG.SYS files. Editing with AkelPad notepad.
In file AUTOEXEC.BAT write the following:
@ECHO OFF
mode con codepage prepare=((866) C:\dos\ega3.cpi)
mode con codepage select=866
keyb en,C:\dos\keybrd3.sys
SET TEMP=C:\
LH DOS\SMARTDRV.EXE
LH DOS\KEYRUS.COM
LH DOS\MOUSE.COM
LH DOS\MSCDEX.EXE /D:CDDRIVER
PROMPT $p$g
PATH C:\DOS
SET TEMP=C:\DOS
In file CONFIG.SYS :
DEVICE=C:\DOS\SETVER.EXE
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\DISPLAY.sys con=(ega,1)
DEVICEHIGH=C:\DOS\VIDE_CDD.SYS /D:CDDRIVER
Country=007,866,C:\dos\country.sys
DOS=HIGH
FILES=30
It seems that your entire system should be Russified, and you can already use the full-fledged MS DOS 6.22 rus.
If suddenly you have some kind of error, check that the OS is now loaded from the hard disk.
Let's run MS DOS 6.22 rus and see if everything works fine.
For control, we simply use commands. What commands you can find out, you need to enter the help command.
For each command, type xcopy /?
If you find it difficult to manage the command line, in the file
the following after the line LH DOS\MSCDEX.EXE /D:CDDRIVER:
LH DOS\MSCDEX.EXE /D:CDDRIVER
SET SHELL=COMMAND.COM
You can also put another program on autoload by changing the entire path.
My article will be somewhat unusual, because in it I will tell you how to bet on new computer old OS DOS.
Why dos? Because it's a great operating system. My article is addressed to her lovers.
If you are a visitor to such sites as www.386.by.ru, www.dos-systems.narod.ru and the like, then you already know about the advantages of this wonderful system.
Publications about installing on a computer above 433 megahertz Windows 95 I met. Also about installation Windows 3.11 to a new car.
But what if a person cannot reboot in mode MS-DOS due to ATX motherboard form factor? And work with dos I want to. This is where the logical solution comes in - we put dos! About Compatibility MS-DOS and other operating systems on new machines, I'll tell you. Also about the problems associated with the installation.
Let's start with a story that happened to me. My friend had a COMPAQ PENTIUM-100 laptop. And suddenly ... Windows ordered to live long. Since all devices are built-in in the laptop, and the CD-ROM uses the PCMCIA bus (and only one drive can be connected), it ran into a problem - you need to boot and install the system, but from where? It didn't have a bootable CD-ROM.
That is, it is impossible to rewrite anything from CD-Rom to the hard drive, and the DOS driver MSCDEX won't help here. Later I learned that the driver PCMCIA for the drive is in the very BIOS, or rather its full support. This architecture is found only in the company COMPAQ. At least I haven't heard of others. Of course, it was possible to download a special boot disk from www.compaq.com, but we didn't know about that at the time.
This is where the boot floppy from the kit came in handy. Windows 98! The fact is that other boot floppy disks do not allow the sys command to be done on a non-empty hard drive, an error “it is impossible to specify a disk” is issued. And in Win98, the FORMAT utility supports the format c: /b switch.
This means that the disk will be formatted with forced transfer of system files to it. After this operation, I managed to boot from the hard drive, access the CD-ROM and install the system.
So, to install MS-DOS we will need:
Win98 boot floppy, boot floppy and distribution MS-DOS.
First of all, of course, let's decide on the place of the disk: its layout should look something like this:
Partition C with the FAT or FAT 16 file system up to about 2 gigabytes in size ( MS-DOS 6.22 larger partitions are not supported). It will be installed on it. dos, because it can only boot from the primary partition. The rest is up to the user. So, change the size C to acceptable for dos. I would recommend changing the partition structure not with the FDISK utility, but with PARTITION MAGIC for dos, since it does everything much faster, and it does not require you to format partitions after they are created or reorganized. We need to format the C partition using the FORMAT C: /B key. This is done after booting from a Win98 floppy disk. Then convert this partition to FAT using PARTITION MAGIC (just FAT, not FAT32).
Now you can boot from floppy dos and give the command sys a: c:. This means that we are moving the system from A to C. Other sections dos will not see it, because they have a different file system.
After that, we boot again from the Win98 floppy disk and copy the distribution kit from another partition dos to disk C.
Then we boot from the hard drive and issue the setup / G command from the distribution kit
The G key means that the installer dos will not create backup floppies.
All! dos installed. Now you need to install another operating system, already modern.
Let's make a choice. You can put any on another section, but I want to tell you in more detail.
WITH Windows XP And 2000 there will be no problems, their built-in loader will see dos and will ask when loading which one to run.
Windows ME do not support REAL-TIME DOS, her boot files autoexec.bat and config.sys are only needed for compatibility with older DOS applications(to define an environment variable TEMP etc.) Therefore, there will be no conflict. But you will need to implant a third-party bootloader in the MBR (master boot record), again, I recommend the company's product POWER QUEST - BOOT MAGIC. Any version.
And here WIN98 will have to be changed so that autoexec.bat And config.sys there were different configurations - for dos and actually WIN 98. Such a change will perform the multi-boot function.
And the last: Windows it is advisable to install not from under a freshly installed DOS, but from the “native” boot floppy.
Install dos on a powerful computer, this is, of course, cool, but the question arises, what's next? Booted up, except for C:\>_ we don't see anything else...
You need to figure out what a simple, inexperienced user needs for everyday work:
File Manager
Text editor
Convenient graphical shell
Programs to maintain the health of the computer
Various viewers
It's time to start choosing a shell, because everyone needs to copy, delete and run programs, I would choose between Norton Commander`om () and Dos Navigator`om (http://www.ritlabs.com/download/files3/dn/dn151.zip), the first is easier to use - suitable for beginners, respectively, the second has more features (LFN support, flexible settings, two built-in games, built-in terminal, CD player, calculator, notebook, understands 22 types of archives...) and is suitable for both beginners and advanced users. Well, if you're used to Windows, and do not want to wean from the window interface, I can offer GVFM (http://homepage.ntlworld.com/gvision/gv/gvfm.zip)
Well, the file manager seems to have been sorted out, now it’s up to the functional text editor, of course, there are people for whom ncview`a is enough, but most, I think, don’t think so, so I suggest such an alternative as: Breeze (http:/ /www.theabsolute.net/sware/files/breeze56.zip), Aurora (http://www-personal.umich.edu/~knassen/aurora/auror30c.zip) (syntax highlighting, HEX editor), Lexicon, Work&Deed (http://winwd.narod.ru/DosWD.exe). In short, all these editors are good, you just need to choose the most suitable and convenient for you. I would recommend Auror or Work&Deed. And finally, for win-dependent comrades, I offer a beautiful text editor with a window interface GVEdit (http://homepage.ntlworld.com/gvision/gv/gvedit.zip)
Naturally, any business user needs to communicate through the World Wide Web. The great and mighty Arachne browser will help us in this seemingly impossible task. Here you have a graphics viewer, and a desktop, and a file manager, and an email client, and, finally, the browser itself. The program itself is easy to set up, has a convenient setup wizard, has its own built-in ppp-packet driver, but you can also connect an external one, the program's capabilities are expandable using plug-ins that can be downloaded from the manufacturer's website http://www.glennmcc.org/ and not only from him...
In principle, if you are not satisfied with Arachne's built-in pop client, you can use third-party utilities such as NetMail, Pegasus Mail, Mutt, POPMail (), Pine. I chose Pegasus Mail, as it is the most functional, but POPMail is enough for normal work with mail, but it requires an external batch driver, and it has practically no disadvantages, and it will suit a user with any level of knowledge.
LADSoft has released a plug-in for the Arachne browser (http://web.archive.org/web/20010312183617/http://ladsoft.tripod.com/lsicq/download.htm) especially for online communication maniacs, which allows you to work with the console ICQ version. If, again, for some reason you need a separate program, then I can offer dosmicq(http://dosinet.chat.ru/ICQ/dosmicq.exe), the program has a built-in dialer...
For creative individuals, I can offer NeoPaint programs - creating, editing images using various filters and the ability to change the format, and NeoBook is a kind of FrontPage program, although the program is intended for creating e-books with illustrations and other ... (Take both programs from http ://www.neosoftware.com)
For complete comfort, it’s also good to listen to music, you say. No problem, there are two most best programs: MPXPlay and DSS, both programs are very solid, with a large set of functions, and MPXPlay () is almost an exact copy of WinAMP - it understands playlists from it, it can adjust the sound volume itself, the processor load indicator ...
For cinephiles, there is a rather versatile Quick View utility (www.multimediaware.com), besides the fact that the program can watch videos, it also plays music and shows pictures ...
Well, that's all, now you have a computer on which you can perform your usual tasks and at the same time do without Windows:)))
That's all, thanks for your attention. I hope the article will help you avoid some problems and enjoy dos!
It's not a fairy tale, Dos is with you...
Installing MSDOS on a hard drive.
Hello. Welcome to the Computer76 blog page, now we will install MS-DOS on the computer. And just why do we need it.
This article predicts the subsequent installation of a more modern windows operating system on a computer or laptop where neither CD / DVD drives nor USB / SD connectors work.
In our case, the usefulness of the installation is determined by the fact that the MS-DOS operating system not tied to installed hardware no ready assembly. By installing it on a USB flash drive or on a hard drive, you can subsequently install any operating system on any computer or laptop (netbook) on the same HDD.
Installing MSDOS. We will need:
First, visit the manufacturer's website and download the DOS distribution by clicking on the green ISO download button. At the time of writing, the layout of the buttons on the page is as follows:
However, it is possible that the interface of the page will change. But I am sure that you will find all the necessary links there.
I want to note right away that there is a possibility, however, some computers do not support booting from USB devices, and sometimes they simply refused to see DOS when set with Boot BIOS with USB. You then have to use the article. The option to boot from a DVD drive is always trouble-free.
AND . After the reboot, you should meet the installation manager window:
 Press key Yopter and you will be taken to the installation menu.
Press key Yopter and you will be taken to the installation menu.

Press key 1. You will be greeted with a language selection menu. I advise you to leave English, in Russian there is still nothing there, or it is likely that it will be displayed in an incomprehensible encoding:

Upon pressing the enter button, the installer will display a message that it cannot determine the volume of the HDD. But the letter WITH he managed to assign to him:

Click again Enter. Let's leave " Prepare the harddisk for FreeDOS...” and press again Enter. You will see a window with your hard drive. I have this, your volume will be different:

Let's continue with the Enter key. An options window will pop up on the top left. Let's choose New Partition–Primary Partition. And we will allocate space for the disk with the future DOS. Remember that DOS does not see large volumes: for sizes from 2 GB, there is no space for DOS at all:

Click Input and confirm in the menu on the right Start of free space. You will be greeted with a dialog box asking you to initialize the space for the partition on the disk before the formatting procedure. Select Yes:

Click Enter. Also in the next window select again Yes and press Input. A new window will display information about what your HDD space will look like if you start working right now. Partition C will be formatted as FAT16 with a capacity of 150 MB, the rest of the space will remain incomprehensible. Let's put things in order there too, it will come in handy in the future:

We will go down with the arrow down and repeat the previous movements, only let the second disk become logical. Click again a couple of times yes, to look at the resulting picture again. Both disks will have the FAT16 file system. For the first disk where msdos will be installed, this is it. But for the second part of the hard drive, this is not necessary. There can be anyone, and you can change it right now. Just click on it again with the enter key and the settings window will appear again at the top right:

Select Partition Type and select the type of disk system you like. I will choose FAT32. Again two times Yes, press F3 and in the query window select Yes to start the utility:

Press enter and:

Might have to wait. The next window will prompt you to reboot. Boot disk (I have this external box, which contains boot images Windows for all occasions) DO NOT REMOVE from the drive and reboot. After the reboot, our HDD is ready to be received on board MS-DOS, and in the window we already know, we select again Install to hard drive. Formatting warning again:

After that, already in the DOS window, you will have to manually enter YES. Press the enter key after the appearance of a series of dialog and guide windows, in the windows of utilities that will be installed as part of MS-DOS, go down with an arrow down and sideways to the word DONE plus the enter key with YES selected:
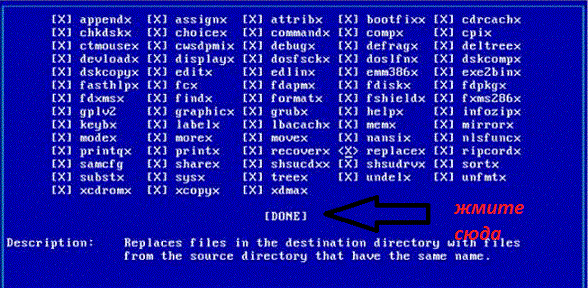
And so on in all windows, until the installation window itself appears. Do not touch anything until the status bar on a blue background interspersed with a flashing screen is thrown at the end of the installation, which will be marked by the entry Done installing this disk series at first. Press any key ( Press any key to continue) and repeat the procedure with windows with DONE no matter how required. When finished, restart your computer by removing the boot disk from the drive. The MSDOS installation is complete.

Choose the first option and you can get to work.
MSDS installation. Part two is an addendum.
As expected, the developers have presented the next part of the DOS OS with the name FreeDOS 1.2. As a result, the installation principle changes from the moment of injection. Therefore, it was decided to continue the article with the installation of FreeDOS 1.2 on the VirtualBox virtual machine.

Downloading zip archive, which we will unpack in a convenient place. There are three files. We need those that have the extension .img and .vmdk. They mean that everything is ready to install msdos on the virtual machine. Copy them closer. If so, let's go.
We start VirtualBox. We create a new car. In order not to get confused in the settings, start writing DOS in the OS name line - VirtualBox will automatically determine the OS you want to install and adjust the parameters to the desired settings. You can leave them as default, but I always add performance if the OS is created not just “for viewing”.
We will immediately indicate the vmdk virtual disk file in the folder that we just got after unzipping. At this point, look at my settings:

click to enlarge
After closing the settings window, click Create. The machine is ready to be launched, but so far nothing has come of it.
Now let's run DaemonTools and mount the disk image from the .img file. Note the letter of the virtual drive - we will need it in further settings virtual machine. We will return to them.
In the VirtualBox window, click in the created OS toolbar at the top Tune – carriers. The Virtual Hard and Optical Disks window will open. Add two devices at once: a dynamic hard disk and an optical drive. To create a disk, use the button with a floppy disk at the bottom:

as you can see, I already have all the media added - do the same
In the window that appears after, select Create a new disk, leave type VDI, Dynamic…disk.
To select a drive, highlight in the window carriers information figure with a blank and on the right in the window Attributes click on the same icon and in the list Select optical disc image specify the path to the virtual drive created by DaemonTools:

That's it. You can run. The installation language is English. In this window, the installer will ask you to install to hard or return to the window in command mode:


After a short time, the installer will be asked to reboot. Agree and in the next session you are already in MSDOS:

Welcome to another article. Today I will tell you how to install MS DOS 6.22 rus in Oracle VM VirtualBox.
The installation process is very little different from the usual installation on a computer.
First we need to load MS DOS 6.22 (floppy image files.img). After downloading additional files so that MS DOS 6.22 can recognize Russian characters.
You can download Oracle VM VirtualBox from this link (http://www.virtualbox.org/).
Install and run VirtualBox program.
Click the item Create, the Wizard for creating a new virtual machine will open, click Next.
Fill in the machine name and operating system type.
We set the amount of RAM that will be available to the OS, usually it is determined automatically, you add it at your discretion, you can usually just click Next.

Next, we indicate the maximum size of the virtual hard disk, usually determined automatically, if you need more space, you can add it.
But first we need to create a new hard drive, for this we click Next, we select the type at our discretion, but I recommend choosing VHD, since it is most compatible with other OS virtualization systems.
Hard Disk Attributes I recommend installing a virtual dynamic disk, as it takes up less space during migration and grows as it fills with information.
Next, you need to specify the location of the virtual disk on our computer, by default it is located in the user folder, the VirtualBox VMs folder.
In the same place, we indicate the size by moving the label or manually enter the size of the disk in MB in the field.

Finally, click the Create button.
Extract the floppy disk images from the archive that we downloaded to a temporary folder.

Add a floppy and select an image, specifying the path to the first floppy image.

We switch to the System item and check whether the download from the floppy is located, waiting for this it should be placed at the very top.
If this is not the case, select our device and click on the arrows on the right to move it up or down. We can also edit other settings.
After finishing the system setup, click ok.
Next, in the list of programs, select our virtual machine, click the Start item.

After that, the MS DOS 6.22 installation window will open.

To continue the installation, press Enter, for help, press F1, to install on a floppy disk, press F7. Following the instructions of the master.
Select Configure unallocfted disk space and Enter.
After that, a window will appear with a warning that you need to restart the computer and insert the first floppy disk, but we don’t need this, since we have already configured (inserted), just press Enter.

We are waiting for the preparation to be completed and a window with parameter settings will appear in front of us, all that can be set so far is the date and it will be determined automatically, therefore we select The setting are correct and press Enter.
Next, you need to specify the disk where the OS will be installed. By default in VirtualBox it will be C:\DOS, all that remains is to press Enter, but if you need to install DOS in another place, just write where, for example D:\DOS.

Next, we need to insert floppy disk number 2 and press Enter.
To do this, at the bottom of the window on the right, right-click on the floppy icon and select floppy disk image number 2.

We continue the installation, install the following image, similarly to the previous method.
Finally, at the bottom of the window on the right, right-click on the floppy icon and select Eject disk from drive. Press Enter.
Here is the window that announces that our MS DOS 6.22 has been successfully installed, we reboot.

Now it remains for us to Russify our MS DOS 6.22.
To do this, we need to copy the files from the second archive along the C:\DOS path.
All this can be done using the command line, but it is not given to everyone to understand and it is not so easy to implement if we first encountered it.
I will describe later how to do it using the command line, but now we will do it more cunningly.
But for this we need additional manipulations.
So we need to install in VirtualBox - Windows XP, here I will not describe the installation process for now, but if necessary I will definitely write.
Let's assume that you have successfully installed Windows XP. Let's get down to business, select Windows XP from the list and click Properties - Media.
Click to add a new hard drive - select an existing drive, specify the path to the drive with our MS DOS 6.22

Loading Windows XP. Using the file manager, we load files along the path D:\DOS - where D: is a disk with MS DOS 6.22. I also recommend copying some kind of DOS file manager - Volkov Commander or Norton Commander.
Next, you need to edit the AUTOEXEC.BAT, CONFIG.SYS files. Editing with AkelPad notepad.
In file AUTOEXEC.BAT write the following:
@ECHO OFF
mode con codepage prepare=((866) C:\dos\ega3.cpi)
mode con codepage select=866
keyb en,C:\dos\keybrd3.sys
SET TEMP=C:\
LH DOS\SMARTDRV.EXE
LH DOS\KEYRUS.COM
LH DOS\MOUSE.COM
LH DOS\MSCDEX.EXE /D:CDDRIVER
PROMPT $p$g
PATH C:\DOS
SET TEMP=C:\DOS
In file CONFIG.SYS :
DEVICE=C:\DOS\SETVER.EXE
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\DISPLAY.sys con=(ega,1)
DEVICEHIGH=C:\DOS\VIDE_CDD.SYS /D:CDDRIVER
Country=007,866,C:\dos\country.sys
DOS=HIGH
FILES=30
It seems that your entire system should be Russified, and you can already use the full-fledged MS DOS 6.22 rus.
If suddenly you have some kind of error, check that the OS is now loaded from the hard disk.
Let's run MS DOS 6.22 rus and see if everything works fine.
For control, we simply use commands. What commands you can find out, you need to enter the help command.
For detailed description each command you need to type xcopy /?
If you find it difficult to manage the command line, in the file
following the line LH DOS\MSCDEX.EXE /D:CDDRIVER.
The MS-DOS operating system is made up of many different files. They include the actual operating system files IO.SYS, MSDOS.SYS, and the COMMAND.COM command processor. In addition to these three files, which are a workable core of MS-DOS, the distribution of the operating system includes files of so-called external commands, such as FORMAT, FDISK, SYS, drivers for various devices, and some other files.
The IO.SYS file contains an extension to the basic input/output system and is used by the operating system to communicate with the computer's hardware and BIOS.
The MSDOS.SYS file is, in a sense, a set of interrupt handlers, specifically the INT 21H interrupt.
The command processor COMMAND.COM is designed to organize a dialogue with a computer user. It analyzes the commands entered by the user and organizes their execution. The so-called internal commands - DIR, COPY, etc. are processed by the command processor.
The rest of the operating system commands are called external. The external commands are so named because they are located in separate files. Operating system external command files contain utility programs for performing various operations, such as formatting disks, sorting files, and printing texts.
Drivers (usually files with the SYS or EXE extension) are programs that support various hardware. The use of drivers easily solves the problems of using new hardware - just connect the appropriate driver to the operating system.
Application programs interact with the device through the driver, so they will not change when the hardware changes. For example, a new disk device may have a different number of tracks and sectors, other control commands. All this is taken into account by the driver, and the application program will work with the new disk as before, using DOS interrupts.
The operating system files IO.SYS, MSDOS.SYS, and COMMAND.COM must be written to a specific location on disk. You must not copy them to other directories on the disk.
If you need to make a boot floppy that you can use to boot MS-DOS on your computer, it's not enough to just copy the main operating system files - IO.SYS, MSDOS.SYS, and COMMAND.COM - to the floppy.
To make a system diskette, you must use either the FORMAT or SYS commands, or special programs, such as the Safe Format program from the Norton Utilities package.
The easiest way to make a blank floppy bootable is to use the external MS-DOS command SYS. To use it, insert a blank floppy disk into the drive and from the root directory of drive C: issue the command:
SYS A: or SYS B:After executing the SYS command, the floppy disk will contain the files IO.SYS, MSDOS.SYS, and COMMAND.COM written to specific locations on the floppy disk. You can boot MS-DOS from this floppy by inserting a system floppy into the A: drive before turning on the power.
9.2.
When the computer is powered on, control is transferred to the bootstrap procedure located in read-only memory located on the computer's motherboard. The bootstrap procedure checks the computer's hardware, forms the initial part of the interrupt vector table, initializes external devices, and begins the process of loading the operating system.
Loading the operating system begins with the boot procedure attempting to read the very first sector of the floppy disk inserted in drive A: (on a boot floppy, this sector contains the operating system loader). If a system diskette is inserted into the drive, the bootloader is read from it and control is transferred to it.
If the floppy is not a system floppy, that is, it does not contain a boot record, a message appears on the screen asking you to replace the floppy.
If there is no diskette in drive A: at all, then the BIOS reads the master boot record of drive C: (Master Boot Record). This is usually the very first sector on the disk. Control is transferred to the bootloader, which is located in this sector. The boot loader analyzes the contents of the partition table (it is also in this sector), selects the active partition and reads the boot record of this partition. The boot record of the active partition (Boot Record) is similar to the boot record located in the first sector of the system floppy disk.
The active partition boot record reads the IO.SYS and MSDOS.SYS files from disk and loads them into the computer's RAM. Then the contents of the configuration file - CONFIG.SYS - are analyzed. This file specifies the drivers and resident programs that need to be loaded into RAM. After loading the drivers and resident programs specified in the CONFIG.SYS file, control is transferred to the COMMAND.COM command processor.
The command processor consists of three parts - resident, initializing and transitive. The resident part is loaded first. It processes interrupts INT 22H, INT 23H, INT 24H and manages the loading of the transit part. This part of the shell handles MS-DOS errors and prompts the user for action when errors are encountered.
The transit part of the command processor is located in high memory addresses. This part contains DOS internal command handlers and a batch file interpreter with the .BAT extension. The transitive part issues a system prompt (for example, A:>), waits for the operator's command to be entered from the keyboard or from a batch file, and organizes their execution.
The initializing part is used only in the process of loading the operating system and does not remain resident in RAM. The initialization part, apart from some other actions, initializes the execution of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file. The AUTOEXEC.BAT batch file can list programs that must be run when the computer's operating system boots up.
After loading the command processor and performing the initial procedures listed in the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, system preparation for operation is completed.
9.3. What are the types of MS-DOS distributions?
The MS-DOS operating system comes in two flavors. The first option is intended for installation on an unprepared (unformatted) computer disk and is usually supplied with the computer. The second option is designed to upgrade the version of an already installed operating system, is sold separately, and has the word "Upgrade" in its name.
To install the starter version, you just need to insert the first diskette of the distribution kit into drive A: before turning on the computer. After you turn on the power and check the computer's systems, the MS-DOS operating system will start loading from the floppy disk you inserted. At the end of the download process, the installer will automatically launch. The installer will guide you through the steps to install MS-DOS on your computer's hard drive.
If your computer disk already contains an MS-DOS operating system, you should find out the version of MS-DOS. This can be done using the VER command, in response to which the line will be displayed on the console:
MS-DOS Version 5.0If the version of the operating system installed on your computer is lower than 6.0, you should (although not required) update it to 6.0. This can be done with the upgrade variant of the MS-DOS distribution.
9.4. How to install MS-DOS version 5.0
In this section, we'll look at installing MS-DOS version 5.0 on a computer with an unprepared (unformatted) hard drive.
If your computer has an unformatted or unpartitioned disk, then you need to install MS-DOS using the distribution's starter version.
In the "How to Upgrade MS-DOS to 6.0" section, we'll look at the version of the MS-DOS distribution that is meant to be upgraded.
To run the installation program for the starter version of the distribution kit, you must insert the first diskette of the distribution kit into drive A: before turning on the computer. After you turn on the power and check the computer's systems, the MS-DOS operating system will start loading from the floppy disk you inserted. At the end of the download process, the installer will automatically launch.
After determining the configuration of the computer, the installer displays a splash screen on the display screen. You can either continue with the MS-DOS installation process by pressing the key
In case you proceeded with the MS-DOS installation by pressing the
This menu sets the current date and time, the name of your country, keyboard settings, the media on which MS-DOS will be installed. If you want to change the current date, time, country name or keyboard settings, select the desired menu item and press the key
If you have an IBM PC AT computer, changes to the current date and time will be written to CMOS memory and the correct time will automatically be set the next time MS-DOS is booted.
International support is set using the "COUNTRY" and "KEYBOARD" items of this menu. Select the item "COUNTRY" and press the key
If there is Russia in this list, place the cursor in the corresponding position and press the key
If you have modified "COUNTRY", make the same changes to the "KEYBOARD" element.
Once you've made changes to this menu, continue with the MS-DOS installation process by selecting "The settings are correct" and clicking
The following menu will appear on the screen:
Install to: C:DOS Run Shell on startup: YES The listed options are correct.The "Install to" line specifies the directory where MS-DOS will be installed. By default, MS-DOS files will be written to the C:DOS directory. You can change the location of the MS-DOS directory if necessary. To do this, select the "Install to" line and click
The line "Run Shell on startup: YES" means that in the future, after the operating system is loaded, the Dos Shell will automatically start. If you do not intend to use the Dos Shell, select the line "Run Shell on startup:" and press the key
To prevent auto start MS-DOS Shell select the line "Do not run MS-DOS Shell on startup" and click
When you have finished all changes, select the line "The listed options are correct" and press the key
If your computer's hard drive is not formatted, a message will appear on the screen:
Your system has one or more hard disks with free space. This space need to be partitooned and formatted before MS-DOS version 5.0 can use it.This message informs you that the computer has one or more hard drives. To use them, you must first create partitions and logical drives on them, and then format them. A menu of three items will be displayed below:
Allocate all free hard space for MS-DOS Allocate all free hard space for MS-DOS Do not allocate free hard space for MS-DOSIf you select the line "Allocate all free hard space for MS-DOS", then all the space on the computer's hard disk will be allocated to MS-DOS. The installer will automatically partition and format the computer disk. This will create one C: drive.
If you want to save disk space for another operating system, or if you are going to create multiple logical disks, select the line "Allocate all free hard space for MS-DOS" and press the key
In this case, the installer will first run the FDISK.EXE program. You will have to partition the hard disk using FDISK yourself - create partitions and logical disks on it. Instructions for using the FDISK.EXE program can be found in the "How to create logical disks" section.
After you finish working with FDISK.EXE, control will return to the installer and it will automatically perform high-level formatting of the logical disks you created.
The line "Do not allocate free hard space for MS-DOS" means that you do not want to allocate free hard space for MS-DOS, and thus refuse to install the operating system on the hard disk.
When installing MS-DOS for the first time, we recommend that you create one logical drive by selecting "Allocate all free hard space for MS-DOS" from the menu.
To continue the installation process, press the key
When 100% of the disk is formatted, the process of copying the operating system files from the distribution kit to the computer's hard drive will begin.
As you copy the distribution diskettes, the installer will ask you to insert new disks into the drive:
Insert the disk labled MS-DOS 5.0 Disk 2 into drive A: When ready, press ENTER.After copying the last distribution diskette, the installer will report that the MS-DOS installation is complete:
Setup is now complete. Please remove any floppy disks from your drives and then press ENTER to start MS-DOS version 5.0.This completes the installation process of the MS-DOS version 5.0 operating system. Remove the last distribution diskette from the drive and press the key
The installer will automatically create the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT configuration files. Their content depends on the hardware configuration of your computer.
The CONFIG.SYS file will look like this:
DEVICE=C:DOSSETVER.EXE DEVICE=C:DOSHIMEM.SYS DOS=HIGH FILES=10The automatically generated CONFIG.SYS file loads the SETVER.EXE resident program and the HIMEM.SYS driver (on machines with 80286, 80386, and 80486 processors only).
The HIMEM.SYS driver is used to manage extended memory. Without this or another similar driver, extended memory cannot be used.
The SETVER.EXE program is required for programs designed for older versions of MS-DOS. When such programs ask for a version number, SETVER.EXE "tricks" them and returns predefined values for them.
The DOS=HIGH command tells MS-DOS to use a portion of extended memory (high memory area) to house its own modules and buffers. In this case, the amount of main memory available for programs increases slightly.
The FILES=10 command means that MS-DOS can have up to 10 files open for reading or writing at the same time. Depending on what software you intend to use, you may need to change this value. For example, when using databases, as a rule, it is necessary to increase the number of possible open files from 10 to 50. Such an increase is not in vain, an increase in the number of FILES entails additional consumption of computer RAM.
For novice users, we do not recommend changing the contents of the CONFIG.SYS file unless absolutely necessary, as incorrect changes may result in decreased performance of the operating system or other troubles.
In addition to the CONFIG.SYS file, the batch file AUTOEXEC.BAT is automatically created. It may contain the following commands:
The @ECHO OFF command cancels the display of the text of a batch file during its execution. In this case, this means that when the computer boots up, the text of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file will not be displayed on the screen.
The PROMPT command defines the appearance of the MS-DOS prompt. In our case, the PROMPT $p$g command generates a prompt string that displays the full path of the current directory followed by the ">" character. By giving the PROMPT command other options, you can customize the MS-DOS prompt as you wish.
The PATH command sets the paths of the directories in which the files to be executed will be searched.
The SET TEMP=C:DOS command sets the TEMP environment variable. This variable specifies the directory where MS-DOS temporary files will be created.
9.5. How to update the MS-DOS operating system version to 6.0
In this section, we cover the procedure for upgrading the MS-DOS operating system to version 6.0.
To upgrade your MS-DOS version, you need to insert the first distribution diskette and run the SETUP.EXE program that is on this diskette. The floppy disk can be inserted into any drive. For example, if you inserted a floppy disk into drive B:, then you would enter the following command:
B:SETUP.EXE /GThe /G option tells the installer not to save the old version of MS-DOS.
Once launched, the setup program (installer) checks the hardware and software configuration of your computer.
After determining the configuration of the computer, SETUP.EXE displays a splash screen on the display screen. You can either continue with the MS-DOS installation process by pressing the key
In case you continued the installation process by pressing the key
Rice. 9.1. Configuration Definition
This menu determines the type of operating system previously installed on the computer, the location of the directory where the operating system files will be placed, and the type of video adapter. We are most interested in the location of the MS-DOS directory. The type of operating system and type of video adapter is automatically determined by the SETUP program and, as a rule, do not need to be changed.
By default MS-DOS files will be written to the directory containing MS-DOS files old version. You can change the location of this directory, although you should not do so unless necessary. To change the location of the directory, select "MS-DOS Path" from the menu and press the key
If you agree with the proposed configuration or have already made all the necessary changes, select the item "The setting are correct" from the menu and press the key
MS-DOS version 6.0 includes the Microsoft Backup program, designed to dump the contents of computer hard drives to floppy disks, the Microsoft Undelete program to recover deleted files, and the Microsoft Anti-Virus package to detect and remove viruses. The distribution includes both MS-DOS and Windows versions of these programs. After you determine your MS-DOS configuration, you can choose which of these programs to install on your computer's hard drive. To do this, the installer displays a menu (see Figure 9.2).
Sequentially selecting with the cursor keys from the menu fig. 9.2 "Backup:", "Undelete:", "Anti-Virus:" elements responsible for these programs and pressing the key
Rice. 9.3. Menu for selecting software version
The first line in the menu - "Windows and MS-DOS" means that the DOS and Windows versions of this program will be installed. The second one is for Windows only, the third one is for DOS only and the string "None" means that you will not install this program for either MS-DOS or Windows. Select the desired configuration and click
Windows versions of programs can only be installed if the Windows operating system is already installed on the computer. Otherwise, you can only install MS-DOS programs in the first step. After Windows installation you can repeat the MS-DOS setup process by running SETUP.EXE with the /E option. In this case, the Microsoft Backup, Microsoft Undelete and Microsoft Anti-Virus programs are installed, the rest of the operating system files are not copied.
When you have finally decided which programs you want to install, select fig. 9.2 item "Install the listed programs" and press the key
The installer will now give you one last opportunity to abort the MS-DOS installation process. To interrupt the installation process, press the F3 key. If you intend to proceed with the MS-DOS installation, press the key
After you press the key
When all diskettes have been copied, the installer will correct the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files. It will then ask you to remove the last floppy disk from the drive and press the key
A message will appear on the screen stating that the installation of the operating system is complete. Press the key again
If the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files did not exist on the hard drive before installing MS-DOS (you install the starter distribution or removed these files yourself), they are automatically created by the installer. Their content depends on the hardware configuration of your computer.
The CONFIG.SYS file might look like this, for example:
DEVICE=C:DOSSETVER.EXE DEVICE=C:DOSHIMEM.SYS DOS=HIGH FILES=30 SHELL=C:DOSCOMMAND.COM C:DOS /pCompared to the CONFIG.SYS file automatically created when MS-DOS version 5.0 was installed, the FILES value has been increased and the SHELL command has been added. The command SHELL=C:DOSCOMMAND.COM C:DOS /p specifies that the command processor is located in the C:DOS directory.
In addition to the CONFIG.SYS file, the AUTOEXEC.BAT batch file is automatically created. The contents of the AUTOEXEC.BAT file are the same as the AUTOEXEC.BAT file created when installing MS-DOS version 5.0:
@ECHO OFF PROMPT $p$g PATH C:DOS SET TEMP=C:DOSAfter installing MS-DOS from the distribution, you will not be able to get started yet. Without additional settings, Russian characters may not appear on the display screen, other characters will be displayed instead. Moreover, even if the video adapter of your computer is Russified at the hardware level and Cyrillic characters are still displayed, you will not be able to type them on the keyboard.
Thus, immediately after installing MS-DOS, it's time to start its Russification. Russification process is described in the section "How to Russify MS-DOS".
9.6. How MS-DOS version 6.0 differs from MS-DOS version 5.0
The new MS-DOS version 6.0 operating system has several important features not available in earlier versions:
- the ability to branch when executing the CONFIG.SYS file;
MS-DOS version 6.0 allows you to create on-screen menus and branch at the time the CONFIG.SYS file is executed, depending on the line selected by the user. In this case, with the help of a special variable, branching can be further carried out in the AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
- dynamic file compression tool - DoubleSpace, similar to the Stacker package from Stack Inc.;
Using the dynamic compressor DoubleSpace, by compressing information on hard drives you can increase their capacity. In this case, there is no need to separately purchase dynamic compression tools such as the Stacker package, since DoubleSpace is included in the MS-DOS version 6.0 distribution kit.
- MS-DOS version 6.0 includes a file defragmentation program - Defrag;
The Microsoft Defrag program allows you to defragment files on disks, increasing their performance. Until now, programs like this had to be purchased separately.
- MS-DOS version 6.0 includes Microsoft Anti-Virus;
With the Microsoft Anti-Virus program, you can perform preventive work to detect and remove viruses from your computer's operating system.
- disk unloader Microsoft Backup;
With the Microsoft Backup program, you can periodically backup information from computer disks. Backup will save valuable data stored on hard drives in case of various emergencies.
- availability of Microsoft Undelete, Microsoft Anti-Virus, and Microsoft Backup for Windows system maintenance programs;
For the first time, MS-DOS includes programs specifically designed to run on the Microsoft Windows operating system.
After installing Microsoft Undelete, Microsoft Anti-Virus and Microsoft Backup, the "Microsoft Tools" group containing their icons is added to the main Program Manager window. The "Tools" menu is added to the main Program Manager menu.
- new version of EMM386.EXE driver;
The new version of the EMM386.EXE driver provides access to more high memory blocks. This frees up more main memory for MS-DOS programs.
- new versions of LOADHIGH and DEVICEHIGH commands;
Newer versions of the LOADHIGH and DEVICEHIGH commands allow you to specify the location in memory where programs and drivers are loaded.
- a tool for optimizing the use of computer RAM - the MemMaker program;
MS-DOS version 6.0 includes the MemMaker program, which allows computers with 80386 and higher processors to optimize the use of RAM. MemMaker adjusts the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files so that drivers and resident programs are loaded into extended memory whenever possible. This increases the amount of main RAM available to MS-DOS programs.
- the possibility of step-by-step execution of commands in the CONFIG.SYS file.
If, when loading the operating system, when the screen displays the inscription "Starting MS-DOS ...", press the key
You can also step through the commands in the CONFIG.SYS file, confirming that each command has been executed. To do this, at the time of loading MS-DOS, you need to press the key
The next command will be displayed on the screen followed by the menu "?". If we now press the key
9.7. How to create a menu in CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT
The hardware and software configuration of the computer is defined in the CONFIG.SYS configuration file and in the AUTOEXEC.BAT command file.
If you have multiple people working on your computer, or you are using incompatible software products, then you have to store multiple CONFIG.SYS configuration files and multiple AUTOEXEC.BAT batch files. As needed, you will need to rename them and restart your computer.
MS-DOS version 6.0 provides a facility for defining several different configurations in a single CONFIG.SYS file. The required configuration is selected using a menu that can be described in the CONFIG.SYS file.
MS-DOS version 6.0 defines several special commands to describe menus:
Computer configuration commands and menu description commands are grouped into so-called command blocks and menu description blocks. Blocks start with headings. The header consists of the block name enclosed in square brackets. The block ends either with the header of the next block or with the end of the file.
To define several configurations in the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files, you need to perform several actions:
- Define the main menu description block in the CONFIG.SYS file. Menu descriptions begin with a title followed by commands
, , - For each menu item, create a command block in which to describe the required configuration. This configuration will be set when you select the corresponding menu item. Each block must begin with a block header. The block header is the name of the block enclosed in square brackets.
- If necessary, you can add a command block with the reserved name to the CONFIG.SYS file. The commands from this block are executed when any configuration is selected. It is recommended to add an empty command block at the end of the CONFIG.SYS file named .
- When the user selects an item from the configuration menu, its name is stored in the CONFIG environment variable. With the GOTO %CONFIG% command, you can organize the execution of different commands depending on the selected configuration. AUTOEXEC.BAT
Let's take a closer look at the individual menu description commands.
INCLUDE
The command is used to include commands from one configuration block into another. The format of this command is shown below:
INCLUDE=blocknameThe single parameter blockname specifies the name of the configuration block to include.
MENUCOLOR
Specifies the text color and background color of menu items. This command can only be used inside a menu description block. The MENUCOLOR command has the following format:
MENUCOLOR=x[,y]The x parameter specifies the text color of the menu items, and the y parameter specifies the background color of the menu. The color is defined by numbers from 0 to 15 according to the following table:
Do not set x and y to the same value, as this will cause the menu item text to blend into the background.
MENUDEFAULT
Specifies the configuration that is loaded after the specified time has elapsed if the user has not selected another configuration. The MENUDEFAULT command can only be used inside the menu description block of the CONFIG.SYS file. The format of this command is shown below:
MENUDEFAULT=blockname[,timeout]The blockname parameter specifies the name of the configuration block that is loaded after the time specified by the timeout parameter has elapsed. The timeout parameter is specified in seconds and can be from 0 to 90 seconds.
MENUITEM
The MENUITEM command defines configuration menu items. This command can only be used inside a menu description block. One menu can have up to nine items. If this is not enough for you, you can use the additional menu (command
The blockname parameter specifies the name of the configuration block corresponding to this menu item. When the user selects a menu item, the commands from the configuration block named blockname will be executed. The block name must be shorter than 70 characters and must not contain the following characters: slash (), backslash (/), colon, semicolon, equal sign, and square brackets.
The menu_text parameter specifies the text you wish to display in this menu item. If the menu_text parameter is not defined, then the name of the configuration block will be displayed in the menu. The text specified by the menu_text parameter must be shorter than 70 characters and can contain any characters.
SUBMENU
The SUBMENU command adds a new item to the main configuration menu. When you select a menu item specified by the SUBMENU command, an additional menu appears.
The format for calling this command is shown below:
SUBMENU=blockname[,menu_text]The blockname parameter defines the name of the additional menu description block. Unlike the description block of the main menu, which has the name , the additional menu must have a different name. The length of the additional menu block name should not exceed 70 characters. The block name must not contain a slash (), backslash (/), colon, semicolon, equals, or square brackets.
The optional parameter menu_text specifies the text corresponding to the new menu item. If you don't specify the menu_text parameter, the new menu item will display the name of the sub-menu description block specified by the first parameter of the SUBMENU command.
An example of using the new commands
Let's assume that there are three people working on an IBM PCAT 386 computer. The first one works in the operating room Microsoft system Windows and uses a word processor Microsoft Word. The second prefers to use the Lexicon text editor for editing documents. The third one does not work with either Microsoft Windows or Lexicon.
In MS-DOS version 5.0, each of these users had to keep their own versions of the computer's configuration files, CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT, and permanently rename them.
The MS-DOS version 6.0 operating system has been supplemented with new commands (described above) designed to organize the configuration selection menu at the stage of interpreting the CONFIG.SYS file.
Here is an example of a CONFIG.SYS file that might be installed on this computer:
menuitem=Windows, Windows Configuration menuitem=Lexicon, Lexicon Configuration menuitem=Standart, Standard Configuration device=c:doshimem.sys dos=high buffers=15 device=c:dosemm386 NOEMS dos=high,umb devicehigh=c:dosSMARTDRV. EXE 2048 1024 device=c:dosSMARTDRV.EXE 2048 device=c:dossetver.sys device=c:dosemm386 NOEMS dos=high,umb devicehigh=c:dosSMARTDRV.EXE 2048 devicehigh=c:dossetver.sys files=40This CONFIG.SYS file contains descriptions of three different configurations - the configuration for working under the Windows operating system, the configuration for working with the Lexicon word processor, and the configuration for working in the MS-DOS operating system.
For all three configurations, the commands in the block are executed. There are two commands there: DEVICE=C:DOSHIMEM.SYS and DOS=HIGH. These commands load the extended memory manager HIMEM.SYS, and enable MS-DOS to use the high memory area (HMA).
After executing these two commands, the main menu appears on the screen, defined in the block:
_ Configuration for Windows Configuration for Lexicon Standard configurationWhen you have selected the configuration you wish to download, press the key
Finally, the files=40 command located in the last block is executed. This completes the interpretation of the CONFIG.SYS file and MS-DOS starts executing the batch file AUTOEXEC.BAT.
You can optionally branch within the AUTOEXEC.BAT file based on the configuration selected from the CONFIG.SYS file menu. The special environment variable CONFIG is intended for this purpose. When executing commands in the CONFIG.SYS file, the CONFIG variable is set to the name of the selected configuration block.
In the batch file AUTOEXEC.BAT you can check the value of the CONFIG variable and execute various commands depending on its value. To check the state of the CONFIG environment variable, you can use the commands
Let's take AUTOEXEC.BAT as an example for the previous example.
set temp=c:temp c:dosmode >nul CON CP PREP=((866) c:dosega.cpi) c:dosmode >nul CON CP SEL=866 loadhigh c:utswakeyb.com rem !!! Let's move on to the label corresponding to the value of rem !!! environment variable CONFIG goto %config% :Windows path c:win;c:dos;e:nc;c:ut;d:nu7;e:bcbin;d:winword; loadhigh c:winSMARTDRV.EXE 2048 1024 loadhigh c:winmouse.com win goto end_ :Lexicon path c:lex;c:dos;e:nc;c:ut;d:nu7;e:bcbin; c:dosSMARTDRV.EXE 2048 c:mousemouse.com lex goto end:Standart path c:dos;e:nc;c:ut;d:nu7;e:bcbin; loadhigh c:dosSMARTDRV.EXE 2048 loadhigh c:mousemouse.com nc goto end:endWhen MS-DOS starts executing commands from the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, the TEMP environment variable is set first, then fonts containing Cyrillic characters are loaded.
Then, with the GOTO %CONFIG% command, control is transferred to the label corresponding to the name of the selected configuration block. The configuration block names are listed in the menu description block in the CONFIG.SYS file.
Thus, depending on which configuration is selected in the menu, control will be transferred to one of three labels - Windows, Lexicon or Standard. In this case, only its own commands are executed for each configuration. After executing the commands following the labels, control passes to the END label and the execution of the batch file AUTOEXEC.BAT ends.
For example, if, when interpreting the CONFIG.SYS file, you select the main menu item labeled "Configuration for Windows", then the CONFIG environment variable will be set to Windows and control will go to the label:Windows.
Here the PATH environment variable is set, the disk cache driver and the mouse driver are loaded. Then the Windows operating system is loaded.
9.8. Why are there no Russian characters in MS-DOS?
The set of characters that can be displayed on your computers screen in MS-DOS text and graphics modes is located on the read-only memory (ROM) chip on the video adapter.
The Windows operating system, unlike MS-DOS, does not use characters from the video adapter's ROM. To display characters, Windows uses font sets stored in special files.
Usually, the so-called standard extended set of ASCII characters is stored in the ROM of the video adapter. This set does not contain Cyrillic characters and therefore the computer cannot display them on the display screen.
To "russify" video adapters, you can either reprogram the adapter's ROM, or use special resident programs that replace the video adapter character set with your own.
"Russification" of video adapters at the ROM level allows you to save a few kilobytes of computer RAM in the future, since there is no need to use special resident programs. In addition, if you are unlucky and have a CGA or Hercules video adapter installed on your computer, then flashing the ROM is the only possibility (except, of course, replacing the video adapter, which, by the way, is preferable in this case) to display Cyrillic characters in text modes.
However, flashing the video adapter's ROM requires special hardware and information about the location of the font set in the ROM. Thus, flashing a ROM is a very difficult task and can only be performed by highly qualified specialists.
When "russifying" the video adapter with the help of special programs, it is necessary to load a small resident module into the computer's RAM. This resident module will replace the character set stored in the video adapter's ROM.
In the "How to Russify MS-DOS" section, the process of Russifying a video adapter will be described in more detail.
In addition to Russification of the video adapter, it is necessary to "Russify" the computer keyboard. Usually keyboards do not contain special keys for entering Russian characters. Special resident programs are designed to "russify" the keyboard. After loading, they remain in RAM and track the user pressing a certain key combination, for example, the right key
Now pressing the keyboard keys will cause the input of not Latin, but Russian characters. Usually, the keys are reassigned in accordance with the domestic standard for typewriters ("YTSUKEN"). Next to the Latin characters located on the keyboard keys, we recommend placing stickers with Cyrillic characters. It is convenient if Latin characters are black and Cyrillic characters are red.
More detailed information about the Russification of the keyboard is presented in the section "How to Russify MS-DOS".
9.9. How to Russify MS-DOS
The MS-DOS version 6.0 operating system contains commands and programs for international support.
For Russification, after installing MS-DOS version 6.0, we suggest that you replace the files of commands and international support programs with the corresponding files from the Russian version of MS-DOS. Russian versions of MS-DOS 4.01, 5.0 and 6.0 are currently released.
If you do not have the Russian version of MS-DOS, copy from the Russian version 4.0 or 5.0 of the MS-DOS operating system the following files: COUNTRY.SYS, DISPLAY.SYS, KEYBOARD.SYS, KEYB.COM, as well as files with the CPI extension. Replace these files with the appropriate files in the MS-DOS directory.
Since the DISPLAY.SYS driver and the KEYB.COM program check the version of the operating system, they must be "fooled". To do this, run the following commands:
C:DOSSETVER KEYB.COM 4.01 C:DOSSETVER DISPLAY.SYS 4.01Then, using any text editor, you need to add international support commands to the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files. In the CONFIG.SYS file, you must load the SETVER.EXE driver, add a call to the COUNTRY command, and load the DISPLAY.SYS driver:
DEVICE=C:DOSSETVER.EXE COUNTRY=7,C:DOSCOUNTRY.SYS DEVICE=C:DOSDISPLAY.SYS CON=(EGA,437,1)In the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, you need to add a call to two MODE commands and load the KEYB resident program:
c:dosmode CON CP PREP=((866) C:DOSEGA.CPI) c:dosmode CON CP SEL=866 D:DOSkeyb RU,D:DOSKEYBOARD.SYS /ID:093After making all the changes to the CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files, restart your computer. When the computer is restarted, the resident modules of the Russification programs are loaded into the RAM.
Do not use word processors to edit CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT files that save edited files in special formats. When you save editable text in a file that has a special format, other control information will be written to it, in addition to the text. As a result, MS-DOS will not be able to interpret these files, and the computer will not boot properly.
Now you can view and edit documents written in Russian, in addition, you will have all the benefits of MS-DOS version 6.0.
When editing texts in Russian, switch the keyboard to the Cyrillic character input mode. To do this, press the right key
9.10. What are viruses and trojans
The most general definition of a virus can be given as a program code that self-propagates in the information environment of computers. According to the way viruses spread, they can be divided into the following main groups:
- programs embedded in executable files - files with COM and EXE extensions;
- propagating through the boot sectors of floppy disks and hard drives, as well as through the boot sector of hard drives;
- infecting driver files - files with SYS and EXE extensions;
- propagated through translator object library files.
In addition to the above groups, there are others, such as viruses that infect batch files - files with the BAT extension. "Progress" in the world of viruses does not stand still and we can expect the emergence of new groups of viruses.
The action of most viruses, unfortunately, is not limited to reproduction and spread. They can cause relatively harmless or devastating effects.
Outwardly, the action of viruses can be expressed in the fact that periodically, for example, after reaching a certain time, the virus is activated and performs some operations. In particular, viruses can: display extraneous inscriptions and symbols on the screen, "shower" symbols already displayed on the screen, restart the computer, slow down the computer, play all kinds of melodies, delete files and directories, erase randomly selected sectors of hard and floppy disks.
In principle, viruses can perform any action. They are limited only by the imagination of the author of the virus and the capabilities of the computer.
Trojans are much less common than viruses. Trojans are programs that do something useful features, however, at some point, they can additionally perform some malicious actions, such as formatting a hard drive.
Currently, the spread of viruses has reached truly gigantic proportions and threatens users with irretrievable loss of data stored on a computer.
To increase the security of data on your computer, it is necessary to limit the exchange of executable program modules, as well as periodically carry out preventive work to detect viruses. For more information on how to deal with viruses, see the "How to deal with viruses" section.
9.11. How to deal with viruses
If you do not periodically carry out work to prevent and treat computers from viruses, the possibility of losing stored information and destroying the operating environment becomes more than real.
The negative consequences of your negligence may be different, depending on which virus gets into your computer. You can lose either part of the information from the files stored on the computer, or entire files, or even all the files on the disk.
Work on the prevention and treatment of computers from viruses may include the following actions:
- installation software should be carried out only from distributions;
- limit the exchange of programs and diskettes, scan such programs and diskettes for viruses;
- periodically check the computer's RAM and disks for viruses using special anti-virus programs, such as the AIDSTEST.EXE program;
- use special protection programs that, after being launched, remain resident in the computer's memory and monitor all suspicious actions of programs (for example, writing programs to a file or system disk areas).
Currently, there are thousands of different viruses and hundreds of programs to combat them. The most famous anti-virus programs for MS-DOS are: AIDSTEST, SCAN, ANTI4US, VAKCINA, ADINF.
The problem of fighting viruses has become so serious that Microsoft included in version 6.0 of the MS-DOS operating system its own software tools: Microsoft Anti-Virus for MS-DOS and for Windows.
There are even special programs for fighting viruses in networks. For example, NetShield is loaded on a Nowell NetWare 3.11 server as an NLM process. It can scan server disks for viruses once a day. If a virus is detected, a corresponding warning message will be sent to all network users. You can also set the mode in which NLM Anti-Virus will scan all files written to or read from the server for virus infection.
Consider the most common software tools designed to detect and remove viruses - AIDSTEST.EXE and Microsoft Anti-Virus.
AIDSTEST.EXE
The author of the AIDSTEST.EXE anti-virus program is Lozinsky Dmitry Nikolaevich. AIDSTEST can detect a wide variety of viruses and can also remove detected viruses.
A description of the AIDSTEST options can be obtained by running AIDSTEST with the /h option. We will allow ourselves to give only the most important parameters of this program. The format of the AIDSTEST call is as follows:
AIDSTEST path [options]The first, mandatory, path parameter must specify the directory in which the virus scan will be performed. This automatically checks all subdirectories. If you specify only the drive name as the first parameter (eg AIDSTEST C:), then the entire drive will be checked.
If you don't give the AIDSTEST program any additional parameters, it will only scan for viruses. In the event that you want to remove the viruses found, you need to specify additional parameter/F. AIDSTEST will fix virus-infected programs and erase those that cannot be repaired. In order for AIDSTEST to ask for permission to remove corrupted program files, you must additionally specify the /Q option.
Below is an example of using the AIDSTEST antivirus to detect and treat viruses on the C: drive.
AIDSTEST C: /F /QThe use of anti-virus software cannot guarantee that your computer will be completely protected from viruses. The fact is that antiviruses like AIDSTEST are configured to detect already known viruses and their clones. New viruses may not be known to AIDSTEST and may not be able to detect them. We emphasize once again that, in our opinion, the most reliable way to protect your computer from attack by viruses is to install software only from distributions and limit the use of floppy disks for program exchange.
Microsoft AntiVirus
Microsoft Anti-Virus is included with the MS-DOS version 6.0 distribution. At the same time, Microsoft Anti-Virus is presented in two versions - for MS-DOS and for Windows.
The detailed procedure for installing these anti-virus programs is described in the "How to install MS-DOS" section. Here we only note that for Microsoft installations Anti-Virus for Windows requires Windows to be installed on your computer's hard drive.