The motherboard is an irreplaceable multifunctional "basis" of a personal computer, which ensures the operability of the rest of the system components: RAM, video card, processor, hard drives. The choice of the motherboard depends on the compatibility of the future assembly, and the overall performance, and even potential savings. For example, if you buy a processor with no chance of overclocking, why take an expensive "base" with a gaming chipset? The same is the case with RAM - if the strips are already limited in frequency, why pay more? Therefore, it is important to feel the balance and understand the details even before contacting the online store for a purchase.
Choosing the right hardware often starts with sorting by price, motherboard manufacturer, and gaming segment. But, as practice suggests, neither the first, nor the second, nor even the third indicator determines the level of quality, does not guarantee stable operation for ten years and does not increase performance (still, the rest of the details are responsible for this - the processor, video cards, RAM). It is worth starting your acquaintance with the segment with completely different characteristics and parameters:
- Form Factor. The classic of the genre is ATX. The size of the board is 305x244 mm. From the offered interfaces, slots and connectors, it is easy to assemble office computers that can work with documents and a browser, and powerful professional PCs that can cope with any workload - from graphics processing to games in 4K resolution. Of the advantages of ATX - an impressive variety, the availability of both expensive and cheap models, compatibility with almost any equipment. Of the minuses - dimensions. For multimedia platforms, ATX is definitely not suitable. But Micro-ATX - with ease. The dimensions are noticeably smaller - 244x244 mm, the interfaces are practically the same, and there is no need to allocate a lot of space under the table. The E-ATX solution deserves special mention - flagship models with advanced technologies and focus on premium markets. Size - 305x330 mm. Attention! The size of the case also depends on the choice of the form factor, and if there is not enough space in the room, it is worth stopping at the Micro-ATX option.
- Socket. The "socket" responsible for the health of the processor. More important than characteristics the motherboard cannot be found with a strong desire. Before buying the "base" directly, you will have to figure out which process will be used in the assembly (it is important to know the manufacturer - AMD or INTEL and the model name), and for what purposes. If you first select a motherboard with a specific socket, then the further choice of processors will be limited, and therefore you need to act exactly the opposite - first the processor, then studying the characteristics, and after selecting the platform. It is important to remember that sometimes you can save on the current purchase, but with a reserve for the future.
- Chipset. A parameter indicating the number and type of supported interfaces (for connecting hard drives, USB ports), and at the same time suggesting whether overclocking is possible (this characteristic is especially important on Intel processors, where desired settings are entered directly into the BIOS, greatly simplifying the life of beginners who are not yet familiar with the abnormal increase in hardware power). Chipsets also divide the motherboards available on the shelves by cost. Initial options do not allow overclocking the processor, connect a dozen SSD drives, and sometimes they prohibit the operation of RAM in dual-channel mode. But the older chipsets and Wi-Fi adapters are equipped, and the Bluetooth signal is received, and with two or three video cards in the SLI and Crossfire format it works without any problems. Which chipset should I use when buying? Depends on the wallet and the desired functionality. Most likely, it is worth stopping at some averaged version, but with the support of official overclocking - this is, in fact, the groundwork for the near future, right?
- Memory slots. RAM helps the central processor not to process the same actions ten thousand times a day, but to take the result of the work done directly from RAM. With this approach, a lot of time is saved, and the load on the CPU is greatly reduced. Therefore, it is important to get enough RAM in advance. As practice suggests, 4 slots capable of operating in two-channel mode are the standard of the 2018/2019 season.
- Interfaces and connectors. It is important to understand the SATA connectors (support for the version operating at 6 Gb / s is required) and SATA Express, the presence of USB 3.0 and PCI-e x16. The rest of the elements already belong to either pampering or the premium segment. Such as Wi-Fi adapters, HDMI (and why, if the same interface is available on a video card?).
Choosing for office and study
Which motherboards are the best for office and study? Those based on cheap chipsets for Intel and AMD work on common sockets, to which it is easy to find both cheap and expensive processors "for growth" and are assembled in the mATX or ATX form factor for a standard case. If you also choose a company, then you should pay attention to ASROCK and ASUS - you will definitely not be able to miscalculate.
How to choose a motherboard for games
The situation with the gaming segment is simpler - AM4 and LGA 1151_v2 (not to be confused with the standard 1151!) Are suitable sockets, the chipset must support overclocking, and the memory slots must reach the number “4”, and even work in dual-channel mode. You no longer have to choose the rest of the motherboard indicators - manufacturers will match the parameters described above with the necessary interfaces and technologies.
Which motherboard company to choose
ASUS, Gigabyte and MSI are the top three. The listed brands represent models both in the "basic configuration" for office assemblies, and in the "maximum" for gaming PCs with a bunch of additional functions. Most likely, it is worth keeping somewhere close, not forgetting to look at the characteristics of competitors, such as ASROCK (a subsidiary of ASUS), Zotac and Biostar.
You can also look at articles on topics and

The question is very acute, given that professional electronics engineers recommend building a system unit around it.
The motherboard is the most important component of any computer. The stability of the entire computer as a whole depends on its quality and stable operation. Do not forget that all other components are attached to it in one way or another, and the motherboard coordinates their work. And if we compare the system unit with the house, then it is advisable to compare the motherboard with its foundation.
In total, there are three dozen parameters that can characterize this board, but this article will focus on the most significant of them that really affect the performance and stability of a computer device.

Component manufacturer.
Despite the fact that there are enough manufacturers of computer components in the world, only a few of them make decent motherboards. And so the question which company is better buying a motherboard is quite simple to answer. You should stop your choice on the following four manufacturers:
- Asus.
- AsRock (Subsidiary of Asus. The developments of this company are used with minor changes.).
- Gigabyte.
- MSI.
It is better not to pay attention to such exotic manufacturers as Zotac and Biostar, as they are inferior to the main companies both in quality and functionality. If you need to assemble a server or workstation, then you can take a closer look at Intel products. There is nothing superfluous in such cards and they are optimal for long and uninterrupted operation in 24/7 mode.
Important! By and large, there is no difference between the four main manufacturers, and at home the difference is completely invisible. For the server and workstation, the company's products will be the best choiceIntel.
Processor socket.
Each motherboard has a socket for installing a central processor called socket. This is the most important selection criterion, since only one type of processor can be installed in the selected socket.
How to choose the right processor for your motherboard? First of all, you should decide with the manufacturer of the processor. Only two companies in the world produce decent processors: Intel and AMD. The sockets of these companies are incompatible in principle.
- Intel sockets.
Leading manufacturer of processors and chipsets. It holds about 75% of the market, and only new processors from AMD were able to improve the situation somewhat. The following models of sockets from Intel are relevant:
- LGA 2066.
The newest and most modern socket of an American company. Supports the most productive processors and will be in demand long time... The only drawback of the motherboard on such a socket is the high price.
- LGA 2011-3.
The platform is of the previous generation, but the performance of such processors is still more than enough to solve all household tasks.
- LGA 1151-v2.
The mass segment of processors, which perfectly combines an affordable price and acceptable performance. Ideal for the modern home computer. It should not be confused with the previous LGA 1151 platform, as their sockets are incompatible.
Important! If you need to assemble a mid-range computer for the home, then you should opt for a motherboard with a socketLGA 1151-v2. This is the best option in all respects.
- AMD sockets.
The Canadian manufacturer makes affordable, but not so powerful processors as an eternal competitor to Intel. However, thanks to affordable price and ample overclocking capabilities, AMD processors are quite popular.
The most common sockets are:
- Socket TR4.
The most powerful processors of the company are built on this socket. Supports up to 16 (!!) cores and a four-channel memory controller. Perfect for both a highly productive home computer and workstation.
- Socket AM3 +.
A socket for budget mothers. Low performance and very low price... Suitable only for office computer.
- Socket AM1.
Mass segment of sockets from AMD company. Direct competitor to Intel's LGA 1151-v2. Has similar characteristics. Perfect for home assembly system unit.
Important! If you decide to build a computer based on processorsAMD, then the question how choose a processor for the motherboard the solution is very simple. An ideal choice would be a board with an AM1 socket.
Chipsets of motherboards.
A chipset is a chipset that provides the functionality of the motherboard as a whole. It determines how many hard drives or video cards can be connected and how quickly they will work. The socket and the chipset determine 80% of the final cost of the motherboard.
By and large, chipsets differ from each other only in the type and number of supported interfaces. All existing chipsets can be classified into three large groups:
- First level.
Motherboards based on such a set of microcircuits can only be used in office computers or in extremely cheap system units. entry level... AMD 760G or NVidia 7025 can be classified as such chipsets from AMD. Intel has H110 or H170 (270) chipsets.
- Average level.
Golden mean. Fully suitable for forming home system blocks. Allows you to connect the required number of hard drives and USB devices. How to choose a motherboardAMD with sufficient functionality? Just choose devices with a chipset and B350 or X370. For mothers on Intel processors, such chipsets would be Intel B350 or Intel Z350.
- High performance chipsets.
Maximum functionality for a lot of money. An almost unlimited number of hard drives, USB devices and at least 2 video cards can be connected to such a motherboard. Some models contain Wi-Fi or Bluetooth modules.
For mothers on Intel, such a chipset is X299. For AMD, the maximum functionality can be obtained on AMD X399.
Important! For a computer costing up to a thousand dollars (about 60,000 rubles), a chipset is more than enoughZ350 (Intel) orX370 (AMD).
Motherboard dimensions.
Modern motherboards differ from each other not only in functionality, but also in size. This is also worth considering when collecting computers. There are five standard sizes in total:
- E-ATX.
The largest items. Typically, this size is used for the most advanced mothers with flagship processors and elite chipsets. The size is 30.5 * 33 centimeters. An expensive, large enclosure is required for assembly.
- ATX.
Classic size, most motherboards have that. Dimensions 30.5 * 24.4 centimeters. The smartest choice for building a computer, as most cases are manufactured for this size.
- Micro —ATX.
Reduced version of mother ATX. In most cases, it has reduced functionality and is created on simplified mid-range chipsets. Dimensions 24.4 * 24.4 centimeters. It is considered a budget option.
- Mini —ATX.
Such a mother is intended for assembling compact systems with little or no video cards. The functionality of the chipset has been cut down. Most budget system units are built on mothers of this size. The physical size of the board is 17 * 17 centimeters.
- Mini —STX.
A very miniature printed circuit board measuring 14 * 14 centimeters. Designed specifically for the creation of multimedia centers and ultra-compact computers for video playback. They are used where the greatest compactness is required.
Important! ATX andMicro —ATX - the most suitable sizes of motherboards for a universal home computer.
The number of slots for RAM.
In most cases, the motherboard has either 2 or 4 RAM slots. There is an extremely small group of elite mothers who can boast 8 slots for memory strips, but such devices are few and they are very expensive.
Important! It is most profitable to buy boards with 4 memory slots. This will make it possible to quickly add RAM without changing the entire device.
Rear panel connection interfaces.
A wide variety of connectors can be located on the rear panel, including such unusual ones as S / PDIF or an antenna for Wi-Fi. Modern boards are equipped with multiple USB ports, audio jacks, and a PS / 2 port for connecting a keyboard or mouse. RJ-45 is mandatory for Internet connection.
Important! NumberThere must be at least 6 USB ports on the rear panel, and 2 of them must beUSB 3.0. In addition, the presence of a port will not be superfluous.USB -C (all modern phones) andHDMI (it will be convenient to connect a TV or monitor).
Pay special attention to the audio connectors. It is best if the motherboard will natively support 5.1 or 7.1 sound. This will eliminate the need to purchase an additional audio card.
Connecting hard drives (HDD and SSD).
Today, even budget motherboards have at least 4 SATA connectors, where you can connect any hard drives (including solid-state drives) and DVD drives, if you still need them.
An average budget device may have 8-10 SATA connectors, which will not be superfluous if you plan to store a large amount of information.
Important! The connector will not be superfluousSATA Express required for connectionSSD drives and allowing them to run at full speed.
Expansion board connectors.
The motherboard must have at least one PCI-x16 slot for connecting a modern video card. Several PCI-x1 slots will also come in handy, where you can connect additional sound cards, video capture cards, TV tuners and much more.
Important! If you plan to play a lot and actively play games, then you should think about purchasing a device with twoPCI -x16 connectors. This will allow you to connect two video cards at once.
Selection results.
Summarizing all of the above, we can summarize the following.
For an office computer, a motherboard with AMD AM3 + socket with an integrated video card, two lines of RAM and a minimum number of connectors and interfaces will be quite enough.
If you need a universal home computer, the best choice would be a board with an LGA 1151-v2 socket, with four lines of RAM and with all common interfaces.
If you want to play at maximum performance or deal with video processing, you should pay close attention to the LGA 2066 socket, which will provide maximum performance and functionality.
To the choice motherboard it is important to approach with full responsibility, since it is one of the main elements that bind the components of a computer. Even the mouse and keyboard are connected to the motherboard connectors, not to mention the organization of communication with the main components of the PC. The motherboard must be compatible with the processor, so you should choose them either together, or select one of the devices for another. In addition, it will not be superfluous to take care of a further upgrade in advance, if it is planned in the future. Often, building a computer starts with buying a processor and video card. In this case, the appropriate motherboard is selected, for example, when you purchase an Intel CPU with the K index, that is, for overclocking, the motherboard chipset must have a Z index that supports this feature. Certain boards are suitable for each processor model, and it's not just the manufacturer and the socket. There are also exceptions when, with a suitable connector, device interaction is not ensured. When buying a motherboard, many parameters are decisive, including sockets (socket for the processor, which determines which model can be installed), chipsets, form factor (dimensions also matter), interfaces (number and type of connectors), memory slots and others. nuances. , which are the main component of the motherboard, in what their functions are expressed, as well as which chipset is better to choose in this or that case. This motherboard element can also be purchased separately, if circumstances require it.
The correct choice of motherboard chipset in 20148.
The chipset of the motherboard of a PC or laptop is a set of microcircuits, its purpose is to ensure the harmonious operation of all components, including a processor, video card, hard drives, memory cards and other peripheral devices. In the architecture of the motherboard in its classic design, there are south and north bridges (relevant for AMD platforms, Intel has integrated the lion's share of the north bridge functions in the CPU), slots for installing RAM (DDR4, DDR3). The north bridge connects the processor with the graphics adapter, memory card and south bridge; the parameters of the system bus, operative and video controller functioning also depend on it. Despite the fact that in a modern assembly, computer performance does not depend on the chipset, since the northbridge has migrated to processors to increase data exchange speed and reliability, the role of the southbridge should not be underestimated either. The functionality of the motherboard depends on it, thanks to it, communication with the periphery is ensured.
Often, a cooling chip is added to the north bridge, since excess load can cause it to overheat. The south bridge breaks down for other reasons, for example, shorting the USB port, contact with a faulty drive, etc. It is not necessary to change the entire board. If the motherboard is from a range of top-end ones, it makes sense to change only the chipset; with budget options, such actions are inappropriate. The main chipset manufacturers are Intel and AMD, which are familiar to everyone from their processors. They represent the largest market share. Also, NVidea, more familiar with its video cards, was engaged in production, the role of other manufacturers is not so significant.
How to choose a chipset
The main condition for a successful purchase is full compatibility of components, therefore, when deciding on which chipset to choose a motherboard, you need to take into account the model of the processor that is installed or planned for installation. Having initially decided on the platform, Intel or AMD, we proceed to the choice of the CPU. Since the processor and motherboard are closely related, we choose them at the same time or for each other. The question of which manufacturer is better is incorrect in this case, so there will be no answer to it, we will consider chipsets from both AMD and Intel. Both corporations produce quality products and have long established themselves in the market.

In cases where the CPU is already available, the range of options is narrowed. If the choice is most often predetermined with the platform, then you will have to carefully familiarize yourself with the rest of the board parameters in order for the purchase to meet the requirements. So, the costs for the top model do not make any sense if the computer will be used in the office or at home with minimal use of resources, therefore, first of all, it is worth deciding what tasks the board is selected for, the same applies to the processor or other components involved in the assembly. It is not good if a device with great potential will not use even half of its capabilities, while you also need to take into account the material side of the issue, because you have to pay for power and additional functionality. Since all elements go together, they must be in harmony for better synergy.
Top motherboards are built on the Z chipset, but this does not mean at all that you need to chase devices from the first lines of the rating. After all, the compatibility of the elements and the expediency of the purchase are more important. To determine which chipset of the motherboard will be better, you can look at the parameters of the processor, the decisive factor is also a clear idea of what tasks the computer is used for. Having designated the goals, we begin the selection. In general terms, it looks like this:
- For an office or home computer (provided that it is not a gamer's computer), a budget assembly is suitable, because equipping the device with high-power components is simply unnecessary. A board that interacts with a CPU with an integrated graphics core is quite suitable for working in conjunction with the same processor. For a budget assembly, the H110 or H310 chipset is optimal choice... One should not expect great functionality from motherboards based on chipsets of this level, but this does not mean at all that they are bad;
- If the user is more serious about graphics, for example, uses graphics applications, plays games with average system requirements, an additional video card is purchased, then there is no need for a graphics chipset, it should only support the functioning of the installed video adapter. For assemblies of average power, motherboards on B 150, B 250 chipsets are suitable.

The range of motherboards based on mid-level microcircuit sets is quite wide. Here you can find models with decent equipment among both Intel and AMD representatives;
- For a powerful computer on which professional work with graphics, demanding programs is carried out, heavy games are launched, both a high-performance processor and an appropriate board that also supports several video cards are selected. Chipsets Z 270 or Z 170 are ideal for overclocking RAM, processor. For some motherboards based on Z170, there is a modified BIOS, due to which you can overclock processors that do not have the K index over the bus (relevant for Skylake 6th generation). Overclockers will find a suitable motherboard model for themselves precisely among the range of motherboards with senior chipsets. Such motherboards have the best equipment, so find a copy with an integrated Wi-fi module or Bluetooth (if necessary) or other additional buns in this category of models will not be difficult. By the way, if the board and the processor do not support overclocking, this does not mean that a computer with such equipment will not be a gaming one. For a gaming computer on Intel, chipsets Z370, H370, B360 are suitable.

The best Intel and AMD motherboard chipsets
As mentioned above, the concept of "the best chipset" is very arbitrary. The best choice will always be the most suitable option for a particular assembly. Nevertheless, Intel has appointed chipsets for motherboards with the Z index at the top of the "food chain", as a rule (although not always), equipped with great functionality, so that they will be at the top of the rating.
Intel Chipsets
In addition to the letter marking, the chipsets are divided into series (the 300th, 200th, 100th series are relevant today). The 300 is adapted for the eighth generation of processors, the 200 is suitable for the seventh and sixth, the 100 is for Intel Core, Pentium and Celeron. Indices Z, H, B, Q denote the categories of chipsets (Z - gaming with overclocking, H - functional mainstream chipsets, B - for office or home, Q - for business).
300
Let's start the list of Intel chipsets from the top. Motherboards equipped with these particular chipsets are shining in the ratings today.
- Z370 / 390. The difference between the chipsets is not that great. The Z370 chipset is a pioneer of the series, one of the best, but, despite the overclocking capability, some functionality inherent in subsequent instances of the 300 is missing (compare the same H370 with the new USB1 Gen 2 and support wireless networks). The new Z390 is a slightly more modernized analogue of the Z370 with the same configurations of PCI-Express channels and USB drives, but with the addition of USB 3.1 Gen 2 and Intel Wireless-AC MAC;
- Q As in Z-chipsets, the use of multiple video cards is supported, but there is no overclocking option. It is adapted to business needs, so there is no need to rely on an assortment of motherboards with its participation;
- The H370, located one step below, is very similar to its fellow Z370, and although it has no overclocking capability, and the PCI-Express and USB channels are slightly less, the H370 surpasses the presence of USB1 Gen 2 and supports Wi-fi and Bluetooth 5.0. If the mainland is not purchased for the purpose of overclocking, then this chipset is worth paying attention to when assembling a productive computer;
- B360 - not such a fancy chipset as the one discussed above, but also not as limited in functionality as the H310, has a dual-channel memory controller, USB1 Gen 2, supports version 3.0 buses, and also allows the use of a graphics core integrated into modern Intel processors;
- Н310 is a budget variant of the series with a minimum set of functions for undemanding users. The chipset does not support PCI-Express 3.0, like the rest of the series, there is a second bus with lower bandwidth. The situation is the same with the DMI version, the memory controller is single-channel, and in general many features have been cut down.

100 and 200
There is no strong difference between the series, although the 200th or more is modernized.
- X299 deserves special attention, it is designed for the line of high-performance CPUs Kaby Lake-X and Skylake-X without integrated graphics and supports overclocking;
- Z170 / 270. Like other carriers of the Z-index, the chipsets are ideal for overclocking processors and are equipped with good functionality;
- H170 / 270. With motherboards equipped with H chips, the user has much more options than with B, while there is no overclocking on such motherboards;
- В150 / 250 is the golden mean between the budget option and the gaming one. Boards based on these chipsets are installed in a medium-power assembly, sufficient to perform various everyday tasks on a PC;
- The H110 has limited functionality, while it is great for budget assemblies, because it is unreasonable to purchase an expensive motherboard with many features, for example, in the case of office work, etc.
Chipsets with the Q index are not too different from H, while they have a certain set of corporate goodies. In all Intel series, a certain structure can be traced, ranking the models taking into account their inherent bells and whistles. The announced X399 chipset may soon become the cherry on top of Intel's cake (the name echoes AMD's model for the Ryzen Theadripper CPU).

AMD Chipsets
The company offers two options for configurations of chipsets - chipsets, where the south and north bridges coexist in one set and existing separately from each other. The combined variations are intended for processors with new AM4 and TR4 sockets; a separate configuration is used for earlier sockets.
TR4 processors
For powerful CPUs AMD Ryzen Theadripper company released the X399 chipset. A significant proportion of controllers have now migrated to the processor, which has increased performance and reliability (it's no secret that the processor is cooled better). The equipment includes 4-channel RAM, NVMe device connection and other useful things. Overclocking is supported.
AM4 processors
Chipsets for AM4 also have a combined version, and the lion's share of controllers has moved to the processor, only the periphery remains for the chipset.
- The X470 is a new top-end chipset, which is a more modernized version of the X370. The chipset is perfect for gamers and overclockers. Among the possibilities are overclocking, support for multiple video cards, booting from NVMe RAID, etc. In addition, the X470 supports AMD StoreMI technology, which allows you to combine hard drives into one volume and move to automatic mode frequently used files on SSD .;
- В350 is a more modest representative of chipsets for motherboards of gaming computers, while also providing the ability to overclock and work with multiple video cards;
- A320 is an option for "workhorses" operating with one video adapter. Overclocking is not supported in this case, but the chipset's capabilities are quite enough for solving urgent tasks.

Chipsets X300 (analog of gaming X370) and A300 (analog of A320) are produced for motherboards of small form factor. The difference lies in the stripped-down support for connection interfaces.
AM3 + processors
Chipsets for AM3 + sockets are produced in the "north and south bridge" configuration.
- The 990FX and 990X chips are designed for gaming platforms, support overclocking and OverDrive control, no integrated graphics. 990FX supports 4 video cards, 990X - two;
- There is also an AMD 970 chipset with similar specifications, but it supports one video adapter;
- The 980G with integrated graphics is ideal for office and low-power home PCs without a graphics card attached. It will be possible to play not too demanding games, if the processor power allows, one connector for a video card is available.

FM2 + processors
FM2 + chipsets and similar sockets are suitable for use with A-Series and Athlon APUs.
- А88Х provide overclocking capability, support the connection of two video cards, RAID functionality (it is advisable to use with AMD А8 - А6);
- A78 also has an arsenal for overclocking, supports one video adapter (it is better to use the A6 - A4 lines on the CPU);
- A58 and more advanced brother A68H. Both chipsets support dual graphics (improving the performance of the graphics system is achieved through the use of hybrid processors in conjunction with some graphics adapters from AMD).

Outcomes
Considering the modern market, it should be borne in mind that Intel's Coffee Lake generation processors are compatible only with the new 300 chips and the LGA1151v2 socket, while new AMD processors, including the second generation Ryzen, are compatible with AM4. Chipsets from Intel, labeled Z or X, allow you to overclock the machine, while others do not, even with a processor with a free multiplier, suggesting similar manipulations with its frequency. With AMD, overclocking can be performed on a motherboard with an X or B chipset.
When the goals are completely different and the unnecessary waste of funds is not justified or a very limited budget for the assembly plays a decisive role, you can get by with not particularly outstanding motherboards. By the way, among them you can find interesting specimens with a good set of interfaces and connectors.
- this is the basis of a computer, and that is why, when assembling a computer, first of all, it is worth paying attention to this particular component of the system. The performance of the computer and the stability of its operation largely depend on the characteristics and workmanship of the motherboard. Today we will try to talk about what the main characteristics and features of the motherboard you need to pay attention to.
We decided that the information would be better perceived if, when choosing a motherboard, we refer to motherboards from one of the leading manufacturers - for the simple reason that it is the world famous motherboard manufacturers who equip their products maximum number technologies that improve and help in working with computers. In addition, only these manufacturers create their boards using the highest quality and most expensive components and only on the most modern equipment, because when it comes to trust, large manufacturers simply cannot, as they say, miss the mark, because if this happens, they will lose their customers and, naturally the lion's share of the profits.
The choice fell on ASUS.
|
|
For this article, we immediately selected a well-known manufacturer. ASUS is the largest player in the market of computer components, as well as laptops, high-performance computers and peripherals. ASUS made the main stake in the production of motherboards on several important points- quality, reliability, innovative approach and constant improvement of the line of motherboards both with the help of constructive additions and with the help software products of our own design.
So how do you choose a motherboard?

First you need to decide on the purpose of the computer and the manufacturer of the processor that will be used in the computer. Then explore the capabilities of suitable motherboards. In most cases, the motherboard is chosen for either office or home use universal computer, or for a powerful game system or a workstation that enthusiasts are going to use to its maximum potential.
In any case, ASUS offers the widest choice of motherboards for creating both simple office or home computers, and gaming computers, workstations and servers. In this case, you can choose a suitable ASUS motherboard for modern AMD processors, and for the latest Intel processors.
Motherboards for office or general-purpose home computers.
If you need a reliable office computer, a universal home computer or HTPC, then first of all you need to pay attention to relatively inexpensive, but high-quality ones, since it is quality and reliability that play a key role here, and performance recedes into the background.
For office computers, as well as for general purpose home computers, will work great as well. These ASUS motherboards differ from the others in one common advantage - they are equipped with a video adapter built into the chipset or simply have video outputs for using the video core built into the processors. This means that having bought such a motherboard from ASUS, you can not be puzzled by the purchase of a discrete video card, the use of which in most cases is absolutely not justified when using an office computer.
|
|
|
|
|
|

First of all, ASUS thinks about reliability, so all, including inexpensive solutions, use a full set of technologies. ASUS Protect 3.0 or some of its components that are able to protect the computer, the user himself and can significantly reduce the power consumption of the computer.

The first key component of ASUS Protect 3.0 is the unique chip EPU (Energy Processing Unit) responsible for efficient energy consumption. By increasing the efficiency of the processor power circuit using a separate chip, it is possible to reduce the power consumption of the system by almost half in comparison with motherboards where there is no such controller and where only software utilities are responsible for reducing power consumption.
 |
The second important and unique component of ASUS Protect 3.0 is the technology ASUS Anti Surge... This technology protects all microcircuits of the main elements of the motherboard and other installed equipment from power surges and possible short circuits. In the event of an unstable power supply issued by the computer's power supply, it turns off, thereby protecting itself and all devices connected to it from failure.

To protect the user from electromagnetic radiation, ASUS engineers manufacture the boards using the technology ASUS Low-EMI, which negates the electromagnetic radiation of the board while the computer is running.

To improve the reliability of the motherboard and extend its lifespan, ASUS equips its motherboards with solid-state capacitors. Solid Capacitors are able to work up to several decades, in contrast to liquid tantalum capacitors, which over time can dry out or explode even with a slight increase in load or temperature.

Almost all use the new UEFI BIOS with a beautiful and easy-to-use multilingual graphical interface. By using ASUS UEFI BIOS even a novice user can easily perform basic operations in Motherboard BIOS boards. In just a couple of mouse clicks in a simplified window ASUS EZ Mode you can configure the system, set the desired boot priority, view information about the state of the computer, and for advanced users, a full set of tools is available in the Advanced Mode tab. To update the BIOS firmware of the motherboard, you should use the function ASUS EZ Flash, for the operation of which you only need to point to the firmware downloaded from the manufacturer's website, and the motherboard will do the rest on its own.
Thanks to the high-quality components from which they are made, it became possible to increase performance by overclocking the processor and video card installed on the motherboard. It is important that this feature is implemented even in inexpensive motherboards, which proves their reliability and readiness to work in the most difficult conditions.
|  |
To increase system performance by hidden opportunities processor and video card ASUS offers several software tools at once. The first tool is named Turbo V and is implemented as a convenient utility that allows you to quickly and easily safely overclock the processor without having to reboot the system or complex manipulations in the motherboard BIOS. Sometimes a similar mechanism is implemented in the form of a switch located on the board, when turned on, the motherboard itself selects the optimal settings and overclocks the processor. This technology is named Turbo key ii... Turbo Key II can be used with technology Turbo V EVO allowing you to achieve truly incredible system performance.
also support technology ASUS Core Unlocker to unlock hidden cores on select AMD processor models, delivering significant performance gains.
|
|
To overclock the video core built into the processor or motherboard chipset, ASUS has a separate utility called iGPU Boost... In operation, it is also simple and straightforward like Turbo V - a few clicks of the mouse and the built-in video core works much faster. This technology on some boards it can also be implemented as a hardware switch on the board.
Due to the fact that the number of technologies implemented in is constantly growing, ASUS programmers have developed a unique software shell... This software package combines all the power management and overclocking capabilities of the system, and also allows you to change the rotation speed of all fans installed in the system unit to optimize cooling and reduce noise. Monitoring of the state of key system components is also available.

By the way, the speed of data transfer to external USB drives becomes a very important factor for both a modern office computer and a computer for the home, therefore practically, due to which the data transfer speed increases up to 10 times compared to USB ports 2.0.
(Small Business Advantage) is a combination of software and hardware that facilitates administration and improves data security in computers intended for small business use. To use it, you need a motherboard based on Intel B75 or Q77 chipsets and a processor from the Core i3 / i5 / i7 series.
Gaming and workstation motherboards for the enthusiast.
|
|
When choosing a motherboard for a gaming computer, especially enthusiasts who plan to closely engage in overclocking the system should pay attention not only to the quality of the motherboard, but also to hardware improvements that will allow using the motherboard and the computer as a whole, as they say, to the maximum ... For creating game configurations will do as well. These ASUS motherboards use the most advanced technology developed by ASUS engineers.
The best uses technology ASUS Stack Cool3 +, which combines a well-optimized PCB design with additional layers of copper inside the PCB, which improve heat dissipation from all heating elements. This approach allows not only to reduce heat, but also to extend the life of the gaming motherboard.
 |  |
Second, to provide the processor with a stable power supply, achieve the highest possible overclocking when performing resource-intensive tasks, and minimize power consumption during idle or standard computing, ASUS uses a digital power system. SMART DIGI + and technology Dual Intelligent Processors the third generation, the principle of operation of which is based on the introduction of several hardware controllers into the motherboard. Controller Smart Digi + responsible for fine tuning each VRM phase and keeps track of the optimal balance of performance and temperature. EPU is responsible for the energy efficiency of the computer, and TPU (separate microprocessor for overclocking) deals with the calculation, testing and optimization of overclocking parameters. By the way, each of these processors is found on others, which speaks of the versatility of the technologies developed by ASUS engineers.
Specialized series of ASUS ROG and TUF motherboards.

ASUS also has a range of ROG (Republic of Gamers) motherboards specially designed for gamers, which includes motherboards such as, and others. These motherboards incorporate all the latest technological developments from the company and are complemented by even more convenient tools to increase system performance and comfortably play the latest games. For example, on the motherboard, you can not only control system overclocking and monitor hardware using OC Zone but also take advantage of the technology ROG Connect, which allows you to monitor system performance and control overclocking using a dedicated ROG Key controller or a laptop connected to a PC via a USB port.

|  |
Another series of ASUS motherboards, differs from the rest with even higher quality components (chokes, solid-state capacitors, MOSFETs), passed the military acceptance and tested according to the server standard. CeraM! X, which, due to the porous surface, better cool the "hot" elements of the board. Some boards in this series are equipped with a special casing TUF Thermal Armor which allows you to direct air flow along the motherboard from the CPU cooler, as well as from the additional fans included in the kit, thus cooling almost the entire surface of the motherboard. Ultra high quality components and an improved CPU Power Circuit (VRM) make TUF Sabertooth motherboards a favorite of overclockers.
Convenience of assembling a computer and solving possible problems with starting the system.
|  |  |
Do not forget about such a simple but important thing as convenience when assembling a computer system unit. The company has developed several simple solutions to make life easier for both professional PC assemblers and users who assemble their own computer.
Q-Shield Designed to simplify the installation of a shield plug between the motherboard connector panel and the hole on the back of the case, protecting the motherboard from static electricity. When installing ordinary plugs, the user is often hindered by the antennae of the plug (they are also contacts for removing static), which strive to get inside the motherboard connectors and with which it is easy to cut yourself. ASUS Q-Shield does not have these very antennae - instead of them, a soft pillow covered with a conductive foil is used, which is pressed against metal cases connectors on the outside of the motherboard.
Q-Connector helps to avoid the inconvenience associated with connecting miniature contacts coming from indicators, Power buttons and Reset on the case, as well as the speaker. Now you can connect the pins to the dedicated Q-Connector outside the computer case, and then connect the entire bundle of wires to the connector group on, as if connecting just one cable.

In order to understand why the computer you have assembled does not start (if God forbid it happens), he suggests using the technology Q-LED... The Q-LEDs located on the board near the processor, memory modules and PCIe slot with the installed video card will indicate the problematic component of the system. Memory compatibility issues are easily resolved with technology ASUS MemOK!... Single press of the MemOK button! - and itself will select the memory timings settings for the correct start of the system.

The technology used in some of the latest boards allows you to upgrade BIOS boards, having only a USB flash drive with a recorded BIOS image (you also need to rename it in accordance with the name of the board) and a power supply suitable for the board. Everything! No processor, memory or video card needed! The reprogramming process is initiated by pressing the BIOS FlashBack or ROG Connect button on the board's connector panel. This technology removes the known problem when the purchased processor is not supported by the BIOS version of the board flashed at the factory, and there is no possibility to install an older CPU for a given socket.

Most ASUS LGA1155 boards will fully support the bus PCI-E version 3.0 after updating the BIOS and installing a 22nm processor. This significantly increases the modernization potential of the system as a whole, especially if you plan to use a high-performance video card or even two.
We hope that after reading this article, our customers will make right choice motherboard and this board will certainly become.
A motherboard chipset is a block of microcircuits (literally a chip set, that is, a set of chips) that are responsible for the operation of all other computer components. It also affects the performance and speed of the PC.
As you understand, in addition, you should pay close attention to the chipset located on it, especially when it comes to modern powerful home or gaming computers.
It is easy to identify them visually on the motherboard - these are large black microcircuits, which are sometimes covered with cooling radiators.
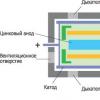
Dual bridge motherboard architecture
In the already outdated scheme for constructing a motherboard, the chipset microcircuits were divided into two blocks - the north and south bridges according to their location on the diagram.
The functions of the north bridge are to ensure the operation of the processor with RAM (RAM controller) and a video card (PCI-E x16 controller). The southern one is responsible for connecting the processor with other computer devices - hard disks, optical drives, expansion cards, etc. via controllers SATA, IDE, PCI-E x1, PCI, USB, sound.
The main characteristic of the performance of the chipset in this architecture is the data bus (System Bus), intended for the exchange of information between the various parts of the computer. All components work with the chipset via buses, each with its own speed. This can be clearly seen on the chipset diagram.

The performance of the entire PC depends precisely on the speed of the bus that connects it to the chipset itself. In the terminology of Intel chipsets, this bus is referred to as FSB (Front Side Bus).
In the description of the motherboard, it is referred to as the "bus frequency" or "bandwidth" of the bus.
Let's take a closer look at these characteristics of the data bus. It is determined by two indicators - frequency and width.
- Frequency is the data transfer rate and is measured in megahertz (MHz, MHz) or gigahertz (GHz, GHz). The higher this figure, the higher the performance of the entire system as a whole (for example, 3 GHz).
- Width - the number of bytes that the bus is able to transfer at a time in bytes (for example, 2 Bt). The wider the width, the more information the bus will be able to transmit in a certain period of time.
When multiplying these two values, we get the third, which is exactly indicated on the diagrams - the bandwidth, which is measured in gigabytes per second (GB / s, Gb / s). From our example, we multiply 3 GHz by 2 Bytes and get 6 Gb / s.
In the picture below, the bus bandwidth is 8.5 gigabytes per second.

The connection between the north bridge and the RAM occurs with the help of a two-channel controller built into it through the RAM Bus, which has 128 contacts (x128). When working with memory in single channel mode, only 64 tracks are involved, so for maximum performance it is recommended to use 2 memory modules connected to different channels.
Architecture without the north bridge
In the latest generation processors, the northbridge is already built into the chip of the processor itself, which significantly increases its performance. Therefore, on new motherboards, it is absent altogether - only the south bridge remains.
In the example below, the chipset lacks a north bridge, since its function is taken over by a processor with an integrated video core, but from it we also see the designation of the data bus speed.

In the work of modern processors, the QPI (QuickPath Interconnect) bus is used, as well as the PCI-e x16 graphics controller, which was previously in the north bridge, but is now integrated into the processor. As a result of their being built-in, the characteristics of the main data bus are not as important as they were in the previous generation dual-bridge architecture.
In modern chipsets on new motherboards, there is another parameter of the bus operation - transfers per second, which indicates the number of data transfer operations per second. For example, 3200 MT / s (megatransfers per second) or 3.2 GT / s (gigatransfers).
The same characteristic is indicated in the descriptions of the processors. Moreover, if a chipset has a bus speed of 3.2 GT / s, and a processor has, for example, 2 GT / s, then this bundle will work at a lower value.
Chipset manufacturers
The main players in the market of chipset manufacturers are the firms already familiar to us from Intel and AMD, as well as NVidea, which is better known to users for its video cards, and Asus.
Since the main manufacturers are the first two today, let's take a look at the modern and already outdated models.
Intel Chipsets
Modern - 8x, 7x and 6x series.
Obsolete - 5x, 4x and 3x, as well as NVidea.
The marking of the chipset with a letter in front of the number means the power of the chipset within one line.
- X - maximum performance for gaming computers
- R - high performance for powerful computers mass use
- G - for a regular home or office computer
- B, Q - for business. The characteristics are the same as "G", but have additional functions, such as remote maintenance and access monitoring for administrators of large offices and enterprises.
V recent times for the new LGA 1155 chipset, several more new series were introduced:
- H - for ordinary users
- R 67 - for enthusiasts who are planning further modernization and overclocking of the system
- Z - a universal option, combines the characteristics of the two previous
From the chipset diagram, one can easily understand which built-in and external functions he supports. For example, let's take a look at the diagram of a modern high-performance Intel Z77 chipset.

The first thing that attracts attention is the absence of the north bridge. As we can see, this chipset works with processors with integrated graphics core (Processor Graphics) Intel series Core. For a home computer, the built-in kernel will be enough for working with documents and watching videos. However, if high performance is required, for example, when installing modern games, then the chipset supports the installation of several video cards in the PCI Express slot 3. Moreover, when installing 1 video card, it will use 16 lines, two - each with 8 lines, or one 8, the other 4 , and the remaining 4 lines will be used to work with devices using Thunderbolt technology.
The chipset is also ready for further upgrades and system overclocking (Intel Extreme Tuning Support).
For comparison, let's take a look at another chipset - Intel P67, which is shown below. Its main difference from the Z77 is that it does not support the integrated video core of the processor.

This means that a motherboard equipped with a P67 will not be able to work with the integrated graphics core of the processor and you will definitely have to buy a discrete (separate) graphics card for it.
AMD Chipsets
Modern - the Axx series (for processors with an integrated video core), 9xx and 8xx.
Outdated - 7xx, nForce and GeForce, with the exception of some models.
The weakest in terms of performance are those models with only numbers in their names.
- The letters G or V in the model name indicate the presence of an integrated video card in the chipset.
- X or GX - support for two separate (discrete) video cards, but not at full capacity (8 lines each).
- FX are the most powerful chipsets that fully support multiple graphics cards.
The bus that connects the processor and chipset at AMD is called Hyper Transport (HT). In modern chipsets working with sockets AM2 +, AM3, AM3 + it is version 3.0, in AM2 - 2.0.
- HT 2.0: max frequency - 1400 MHz, width 4 bytes, bandwidth 2.8 GT / s
- HT 3.0: max frequency 2600 MHz, width 4 bytes, bandwidth 5.3 GT / s

Let's look at an example of a description of a motherboard on the site and determine which chipset is located on it.

In this picture we have a model MSI Z77A-G43 - from the very name it is clear that it is equipped with Intel chipset Z77, which is also confirmed in the detailed description.

And here - ASUS board SABERTOOTH 990FX R2.0 with a productive chipset from AMD 990FX, which is also evident from both the name and the detailed description.
What's the best motherboard chipset?
Let's summarize - which chipset is the best for your computer?
It all depends on the purpose for which you are assembling your PC. If this is an office or home computer on which you do not plan to install games, then it is advisable to choose a chipset that works with processors with an integrated graphics core. By purchasing such a board and, accordingly, a processor with integrated video, you will receive a kit that is quite suitable for working with documents and even watching videos in good quality.
If you need more advanced graphics work, for example for average video games or graphics applications, then you will use a separate video card, which means there is no point in overpaying for a graphics chipset that supports work with an integrated video processor - it is better if it provides the maximum operation of the video card.
For the most powerful gaming computers, and to a lesser extent for those that will work with graphics-intensive professional programs, choose the most productive models that fully support work with multiple video cards.
I hope this article has opened a little for you the curtain over the mystery of the motherboard chipsets and now you can more correctly choose these components for your computer! Well, to consolidate your knowledge, watch the video tutorial posted at the beginning of the article.
Thanks! Did not help