The presence of many sensors in modern mobile devices ah, this is a known fact, but how many of them and what these sensors are used for is a mystery. Many manufacturers indicate only the main well-known sensors in phones like accelerometer, gyroscope and proximity sensor... But the overwhelming majority of manufacturers write little at all about the sensors used and other electronics with which their device is crammed.
We decided to clarify the situation with the sensors of smartphones and tablets. The purpose of the article is to tell you what sensors are, what they serve, in which devices they can be found and how.
Sensors are called various devices reading additional information. These solutions make working with a phone, tablet or other gadget more convenient and add functionality to the device.
The presence of many sensors in modern mobile devices is a known fact, but how many of them and what these sensors are used for is a mystery. Many manufacturers list only the main well-known sensors, such as accelerometer, gyroscope and proximity sensor. But the overwhelming majority of manufacturers write little at all about the sensors used and other electronics that are stuffed with their device.
We decided to clarify the situation with the sensors of smartphones and tablets. The purpose of the article is to tell you what sensors are, what they serve, in which devices they can be found and how.
Essential sensors in smartphones and tablets
Accelerometer
(accelerometer, orientation sensor, acceleration sensor) Is the simplest sensor found in any smartphone or tablet. Serves mainly for registering the rotation of the smartphone from portrait to landscape orientation. Often, it is the accelerometer that is called the G-Sensor. In general, an accelerometer registers the difference between an object's acceleration and gravitational acceleration along three axes. The electronics then calculates the difference, draws conclusions and sends a signal to the software - when and in which direction to turn the screen. Hence the main disadvantage of the accelerometer - if there is no acceleration or it is not great, then the accelerometer stops registering the position of the device in space or does it with a large error. This negatively affects the accuracy of control of the device, for example, in games or when controlling a quadcopter. This is where the next sensor comes in.
Gyroscope
(gyroscope)- also serves to register the position of the device in space, but, unlike an accelerometer, it can register the tilt angle along three axes of even a stationary device. With the help of a gyroscope in games, accuracy is increased, since developers will have access to information about the deviation of the device in degrees with an error of only 1-2 degrees. Many believe that even inexpensive smartphones and tablets are equipped with a gyroscope. However, our experiment showed that inexpensive smartphones and tablets cannot boast of a gyroscope - only an accelerometer. Here are some smartphones and tablets where the gyroscope could not be detected:We also did not find a gyroscope in,
And here's where the notorious sensor is:
We also found a gyroscope in,. And there is no doubt that the gyroscope and a solid set of other sensors are contained in TOP solutions like, and other best modern smartphones.
Surprisingly, in the LG G4S and Asus FonePad 8 (about which we already wrote -) the gyroscope is not visible in the list of sensors, but there are a lot of auxiliary sensors:
For the sake of fairness, it should be noted that the auxiliary sensors, which we considered at the very end of the article, can neutralize the absence of a gyroscopic sensor, but, we believe, not completely.
Geomagnetic sensor
(geomagnetic field sensor, magnetometer)- a sensor that responds to magnetic fields land. It can be used to determine the cardinal points, which is why it is often called an electronic compass. In particular, the presence of such a sensor will greatly help devices without GPS module determine the location (not without the help of WiFi and towers cellular, of course). The magnetometer is one of the key sensors that, together with the accelerometer and gyroscope, enables developers to use the device at full capacity. Sometimes, to further improve accuracy, additional hardware sensors are added with similar but simplified functionality like the Geomagnetic Rotation vector sensor. Naturally, the magnetometer can be used for its intended purpose: as a metal detector, to search for wiring in the walls, as a compass - look for what you need in app stores.
Some smartphone apps using the geomagnetic sensor
Proximity sensor
(proximity sensor)- the sensor allows you to determine the object in front of you and the distance to it. It is an infrared emitter and receiver. When no radiation arrives at the receiver, there is no object, and when it does, there is an object from which the beam is reflected. This sensor makes it possible to turn off the display when you bring your ear close to the smartphone to make a call. Advanced versions of the sensor are used as a gesture sensor - a smartphone can recognize certain hand gestures and perform a given action. In some cases, a proximity sensor can be used to turn off the display when using a case (a cheap alternative to a Hall sensor).Light sensor
(light sensor, light sensor)- allows you to calculate the level of ambient light. A smartphone or tablet with a light sensor can independently increase or decrease the brightness of the screen backlight, which is very convenient, since adjusting the brightness several times a day is not the most pleasant experience. In TOP smartphones and tablets, an advanced version of the light sensor can be used - RGB sensor, which is able to capture the intensity of the primary colors (red, green and blue) for further customization pictures on the display or to adjust the balance for photographing. Such a sensor can be found in Galaxy Note 3, for example. And in the Galaxy Note 4, the functionality of the light sensor has expanded to measure not only in the visible range, nor in ultraviolet light. With this UV sensor, you can measure the level of radiation and determine the time of day suitable for tanning.
Conclusion on the main sensors
So, the presence of an accelerometer exclusively in a smartphone or tablet means that this device is of the lowest price range and can only “rotate the screen”. This is the lot of cheap smartphones and tablets. Of course, there is a possibility that the manufacturer did not give sane information about the types of sensors used - in this case, you need to start reading reviews in which the hardware filling of the device is studied in detail using System applications Info for Android, for example.
The presence of an accelerometer, a geomagnetic sensor, a proximity and light sensor in a smartphone indicates its sufficient equipment, but it is still not very good for controlling a quadcopter or games where tilt / turn control is assigned to the user's movement of the smartphone. The gyroscope solves this problem - devices with a gyroscope accurately track the slightest deviations.
The presence of all the above sensors, a large set of auxiliary sensors (discussed at the end of the article) and most of the sensors listed below testifies to the fact that you have an advanced device in front of you, the use of which will be a pleasure, and its capabilities will exceed all your expectations - this is best tablets and smartphones.
Sensors in expensive smartphones and tablets
Hall Sensor
(Hall sensor)- captures a magnetic field, like a magnetometer, but has a simple principle of operation, that is, it reacts only to field amplifications, and does not register the tension along the axes. Used to use covers such as Smart Cover - allows you to turn off the screen when you approach it with a magnet built into the cover. This sensor is rarely indicated by manufacturers, so pay attention to available accessories for a smartphone or tablet - if among them there are “ smart case», Then a Hall sensor is present.
Barometer
(pressure sensor)- a sensor that measures atmospheric pressure. It can be used both for its intended purpose and as an assistant to GPS / GLONASS modules to accelerate the determination of the device's location and altitude (altimeter).
Thermometer
(ambient temperature sensor)- ambient temperature sensor. First introduced with the Galaxy S4 to improve the S-Health app, but is now used in a variety of other expensive smartphones.Humidity sensor
(hygrometer)- also first appeared on the Galaxy S4 as an extension to S-Health functionality.
Pedometer
(pedometer, step detector)- the speaking name of the sensor hints that it determines whether a person has taken a step or not. It is truly a separate sensor, allowing for more accurate steps detection and less stress on the accelerometer, which is the pedometer found in most smartphones without a dedicated sensor. To help the pedometer, a Step Counter sensor is sometimes added and, even, a pedestrian activity motion sensor - a step counter and a pedestrian activity sensor (probably estimates the pace of walking). There is such a sensor, for example, in the LG Nexus 5 and Galaxy Note 3.
The fingerprint scanner
(fingerprint sensor, Touch ID)- a sensor that reads a unique fingerprint pattern. It is strange to see a fingerprint scanner in the article about sensors - it would be better to refer it to the section of the article about securing the device. However, this sensor can rightfully be considered one of the most important sensors of a modern smartphone. With its help, you can not only secure your smartphone, but also use it to open certain applications or confirm a payment.
Retina scanner
(retina scanner)- a unique retina reader, this is the first place on the safety pedestal. Such a sensor has long been heard, but it practical implementation in smartphones or tablets, so far, has not been seen.
Heart rate sensor
(heart rate monitor, heart rate monitor)- first appeared in the Galaxy S5 to make the smartphone a full-fledged personal trainer. The S-Health app began to receive more data about a person before, during and after training and was able to provide more accurate personal recommendations.

Dosimeter
- determines the dose of ionizing radiation or its power. In other words, the radioactive background can be measured. We haven’t met a device with a built-in dosimeter, but they say that in Japan there is a Pantone 5 smartphone equipped with this sensor. We are not surprised.
Auxiliary sensors found in many smartphones and tablets
Sometimes, to further improve the accuracy, additional hardware sensors are added with similar but simplified functionality (you may have seen them in the screenshots above).
Surely there are other sensors, but the secrets of their use are still known only to the developers of operating systems and other software.
 A modern smartphone is not just calls and SMS, but much more. But today we will not talk about how to go online from these devices, not about their hyper-communication capabilities and not about the advantages of a particular mobile operating system. The article will be devoted to the sensors and sensors that developers equip modern devices to make their functionality even more diverse. So what are gauges and sensors? These are microdevices in the smartphone itself (player, tablet, navigator, laptop, digital camera, game console, etc.) that make it smart and also communicate with the outside world. Without them, the smartphone will not be so interesting and in demand, since the gadget will be without connection with the environment. It is with the help of sensors and sensors that a connection with the world around appears, which means that new amazing functions appear.
A modern smartphone is not just calls and SMS, but much more. But today we will not talk about how to go online from these devices, not about their hyper-communication capabilities and not about the advantages of a particular mobile operating system. The article will be devoted to the sensors and sensors that developers equip modern devices to make their functionality even more diverse. So what are gauges and sensors? These are microdevices in the smartphone itself (player, tablet, navigator, laptop, digital camera, game console, etc.) that make it smart and also communicate with the outside world. Without them, the smartphone will not be so interesting and in demand, since the gadget will be without connection with the environment. It is with the help of sensors and sensors that a connection with the world around appears, which means that new amazing functions appear.
Of the main sensors and sensors, known to many, and without which today one can not do except for the very budget ones mobile phones, the following can be distinguished:
1. Proximity Sensor
2. Accelerometer
3. Light Sensor
4. Gyroscope Sensor
5. Magnetic Field Sensor (a magnetic compass is usually not considered a sensor, but we still included it in the list)
Proximity Sensor
The proximity sensor allows you to determine the approach of an object without physical contact with it. For example, a proximity sensor installed on a mobile phone can turn off the backlight when the phone approaches the user's ear during a call. That is, its main task is to block the smartphone so that the user does not accidentally press, say, with his cheek to hang up. By the way, in this case the charge is also saved. battery... Naturally, manufacturers are trying in every possible way to expand the capabilities of this function. For example, a year ago in Samsung Galaxy S3 introduced the "Direct Call" function, which, when the device is held up to the face, allows you to call a contact whose information, call log or message data is displayed on the screen. Also, a phone with this sensor can be safely put in a pocket or case, without fear of accidentally making an unnecessary call.
 In general, motion control is the next stage in communication between man and technology, on which a lot of manufacturers are working today. For example, last year Pioneer introduced the lineup car multimedia and navigation GPS-systems, which can be controlled using gestures. Pioneer named its development "Air Gesture". If the user brings his hand to the front of the screen of the multimedia and navigation system, it displays a window with the name of the currently playing song and frequently used control commands: "Set as destination" and "Set favorite place as destination". As soon as the user takes their hand away from the screen, these commands disappear, and navigation map will be displayed on the full screen again. In addition, by moving the hands horizontally, certain user-defined functions can be invoked without pressing a button. You can set one of 10 functions, including “Switch between navigation and AV function” and “Skip the current song / Play the previous song”. The sensor, which detects hand movements, consists of two infrared emitting parts and one receiver between them. When the hand moves to the front of the screen, the receiving IR sensor detects reflections of infrared light. With a horizontally moving hand, the IR sensor detects the change in the timings of infrared radiation from the right and left emitting parts so that it becomes clear in which side the hand is moving. By the way, the production of models with user interface management Air gestures The Gesture has already begun.
In general, motion control is the next stage in communication between man and technology, on which a lot of manufacturers are working today. For example, last year Pioneer introduced the lineup car multimedia and navigation GPS-systems, which can be controlled using gestures. Pioneer named its development "Air Gesture". If the user brings his hand to the front of the screen of the multimedia and navigation system, it displays a window with the name of the currently playing song and frequently used control commands: "Set as destination" and "Set favorite place as destination". As soon as the user takes their hand away from the screen, these commands disappear, and navigation map will be displayed on the full screen again. In addition, by moving the hands horizontally, certain user-defined functions can be invoked without pressing a button. You can set one of 10 functions, including “Switch between navigation and AV function” and “Skip the current song / Play the previous song”. The sensor, which detects hand movements, consists of two infrared emitting parts and one receiver between them. When the hand moves to the front of the screen, the receiving IR sensor detects reflections of infrared light. With a horizontally moving hand, the IR sensor detects the change in the timings of infrared radiation from the right and left emitting parts so that it becomes clear in which side the hand is moving. By the way, the production of models with user interface management Air gestures The Gesture has already begun.
The same function is implemented in the new Samsung flagship Electronics - Galaxy S4. In addition to the proximity sensor, there is another sensor located next to the front camera, which is used for gesture recognition. It recognizes hand movements by receiving infrared rays that bounce off the user's palm and works in tandem with the Air Gesture feature, giving users the ability to answer a call, change songs, or scroll up or down a web page with just one wave of the hand.
Accelerometer
Perhaps this is the most common sensor. The G-sensor, as many manufacturers call it, can be found in almost every modern device today. The task of the accelerometer is simple - to track the acceleration that is given to the device. The question seems to be, why measure the acceleration of a smartphone? But let's think about it, the moment we turn the phone over, there is an acceleration movement. The accelerometer registers it and, based on the data received from it, starts a process, for example, changing the screen orientation. The sensor is also used to scale browser pages when the smartphone is tilted, updating the list of Bluetooth devices when shaken, in specific applications, and, of course, in games, especially in simulators. In addition, the accelerometer is used as a pocket foot pod for counting the number of steps taken by the user.

In cameras, the accelerometer is used to rotate the captured frame, and in laptops - for urgent parking of the heads. hard disk if suddenly the computer crashes. And in cars, it serves to deploy the airbags on impact. Simply put, the accelerometer deals with the position of the device in space and the tilt of the body, while relying on its acceleration when changing this position.
Light Sensor
The tasks of this sensor are extremely simple and are to determine the degree of ambient light and adjust the brightness of the screen accordingly. Thanks to this automatic brightness adjustment, it is possible to save energy, especially if you want to optimize the consumption of your battery. Perhaps this is the oldest sensor in the mobile world, and even though this sensor does not seem to have any opportunities to improve functionality, manufacturers in this case are trying to make working with a smartphone even more comfortable.
 For example, in mobile operating system iOS 6 from Apple introduced the ability to adjust auto brightness. Previously, the light sensor was fully automated and adjusted the brightness of the screen at its discretion. Now the user has the opportunity to control the operation of this sensor. You can easily determine the brightness level that is comfortable for you, and iOS takes that choice into account when calculating the brightness level for new lighting conditions. However, in order for the sensor to function correctly, it is necessary to make a small adjustment to the device.
For example, in mobile operating system iOS 6 from Apple introduced the ability to adjust auto brightness. Previously, the light sensor was fully automated and adjusted the brightness of the screen at its discretion. Now the user has the opportunity to control the operation of this sensor. You can easily determine the brightness level that is comfortable for you, and iOS takes that choice into account when calculating the brightness level for new lighting conditions. However, in order for the sensor to function correctly, it is necessary to make a small adjustment to the device.
Gyroscope Sensor
If the capabilities of the accelerometer are by and large exhausted, and the scope of its application is clearly limited, then the device of another inertial sensor, which is a gyroscope, has not yet been fully mastered in smartphones. The history of the use of gyroscopes dates back to the end of the 19th century. At that time, inertial sensors were common in the fleet, since with the help of a gyroscope it is most accurately possible to determine the location of the cardinal points. Later, thanks to such a unique function, the gyroscope became widespread in aviation. By its design, the gyroscope in mobile phones resembles classic rotary ones, which are a rapidly rotating disc mounted on movable frames. Even if the position of the frames in space is changed, the axis of rotation of the disk will not change. Thanks to constant rotation disk, for example, using an electric motor, and it is possible to constantly determine the position of an object (in which there is a gyroscope) in space, its tilts or rolls.
 Gyroscopes in modern devices are based on a microelectromechanical sensor, but the principle of operation of the inertial sensor remains the same. The same family includes accelerometers, magnetometric and other highly specialized sensors. The market for these diminutive elements, also known as MEMS, got a major boost when Apple began installing the gyroscope in the iPhone 4 and then the iPod Touch. Successful sales of mobile devices have led MEMS element manufacturers to successfully enter the mobile market. Apple iPhone 4, which pioneered the use of a gyroscope and two MEMS microphones for noise cancellation, had a huge impact on the phone industry. For example, at the end of 2010, fewer than five phones launched on the market boasted a gyroscope, and in 2011 there were already more than 50 models of phones and tablets with a gyroscope.
Gyroscopes in modern devices are based on a microelectromechanical sensor, but the principle of operation of the inertial sensor remains the same. The same family includes accelerometers, magnetometric and other highly specialized sensors. The market for these diminutive elements, also known as MEMS, got a major boost when Apple began installing the gyroscope in the iPhone 4 and then the iPod Touch. Successful sales of mobile devices have led MEMS element manufacturers to successfully enter the mobile market. Apple iPhone 4, which pioneered the use of a gyroscope and two MEMS microphones for noise cancellation, had a huge impact on the phone industry. For example, at the end of 2010, fewer than five phones launched on the market boasted a gyroscope, and in 2011 there were already more than 50 models of phones and tablets with a gyroscope.
Gyroscopes built into mobile phones make the quality of games the highest. By using of this sensor the game can be controlled not only by the normal rotation of the device, but also by the rotation speed, which provides more realistic control. In addition to games, the gyroscope is used in augmented reality browsers for more accurate positioning of the device in space, as well as in radio models of aircraft controlled using smartphones on iOS and Android platforms.
Magnetic Field Sensorcompass)
After the arrival of GPS receivers in our world, digital compasses also appeared, however, in the era of the development of navigation technologies, they are not so useful. The magnetometer, like the usual magnetic compass, tracks the orientation of the device in space relative to the earth's magnetic poles.
 The information obtained from the compass is used in mapping and navigation applications. In practice, this device has shown itself quite well and today is indispensable in a number of games and applications, for example, in the Layar augmented reality browser.
The information obtained from the compass is used in mapping and navigation applications. In practice, this device has shown itself quite well and today is indispensable in a number of games and applications, for example, in the Layar augmented reality browser.
Other sensors and sensors
Barometer
This sensor also helps with positioning. The barometer started appearing in smartphones quite recently, with the release of the Samsung Galaxy Nexus, and can reduce the time it takes to connect to a GPS signal. The built-in barometer measures the atmospheric pressure at the current location of the smartphone owner and determines the altitude. Many flagship smartphones today are equipped not only with GPS and GLONASS receivers, but also with a barometer, due to which the capture of the signal from the satellite and the determination of the initial location occurs instantly. This function is also useful in the case when the user moves along inclined planes, be it a hill or a mountain, because depending on atmospheric pressure and altitude, can calculate the exact number of calories that are burned while walking. Well, and, accordingly, to determine the pressure and weather conditions directly from your smartphone.
Let's consider the principle of operation of this sensor using an example Samsung smartphone Galaxy S III, where the determination of the pressure difference can be recalculated about 25 times per second. This speed makes it possible to clearly determine the movement of a person up and down, that is, to use navigation not only in the horizontal plane, but also in the vertical one. Thus, we get a volumetric navigation that is fully consistent with reality. For example, when navigating to mall a regular GPS navigator will not be enough for you, as it will indicate a point on the plane of the earth, and not at what altitude your route is. And car navigators can navigate in multi-storey parking lots and multi-tiered roads.
 The pressure sensor allows you to do this, and you will receive not only the exact coordinates of a given place, but also information on which floor or height your route lies. Typically, such sensors include a data processing system, and their dimensions are within 3x3x1 mm. The tiny sensor reacts to changes in height with an accuracy of 50 cm. The technique is implemented by comparing external atmospheric pressure with respect to the vacuum chamber inside the sensor. In addition to the vacuum chamber and sensors, a built-in microprocessor, an analog amplifier, a digital co-processor and a non-volatile memory element were placed in the miniature body of the device.
The pressure sensor allows you to do this, and you will receive not only the exact coordinates of a given place, but also information on which floor or height your route lies. Typically, such sensors include a data processing system, and their dimensions are within 3x3x1 mm. The tiny sensor reacts to changes in height with an accuracy of 50 cm. The technique is implemented by comparing external atmospheric pressure with respect to the vacuum chamber inside the sensor. In addition to the vacuum chamber and sensors, a built-in microprocessor, an analog amplifier, a digital co-processor and a non-volatile memory element were placed in the miniature body of the device.
Temperature / humidity sensor
This sensor is a new addition to the Samsung Galaxy S4. It detects ambient temperature and humidity levels through a small hole located at the base of the smartphone. The sensor then determines the optimal comfort level and displays this information on the S Health app screen. In addition, the temperature sensor allows you to correct pressure errors caused by changes in air temperature. Those who want to immediately take advantage of the capabilities of the temperature sensor can pay attention to the development of scientists at Robocat.
 They created a tiny Thermodo electric thermometer that connects to the phone via a headphone port. Thermodo consists of passive temperature sensors built into a standard 4-pole headphone jack in a robust housing. No network connection is required, the device is powered by the phone and consumes little power. When temperature measurement is not required, Thermodo can be hung on the keys like a key fob. With Thermodo you can measure the temperature both indoors and outdoors.
They created a tiny Thermodo electric thermometer that connects to the phone via a headphone port. Thermodo consists of passive temperature sensors built into a standard 4-pole headphone jack in a robust housing. No network connection is required, the device is powered by the phone and consumes little power. When temperature measurement is not required, Thermodo can be hung on the keys like a key fob. With Thermodo you can measure the temperature both indoors and outdoors.
3D sensor
A sensor that continuously scans the surrounding area and creates a computer virtual model with high precision. Something similar is the Kinect, but a new version Google Nexus 10 tablet received a sensor much more compact and there are already ready-made applications that can work on the tablet and demonstrate the capabilities of not only the most modern games.
 Among other things, the Capri 3D sensor, which was presented at the Google I / O 2013 conference by PrimeSense, is able to register movements and obtain metric parameters of objects. Incidentally, this development of this technology proves IBM's assumption that in the middle of this decade, communication using video conferencing applications will begin to resemble 3D holograms.
Among other things, the Capri 3D sensor, which was presented at the Google I / O 2013 conference by PrimeSense, is able to register movements and obtain metric parameters of objects. Incidentally, this development of this technology proves IBM's assumption that in the middle of this decade, communication using video conferencing applications will begin to resemble 3D holograms.
Security
Recently, Professor of Swarthmore College (Pennsylvania, USA) Adam J. Aviv demonstrated the possibility of carrying out attacks using data obtained from a smartphone accelerometer. It turned out that the data obtained by the smartphone's sensors can help attackers gain access to the device's unlock codes. They can find out the pin codes and passwords of the user. Receiving information through sensors is much easier than through applications downloaded to a smartphone, says the professor. The researchers analyzed the data obtained by the accelerometer and compiled a kind of "dictionary" of smartphone movements when entering a password, after which they developed software, which allows decrypting Pin-codes using data obtained from an accelerometer. In the course of research, scientists were able to correctly identify the Pin-code in 43% of cases, and the password in 73%. The system malfunctions when the user is in motion while using the device, as movements create additional interference, and it is very difficult to obtain accurate data from the accelerometer.
Mobile security experts also believe that the more sensors a smartphone has, the more data they can capture, which means that the problem of protecting the device becomes more acute. Researchers are now developing methods to prevent leakage of data collected by gyroscopes, accelerometers, or other sensors. So it can be assumed that with the development of technology and the expansion of the functionality of sensors, the security situation will only escalate.
Perspectives
Recently American inventor Jacob Fraden founded Fraden Corporation and patented a non-contact temperature measurement system for mobile devices. On the back of the smartphone is a small infrared sensor that can take readings of the user's body temperature in just a second. Thus, in the future, smartphones may well turn into our personal medical assistants. Fraden also intends to create instruments for measuring ultraviolet radiation and electromagnetic pollution. But employees from the Next Lab at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology claim that sensors in smartphones will soon be able to detect arrhythmias and tachycardia, which will force users to seek medical help in a timely manner.
 According to experts from IBM, smartphones will have a sense of smell by 2017. Tiny odor sensors can be built into smartphones and other mobile devices. The detected traces of chemical compounds will be transmitted to a powerful cloud application capable of analyzing everything from carbon monoxide to the flu virus. As a result, if you sneeze, your phone can tell you about your illness.
According to experts from IBM, smartphones will have a sense of smell by 2017. Tiny odor sensors can be built into smartphones and other mobile devices. The detected traces of chemical compounds will be transmitted to a powerful cloud application capable of analyzing everything from carbon monoxide to the flu virus. As a result, if you sneeze, your phone can tell you about your illness.
All the most interesting is just beginning, and today work is going on in a variety of areas. For example, it is possible that in the near future your smartphone will learn to simulate tactile sensations using a certain kind of sensors. You will be able to distinguish between fabrics, textures and weaves. And sound sensors combined with massive cloud computing systems will have superhuman hearing capabilities. Oh, what can not be assumed, especially since the mass of assumptions, calculations and even fantasies in recent years began to come true with an amazing speed.
If you remove all sensors from a smartphone, it will lose an impressive part of its functions and turn into a rather primitive device. Even such actions familiar to users as changing the screen orientation when moving the gadget to a horizontal position and automatic shutdown display during conversation, would not be performed without sensors.
In an effort to win the competition in the market, manufacturers of modern mobile technology equip their devices with a huge number of sensors - after all, this increases functionality. In this article, we will tell you about all the known sensors of smartphones - including those that are installed in the latest models.
Accelerometer- one of the main sensors of a smartphone; it is also called G-sensor... The accelerometer function is to measure the linear acceleration of a smartphone along 3 coordinate axes. The data on the movements of the device are accumulated and processed by a special controller - of course, this happens in a matter of fractions of a second. Places a tiny sensor roughly in the center of the smartphone body. Self-replacement of the accelerometer in the event of a breakdown is excluded - you have to go to the service.
Who should thank the developers for the accelerometers in smartphones? First of all, fans of racing simulators who are able to control virtual cars by simply tilting the device left and right. It is the accelerometer that allows the gadget to change the screen orientation from portrait to landscape when the user turns the device over.
For the first time an accelerometer appeared on the phone 5500 ... This sensor aroused enthusiasm among proponents of an active lifestyle, because it allowed them to use a pedometer.
The accelerometer has one significant drawback: it can fix the position only when there is acceleration- that is, when the gadget moves in space. The accelerometer is unable to determine the position of the device lying on the table. The “partner” sensor called. This sensor measures the rate of angular rotation and provides higher data accuracy than an accelerometer. For a gyroscope that has passed the calibration procedure, the error will not be more than 2 degrees.

The gyroscope is actively used in mobile games- in combination with an accelerometer. In addition, this sensor does possible cameras, creating panoramic images (the gyroscope determines how many degrees the smartphone has been turned), gesture control.
The first smartphone with a gyroscope was 4 ... Now the gyroscope is far from exotic; most modern devices are equipped with it (as well as an accelerometer).
Proximity and lighting sensors
The presence of a proximity sensor (Proximity Sensor) in a smartphone is an objective necessity. If such a sensor were absent, the user would have to endure inconvenience every time they talk on the phone. It would be easy enough to touch the reset button with your cheek - and the conversation is over, you need to call the subscriber again. The function of the proximity sensor is obvious: it locks the screen of the gadget as soon as the user brings the device to his ear... This sensor allows the owner of the smartphone not only to communicate comfortably, but also to save battery power.

The proximity sensor "hides" under the front glass of the mobile device. It consists of 2 elements: diode and detector... The diode sends out an infrared pulse (invisible to the human eye), and the detector tries to catch its reflection. If the detector succeeds, the screen "dims". The sensor is capable of registering only 2 states: “ foreign object closer than 5 cm" and " foreign object more than 5 cm».
The company has achieved amazing results in experiments with a proximity sensor. Based on this sensor, the Korean manufacturer created gesture sensor, thanks to which it became possible to control the smartphone without contact. The first gesture sensor appeared on the Samsung Galaxy S3 - in 2012 it was a real breakthrough.
The Light Sensor is not in vain considered paired with a proximity sensor - as a rule, these two sensors are located in close proximity to each other. The light sensor is the “oldest” of all the sensors used in mobile electronics. It is also the simplest one - from a design point of view, this sensor is a semiconductor that is sensitive to the flux of photons. The function of the light sensor is not as important as that of the proximity sensor: Light Sensor only adjusts the brightness of the display in accordance with the surrounding conditions.

In some Samsung models(e.g. Galaxy Note 3 and Galaxy S5) installed RGB sensors... The RGB sensor is able not only to change the brightness of the display, but also to correct the proportions of red, green, blue and white colors of the image on the screen.
The developers of the Samsung Galaxy Note 4 have gone to the point of absurdity: they have taught the sensor to measure illumination in a range invisible to humans - ultraviolet. Thanks to this curious innovation, the user can, for example, choose the optimal time for sunbathing.
Barometer and temperature sensor
A person with high sensitivity to sudden changes in atmospheric pressure simply needs to have a barometer application in their smartphone. V Google play, for example, one of these programs is called “Barometer”.

The barometer sensor is able not only to warn the user about the approach of a cyclone - anticyclone; this is not even its main function. The sensor increases the efficiency and accuracy of the gadget's GPS navigator. GPS satellites show where in the world the desired location is - but not at what height... This shortcoming of their work is eliminated by the barometer. A pressure sensor can help you find, say, a certain company's office in a multi-story business center building.
Temperature sensors, unlike barometers, are present in most smartphones - however, you cannot measure the temperature outside with their help. This is about internal thermometers, whose task is to ensure that the gadget does not overheat. One smartphone can have a lot of such sensors: the first controls the graphics accelerator, the second controls the processor cores, and so on. If overheating occurs, the internal thermometer will automatically stop charging or reduce the output amperage.
External thermometers on gadgets, too, are found, but they are still "a wonder". The first smartphone with a built-in thermometer was the Samsung Galaxy S4. The sensor turned out to be necessary to improve performance preinstalled app S Health.

Alas, external thermometers of mobile devices have a significant drawback - low accuracy. The data is distorted due to the heat emanating from the user's body and the insides of the device itself. The developers have not yet been able to solve this problem.
For the needs of the S Health application, another curious sensor was installed on the Samsung Galaxy S4 - hygrometer... This sensor measures the level of humidity, allowing the user to effectively manage the indoor climate.
What sensors allow you to monitor your health?
A person striving to lead a healthy lifestyle does not hurt to get a gadget that is equipped with the following sensors.
Pedometer (pedometer)
The pedometer function is to count the distance covered by the user based on the number of steps taken. The accelerometer is also capable of performing this function, but the accuracy of its measurements leaves much to be desired. The pedometer as a standalone sensor first appeared on the Nexus 5 smartphone.
Heart rate monitor (heart rate sensor)
The built-in heart rate monitor is one of the Samsung Galaxy S5 innovations. Samsung developers considered that it was the heart rate sensor that was lacking for the S Health program so that it could be considered a full-fledged personal trainer. Among users, the Samsung heart rate monitor has not yet become popular, because it is picky enough. To provide accurate data, the sensor needs close contact with the part of the user's body where the blood vessels are shallow - for example, the fingertip. Jogging with your finger on the sensor is not a big pleasure.
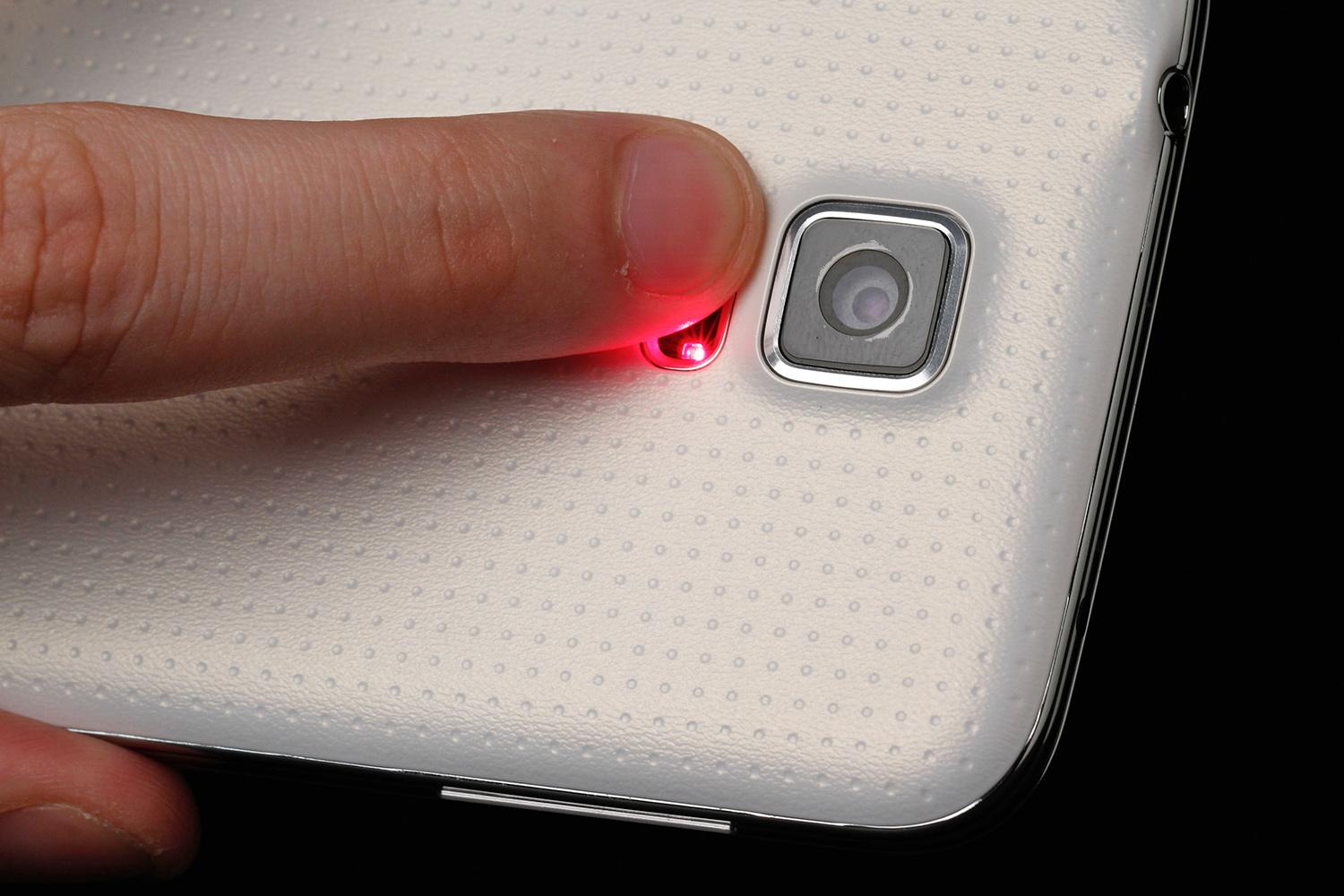

Blood oxygenation sensor (SpO2 sensor)
This sensor measures the oxygen saturation of the blood. It is present only on 2 Samsung smartphones (Galaxy Note 4 and Note Edge) and is tailored for the S Health application. On devices, the SpO2 sensor is combined with a camera flash and a heart rate monitor. The user just needs to activate the corresponding application and put his finger on the flash for 30-40 seconds - after which he will see the result of the measurement as a percentage on the screen of the gadget.
Dosimeter
The Pantone 5 smartphone released in Japan is equipped with such a sensor. The dosimeter's function is to measure radiation. For the Japanese, this function is important, because after the accident at the nuclear power plant in Fukushima in 2011, they are forced to monitor the radiation background more closely. There are no smartphones with dosimeters on the European market.
Fingerprint and retinal scanners
Users who think that the first appeared on the iPhone 5S are greatly mistaken. Phones that can scan fingerprints have been around before. Back in 2004, the Pantech GI 100 was sold, equipped with similar technology. 7 years later, it introduced the Atrix 4g model with a fingerprint sensor. In both cases, users were pretty cool about the technology.
When, in 2013, Apple built the iPhone 5S Home button, the Apple company was applauded by both experts and ordinary consumers. Apple was more fortunate with the era: in the "zero" the issue of the security of cashless payments was not so acute.
The fingerprint scanner relieves the user of the need to use digital passwords to protect the data stored on the gadget. Passwords are easy to crack; it is more difficult to deceive a fingerprint sensor at times (although it is also possible).
Now it has become fashionable to install fingerprint scanners in smartphones. This technology is used not only by long-term market leaders - Samsung, Apple,. However, this technology became discussed only after Samsung turned to it - the Galaxy Note 7 was installed iris scanner.
The Note's sensor is different from those found in smartphones from Chinese companies. Samsung's idea can be called revolutionary because the Note 7 has a camera that is responsible just for an eye scan... The "Chinese" also read information from the retina with a selfie camera.
The method used by Chinese gadgets is ineffective. The fact is that the eye must be scanned with an infrared (IR) beam, but on front cameras The IR spectrum, as a rule, is filtered - after all, because of it, they deteriorate. It turns out that Samsung is so far the only smartphone manufacturer that does not force users to choose between high-quality "selfies" and the security of personal data.
Conclusion
Any modern smartphone equipped with at least 5 sensors. In flagship models, the number of sensors reaches the "damn dozen", and manufacturers are not going to stop there. IBM experts predict that already in 2017 gadgets will receive a sense of smell, thanks to which they will be able to warn the user, for example, of a high concentration of foul gas and the presence of a flu virus in the air. We look forward to innovations - isn't it to be continued?
The accelerometer measures acceleration and allows the smartphone to determine the characteristics of movement and position in space. It is this sensor that works when the vertical orientation changes to horizontal when the device is rotated. He is also responsible for counting steps and measuring the speed of movement in all kinds of map applications. The accelerometer provides information on which direction the smartphone is turned, which becomes an important function in various applications with.
This sensor itself consists of small sensors: microscopic crystalline structures, under the influence of acceleration forces turning into a stressed state. The voltage is transmitted to the accelerometer, which interprets it into data about the speed and direction of travel.
Gyroscope
This sensor helps the accelerometer to navigate in space. For example, it allows you to do it on a smartphone. In racing games, where control occurs by moving the device, it is just the gyroscope that works. It is sensitive to the rotation of the device about its axis.
Smartphones use microelectromechanical systems, and the first such devices that keep the axis when cornering appeared at the beginning of the 19th century.
Magnetometer
The last in the trio of sensors for orientation in space is a magnetometer. It measures magnetic fields and, accordingly, can determine where north is. The compass function in various map applications and individual compass programs work with the magnetometer.
There are similar sensors in metal detectors, so you can find special applications turning a smartphone into such a device.
The magnetometer works in tandem with an accelerometer and GPS for geolocation and navigation.

Gps
Where would we be without GPS (Global Positioning System) technology? The smartphone connects to multiple satellites and calculates its position based on the intersection angles. It happens that satellites are unavailable: for example, in case of large clouds or indoors.
GPS does not use data mobile network, therefore, geolocation works outside the cellular coverage area: even if the map itself cannot be loaded, the geolocation point will still be there.
At the same time, the GPS function consumes a lot of battery power, so it is better to turn it off when not needed.
Another way of geolocation, although not very accurate, is to determine the distance from cell towers. The smartphone adds other information to the GPS data, such as power mobile signal, to clarify the location.
Barometer
Many smartphones, including iPhones, have this sensor that measures atmospheric pressure. It is needed to register weather changes and determine the height above sea level.
Proximity switch
This sensor is usually located near the speaker at the top of the smartphone and consists of an infrared diode and a light sensor. It uses a beam invisible to humans to determine if the device is near the ear. This is how the smartphone “understands” that the display should be turned off while talking on the phone.
Light sensor
As the name suggests, this sensor measures the ambient light level, which automatically adjusts to a comfortable display brightness.
Sensors with each new generation of smartphones are becoming more efficient, smaller and less energy-consuming. Therefore, you should not think that, for example, the GPS function in a device that is already several years old will work as well as in a new one. And even if the information about new smartphones does not indicate the characteristics of all these sensors, rest assured that they are the ones that allow you to enjoy many of the impressive functions of modern gadgets.