Despite the end of the floppy era, 3.5 floppy disks are still used in everyday life.
Let us consider in more detail where they can be found, what is special about them and why the floppy disk is still one of the most or transmission of secret information.
Content:
Basic concepts and history of use
Floppy disk Is a physical storage medium with which data can be repeatedly moved, erased, and rewritten.
In simple words, this is a simplified version of modern flash drives and disk drives.
The floppy disk was the first to appear.
Externally, the device has a rectangular shape and a plastic case. A ferrimagnetic layer is applied on top, with the help of which the floppy drive reads information. You cannot read a floppy disk with. This requires a special floppy drive.
Today it can only be found in older desktop computers. Typically, the drive is located at the bottom of the case and looks like this:
The first floppy disk was created in 1967 by Alan Sugart- at that time one of the leading specialists of the IBM company. Until 1076, Shugart created and developed his own company, which began supplying drives to computer system developers. This was the beginning of the era of using floppy disks. The most popular floppy disk format was developed by Sony in 1981. The drive with a diameter of 3.5 inches can still be found in stores. Also, it is this kind of floppy disk that is recognizable. In most programs, the key with the 3.5-inch floppy icon means save actions.
Floppy disks were distributed among users in the period from the 70s to the 90s of the last century.
With the invention of optical discs, the popularity of floppy disks gradually began to decline. As you know, optical discs are already being removed from everyday life.
Many laptop and personal computer manufacturers have completely abandoned the use of floppy drives.
Despite this, floppy disks are still produced and sold.
With the onset of the 2010s, all the world's IT corporations began to abandon the production of floppy disks.
For example, in 2011 Sony announced that it would completely cease making and sell 3.5-inch floppy disks.
Now they can only be made by order of the government.
Other floppy disk failures:
- year 2014- Toshiba announced the closure of the disc factory. In the same year, the plant was converted into a huge farm of organic vegetables;
- 2015 year- Microsoft developers decided not to create floppy disk support in. This OS does not work with floppy disks and it will be impossible to connect an external drive. The system simply won't "see" the device;
- 2016 year- The Pentagon drew up a modernization plan, one of the goals of which was to stop using floppy disks. The implementation of the plan is scheduled for the end of 2018.

Floppy disk formats
The types of floppy disks are divided depending on the diameter of the drive. For the entire time of floppy disk distribution the following formats existed:
- 8-inch;
The first type of floppy disk that has become widespread among PC users is an eight-inch drive.
Outwardly, it has a rectangular shape, made of polymer materials.
The magnetic mechanism itself is located inside a plastic case. Inside there is a special notch with which the drive reads information from. After starting the drive, the device reads the location of the first track. This is how the process of "decrypting" information from a floppy disk begins.
An eight-inch floppy disk can be 80KB, 256KB, or 800KB in size. Over time, such a volume of information was not even enough, so the development of floppy disks with a larger volume began.

- 5.25 inches;
This generation of floppy disks is virtually indistinguishable from eight-inch drives.
The only difference- Improved index holes for reading data.
Thanks to the use of a new technology for creating a material for the case, the disc was stored for a longer time, was resistant to scratches and drops from a small height.
Floppy disks of this type were either single-sided or double-sided. To start using the additional side, it was enough to turn the drive over. On single-sided models, this action could thin the drive.
5.25-inch floppy disks could store 110 KB, 360 KB, 720 KB, or 1200 KB of information.
The release of such floppy disks ended in the early 2000s.

- 3.5 inches;
The 3.5-inch floppy disk is the most popular floppy disk option.
Outwardly, it differs from previous generations in an even more durable body, as well as a completely solid surface.
This type of diskette now has the ability to install.
it can be configured by the user of the floppy disk before the first writing of information to removable media.
The size of the 3.5 floppy disk is determined using the square holes in the lower right corner of the device. One square - capacity 720 KB, two - 1.44 MB and three - 2.88 MB.

Despite all the disadvantages of using floppy disks, namely small capacity and sensitivity to the influence of magnetic fields, the 3.5 floppy disk was popular even after the release of optical discs.
All because of the convenience in data transfer and the cheap cost of floppy disks and disk drives.
Iomega Zip.
This type of storage has become intermediate between the era of floppy disks and optical discs.
Externally, the Iomega looks like a floppy disk, but the device is flexible.
Due to its high cost and manufacturer's lack of interest in such a floppy disk, Iomega never became more popular than standard 3.5-inch floppy disks.
The Iomega capacity reached 750MB.
Also, the device had a high speed of reading and processing data.

What is a floppy disk for today?
Despite popular belief that the era of floppy disks is over, floppy disks can still be encountered in many areas.
In the CIS, floppy disks are still used by government agencies to keep track of citizens' data.
For example, tax offices store data on taxpayers in the form of floppy disks. The use of such an outdated drive is explained by the fact that records of 10 or even 20 years ago are still stored on them. Information is not transferred to newer devices due to lack of funding or lack of new computers.
Also, 3.5-inch floppy disks are used in schools.
Floppy drives are still common in any computer science office.
On them, students bring homework and hand it over to the teacher. This property is not typical for all, but for most schools. This is explained by outdated equipment.
Floppy disks 3.5 and the Pentagon
One of the more interesting uses of floppy disks in the modern world is the Pentagon.
The most hi-tech and popular state-level security center still works with ordinary floppy disks.
Of course, Pentagon employees do not store absolutely all information on floppy disks.
According to the organization's official report for 2015, floppy disks work as an additional method of protecting information.
They store data on vigorous weapons and other classified information.
To read and process data, the Pentagon uses old models of computers that do not have and work without being connected to any networks.
This approach eliminates the possibility of a hacker attack "over the air", which the Pentagon has encountered countless times.
According to the plan of the US Department of Defense, the floppy disks are to be decommissioned at the Pentagon by the end of 2018. It is reported that in order to increase the level of security of classified data, it is planned to introduce ultra-strong algorithms and constant monitoring without using the Internet.
Thematic videos:
The other uses (used) special external media (floppy disks and disks). Naturally, technologies do not stand still and more and more new devices are being invented, or the old ones are being improved in terms of data transfer speed and memory capacity.
In this article we will look at how and when the first disks, floppy disks appeared, as well as their main characteristics and features.
Floppy disk 8 "(inches)- In 1971, the 8-inch floppy disk and disk drive for it was first introduced. This diskette was released by IBM. The disc itself consists of a magnetically coated polymer material in a plastic wrap. Depending on the number of sectors, such floppy disks had different sizes and were subdivided into 80 kb, 256 kb and 800 kb.

5.25 "floppy disk - In 1976, Shugart Associates designed and manufactured the 5.25" floppy disk drive and floppy disks. 5-inch floppy disks quickly gained popularity and supplanted their predecessors. This floppy disk was not much different from the 8-inch parents, except that it was smaller in size, the plastic cover was stiffer, and the edges of the drive hole were reinforced with a plastic ring. Such disks (depending on the format) contained 110, 360, 720 or 1200 kilobytes of data.
3.5 ”Floppy Disk - In 1981, Sony introduced the 3.5” floppy disk for the first time. This diskette was already specifically different from the previous ones. The floppy disk was covered with a hard case, in the center of the floppy disk there was a metal sleeve, which allowed it to be correctly positioned in the disk drive. Floppy disks were mostly 1.44 MB, but there were 720 kb, as well as 2.88 MB. This type of floppy disk has survived the most on the market and is even still used in many structures and institutions.
Iomega ZIP - In the mid-90s, 3.5-inch floppy disks were replaced by ZIP disks. Outwardly, they resembled 3.5 ”floppy disks, but were slightly thicker. They were supposed to replace the previous generation, as 1.44 MB was no longer enough to store data. ZIP disks were issued in sizes of 100 MB and 250 MB (At sunset, there were even 750 MB). But the disks did not gain popularity, since the drives and the disks themselves were very expensive, so people remained loyal to their 3.5 ”comrades.
COMPACT DISCS (CD-ROM / CD-RW / DVD-ROM / DVD + R / DWD-R / DVDRWBlueRay)
The CD was first developed by Sony as early as 1979, and mass production of these discs began in 1982. Initially, they wanted to use CDs only for audio recordings, but later they began to store all digital data on them. The vice-president of Sony insisted that Beethoven's ninth symphony, which took 74 minutes (under the direction of Wilhelm Furtwängler), could fully fit on the disc, then any classical work would fit on such a disc. If we take the amount of data, then such a floppy disk contained 650 MB. Starting somewhere in 2000, 700 MB (80 minutes) disks began to be produced.
The disc itself consists of polycarbonate coated with a thin layer of metal (aluminum, silver), which in turn is covered with a thin layer of varnish.
In 1988, the format appears CD-R(Recordable - Recordable). This is the same CD, but empty, in other words "Blank". Any information could be recorded on it, but then it was impossible to delete it from the disk.
In 1997, the format appears CD-RW(ReWritable - Rewritable). This is also the same CD-R, only now the data from it could be erased and others written.
DVD(Digital Video Disk - Digital Video Disk) - the disk had the same dimensions as a regular CD and externally was no different, but had a more dense structure. The first discs appeared in Japan in 1996, and their volume was 1.46 GB (DVD-1), which was twice as much as regular CDs. The most popular are the 4.7 GB DVD (DVD-5). The maximum capacity for a DVD is 17.08 GB (DVD-18).
DVD-R- The first DVD-R was released in 1997 at a price of $ 50 and a volume of 3.95 GB. Many people ask the question: what is the difference between DVD-R and DVD + R? Everything is very simple. You cannot erase information from both of them, but you can write on "+" before, and you cannot write on "-".
DVD-RAM- Rewritable discs, but unlike DVD-RW, they can be rewritten at least 100,000 times (the usual ones are designed for 1,000). Also, information is read much faster and writing to it occurs as on a removable hard disk, i.e. without additional software. Of course, such a disc is more expensive, and even not all players can read it.
BD (BlueRay Disc)- a disc with a higher density than DVD. Mainly designed to record high definition movies there. The disc was first introduced to the general public in 2006. Its volume is 25 GB (single layer) and 50 GB (dual layer). Mini BD 7.8 GB are also available.
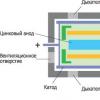
Diskette, floppy disk (GMD), Floppy Disk, jarg. flop- portable magnetic data carrier. It is a plastic disk covered with a magnetic material and placed in a protective envelope.
Reading and writing information to a floppy disk is done by means of a floppy drive. Writing is done by the drive head sliding the spinning disc and magnetizing the surface.
History
· 1971 - The first 200 mm (8 ″) floppy disk with an appropriate disk drive was introduced by IBM. Usually the invention itself is attributed to Alan Sugart, who worked at IBM in the late 1960s.
1973 - Alan Shugert founds his own firm, Shugart Associates.
· 1976 - Alan Schugert develops the 5.25 ″ floppy disk.
1981 - Sony introduces a 3.5 ″ (90 mm) floppy disk to the market. In the first version, the volume is 720 kilobytes (9 sectors). The later version has a volume of 1440 kilobytes or 1.40 megabytes (18 sectors). It is this type of floppy disk that becomes the standard (after IBM uses it in its IBM PC).
Later, the so-called ED floppy disks appeared (from the English. ExtendedDensity- "extended density"), which had a volume of 2880 kilobytes (36 sectors), which did not become widespread
Floppy disk design
The main components of a floppy disk are a magnetic disk that stores information and an envelope that acts as a protective disk for the disk.
The envelope of 8- and 5.25-inch floppy disks was made from a material that allows it to bend easily enough, which became the reason to call them "flexible". 3.5-inch floppy disks were already produced in a hard plastic case, but the name remained with them.
There are two main holes in the envelope: one in the center so that the spindle motor can grip and rotate the magnetic disk, the other is elongated from the center to the edge, and serves so that the heads can touch the surface of the disk. double-sided floppy disks have a hole on each side for this. For 3-inch floppy disks, the holes for the heads during transportation are closed by a shutter, which is opened by the mechanics of the drive when the floppy is inserted.
The envelope also has a write-protect window or cutout. For 8- and 5-inch floppy disks, you need to glue the cutout for protection (for which a piece of paper with an adhesive layer was supplied with the floppy disk). On a 3-inch floppy disk, just move the slider in the window to open it.
Organizing information on a floppy disk
Physically, information on a floppy disk is a sequence of sections magnetized in different directions, the magnetization sequences are determined by error-resistant coding.
Data is written to a floppy disk in concentric tracks along the direction of rotation of the disk. By default, 40 or 80 tracks fit on the side of a floppy disk. Usually it is possible to record 2-4 more tracks, but this is already determined by mechanical stops.
In this case, each track is divided into several sectors. Sector-by-sector writes provide random access in fairly small chunks. Some systems read and write the entire track, and then the division into sectors may either not be performed, or be purely logical. Typical sector sizes are 512B, although some systems use values between 128 and 1024B. 512-bit sectors typically fit on floppy 9 (double density), 15 (5-inch high-density floppies), or 18 (3-inch high-density floppies). density).
It should be noted that the actual capacity of the floppy disks depended on how they were formatted. Since, apart from the earliest models, virtually all floppy disks did not contain hard-coded tracks, the road was open for system programmers to experiment with more efficient use of floppy disks. The result was the emergence of many incompatible floppy disk formats, even under the same operating systems. For example, for RT-11 and its versions adapted in the USSR, the number of incompatible diskette formats in circulation exceeded ten. (The most famous are MX, MY used in DCK).
Added to the confusion was the fact that Apple used floppy drives in its Macintosh computers that use a different encoding principle for magnetic recording than the IBM PC. As a result, despite the use of identical floppy disks, transferring information between platforms on floppy disks was not possible until Apple introduced high-density SuperDrives that worked in both modes.
The "standard" formats of IBM PC floppy disks differed in disk size, number of sectors per track, number of sides used (SS stands for single-sided floppy, DS stands for double-sided), and the type (recording density) of the drive. The drive type was marked as SD - single density, DD - double density, QD - quadruple density (used in clones such as Robotron-1910 - 5.25 "floppy disk 720 K, Amstrad PC, PK Neuron - 5.25" floppy disk 640 K , HD - high density (differed from QD by the increased number of sectors), ED - extended density.
8-inch drives have long been included in the BIOS and were supported by MS-DOS, but there is no exact information about whether they were supplied to consumers (perhaps they were supplied to enterprises and organizations and were not sold to individuals).
In addition to the above format variations, there were a number of improvements and deviations from the standard floppy disk format.
The most famous ones - 320/360 KB floppy disks Iskra-1030 / Iskra-1031 - were actually SS / QD diskettes, but their boot sector was marked as DS / DD. As a result, the standard IBM PC drive could not read them without using special drivers (800.com), and the Iskra-1030 / Iskra-1031 drive, respectively, could not read the standard DS / DD diskettes from the IBM PC.
Special drivers-extenders BIOS 800, pu_1700 and a number of others allowed formatting floppy disks with an arbitrary number of tracks and sectors. Since floppy drives usually supported from one to 4 additional tracks, and also allowed, depending on design features, to format 1-4 sectors per track more than the standard, these drivers provided the appearance of such non-standard formats as 800 KB (80 tracks, 10 sectors) 840 KB (84 tracks, 10 sectors), and so on. The maximum capacity consistently achieved with this method on 3.5 ″ HD drives was 1700 KB.
This technique was later used in Windows 98, as well as Microsoft's DMF floppy disk format, which expanded the floppy disk capacity to 1.68 MB by formatting the floppy disks into 21 sectors in a similar IBM XDF format.
XDF was used in OS / 2 distributions, and DMF was used in distributions of various Microsoft software products.
The pu_1700 driver also allowed for sector-shifting and interleaving formatting, which accelerated sequential read-write operations, but made it incompatible even with a standard number of sectors, sides, and tracks.
Finally, a fairly common modification of the 3.5 ″ floppy format is to format them at 1.2 MB (with a reduced number of sectors). This feature can usually be enabled in the BIOS of modern computers. This use of 3.5 ″ is typical for Japan and South Africa. As a side effect, activating this BIOS setting will usually read floppy disks formatted with type 800 drivers.
Additional (non-standard) tracks and sectors sometimes contained copy protection data of proprietary floppy disks. Standard programs such as diskcopy did not transfer these sectors when copying.
The unformatted capacity of a 3.5 ″ floppy disk, determined by recording density and media area, is 2 MB.
The height of a 5.25 "floppy disk drive is 1 U. All CD drives, including Blu-ray, are the same width and height as a 5.25" drive (this does not apply to notebook drives).
The 5.25 ″ drive is nearly three times the height. This was sometimes used by the manufacturers of computer cases, where three devices, placed in a square "basket", could be reoriented with it from horizontal to vertical arrangement.
Disappearing
One of the main problems with floppy disks was their fragility. The most vulnerable element of the floppy disk design was a tin or plastic casing that covered the floppy disk itself: its edges could be bent, which led to the floppy disk getting stuck in the disk drive, the spring that returned the casing to its original position could be displaced, as a result, the floppy disk casing was separated from the case and never returned to starting position. The plastic case of the floppy disk itself did not provide sufficient protection for the floppy disk from mechanical damage (for example, when a floppy disk fell on the floor), which rendered the magnetic medium out of order. Dust may have entered the crevices between the diskette case and the casing.
One of the oldest devices for storing information on a personal computer is a floppy drive or, for short, FDD (Floppy Disk Drive). This device, widely used during the 1970s and 2000s, is now rarely found in modern computers. Nevertheless, in some cases, you can still see a floppy drive installed in an old PC. In addition, sometimes external floppy disk drives are used, which are connected to the computer through the I / O ports.
The first floppy drive and floppy disk were 8 inches wide and were invented by IBM engineer Alan Sugart in the early 1970s. In the mid-1970s, he also developed a 5.25-inch floppy disk and a drive for reading it. In 1981, Sony developed a 3.5-inch floppy disk and drive. Initially, the capacity of such a floppy disk was 720 KB, but later its capacity was doubled.
There have been repeated attempts to improve floppy disks based on the 3.5-inch format. For example, in 1987 a 2.88 MB floppy disk drive was developed, and at the end of the 1990s. - LS-120 standard with even larger disk capacity - 120 MB. However, all these modifications are not widely used, largely due to the high cost of drives and media.
Principle of operation
In principle, FDDs are a lot like hard drives. Inside the floppy disk, just like inside the hard drive, there is a flat disk with a magnetic layer applied to it, and information from the disk is read using a magnetic head. However, there are some differences. First of all, a floppy disk is not made of a hard material, but a flexible polymer film, similar to a magnetic tape film. That is why this type of disk is called floppy. In addition, the floppy disk does not rotate constantly, but only when a request is received from the operating system to read information.
The advantage of FDD in comparison with a hard drive is the removable media. However, floppy drive also has a lot of disadvantages. In addition to the extremely low speed of work, this is the low reliability of information storage, as well as the low storage capacity - about 1.44 MB for 3.5-inch floppy disks. True, when using non-standard formatting methods, the capacity of the floppy disk can be slightly increased, but, as a rule, this leads to an even greater decrease in the reliability of the record.
Varieties
In personal computers such as the IBM PC, two main varieties of FDDs were used - 5.25-inch and 3.5-inch. Both types of floppy disk drives are designed for different types and sizes of floppy disks and are not compatible with each other. This situation is different from that of optical drives, which can read both 3.5 "and 5.25" discs. At one time, there were also 8-inch FDDs, but already in the 80s. such drives have fallen out of use. Around the 1990s. 5.25-inch floppy drives were finally out of use. 3.5-inch floppy drives lasted longer, until the late 2000s, and even now they can be found occasionally in some places.
Comparative sizes of internal 8, 5.25, and 3.5-inch drives

Examples of Floppy drives in order of priority: 8-inch, 5.25-inch, and 3.5-inch
5.25-inch floppy disk is a disk in a cardboard case resembling an envelope and has a slot for a read head. Such a floppy disk fully justifies its name "flexible", since its body can be bent by hand without much effort. However, it is not recommended to intentionally bend the floppy disk too much, as this will almost inevitably lead to its failure.
A 3.5-inch floppy disk lacks this drawback. In it, the magnetic disk is enclosed in a hard plastic case and it is not so easy to bend it with your hands. In addition, the 3.5-inch floppy disk has a special metal shutter that hides the slot for the read head. Another feature of the floppy disk is the presence of a switch that blocks writing to the disk. The standard 3.5-inch floppy disk has a capacity of 1.44 MB, which is larger than the maximum 5.25-inch floppy disk capacity of 1.2 MB.

Examples of floppy disks are from left to right 8, 5.25, and 3.5.
The design of the 3.5 "FDD is also different from the design of the 5.25". If, when inserting a floppy disk into the slot of a 5.25-inch drive, the user needs to fix the floppy disk by turning the lever, then the 3.5-inch one is fixed in the drive automatically, and the floppy disk is ejected back using a special button.
As with many other drives, there are mobile versions of floppy drives - external floppy drives. An external floppy drive is convenient because it does not take up space in the system unit, especially if you rarely need to use floppy disks. A similar FDD drive can be connected to a PC using a USB connector or LPT connector.
Application
Although hard drives appeared in the first IBM-compatible personal computers, nevertheless, no computer could do without a device for removable drives. A floppy drive became such a device, which quickly gained popularity due to the simplicity and low cost of both the drive itself and the storage media - floppy disks.
However, in some cases, a floppy drive could completely replace a hard drive. When the author of these lines got the first IBM-compatible computer, he did not have a hard drive, let alone an optical drive, but only a 3.5-inch floppy drive and a set of floppy disks with software provided by the PC seller. At the same time, the computer was fully functional. Of course, there was no question of using Windows 3, or of launching some voluminous programs, but when using MS-DOS, one could deal with most of the programs and games existing at that time (early 90s). This suggests that floppy disks are capable of satisfying the user's basic storage needs. In addition, floppy disks were once indispensable in the case when it was necessary to restart the computer for a preventive check or install a new OS.
Configuring a floppy drive in BIOS
There are several options in the BIOS that allow you to customize the floppy disk drive settings. For example, the option allows you to disable the floppy drive controller if not in use in the system, thereby freeing up one system interrupt. Also, in some BIOSes, you can manually set the type and size of the drive media, as well as disable writing to floppy disks.
Conclusion
Today, many users may not know what a floppy drive looks like, or even a regular floppy disk. Their functions were taken over by memory cards and flash drives. In most system units, only the 3-inch external bay left for them reminds of a floppy drive, and in Windows operating systems - unused first letters of logical drives (A and B) reserved for floppy drives. However, floppy disk drives are often found in older computers. In addition, floppy drives can be useful when booting a PC in order to carry out preventive measures for computer maintenance or when installing an OS.
April 26, 2010, having lived her last, 3.5-inch, 24-year-old life. If someone doesn't remember, floppy disks are black square memory devices that once could be called flat, with 1.44 MB. Just a third of an mp3 song or several documents previously archived could fit. The Ministry of Defense is buying them most actively in Russia: one of the experts interviewed told Life that "the archaic nature of floppy disks does not affect the trajectory of missiles." The American authorities, by the way, also buy floppies, the owner of the floppydisk.com store, Tom Persky, told us.
"I don't know of any company that makes floppy disks at the moment. It looks like the last floppy disk has already been released."
For most users, Sony's announcement of the discontinuation of floppy disks passed unnoticed. Prior to that, manufacturers gradually stopped releasing equipment with floppy drives, these drives in Windows were designated by the letter "A" (under "B" were 5-inch floppy drives, so the traditional "C" remained - this is the system hard drive). If you already knew this or are ready to clarify the previous proposal, then we are connected with the feeling of old age.
In 2015, the departments purchased floppy disks for at least 300 thousand rubles, from 2010 to May this year - for 2.3 million rubles. "At least" - because the search function for attached files (technical specifications) has not been working on the public procurement portal for three years, and representatives of the Lanit group refused to repair it. In the new version of the portal, which was launched this year, the function is completely absent.
Most of all floppy disks were needed by the Ministry of Defense - from January 2010 to May 2016, the War Ministry spent 563 thousand rubles on floppy disks, of which 80 thousand rubles were purchases of military enlistment offices.
Floppy disks are purchased for security reasons, for transferring information to the state secret protection service [structure of the Ministry of Defense], - a representative of one of the military registration and enlistment offices told Life. - Mostly floppy disks are used to write secret maps.
What are these cards for and where they are used, the interlocutor did not explain, referring to the state secret. But it is known that floppy disks, for example, are used to control missiles. The US Audit Office reported in its report that the US military still uses 8-inch floppy disks to navigate missiles. The US nuclear forces are still dependent on "flops", they are planned to be removed from service in 2017.
According to a source close to the Ministry of Defense, "the actual archaic nature of the floppy disks does not affect the trajectory of the missiles." The department officially refused to comment on this topic.
For security reasons, floppy disks are also purchased by another law enforcement agency - the Ministry of Internal Affairs, one of the employees of the investigation department told us about this.
You must understand that many [police] departments do not have free access to the Internet due to the observance of secrecy. So we carry our criminal cases to our bosses for verification, downloading them to floppy disks, and they write the corrected files back to them and give them back to them, - says Alexey, adding that at least there is a reason to leave the office sometimes in a whole working day.
He noted that there are still many computers in the Ministry of Internal Affairs that are adapted to work with 3.5-inch floppy disks. And that the incompatibility of a number of government agencies with optical disks and flash drives is connected not only with secrecy - supposedly, we are talking about saving.
It's good that in the 21st century you can buy a regular floppy disk. We are not given money for flash drives, they say that it is expensive. They cost 150 rubles each, and you can buy a floppy disk on the wholesale market for 25-30 rubles. Well, if the markets are not there, then you have to go to large stationery or computer stores. There a box with ten Hong Kong floppy disks costs 400 rubles. The check can be handed over to the accounting department, and in six months the money will be returned. They are just enough for a modest lunch, in a cafe opposite the investigation department, - said the policeman.
But the Ministry of Internal Affairs did not make it into the top ten buyers - because the police, according to Alexei, themselves stock up on floppy disks. True, they will probably be needed soon - the Ministry includes the Federal Drug Control Service (FSKN), which purchased these media. The Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation told us that diskettes are a necessary part of the operational activities of customs authorities:
"A 3.5-inch floppy disk, of course, looks wildly against the background of iPhones and the mobile Internet, but it is precisely because of the huge number of loopholes through which classified information can leak, and old floppy disks are needed that allow you to store and transfer information in your your pocket, not through a sieve called the Internet "
Oleg Shaburov, Information Security Director of the Softline system integrator (previously worked at the antivirus company Symantec), noted that he does not see any advantages in floppy disks and cannot be called an archival tool either - because of the vulnerability to magnetic radiation and moisture, the average shelf life on them does not exceed 3-5 years old. At the same time, Shaburov recalled that the first of the most common viruses were transferred to floppy.
"Well, unless the police and customs officers have a calculation that the attackers will not have a floppy drive - or that the virus will not fit on a floppy disk"
In addition to law enforcement agencies, state universities, hospitals and clinics are also among the largest buyers of floppy disks. From January 2010 to May of this year, they spent 247 thousand rubles and 243 thousand rubles, respectively. Basically, universities and hospitals are forced to use floppy disks due to outdated technology. In March of this year, there was even a stir over the fact that the Russian Academy of Sciences asked young scientists to apply for grants on diskettes, but the requirement was declared optional. The average age of RAS academicians is over 70 years.
The five leaders in the purchase of floppy disks also included the Pension Fund of Russia and city administrations. Over the past six years, they have spent 235 thousand rubles and 90 thousand rubles on floppy disks, respectively. According to Alexander Burtsev, director of the Internet Partner company, state institutions have become hostages of their infrastructure, and the Pension Fund is still not helped by the multimillion-dollar modernization of equipment and software that it regularly pays for.
There are many floppy disk suppliers in Russia. Among them is the Samara company "Spetsstroisnab" by Elena Cheprasova, which is engaged in the supply of computer and printing consumables.
These are regional divisions of the FSB, the Ministry of Internal Affairs, customs, and courts. More often - these are contracts of thousands for 30 rubles, since the state services, even the security forces, do not have free money: the crisis, - said the representative of Spetsstroysnab.
The company purchases floppy disks from larger wholesalers, which are gradually clearing out Asian warehouses. Tom Persky (sells over 200 thousand floppy disks a year) says that he does not often have orders from Russia, and he sells little to the American departments - mostly floppy disks go to companies whose equipment works only "on flops." These are embroidery, stamping machines and other special machines.
Floppy disks are running out - their reserves will last for another five years. Tom Persky now makes more money not on floppy disks, but on a related service - he is ordered to quickly transfer data from large batches of floppy disks to modern media.