USB 3.0 technology appeared in 2008. Nowadays, all new computers or laptops come with USB 3.0 support. But how much more profitable is this technology? How much faster? Can you see an improvement in speed when using USB 3.0 media?
USB 3.0 devices are backward compatible with USB ports 2.0 They will function normally, but only at the maximum speed for USB 2.0. The only drawback is that they are more expensive. In this article, we will look at how usb 2.0 differs from usb 3.0. And also why the latest technology is so much better.
USB is a standard and defines the maximum signal transfer rate through a port. The USB 2.0 standard provides a theoretical maximum signal transfer rate of 480 megabits per second. While USB 3.0 allows data transfer at a speed of 5 gigabits per second. In theory, USB 3.0 is ten times faster than USB 2.0.
If that were all, then the question of upgrading could be considered closed: who would not want a USB drive to work 10 times faster than it is now? But it's not that simple. The standard only defines the maximum data transfer rate. Different devices may have other bottlenecks, for example, for many drives, the transfer time will depend on the speed of the flash memory.
Real speed indicators
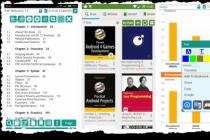
Theory is good, but let's see how USB 3.0 flash drives actually work. Everything here will depend very much on the drive. We took a test run by tomshardware.com. The test also includes USB 2.0 drives, which are at the bottom of the diagram. And we can see a really interesting result.
USB 2.0 drives are capable of delivering write speeds from 7.9 to 9.5 Mb / s, while USB drives 3.0 from 11.9 Mb / s up to 286.2 Mb / s. We can see that the worst USB 3.0 drive is faster than all USB 2.0 drives, but not by much. And the best one is more than 28 times faster.
The slowest drives were the cheapest, while the faster ones were expensive. The fastest media achieves this speed thanks to the four-channel flash memory, which requires a certain investment from the manufacturer.
Technical features
Despite the fact that the standards USB 2.0 vs USB 3.0 are compatible with each other, they have some differences in structure. To support old USB devices 3.0 has all the same four pins. One pair for receiving and transmitting data, and the second for power supply. But this is where the difference between USB 2.0 and 3.0 begins. To organize high speed work, fast charging and other advantages, four more contacts were added, which are designed to work with amperage up to 1 ampere.
Because of this, two more were added twisted pairs NS. Now the cord itself has become thicker, and its maximum length has been reduced from five meters to three. Thanks to the increased amperage, it is now possible fast charging smartphones and connect more devices to one USB port. In addition, magnetic protection has been added to the cable.

What is the difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 in appearance? First, it is the number of contacts. Secondly, manufacturers release USB 3.0 ports in blue or, in some cases, red. Therefore, it will not be difficult to determine which connector is in front of you.
Device price
Price is still a very important factor. Many USB 2.0 flash drives can be obtained very cheaply. For example, you can find an 8 GB flash drive for no more than $ 10, and for 4 GB, even for $ 5.
To see significant speed gains on USB 3.0, you will need to spend over $ 40. Ask yourself how much you are willing to spend and what you will be using the drive for. Do you just need a small, cheap document transfer tool? Then USB 2.0 will do just fine. On the other hand, if speed is more important, especially for transferring hefty files, you will probably need USB 3.0.
Selecting a USB 3.0 Drive
USB 3.0 allows for faster speeds. But before you buy desired device, pay attention to other parameters that will be critical, such as the speed of the flash memory.
If you're looking for a good, fast USB drive for transferring large files, five dollars isn't enough. You need to look at various tests and determine in advance how quickly the selected carrier of a particular brand will work. It can play important role when selecting USB 2.0 or USB 3.0.
conclusions
In this article, we looked at how USB 2.0 differs from USB 3.0. As you can see, there are many differences, but there are nuances everywhere. Now you know how to tell the difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. Please note that not all devices will perform faster just because they are using USB 3.0.
If you have a USB keyboard or mouse, then naturally you will not notice any speed changes when upgrading to USB 3.0. Of course, sooner or later, all devices will switch to this standard. There is nothing wrong. But there is no point in paying more for them now either. You can connect a USB 2.0 device to a USB 3.0 port as they are fully compatible.
I am glad to welcome readers to my blog!
In today's article, we'll talk about USB, or rather, what is the difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 and what possibilities they give for use on your computer.
The ancient parallel LPT and serial ports are almost gone. COM ports... Finally, computer users have begun to get rid of thick communication cables, keyboards and mice with COM tips and PS / 2 connectors. They were replaced by the universal USB interface, in the English interpretation - Universal serial Bus. A universal port that's why it is universal, so that, without hesitation, you can connect various external devices to it: large and small, low-speed and high-speed, powerful and low-power.
The history of the creation of the Universal Serial Bus
The developers of stationary computers and laptops have long had a mature decision to replace motley communication connectors with one universal one, capable of solving all possible problems. The first samples of the Universal Serial Bus interface began to appear in 1994-1996 and were designated as USB 1.0. The novelty spurred the market for external devices, and by 2000, most printers, scanners and other devices began to provide a newfangled interface. A big plus in the development of USB was the appearance in 1999 of the first 8 MB flash drive, which all users liked.
USB 2.0
In 2000 the world saw a new version- USB 2.0. She became forty times more productive than her predecessor. If USB 1.0, according to the specification, had a maximum data exchange rate of 12 Mb / s (megabits per second), now the speed has increased to 480 Mb / s. The success did not come out of nothing - it is known that about 400 interested companies took part in the development of the innovation, including such well-known brands as Intel, IBM, Hewlett-Packard, Compaq, Microsoft, NEC, Philips and many others.
USB 3.0
Fueled by the unheard-of results, the developers did not stop there and in 2008 offered USB 3.0. The new specification made it possible to increase the data exchange rate by another 10 times and reached a value of 4800 Mb / s, which is equivalent to 4.8 Gb / s. At such a speed, information from a 1-terabyte medium can theoretically be pumped in less than 30 minutes (at a maximum possible speed of 600 MB / s), if there are no other restrictions.
It should be noted that the near future belongs to this type, so when buying a new motherboard, make sure that it has support. of this standard connections.
Structural difference between USB 2.0 connectors and USB 3.0
What is the constructive difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0? In fact, they are partially compatible, but the latter contains an additional 4 more pins for connecting two signal twisted pairs. The previous version has only 4 contacts: two signal contacts, power supply and ground, the case is used as a shield. Partial compatibility implies the fact that a USB 2.0 plug can be plugged into the USB 3.0 socket without any problems, and everything will work, only at a reduced speed, according to specification 2.0. The same will happen when you dock the USB 3.0 plug into the USB 2.0 jack. Those connector options that are not included in the connection, of course, will not work.

You can visually distinguish USB 3.0 ports from USB 2.0 by color - version 3 is blue, while version 2 is black. The forks themselves are also different - blue and black.
In addition, there are several design options for USB connectors. Here are the main types of USB 2.0 connectors: Type A regular (4x12 mm), Mini (3x7 mm) and Micro (2x7 mm); type B regular (7x8 mm), Mini (3x7 mm) and Micro (2x7 mm). The overall dimensions of the connecting part of the connector, shown in parentheses, are rounded.

The USB 3.0 connectors currently in use are as follows. For type A, only the normal version applies, for type B there is a regular, Mini and Micro version. For both specifications 2.0 and 3.0, universal connector options have also been developed: Mini-AB and Micro-AB. Mating parts of type A and type B can be docked with them without problems. The USB 3.0 version additionally has a Powered-B type with reinforcement of the power contacts. Also, manufacturers have agreed that all USB 3.0 connectors are blue to visually identify the port specification and its potential.

In practice, you can also use different adapters from one type to another. This is convenient when, for example, you have a mini-usb cable, and you want to connect a phone with a micro-usb socket to your computer. Or if you need to make a version with usb-microUSB out of a usb-usb cable.

How to use the USB of a computer?
Due to the fact that a large number of external devices have now been able to connect via the USB port, the mechanical stress on these connectors has increased dramatically. Frequent connection of flash drives, players, all kinds chargers leads to mechanical abrasion of parts, weakening of electrical contacts. Moreover, the consumer can unintentionally hit the cable connector or flash drive, which will damage the port and require repair. If the connector is installed on a separate printed circuit board connected to the main board by means of a loop, this is still half the trouble. If the USB connector is soldered directly into the motherboard, then repairs will be expensive.

To avoid troubles, the consumer should be careful and use all the USB connectors on the computer evenly. In addition to the built-in connectors, you can purchase an additional card PCI expansion with USB ports. It is installed in the appropriate PCI slot on motherboard and outside the case brings out additional connectors for connecting external devices.

Alternatively, you can purchase a USB port splitter (external hub). It will increase the number of connectors and secure the computer itself.

However, it should be borne in mind that through such a splitter it will not be possible to connect energy-intensive devices, for example external hard disk without additional power supply. In addition, the consumer sometimes allows connection to the main port of powerful loads, such as external hard disk or several loads, which in total exceed the energy capabilities of the supply bus. This can lead to burnout of the protective elements of the circuit and the failure of the interface to work. To prevent this from happening, you need to remember that USB 2.0 can deliver a maximum of 500 mA of current to the power line, and USB 3.0 - 900 mA. For more powerful loads, it is recommended to use external sources nutrition.
Another danger lies in incorrect turning on / off, for example, a flash drive in "hot" mode, as well as in the action of static electricity. Although the developers guarantee the safety of such a mode, it is advisable to carry out all communications with the computer turned off and the external device turned off. When it comes to static electricity, it is enemy number one in dry heated spaces. A dangerous charge accumulates on the body and clothing of a person, and to remove it, you must touch the ground bus, water pipe or hot water radiator.
Now the user has the necessary knowledge about the correct operation of the USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 ports of the computer, and the recommendations given will allow you to solve the tasks without problems and successfully.
Thanks! Did not help
Daily progress in the field information technologies only accelerates its pace. The volumes and speed indicators of the transmitted data are growing. However, to meet the needs of modern software do not forget about the improvement and development of the hardware component.
To transfer data between devices, the connector is widely used USB which appeared in 1996. However, not everyone has an idea that today many modern devices equipped with the third generation of this connector - USB 3.0. In this article we will try to figure out what changes and improvements the developers have "put" into the 3.0 generation and what are the differences between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0.
backward compatibility
In theory, devices equipped with 3.0 ports are backward compatible with those with previous generation USB connectors. The only limitation will be speed indicator... While 2.0 will work at the limit of its speed capabilities, its "big brother" will not use even half of its resources.

Increased performance
In the now outdated, but still widely used USB 2.0 standard, the data transfer rate was within 460-490 Mbps... For the new 3.0 standard, this figure can reach 8 times higher - up to 5 GB per second... What do these numbers mean for the average user? Here's what: now, to transfer large files, such as movies, archives, etc., you will need to spend 10 times less time. However, not all so simple. These indicators characterize only the 3.0 connector standard, and in order to transfer, for example, files to flash memory at high speeds, they must also be supported by the controller microcircuit, the "flash drive" itself.
Technical features
As mentioned above, 2.0 and 3.0 connectors are compatible with each other. But there are still a number of differences, both in design features and in technical characteristics... Both connectors, as before, have four pins for mutual backward compatibility, however, the cord used in conjunction with the 3rd generation of the connector has two additional pins for organizing work at high speeds, increasing the current used to power various devices, as well as for implementation other benefits. As a result, the cord has become slightly thicker, and its recommended length has been reduced from five to three meters. In addition, the cord has become a little stiffer as a result of the introduction of a special shielding coating into the cable to protect it from electromagnetic fields induced in it.

It is also worth noting that now the current strength present in the connector has increased to 950 mA, while in connector 2.0 this figure was 500 mA. As a result, it became possible to use a higher charge current to charge smartphones and other devices, which significantly reduces the time required to fully charge this class of devices. In addition, the number of devices simultaneously receiving a charge from one connector can now be increased.

External differences
At first glance, distinguishing between USB 2.0 and 3.0 is actually very easy. It's all about the color of the plastic insert on which the four connector pins are fixed. In the 3.0 standard, this plastic insert is blue, sometimes even red, while in 2.0 it is black or gray. These two standards have no other external differences.

Price
The average cost for a flash memory equipped with a USB 2.0 connector is about $ 10 for a volume of 8 GB, and $ 5 for 4 GB... This price is, in principle, not very expensive and suits most of the buyers. However, the increase in speed is worth the price and not very little.
The price of a flash drive with a 3.0 connector is an order of magnitude more expensive than 2.0. Average cost is $ 40 and more... This is where the question should arise, are you ready to “shell out” such an amount from your pocket for speed gains. If the purpose of the purchase is a cheap tool for transferring small-volume files, then the choice should still be made in favor of 2.0, but if speed is a fundamental factor in using a "flash drive" then you cannot do without the capabilities of 3.0.

How to choose the right one
Of course, the characteristics of the 3.0 connector allow you to get significant increase in speed, but before choosing it for purchase, you must carefully read the accompanying device technical description... In some cases, it happens that the device is equipped with a 3.0 connector, but the central processor (controller microcircuit) is not at all designed to work at such high speeds. So the connector seems to be blue, but there is no significant increase in speed.
In addition, the 3.0 connector can achieve the fastest data transfer rate when using the same generation of USB connector on the other end of the cable. If, on the one hand, a device with a 3.0 connector works, and on the other 2.0, then the speed will be limited by the capabilities of the second generation connector.
If you plan to connect to the 3.0 connector, for example, devices such as computer keyboard or "mouse", then you will not feel any differences from 2.0.
Output
The new third generation offers a ton of new technical capabilities, however, today it is necessary to pay for them and pay not so little. Of course, over time and as it spreads, the cost of a new generation of connectors will decrease and all devices will be equipped with only this type of connectors.
Before purchasing devices equipped with 3.0 connectors, you need to weigh the pros and cons. Whether you need an increase in speed or will it be enough for the capabilities that the USB 2.0 connector provides.
Updated: 31.05.2019 15:46:48
Expert: David Hoffman
Technological progress in relation to computers is especially pronounced. New technologies, interfaces, systems, chips and other architectures are presented almost every year. This also affects familiar things like USB.
So, for example, starting from 2017-2018, the interface began to be actively implemented USB Type-C. It has a symmetrical, oval connector and is generally not compatible with traditional rectangular Type-A connectors.
But if Type-C differs from Type-A, the differences between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 are not so obvious. Let's figure out what they are and whether it is worth overpaying for a computer or a USB flash drive with a new interface.
USB 2.0 is a relatively old standard. The technology was introduced in early 2000 and at that time offered such a high data transfer rate that it was subtitled High-Speed.
In particular, the maximum data transfer rate regulated by this protocol is 480 megabits (60 megabytes) per second. It is achieved on devices with Hi-Speed support. These are various flash drives, cameras, cameras and so on.
However, the speed parameter is theoretical. In practice, the average data transfer rate is around 20 megabytes per second.
When developing the 2.0 standard, the creators sought to ensure maximum compatibility with legacy interfaces. So, this is still a four-pin connector (5-pin on grounded devices), which carries a current with a voltage of 5 volts and a power of 0.5 amperes on computers. However, the redesign of the bus controller allowed for higher data transfer rates.
In general, at the moment the 2.0 standard is still a universal interface, which will even be supported for at least several years. Low price on controllers, a huge amount compatible devices and a sophisticated interaction mechanism make it suitable for use in home and office environments.
Dignity
A huge number of compatible devices;
Support by the old operating systems;
Low load on power supply or battery.
disadvantages
- Slow.
More precisely, it is relatively slow. Generation 3.0 certainly outperforms it in bandwidth, but the actual transfer rate depends on the performance of the drive, the type of files, file system and many third-party options.

The USB 3.0 interface was introduced in 2008 and, interestingly, was not an improvement on the previous generation, but a complete redesign. The changes even affected the design of the connector!
So, in the Superspeed revisions, nine contacts are used: 2 main signal, 2 main current, 2 additional signal, 2 additional current and - optionally - "ground". However, the main ones are located in the same places as in the 2.0 standard, due to which compatibility with previous generations is achieved.
We also increased the current supplied to the connector - now it is 0.9 Ampere. Thanks to this, it was possible to achieve three indicators:
More devices can be connected to one connector on the motherboard using the "tree-like" method (that is, a keyboard with an external USB connector into the "motherboard", a card reader into the keyboard, and a USB flash drive into it, for example);
Some devices no longer require external power supply for work, he takes all the necessary current from the interface;
Mobile devices connected to the computer charge faster.
But the main advantage of the revision is the increased data transfer speed. In the 3.0 standard, it is up to 5 gigabits (0.6 gigabytes) per second. Of course, this is a theoretical indicator, in practice it is limited by the capabilities of the receiving device.
Generation 3.0 interface paved the way for new possibilities for connected devices. So, in its subsequent revisions you can find:
Compatible with DisplayPort for connecting screens;
Thunderbolt support for the highest possible data transfer rate (this is necessary, for example, for the operation of external video cards);
Support for two-way current transfer (that is, the master is selected, which charges the slave - for example, you can charge a laptop from a smartphone).
The development is not limited to this. In the future, other ways to use the connectors with maximum benefit will be found.
Dignity
Increased data transfer rate;
Increased current for powering connected devices;
Possibility of equipping the connector with additional functions;
Fully backward compatible with legacy USB interfaces.
disadvantages
High cost;
Increased discharge of the laptop battery.
The high cost of the USB 3.0 standard is especially evident in the pricing policy of flash drives and similar external media. So, a device equipped with 2.0, with a capacity of 8 GB, can now be purchased for 3-5 dollars. But for a flash drive of the same volume, but already from 3.0, you will have to pay 10-15 dollars.
Versions 3.1 and 3.2
Further development of the interface led to the fact that the developers faced with hardware limitations. It was not possible to equip the connector with a bunch of connectors and at the same time ensure compatibility with outdated iterations. Then it was decided to rework it.
This is how Type-C was born. This type of interface is equipped with 24 pins, thanks to which many additional features have been achieved. Firstly, it is symmetrical, so you no longer need to twist the flash drive before installing. Secondly, it fully supports Power Delivery and can carry up to 20 Volts of current. And finally, the maximum current in it is 5 Amperes!
True, in the framework of 3.0 these additional features didn't fit. This is how two revisions appeared - 3.1 and 3.2. They managed to use additional data transmission channels, due to which the maximum throughput was 10 gigabits (1.2 gigabytes) per second!
But it is worth noting that there are no devices that support such high speeds yet. Usually there is a limit on the speed of the drive or clock frequency controller.
Comparison
So, USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 differ structurally and technologically. Now is the time to compare them and choose which is best!
|
Parameter |
||
|
Limiting data transfer rate |
60 megabytes per second |
600 megabytes per second |
|
Connector current |
||
|
Compatible with older operating systems |
Windows XP and newer |
Windows 8 and newer. Windows 7 up to SP1 requires drivers to be installed |
|
Legacy compatibility |
Back |
Back |
|
Power-over-USB, USB Power Delivery, Thunderbolt, DisplayPort |
||
|
Comparatively low |
Relatively high |
USB 3.0 is mainly used for data and power transmission. It is necessary for fast work connected flash drives, smartphones and other drives. Also, in some cases, external devices such as video cards, sound adapters, and so on are connected via it.
USB 2.0 is used in devices that do not require highest speed... Even now, in 2019, it can be found in the latest keyboards, mice, printers and scanners. Low price, good compatibility and bandwidth sufficient for most tasks will keep it relevant for a long time.
To the question of how USB 2.0 differs from USB 3.0, we will immediately answer - speed. Moreover, the maximum. But still, I think it will be more interesting for you to learn about all the intricacies of a fairly new standard for data exchange between drives.
Aside from speed, what is the difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0?
USB is a very useful tool. Chances are, even if you don’t know what it is exactly or how it works, you’ve probably heard about it; and even if you didn't, you probably still used it without realizing it.
The main purpose of USB, which stands for Universal Serial Bus (USB), is communication. Basically, it is used to transfer information, data and connections between devices. In the 90s, when computer technology really began to take part in its development and began to grow, the number of devices that were launched and used needed a new format for fast and stable data transfer between gadgets.
Compatibility and best versatility
These devices used various, differential forms of wires and ports to connect to a computer. USB has become universal method of connecting and connecting devices to a computer. Even now, imagine various devices connected to your computer. This list primarily includes mouse and keyboard, but may also include camera, printer, eternal HDD etc. If they are connected then they are using USB. USB is also used to charge your phone, and to copy and transfer data from your phone, external hard disk etc.
USB is one of the most commonly used communication protocols today. It was originally released in January 1996 and was developed by a consortium of Compaq, DEC, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, NEC, and Nortel. The idea was to develop a universal communication protocol to replace the various connectors used by different companies; and they succeeded. USB 2.0, improved version with more fast speed was released in April 2000 and then USB 3.0 was installed in November 2008.
What is the speed of USB 3.0 and 2.0
Besides that USB 2.0 is more old version 3.0 , the main differences between them are speed. USB provides a maximum speed of 480Mbps, while USB 3.0 provides data transfer speeds of up to 4.8Gbps. This difference is almost 11 times. However, in reality, the speed of each will differ from the types of devices used. USB 2.0 and 3.0 are also backward compatible, which means you can plug a USB 2.0 wire into a USB 3.0 port, or vice versa. However, this will also affect the data transfer rate.
Increase in speed data transfer is due to the fact that USB 3.0 has more wires; this allows it to carry more data, hence effectively reducing the time it takes to transfer all of the data. USB 2.0 has 4 internal wires in its cable, while USB 3.0 has 9, which is more than doubled.
Two versions USB also differ in the way of data transfer. USB 2.0 uses a half-duplex method for data transfer. This means that the data stream to USB 2.0 is unidirectional, meaning you can either send data or receive data; they cannot do both. On the other hand, data streaming on USB 3.0 is bi-directional, as it uses a full duplex method to transfer data. This allows the user to send and receive data at the same time.
By the way, earlier we talked about. You can go to the link above.
How to distinguish a wire with USB 3.0 from 2.0?
 Here USB are painted white
Here USB are painted white Continuing to develop the topic of how USB 2.0 differs from USB 3.0, we will catch another difference between USB 2.0 and 3.0, namely, it is visual. The USB 2.0 port is mostly black or gray, while the USB 3.0 port is blue. This is basically done so that people can tell the difference at first glance by looking at a port that looks the same. Also, the USB 2.0 and 3.0 port itself is different. A USB 2.0 port has 4 copper pins, while a USB 3.0 port has 9 copper pins in line with its 9 wires. The pins are located on two different lines, one with 4 and the other with 5.
 USB Type C example
USB Type C example It should also be noted that both USB 2.0 and 3.0 have different ports: Type A ports, which are mainly intended for use on computers and large devices; Type B ports, which are mini and therefore for use in small devices, such as digital cameras, MP3 players, old smartphones, etc. However, most of the mini-B ports have now been replaced by micro-USB ports. This is the one we see on most smartphones.
In 2014, USB 3.1 was released as an upgrade to USB 3.0. It works the same as USB 3.0 but improves speed. However, it is not as widespread in use.
However, the latest craze is USB Type C, which seems to eventually become more popular than USB 3.0. Type C has a removable port, which means both ends are the same. However, it remains to be seen if it will achieve popularity and widespread adoption. using USB 2.0.
conclusions
We hope you understand what is the difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 and what innovations the update of this format has brought for users.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.