There are such form factors of power supplies: TFX, SFX, PS3 / ATX and ATX.
ATX is the most common standard size of power supplies, which are used in the overwhelming majority personal computers... Dimensions (HxWxD): 8.6x15x14 cm.
PS3 / ATX is a type of ATX that is more compact due to reduced depth. The depth depends on the model of the power supply - the range is from 10 to 13.9 cm.
SFX are compact power supplies designed for small PCs or home theaters. With the help of a special adapter, SFX can be installed in ATX case... Dimensions (HxWxD): 5.15x125x100 cm.
TFX - this standard size is used in cases of small height or non-standard shape. Dimensions (HxWxD): 6.5x8.5x17.5 cm. Depending on the PSU model, the depth may be less.
Power
from 120 to 2400 W
The power supply has this power.
This parameter is most important for power supplies. However, the more powerful the system, the higher its energy consumption.
For computers used in offices, 300-400 W is quite enough power, but a powerful PC for gamers will need 450-600 watts. A power supply with a capacity of more than 650 W is needed for top-end configurations with two video cards.
Cooling system
View of the cooling system of the power supply. Today, power supplies with one, two fans are produced, as well as those without fans - fanless.
The most common cooling system is with one fan. In budget models, 80 mm fans are installed, these fans spin up to several thousand rpm, minus - they make a lot of noise. In more expensive models, fans are installed with a much larger diameter - more than 120 mm.
Sometimes a second fan is built into powerful power supplies, which, of course, increases the cooling efficiency, but significantly increases the noise level.
In fanless power supplies, only radiators are used to dissipate heat. The advantage of this type of power supply: they are completely silent. Disadvantages - high cost, as well as power limitation ( this system cooling cannot completely cool powerful power supplies). Today, power supplies that do not have fans do not exceed 600 watts.
Fan diameter
from 14 to 180 mm
Diameter of the fan installed in the power supply.
Typically a fan with a larger diameter operates at a lower speed and therefore produces less noise (cooling efficiency does not change). If you need a quiet ventilation system, buy power supplies with a fan with a diameter of at least 120-140 mm.
Second fan diameter
from 40 to 80 mm
Diameter of the second fan installed in the power supply.
Typically a fan with a larger diameter cools at a lower speed and produces less noise (the cooling performance does not change).
Fan speed
Rotational speed of the fan installed in the power supply.
The higher this value is, the louder the fan is. Many powerful power supplies have a function that automatically changes the fan speed depending on the temperature, this function helps to reduce noise levels.
PFC
Power Factor Correction (PFC) method in the power supply unit.
The power factor is the value obtained as a result of dividing the active power (the power that goes to useful work) to the received power. The closer the power factor is to unity, the better. Two methods of power factor correction have been developed - a passive method and an active one. The active correction method is much better, because the power factor with it reaches of great importance- 0.95-0.99, and with a passive correction method - only 0.7-0.75. A high power factor is needed for those who have low-power UPSs, because to ensure the functioning of a power supply with a passive PFC, a much more powerful (by about a third) UPS is needed than to ensure the functioning of a power supply of the same power, but with an active PFC. By the way, power supplies with active PFC are not so sensitive to undervoltage in the network.
ATX12V version
from 1 to 2.52
The version of the ATX12V standard supported by the power supply.
The ATX12V standard is a list of specifications that defines the design of a power supply. This standard was introduced after the Pentium 4 processor was released. The main difference from the previous standards is a significant increase in power on the +12 V line (before the Pentium 4 processor, power was supplied via the +5 V line). The main differences between the versions of the standard
1.3 - a 20-pin power connector is required for the motherboard, as well as an additional 4-pin power connector for the processor. The current on the +12 V line is at least 10 A.
2.0 - a 24-pin power connector is required for the motherboard, as well as an additional 4-pin power connector for the processor. The presence of at least 2 + 12V lines is mandatory.
2.2 - a 24 (20 + 4) -pin power connector is required for the motherboard, as well as an additional 4-pin power connector for the processor.
TFX12V version
1.3 to 2.4
The power supply supports TFX12V standard. Thin Form Factor standard was developed for small size systems in 2002 by Intel... The power supply is characterized by a narrow, elongated shape. 180-300 W is the typical power supply of the PSU.
EPS12V support
The power supply supports EPS12V standard.
This standard is for servers entry level... Home PC Power Supply Firms Mention this standard in order to emphasize the reliability of their products.
80 PLUS certificate
The compliance of the power supply unit with one of the certification levels implies the compliance of this model with certain energy consumption standards (the efficiency of the power supply unit must be at least 80%). The higher the certification level, the more efficient the PSU.
Connectors
Motherboard connector type
View of the connector for the motherboard. Power is supplied to the motherboard through this connector. Modern motherboards use a 24-pin connector, older motherboards had a 20-pin connector. Many power supplies available today have a collapsible 24-pin (20-pin + 4-pin) connector to establish compatibility with older motherboards.
Number of connectors 4-pin CPU
from 1 to 2
The number of connectors 4-pin CPU.
This connector supplies additional power to the processor. A huge number of motherboards produced today (about half) are equipped with a 4-pin CPU connector.
Number of connectors 4 + 4 pin CPU
from 1 to 2
The number of connectors is 4 + 4 pin CPU.
This connector supplies additional power to the processor. This connector is collapsible, it is compatible with motherboards with an 8-pin CPU connector, and with motherboards that have a 4-pin CPU connector.
Number of connectors 8-pin CPU
from 1 to 2
Number of connectors 8-pin CPU.
This connector supplies additional power to the processor.
Number of connectors 6-pin PCI-E
from 1 to 20
The number of 6-pin PCI-E connectors.
Powerful video cards released today require additional power. Power is supplied to the video card through the 6-pin PCI-E connector.
If you are planning to build a CrossFire or SLI system, then the additional connectors will come in handy.
Number of connectors 6 + 2-pin PCI-E
from 1 to 20
Powerful video cards released today require additional power. Power is supplied to the video card through the 6 + 2-pin PCI-E connector.
Number of connectors 8-pin PCI-E
from 1 to 8
The number of connectors 8-pin PCI-E.
Powerful video cards released today require additional power. An 8-pin PCI-E connector is used to supply power to the video card.
If you are thinking of building a CrossFire or SLI system, then the additional connectors will come in handy.
Number of connectors 4-pin IDE
from 1 to 16
Number of 4-pin IDE connectors.
Thanks to this connector, hard drives and CD / DVD drives with IDE interface are powered.
Number of 15-pin SATA connectors
from 1 to 62
Number of 15-pin SATA connectors.
15-pin SATA connector to CD / DVD drives and hard drives with SATA interface power is supplied.
Number of connectors 4-pin Floppy
from 1 to 8
Number of 4-pin Floppy connectors.
The 4-pin Floppy connector supplies power to the floppy drive.
Current strength
On the +3.3 V line
from 4 to 40 A
The maximum value of the current along the line is +3.3 V.
In previously released PCs, the main load fell on the +3.3 V and +5 V buses. However, with the introduction of the Pentium 4, the +12 V bus became the main energy consumer. That is why the current on the +3.3 V line is not particularly important today, because all power supplies currently being produced has sufficient power on the given bus.
On the +5 V line
from 5.3 to 52 A
The maximum value of the current on the line +5 V.
In previously released personal computers, the main load was on the +3.3 V and +5 V buses. However, after the introduction of the Pentium 4, the +12 V bus became the main consumer of electricity. sufficient power on the given bus.
On the +12 V line 1
from 6 to 200 A
The most "gluttonous" elements modern computers- to the processor and the video card - power is supplied via the +12 V bus. For this reason, the higher the current on this bus, the better.
Usually the +12 bus is divided into several lines for safety reasons.
On the +12 V line 2
from 7 to 85 A
The maximum value of the current on the first line is +12 V.
Power is supplied to the processor and video card via the +12 V bus. The higher the current on this bus, the better.
For safety reasons, the +12 bus is divided into several lines.
On the +12 V line 3
from 6 to 45 A
The maximum value of the current strength on the third line is +12 V.
The +12 V bus supplies power to the video card and processor, these components are the most "power hungry" components. The more current is supplied through this bus, the better.
As a rule, the +12 V bus is divided into several lines for safety reasons.
On the +12 V line 4
from 8 to 45 A
The maximum value of the current strength on the fourth line is +12 V.
On the +12 V bus, power is directed to the video card and the PC processor, these are the most "gluttonous" elements. Therefore, the more current flows through the bus, the better.
Usually the +12 bus is divided into several lines for safety reasons.
On the +12 V line 5
from 15 to 30 A
The maximum value of the current on the fifth line is +12 V.
The +12 V bus supplies power to those components of modern PCs that consume the most energy. Therefore, the higher the current flowing through this bus, the better.
The +12 bus is usually divided into several lines to improve safety.
On the +12 V line 6
from 17 to 30 A
The maximum value of the current strength on the sixth line is +12 V.
On the +12 V bus, power is supplied to the most "gluttonous" components of personal computers, so the more current that goes through this bus, the better.
This bus is usually divided into several lines for safety reasons.
On the +12 V line 7
The maximum current on the seventh line is +12 V.
On the +12 V line 8
from 0.3 to 0.3 A
The maximum current on the eighth line is +12 V.
The +12 V bus supplies power to the processor and video card - the most "power hungry" components of modern PCs. Therefore, the more current on this bus, the better.
As a rule, for safety reasons, the + 12V rail is divided into several lines.
On the -12 V line
from 0.1 to 300 A
The maximum value of the current along the line is -12 V.
A voltage of -12 V is required for the operation of the COM ports.
On the +5 V Standby line
from 0.5 to 12.5 A
The maximum value of the current on the line +5 V SB.
The +5 V SB (Standby) bus is required to perform functions such as turning on the PC via a modem, by local network, by pressing a button on the mouse or keyboard, also for the Suspend-to-RAM mode.
Noise level
Minimum
from 2 to 34 dBA
The minimum noise level created by the cooling system during the operation of the power supply. The lower the value of this parameter, the more comfortable the work will be. But it should be noted that in most computers the main noise comes not from the power supply, but from the processor cooler.
Maximum
from 5 to 45 dBA
The level of noise generated by the cooling system when the power supply is operating.
The lower the value of this parameter, the more comfortable work with a PC will be. However, it should be said that in many PCs the main noise comes not from the power supply, but from the processor cooler. The noise level is measured in dBA. Measuring the value of the noise level in dB is a little incorrect, because the human hearing aid is designed in such a way that the volume perceived by the ear depends on both the sound pressure level and the frequency of the incoming sound. Loudness in dBA is the perceived loudness, that is, the sound pressure value that takes into account the structural features of the human hearing aid.
Input voltage
Minimum
from 85 to 230 V
The minimum input voltage that the power supply supports. Mains voltage in different countries differs: in Europe and Russia, the standard is 220 Volts, in Japan or the USA - 110 Volts. Universal power supplies allow you to maintain the input voltage in certain ranges (the range depends on the device model).
Maximum
from 220 to 280 V
The maximum value of the input voltage that the power supply supports. The voltage in the network differs in different countries: in Europe and Russia, the standard is 220 Volts, in Japan or the USA - 110 Volts. Universal power supplies allow you to maintain the input voltage in certain ranges (the range depends on the device model).
Additional Information
Detachable cables
Unused cables can be detached, then they will not interfere with the assembly of the PC, connecting new devices to it.
Overvoltage protection
The power supply has a system overvoltage protection function.
If the output voltage is higher than the allowable value, then this function will automatically turn off the power supply, this will save the computer components from burnout.
Overload protection
The power supply has an overload protection function.
If the output current is greater than the allowable value, the function will automatically turn off the power supply, this action will save the computer components from burnout.
Short circuit protection
The power supply has a system short circuit protection function.
If a short circuit occurs, the protection system will instantly turn off the power supply, while keeping all computer components and the unit itself from burning out.
Backlight color
The backlight installed in the power supply will give your computer a personalized design. There are models with different illumination colors.
Power supply color
The main color of the power supply case. As a rule, computer equipment is made in neutral calm colors, most often it is black, white or silver devices that will harmoniously fit into any interior.
Dimensions (edit)
Width
from 20.5 to 360 mm
Device width.
Height
from 19 to 190 mm
Device height.
Depth
from 2 to 360 mm
Depth of the device.
The weight
from 0.4 to 140 kg
Device weight.
This work was submitted to our "unlimited" article competition and the author received an award - a PENTAGRAM FREEZONE QVC-100 Cu + cooler, an AMD rug and a branded T-shirt of the site.
Most often, novice users do not pay enough attention to the selection of high-quality components, and when choosing a case, they are only worried about the design of its front panel. Even if the buyer is interested in the power of the power supply (hereinafter referred to as PSU) installed in the case, no one will warn him about the low quality of cheap power supplies (no matter how beautiful the numbers are drawn on them). In the future, with an independent upgrade, the processor, video card is replaced, a hard drive is bought ... but the power supply remains the same, and if problems arise with the stability of the machine, they do not immediately remember its existence. The search for a more powerful power supply begins, but in articles about power supplies and on near-computer conferences (through the efforts of individual illiterate and irresponsible authors, as well as their readers), there are many surprisingly tenacious myths walking around. Some of them will try to expose this material, and at the same time show by examples the differences between a cheap PSU and a high-quality one (not necessarily expensive).
advertising
On the net you can find a lot of articles on the theory of computer power supplies, their tests and guidelines for revision. This material- an attempt to give some generalized recommendations for choosing a power supply without tests, according to the characteristic external signs. The idea itself is inspired by this article.Introduction
It's no secret that the power consumption (and therefore heat dissipation) of PC components is constantly growing. TDP (maximum design heat dissipation) of modern desktop platforms in the near future is 130W (LGA755) and 125W (Socket AM2), respectively. The power consumption of top-end video cards has long gone beyond the permissible currents for both the AGP connector (40W) and PCI Express(75W) and reaches 120W (such video cards are equipped with additional power connectors), and the use of two video cards in SLI or CrossFire mode automatically doubles these requirements (see the section for the list of PSUs certified for SLI and CrossFire systems). The transition DDR-> DDR2 (with a decrease in voltage from 2.5-2.8V to 1.8-1.9V and the reference frequencies by half) is slowly compensated by an increase in frequencies (and voltages in overclocking modules).
First of all, the standard describes the requirements for the input voltage power network with which the power supply should work.
In practice, in recent years, almost all manufacturers of power supplies have mastered circuitry with active power factor correction (Active PF Correction), which makes it possible to create models for an alternating input voltage of any power network in the world, in the range from 90V to 260 V. of power supply circuits from current overload, for which the mandatory presence of a fuse is prescribed.
The basic ATX specification defines the requirements for both the main supply voltages, + 3.3V, + 5V and + 12V, and the auxiliary power rails, -12V and + 5VSB (Standby). In its first revisions, the ATX standard also described the requirements for the -5V bus, since this voltage was required to power the ISA bus, however, after the disappearance of the ISA bus, the requirements for this voltage were removed from the ATX standard.
Initially, in the list of mandatory buses and power connectors, the ATX standard prescribed the mandatory presence of a 20-pin connector for powering motherboards, however, over time, as the components became more complex, the power requirements increased and became more stringent, and the ATX12V standard in editions 2.x prescribes the presence of two motherboard power connectors: the main 24-pin (improved 20-pin version) and an additional 4-pin for powering the central processor.
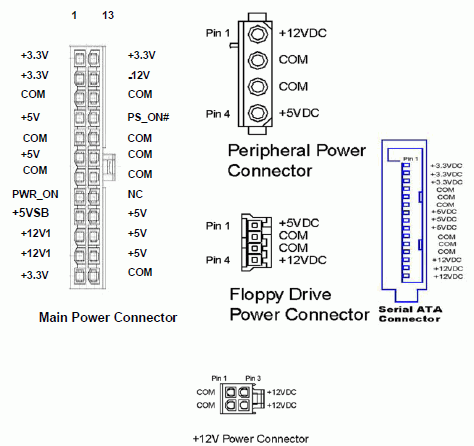
This is how the pinout of a modern 24-pin motherboard power connector according to the ATX12V 2.x standard looks like.
|
24-pin connectorATX12 V 2. x(added 11, 12, 23 and 24 pins to the 20-pin version) |
|||||
|
Colour |
Voltage |
Contact |
Contact |
Voltage |
Colour |
|
Orange |
Orange |
||||
|
3.3V signal |
Brown |
||||
|
Orange |
|||||
|
Without contact |
|||||
|
Orange |
|||||
|
Pins 8, 13 and 16 are signal, not power) |
|||||
|
Pin 20 can be used on ATX and ATX12V systems version 1.2 and older to supply the −5VDC bus (white). In version 1.2 this contact disappeared, and since version 1.3 it is prohibited. |
|||||
Four contacts deserve a separate description, which are entrusted with special functions:
- 8 contact - PWR_ OK, or " PowerGood"- the output signal of the power supply, signaling the final stabilization of the output voltage and the readiness of the power supply unit for stable operation. Usually, the signal remains low for 100-500 ms after the" grounding "of the PS_ON # signal.
- 16 pin - PS_ ON# , or " PowerOn"- signal 5-volt contact. When the contact on the side of the motherboard is connected to the common wire (" grounded "), the power supply turns on.
- 9 contact - +5 VSB, or " +5 Vstandby"- the standby voltage, remains even after the power supply is turned off. It is necessary to power the circuits that control the" Power On "signal.
- 13 contact - supply voltage + 3.3V, ( +3.3 Vsense) - connects to the + 3.3V bus of the motherboard or its power connector, allows you to detect a supply voltage drop remotely.
One of the most important parameters, regulated by the standard, is the stability of the output voltage provided by the power supply, as well as the residual ripple present in the output DC voltage. It is from these parameters that manufacturers make a start when designing circuits for converting, stabilizing and filtering voltages required to power motherboard components.
For key supply voltages, the spread of supply voltages should not exceed ± 5% of the nominal over the entire load range. For less critical voltages, a variation of the order of ± 10% of the nominal voltage is allowed. The table below shows the voltage tolerance and maximum output ripple requirements.
|
Tire |
Deviation |
Range |
Ripple (max.amplitude) |
|
4.75V - + 5.25V |
|||
|
± 10% (± 0.50V) |
4.50V - -5.50V |
||
|
11.40V - + 12.60V |
|||
|
10.8V - -13.2V |
|||
|
± 5% (± 0.165V) |
3.135V - + 3.465V |
||
|
4.75V - + 5.25V |
Of course, the smaller the deviation of the supply voltages from the nominal, the more stable operation can be expected from the system as a whole. Some PSU manufacturers even declare a deviation of the main voltages of no more than ± 3% over the entire range of permissible loads. This is not standardized by the standard, but, at the same time, speaks of a very high quality of this product.
In addition, the standard also describes the cross-load requirements of + 5V and + 3.3V rails depending on the load of + 12V rails for several typical configurations - 250W, 300W, 350W, 400W and 450W. This is, for example, a cross-load diagram for a 450 W configuration:

As noted above, starting with the ATX12V standard version 2.0, the main motherboard power connector has become a 24-pin, while maintaining backward compatibility with the previous 20-pin design, while the additional four pins provide + 3.3V, + 5V power. and + 12V. In addition, in this version of the standard, the additional 6-pin AUX power connector, which appeared in ATX12V versions 1.x, was removed, since the additional + 3.3V and + 5V power rails were integrated into the 24-pin connector.
From this moment (February 2003) the main supply voltage of the system is considered to be + 12V buses, so the standard since that time defines the need for at least two + 12V buses (12V2 for a 4-pin processor power connector and 12V1 for everything else), with independent protection against current overload on each channel. In practice, the most powerful power supplies have since begun to acquire a large number of + 12V buses, however, the standard requires at least two such buses to be present without fail.
Due to the growing "responsibility" of the + 12V buses, the power requirements for the + 3.3V and + 5V buses have been reduced. In addition, starting with this version, the presence of power connectors for Serial ATA devices has become a mandatory requirement.
In ATX12V version 2.01, the standard finally got rid of the -5V bus, and the next revision, ATX12V v2.1, required a 6-pin power connector for PCIe graphics cards, since the PCIe slot, which appeared on motherboards, required power up to 75 W. ATX12V version 2.2 added the requirement to have an 8-pin PCIe power connector, providing a load of up to 150 watts.
The following requirements are adopted with regard to the operation threshold of the output voltage protection:
Short-circuit protection prescribes mandatory operation when the circuit resistance is less than 0.1 Ohm, while the power supply must be turned off.

In terms of noise performance, the standard prescribes a limitation of acoustic noise to a level not exceeding 40 dB.
According to the generally accepted definition, a computer power supply is the power component of the system that provides power to the rest of the PC. From the point of view of circuitry, the PSU is a module for converting AC power network 100-127V (USA, Japan and Taiwan, as well as in some places in South America) or 220-240V (Europe and most other countries of the world) into direct current with levels voltage acceptable to power the computer components.
A power supply is only one of the components of a computer system, so its key characteristics are defined as one of the many recommendations for systems of a certain form factor, and not vice versa. For example, it is the standard form factor ATX (Advanced Technology Extended), developed by Intel in 1995, that determines the dimensions and other characteristics of the power supply, and not the PSU that determines the shape of ATX systems.
Originally designed for desktop power supplies computer systems, for the most part were calculated according to the requirements of the ATX12V standard. This was the case until the version of the standard ATX12 V 2.2 (released in March 2005), after which it was decided to combine in a single document the requirements for all common form factors of desktop platforms, including CFX12V, LFX12V, ATX12V, SFX12V and TFX12V. Over time, a document appeared " DesignGuideforDesktopPlatformFormFactors, Revision 1.1 "(March 2007), relevant to this day.
For reference, the form factors of computers are determined mainly by the format motherboards, the dimensions of some of them are given below in millimeters:
- WTX - 356x425
- AT - 350x305
- Baby-AT - 330x216
- BTX- 325x266
- ATX- 305x244
- LPX - 330x229
- microBTX - 264x267
- microATX - 244х244
- microATX (minimum) - 171x171
- FlexATX - 229x191
- Mini-ITX - 170x170
- Nano-ITX - 120x120
- Pico-ITX - 100x72
- PC / 104 (-Plus) - 96x90
- mobile-ITX - 60x60
Thus, if you see a reference to "compliance with the ATX12V 2.3 standard" in the specifications of a power supply, keep in mind that such a document does not exist in nature. The last separately presented document was ATX12V 2.2, and the version marking "2.3" denotes compliance with the requirements of the subclause "ATX12V Specific Guidelines 2.3" in the aforementioned document of the desktop platform design guide, version 1.1, common to all desktop form factors.
Although ATX12V is only a subset of other PC form factors, we usually refer to this standard when talking about desktop systems. Unless, of course, we are talking about miniature "TV gadgets" for watching videos, compact office machines, server systems and other special cases that do not fit into the definition of a home or gaming desktop system. Today we are talking about ATX12V power supplies.
It should also be noted that the publication of new standards for power supplies does not cancel previous recommendations and requirements, but, as a rule, only toughens them. Therefore, today we will study the ATX12V 2.2 standard, and in addition to it, the additions "ATX12V Specific Guidelines 2.3" from the "Design Guide for Desktop Platform Form Factors, Revision 1.1 ".
The requirements of these documents can be called sufficient for choosing a power supply model suitable for designing the system as a whole, however, if we talk about designing a modern system, at least one more document must be taken into consideration - the 80PLUS recommendations.
And that's why.
One way or another, part of the power supplied to the PC is dissipated directly by the power supply itself during its operation. For example, the total power consumption of the system is about 500 W and the efficiency of the power supply at the level of 75% in practice means that the power supply unit spends on itself a quarter of the energy consumed. About 125 W - and this is the power of a decent soldering iron, they go to the PSU to "heat" itself! If the PSU has a higher efficiency - say, 87%, the cost of paying for electricity, as well as cooling the system, can be significantly reduced.
Another interesting example. Let's say you have planned to buy a "stock" power supply. You never know ... The choice fell on a unit of kilowatt power. Doesn't your pocket fit? Maybe, but not in the case of power supplies. Imagine how a 1 kW power supply unit will "behave" in a system whose maximum load, even at its peak, does not exceed 500 W, at most - 600 W. Rare modern system- even on a 6-core processor and a pair of powerful video cards, it consumes a lot of power.
The power supply is one of the most important parts of a computer. Without it, not a single component will work. At the same time, too little attention is paid to the power supply.
Why is the power supply so important? The reason is simple: every component in the computer depends on a stable power supply - only then everything will work without interruption. Any, even a short voltage change can lead to system crash and component failure, but many users do not even think about it. When PCs become unstable, users often blame overly aggressive memory lags, graphics card or processor overclocking. But the power supply is one of the most problematic components! That is why our laboratory could not ignore him.
ATX12V 2.01 - new specification
There is a certain revival in the PC world today: PCI Express, DDR2 and Serial ATA memory, and many other new technologies have entered the scene. Among them, almost imperceptibly, flaunts the ATX12V 2.01 standard, which is intended to replace ATX 1.3.
Probably the most notable change is the new large ATX plug, which now has 24 pins instead of 20 on the previous version.

Classic ATX plug (left) and new ATX 2.0 plug (right).

Adapter from 24 to 20 contacts.

And a completely clever alternative is a separate block with four contacts.
The four new contacts are the +12 V, +5 V, +3.3 V lines and additional ground. Thus, the old AUX connector goes into oblivion - the new standard no longer supports it. The layout of the remaining 20 pins has not changed, that is, the two standards are compatible, but with some restrictions. To use a 24-pin power supply on an old motherboard, you will need an adapter. However, most manufacturers of power supplies include it in the package. Reverse configuration is also possible as the 20-pin plug fits into the 24-pin connector.
However, mechanics do not always coexist successfully with electronics. The manufacturer decides for himself which combination can be used and which not. Some boards use an additional 4-pin Molex socket, like on optical drives or hard drives, to which the corresponding power supply plug is connected. In general, always read the instructions for the motherboard before installing.

Mechanically connects but does not work. So the manufacturer of the motherboard decided.
Also in the ATX12V 2.0 standard there is a mandatory SATA power connector. It was already seen in the 1.3 standard, but now it has become mandatory. So it's time to say goodbye to power adapters for SATA hard drives. Moreover, as practice shows, they are very inconvenient. But the ATX standard does not specify the number of SATA power connectors.

No more needed: SATA adapter.

SATA power connectors coming directly from the power supply. There is both a straight fork and an angled one.

|
|||
|
| |||