It probably won't be wrong to say that the computing world is entering the era of solid state drives. Indeed, in comparison with them hard drives lose significantly in power. For example, doubling the computer's RAM can increase its performance by no more than 10%. Equipping your computer with an SSD is another matter.
Thus, a solid-state drive for a laptop purchased three years ago is able to increase its capacity by almost 3 times. This means that a laptop "upgraded" by SSD, firstly, the performance becomes almost equal to the modern model in the same price category. Secondly, the launch of all programs is faster, including the conversion of video materials.
Thus, the question of what is a solid-state drive for can be answered briefly - to increase the performance of your computer or laptop. However, SSDs have other important advantages as well.
Plus the first: sustainability. Hard drives with moving heads and rotating magnetic platters are susceptible to damage and shock, unlike solid state drives. SSD memory chips, due to the absence of moving parts in them, are not sensitive to external influences... Therefore, even after dropping your laptop from a low height, all data will be saved and will not be damaged.
Plus the second: silent operation. Solid state drives use flash memory that responds to high-speed data transfers. Plus, thanks to flash memory, SSDs are virtually silent. True, the fan of the computer's cooling system makes this plus little noticeable.
How do I install a solid state drive? Most modern PCs have a compartment where you can install an SSD, and thus use a solid state drive and a hard drive in parallel. But for the performance of the computer to really increase, it will be necessary to transfer the operating system from hard disk on an SSD.
To simplify this procedure, there are special programs, produced by manufacturing companies, as well as external containers costing from 300 rubles. Containers enable you to use your solid state drive as removable media. Transferring data to the SSD using a USB cable, the drive is removed from the external container and installed in the computer. In this case, the data on the hard disk is retained.
But what if your PC or laptop lacks an additional bay where you can install an SSD? In this case, you will have to replace the hard drive with it. To do this, you first need to transfer information system on external hard disk using an SSD with an external container, and then replace it.

How to Choose a Solid State Drive? The main benchmarks are the SSD capacity, a good combination of memory and controller, and a suitable connector. It is these factors that play a significant role in increasing computer performance after installing an SSD. Flash memory and the controller affect the transfer rate of the SSD, for example, it depends on whether the movie will be copied in 45 seconds or in 75 seconds.
When the solid state drive is connected to a laptop or PC, the data is transferred through the SATA connector. Better to choose an SSD with SATA interface 3, it provides a higher transfer speed, however, SATA 2, although it has half the performance, it still significantly outperforms the hard drive in speed. The speed of operation is also influenced by the capacity of the solid-state drive. The performance of computers equipped with SSDs with a capacity of 500 GB is much higher than those with a drive of 250 GB and even more than 120 GB.
Of course, the capacity of an SSD directly affects its price: the more capacity, the more expensive the drive is. However, the ability to remain fully operational for many years will pay off the investment in the long term. So, having dealt with the question of why you need a solid-state drive (SSD), it remains to mention the fastest models of various capacities.


To do this, we will use the results of independent testing. Computer Bild magazine compared SSDs in terms of data transfer rate, power consumption, heat dissipation, and performance. As a result, the Samsung SSD 840 Pro took the top spot among 120GB models, while the OCZ Vector SSDs showed the highest performance among the 250GB and 500GB SSDs.
What should you not expect from solid state drives? Firstly, low power consumption, secondly, increasing autonomous work... Both of these metrics remain unchanged when replacing a hard drive with a solid state drive. Nevertheless, it is already clear now that the future belongs to SSDs, and we hope our review will help you make a good choice.
Advantages and disadvantages of solid-state drives over HDD ... What are they ?! Solid-state drives, or SSDs, having appeared on the market relatively recently, despite their high cost, have managed to gain popularity among users who are interested in speed.
A solid state drive is a storage device based on memory chips. The SSD also includes a control controller. The memory on the basis of which solid-state drives work is divided into two types: flash and RAM.
Most often, SSDs are used in small devices(communicators, laptops, smartphones), where a significant requirement is the resistance of the drive to shock and vibration, as well as its small size. The use of solid state drives in a PC can significantly increase performance.
The popularity of SSDs is growing very quickly: their cost, although at the moment it is noticeably higher than HDD, is gradually decreasing; some companies, such as the one that sold the hard drive business to Samsung to Seagate, have already abandoned HDD production altogether, switching to the development and creation of solid drives.
The history of the emergence and further development of SSD
Despite the fact that solid-state drives have become widespread only recently, the first prototype of such a storage medium was created back in 1978. The first semiconductor storage device based on RAM memory was developed by StorageTek (USA). Four years later, another American company, Cray, began using RAM-based SSDs in its Cray-1 and Cray X-MP supercomputers.

The first semiconductor flash drive was developed in 1995 by M-Systems (Israel).
Since 2005, laptops and netbooks, which included an SSD, have increasingly appeared on the market. The first company to launch a device with a 4GB solid state drive was ASUS. Gradually, the speed and volume of devices increased. In 2008, the developers of Mtron Storage Technology (South Korea) presented at an exhibition in Seoul a 128-gigabyte solid-state disk with write and read parameters of 240 MB / s and 260 MB / s, respectively. In 2009, OCZ developed a 1 terabyte SSD.
SSD advantages
The advantages of solid state drives are obvious. The absence of moving parts has led to their high mechanical resistance, fast reading of files, regardless of the location of their fragments, as well as absolutely silent operation. The read and write speed is many times faster than the bandwidth of the best HDD interfaces, including SATA II, SATA III and others.
The absence of magnetic disks made it possible to significantly reduce the size of the SSD, as well as to reduce the effect on it of external electromagnetic fields, which can easily harm hard drives and the information stored on them.
Also SSD is characterized by a wider temperature range and lower power consumption.
Disadvantages of modern SSDs
The key disadvantage of solid-state drives, due to which not many can afford to install them in a PC, is their high cost, which is directly proportional to their capacity. The price of the more common HDDs today depends solely on the platters included in their composition and increases much more slowly as their volume increases.
The main disadvantage of NAND SSDs (drives based on the use of non-volatile memory) is, first of all, the limited number of rewriting cycles: ten thousand for ordinary flash memory (MLC, Multi-level cell) and one hundred thousand for a more expensive type (SLC, Single-level cell). In order to prevent uneven wear, special circuits are built into the SSD: the controller saves information about which blocks are the least rewritable and, if necessary, begins to use them more actively. The number of cycles for RAM SSD and the latest technology FRAM is almost limitless, enough for 40 years of continuous use.
Impossibility of information recovery
Solid-state drives do not allow information recovery due to the use of the TRIM command, so all recovery utilities become useless. In addition, information on the SSD becomes irretrievably lost if overvoltage or overvoltage occurs. If only the controller board burns in hard drives most often, the solid state drive burns out completely. A hardware failure of an SSD due to the failure of a controller chip or flash memory will lead to the fact that information will be lost beyond recovery.
SSD and Windows operating system selection
The acceleration of SSD wear is also affected by the use of outdated and even a number of up-to-date operating systems that do not take into account their specificity. A decrease in the life of solid-state drives due to the operation of some OS services is due to the fact that they are designed only to work with HDD,

Therefore, they use technologies on SSD that speed up work. hard drives, but do not have any positive effect on the speed of solid-state drives, but on the contrary, reduce their lifespan.

In the OS family Windows optimization work with SSD was introduced only starting with the seventh version. On hard drives, Windows 7 does not use defragmentation or the Superfetch and ReadyBoost technologies needed to speed up reads and writes to hard drives. Previous Windows versions, including the relatively recent Vista OS, require additional tweaks to reduce SSD wear. First of all, you need to disable defragmentation, which still has no effect on the performance of solid-state drives.
Configuring Windows 7 for an SSD
In order to prevent the rapid wear of the SSD, you should disable some services and operations in the system.

First of all, you should disable the use of a paging file in the system, which is designed to store temporary data, which is necessary when there is a lack of RAM. However, writing and rewriting to an SSD so often will cause memory cells to wear out quickly. Therefore, if your memory is more than 4 GB, the best solution is to disable the paging file. If you have less than 4GB of memory, the easiest way is to move the paging file to your hard drive or add more RAM.

Indexing and caching an SSD is completely unnecessary because the SSD is already very fast.


Due to the fact that direct access of the SSD to files is very fast, defragmentation is unnecessary, moreover, it only harms the cells of the SSD.

More components operating system that became unnecessary after installing it on an SSD are Prefetch and SuperPrefetch, which are designed to speed up the startup and launch of programs.

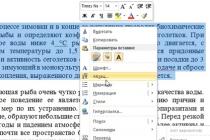
To disable these services, open windows registry and change the EnablePrefetcher and EnableSuperfetch values to zero.
SSD and alternative operating systems
TRIM support for solid state memory was introduced in Mac OS X in version 10.7 (Lion). In 2010 year Apple launched Air computers that were bundled with solid-state memory. Initially, at the request of the buyer, the SSD could be replaced with a regular hard drive, however, starting in 2010, the company completely abandoned the use of HDDs in this line to reduce the size of the computer case, as well as reduce its weight. The Air range ranges from 64GB to 512GB.

In 2012, a new flash-based MacBook Pro went on sale. Optionally, up to 768 GB of flash memory can be installed in the computer.
TRIM support for SSDs in operating rooms Linux systems appeared starting with the kernel version 2.6.33. In the drive mount settings, specify the "discard" option.
SSD vs HDD: which to choose?
Nowadays, solid state drives are increasingly gaining market share from hard drives. And although it is too early to talk about the onset of the period of the final transition to SSD and HDD withdrawal from the sale, it becomes clear that at some point this will become inevitable. Those who have installed a solid state drive as system disk, have already seen the difference in performance, which is noticeable even without using special tests.

Flash drives are characterized by fast access times, high data transfer rates and improved performance, which makes it possible to work with the operating system and installed applications much faster. In addition, SSD is characterized by absolutely silent operation, reliability and low power consumption.
At the moment, there are many solid state drives from various manufacturers on the component market, so choosing the best option among them is not so easy. However, the speed of any SSD model, even the slowest and cheapest, is many times faster than that of a hard drive.
Let's compare each of technical parameters solid state drives and hard drives separately.
Performance
Nearly every SSD is two to three times faster than a traditional hard drive in terms of communication speed. Launching programs and the operating system, exiting hibernation or standby mode, installing applications, working with files (copying, archiving, unzipping) is much faster on solid-state drives.
To determine the higher performance of an SSD, you do not even need to take any measurements, since it is easy to notice even "by eye". Launch software becomes much faster, the operating system also runs smoothly. Especially noticeable is the speed of going into and out of standby or hibernation mode.
SSDs are a great choice for users looking for speed.
Comparison of HDD and SDD performance
When you benchmark one of the current best 3TB 7200 RPM Seagate Barracuda XT HDDs and the previous generation Samsung 470 Series SSD for comparison, it becomes clear how noticeably the difference in performance between hard drives and SSDs is.
Futuremark PCMark 7 mimics typical computer operation and demonstrates that in virtually all applications, an SSD performs a task three to four times faster than a hard drive. At the same time, this test takes into account the performance of the system, taking into account the influence of the CPU and the video card, which allows you to see a picture that is almost the same as that created during normal use.





The only exceptions where HDD and SDD scores are nearly equal are working with video in Windows Movie Maker and loading Windows Media Center.


The most striking example, when a user can see and appreciate the speed of a storage medium, is the transfer and copying of data. On older computers, this time can take such a long period that the user is forced to sit in front of the screen and wait for the file operations to be completed.
Comparing three media, SSD, 7200 rpm HDD and 5400 rpm HDD, shows how much faster SSDs are. In this testing, files were copied and transferred from one logical drive on the other, which led to the fact that the medium read and write data at the same time.

As you can see, the speed of an SSD when working with files and archives is several times higher than the capabilities of a hard drive.
This test allows you to determine how noticeable the performance of the SSD will be when solving the daily tasks that the user constantly faces. Two types of programs were selected for testing: 1) those that are most often used by users, 2) large packages, the installation of which is usually very time-consuming.

Testing has shown that the installation speed of applications on an SSD is two or three times faster than an HDD. The only exceptions are Acronis and Office 2007.

The advantage of SSDs remains even when launching applications, although in this case the time period is so short that it is unlikely to be very noticeable to the user.
File size and storage capacity
If you need a storage medium for storing large amounts of information, such as videos or films, then it would be much better to opt for a hard disk. Buying an SSD to store files on it is an unnecessary luxury, since the cost of solid-state drives is noticeably higher and, moreover, directly depends on its volume. Even the smallest 128GB model is very expensive, while a 500GB hard drive can be purchased at a very low price.
However, if you plan to use an SSD as a system one, then the currently minimum volume of 128 GB will be enough for you. This volume is quite enough to create a working system where Windows 7 will be installed, required programs and even a few games. And for storing multimedia files and archives, you can install an additional HDD. If you are going to install an SSD in your laptop, you can purchase an external hard drive to store your files.
Durability and resistance to shock and vibration
An important parameter of an SSD, which distinguishes it favorably from hard drives, is its reliability in use, which is ensured by the fact that the solid-state drive is absolutely insensitive to shock and vibration. This is especially true for laptops that you often have to carry with you. Such devices are often subjected to shocks, and sometimes only the built-in accelerometer, which turns off the HDD when it falls, saves it from data loss or breakdown.
Using SDD allows you to forget that you have to try not to shake your laptop. For example, when the device just begins to go into sleep mode (and at this time it is very actively writing data to the media), you can already put it in your bag. If you do this with a laptop with a built-in HDD, then the hard disk will be easily damaged.
Durability of SSD and HDD
At the same time, SDDs still outperform hard drives in terms of their durability. Inexpensive first-generation SSDs installed, for example, on EEE PCs, have already begun to fail gradually. And if it is almost impossible to predict the mechanical wear of the HDD, then solid-state drives have a limited number of rewriting cycles, which is currently its main drawback.
It is assumed that the development of technology will lead to the fact that non-volatile memory will be made of other materials, such as, for example, FeRam, but so far there are no such drives on sale. In 2014, HP plans to begin selling drives based on ReRAM technology.
Physical dimensions of both media
For some users, a significant advantage of SSDs is their light weight and size. Solid-state media are noticeably smaller than hard drives, which, firstly, makes it possible to significantly reduce the size of the device (this is especially true for laptops and netbooks), and secondly, it allows you to place more drives in a PC case rack.
SDD vs HDD cost in comparison
Price is the parameter by which SSDs are hopelessly inferior to hard drives. Modern solid state drives cost three to four times the price of an HDD that has three times the capacity.
Whether it is worth spending money on performance and speed is up to you. In our opinion, this makes sense only if your work with a PC or laptop is constantly and active. In this case, you will save not only time, but also nerves, getting rid of the annoyance associated with the fact that the system and applications are very slow.
Where should you opt for?
Although SSD technologies are developing very actively, it is too early to talk about the time when they will completely replace hard drives. SSDs are unmatched for better performance and speed when used as system drives, but they are noticeably inferior to HDDs when it comes to file storage.
For most of the tasks faced by home PC users, a complete set with two media is perfect: an SSD, where the operating system should be placed, as well as executable files and program caches, and a large HDD for storing movies, music, photos and documents.
The budget version of the configuration can do just fine without the use of solid-state drives, while computers that work exclusively with SSDs, due to their unreasonably high cost, are extremely rare.
Solid state drives (SSD) - advantages and disadvantages
First, let's understand the definitions. Hard and solid - what's the difference?
What is HDD , which is also very often called HDD, hard drive, hard, screw, etc.?
HDD (English hard disk drive) is a data storage device based on the principle of magnetic recording. Information is recorded on plates covered with a layer of ferromagnet. The discs are mounted on a spindle that rotates with a very high speed(up to 15,000 rpm). In addition to the mechanical part, there is also an electronics unit, in fact, which controls the entire mechanics of the device.
 The first serial hard drive was manufactured by IBM in 1956, weighed 971 kg, had a total memory capacity of about 3.5 megabytes. History developed rapidly, and by 2011 1 terabyte became the norm for a hard drive. At the moment, there are two and even three terabyte drives.
The first serial hard drive was manufactured by IBM in 1956, weighed 971 kg, had a total memory capacity of about 3.5 megabytes. History developed rapidly, and by 2011 1 terabyte became the norm for a hard drive. At the moment, there are two and even three terabyte drives.
The principle of operation of a hard disk is based on the registration of changes magnetic field near the disc head.
The main players in the hard drive market are Fujitsu, Seagate, Western Digital, Samsung, Hitachi.
The larger the volume of hard drives became, the larger the volume of transmitted information became. In the general mechanical structure of the hard drive lies its main drawback - a relatively low amount of transmitted data per second (average models of manufacturers at the moment have an established data transfer rate of about 100-150 Mb / s). In addition, the higher the data transfer rate, the hotter the hard drive gets.
For many tasks, as well as for everyday use of a computer, these speeds are quite enough, however, with specialized use (graphics stations, professional gaming computers, data centers, etc.), it is the hard disk that imposes significant restrictions on the overall performance of the system.
The first developments on the invention of a fundamentally new carrier began in the 1970s. In 1978, StorageTek introduced the first semiconductor storage device modern type thus laying the foundation for the development of solid state drives. And only in 2008, the South Korean company managed to create the first 128 GB SSD, similar to modern counterparts, which it demonstrated at an exhibition in Seoul.

Mass production was only organized in 2009. At the moment, there are 720 GB drives, the cost of which starts from 60,000 rubles, for example, the IBIS OCZ 3HSD1IBS1-720G model from the OCZ company.
So what is an SSD
Translated from English, solid-state drive means "a disk without moving parts." A solid-state drive is a storage device based on rewritable microcircuits and a controller. Often users confuse terminology and call an SSD a hard drive. This is wrong in view of technical features solid state drives. Distinctive feature of the carrier of this type from the HDD is that when reading data from an SSD, there is no need to perform mechanical operations, all the time it takes only to transfer the address and directly the block itself. Accordingly, the faster the device and controller memory itself, the faster general access to the data.

However, the process of changing or erasing data from SSDs is not so simple. This is due to the fact that memory is written in 4 KB blocks and erased in 512 KB blocks.
When modifying blocks, the following sequence of actions occurs:
1. The block containing the changes is read into the internal buffer.
2. The necessary modification of the bytes is made.
3. The block is erased from flash memory.
4. The new location of the given block is calculated.
5. The block is written to a new location.
During the deletion of files, they are not physically deleted, but only marked by the system as deleted, however, the SSD does not know which data is user and which is deleted, and in fact, all blocks have to be processed according to the above scheme. This system leads to the fact that with a large amount of data on the disk, the total operating time increases significantly, which slows down all work.
SSD security and reliability
If we talk about the possibility of data recovery from SSD, then the following points can be noted:
- The data is not deleted immediately, as in the HDD, even if you overwrite the file at the top with other data.
- The data recovery process is quite time consuming, due to the fact that it is necessary to choose the correct order, combine the results, and also select the necessary algorithm that emulates the operation of the media controller.
The reliability of an SSD directly depends on the reliability of the controller and its firmware, since it is the controller that is located between the interface and the memory chips and the likelihood of its damage in case of power failure is very high.
Rules for working with solid media to extend their life cycle and increase overall speed:
- All data that changes frequently (various temporary data, swop files, etc.) can be transferred to a regular HDD.
- Disable disk defragmentation.
- Update the controller firmware periodically.
- Leaving about 20% of the disk partition permanently free will improve overall performance.
Advantages of SSDs over hard drives:
- Very high read speed of data blocks, which is actually limited only by the bandwidth of the controller interface.
- Low power consumption.
- Silence.
- Lack of mechanical parts, which leads to fewer possible breakdowns.
- Small overall dimensions.
- High temperature resistance.
Disadvantages of SSD:
- A limited number of cycles of rewriting memory cells (from 10,000 to 100,000 times). When the limit is reached, your drive will simply stop working.
- High price. Compared to the price of HDD for 1 GB (about 1.6 rubles / GB for HDD volume 1 TB versus RUB 48 / GB for a 128 GB SSD).
- Low disk space compared to HDD.
- The problem of compatibility with some versions of operating systems (some operating systems simply do not take into account the specifics of solid-state media, which leads to very rapid wear of the media).
SSD companies and manufacturers you can safely trust:
Examples of models:

The average cost is 15,000 rubles.
An excellent member of the solid-state family, with a read speed of up to 355 MB / s and a write speed of up to 215 MB / s, it connects via a SATA 6 Gb / s interface.
 128Gb Kingston SV100S2 / 128G SATA 2.5 "V100-Series
128Gb Kingston SV100S2 / 128G SATA 2.5 "V100-Series
Average price - 6000 rubles.
A good SSD with a SATA-2 connection interface. By technical specifications from the manufacturer - write speed up to 230 MB / s, read speed up to 250 MB / s.
 SSD Corsair CSSD-V64GB2-BRKT
SSD Corsair CSSD-V64GB2-BRKT
Cheaper drive, smaller in size, with a SATA connection interface.
Average cost - 3700 rubles. It has a write speed of up to 130 MB / s and a read speed of up to 215 MB / s.
conclusions
At this stage of technology development, when solid-state media are almost 30 times more expensive than hard drives at the price of 1 gigabyte, the expediency of using an SSD in the everyday life of an ordinary user is controversial, but if you want to speed up the boot time of the operating system and brag about it to your friends, then SSD is definitely For you. It is justified to use SSD in mobile devices, servers with a high load on the disk system, as well as in cases where professional applications that require high speed data access are used.
I recommend purchasing an SSD drive with an optimal speed / reliability ratio of MLC or 3D NAND memory. Read / write speed closer to 500/500 MB / s is considered high enough. The minimum recommended speed for more budget SSDs is 450/300 MB / s.
The best brands are: Intel, Samsung, Crucial and SanDisk. As a more budgetary option, you can consider: Plextor, Corsair and A-DATA. Problematic models are more common among other manufacturers.
For a work or multimedia computer (video, simple games), an SSD with a capacity of 120-128 GB will be enough, and here A-Data Ultimate SU900 on MLC memory will be an excellent choice.
SSD A-Data Ultimate SU900 128GB
For gaming computer the middle class needs a volume of at least 240-256 GB, an SSD from the A-Data Ultimate SU900 or Samsung 860 EVO series will also do.
SSD A-Data Ultimate SU900 256GB
For a professional or powerful gaming computer, it is better to take a 480-512 GB SSD, for example, the Samsung SSD 860 EVO.
SSD Samsung MZ-76E500BW
For computers and laptops with an M.2 connector, a super-fast SSD (1500-3000 MB / s) in the appropriate format would be a good option.
SSD Samsung MZ-V7E500BW
When choosing a volume, you are guided by your needs, but you should not neglect them for the sake of higher speed. If you doubt the correctness of your choice, we recommend reading reviews of specific models.
2. What is the difference between expensive and cheap SSD
Inexperienced users may be puzzled why SSD drives of the same volume, with the same declared speed characteristics, differ so much in price, sometimes several times.
The fact is that in different SSD disks, different types of memory can be used, which, in addition to speed indicators, also affects reliability and durability. In addition, memory chips different manufacturers also differ in quality. Naturally, the cheapest memory chips are installed in cheap SSDs.
In addition to memory chips, an SSD disk has a so-called controller. This is a microcircuit that controls the processes of reading / writing data to memory chips. Controllers are also produced by different companies and they can be both budgetary with lower speed and reliability, and better quality. Cheap SSDs, as you know, also have the worst controllers.
Many modern SSDs use fast DDR3 memory as a clipboard to further improve performance, just like a computer's RAM. Most budget SSDs may not have a clipboard, making them marginally cheaper but significantly slower.
But that's not all, it even comes down to saving on such important components of an SSD drive as capacitors, which are necessary to prevent integrity violations and data loss. In the event of a sudden power outage, the electrical energy stored in the capacitors is used to complete the recording from the clipboard to the memory chips. Unfortunately, not all even high-quality SSDs are equipped with backup capacitors.
The layout itself and the quality of the desoldering printed circuit board are just as different. More expensive models have more sophisticated circuitry, quality of the element base and wiring. The engineering solutions for the lowest-cost SSDs are based on outdated circuits and leave much to be desired. Low-cost SSDs are also more rejected due to assembly in cheaper factories and lower levels of production control.
And of course the price depends on the brand, the more famous it is, the more expensive the SSD. Hence, there is an opinion that you should not overpay for the brand. But the fact is that often it is the brand name that determines the quality of an SSD drive. Most well-known manufacturers who value their reputation will not allow themselves to produce low-quality products. However, there are exceptions here, in the form of well-known and popular brands, which, nevertheless, should not be recommended for purchase.
The main differences between SSDs, which you need to focus on, we will briefly understand in this article and you can easily choose the model that suits you.
3. VolumeSSDdisk
Volume is the most important parameter of an SSD drive.
If you only need an SSD for acceleration Windows boot, office programs and increasing the responsiveness of the system, then, in principle, a volume of 60-64 GB (gigabytes) will be enough.
If you want to speed up the work of serious professional applications (video editing, design systems, etc.), then you need a 120-128 GB SSD drive.
For a gaming computer, it is advisable to purchase an SSD with a volume of at least 240-256 GB, since modern games take up a lot of space (30-60 GB each).
In the future, focus on your needs (how much space you need for your programs, games, etc.) and financial capabilities. It is not advisable to use an SSD for data storage, for this you need a more capacious and cheaper hard disk drive (HDD) with a volume of 1-4 TB (1000-4000 GB).
4. SSD read / write speed
The main indicators of SSD drive speed are read speed, write speed and access time.
According to statistics, the number of read operations on ordinary computers of users is 20 times greater than the number of write operations. Therefore, reading speed is a much more important characteristic for us.
The read speed of most modern SSDs is in the range of 450-550 MB / s (megabytes per second). The higher this value, the better, but 450 MB / s is, in principle, quite enough, and taking an SSD with a lower read speed is impractical, since the price difference will be insignificant. But do not blindly trust the representatives of budget brands, as the speed of cheap SSDs can significantly drop as the disk space fills up. The speed of a particular SSD disk model in real conditions can be found out from tests on the Internet.
The write speed of most SSDs is in the 350-550 MB / s range. Again, the faster the better, this is understandable. But due to the fact that write operations are performed 20 times less frequently than read operations, this indicator is not so critical and the difference will not be very noticeable for most users. But the price of discs with a higher write speed will be noticeably higher. Therefore, 350 MB / s can be taken as the minimum record speed. Purchasing an SSD with an even lower write speed will not bring significant savings, so it is impractical. Please note that some manufacturers specify write speed for the entire line of SSD drives, in which there are different capacities. For example, Transcend's SSD370S line has drives ranging from 32GB to 1024GB. The write speed for the entire line is indicated at 460 Mb / s. But in fact, only 512 and 1024 GB models have this speed. The photo below shows a fragment of the Transcend SSD370S package with a capacity of 256 GB with a real write speed of 370 MB / s.

The access time determines how fast the disk finds the required file after receiving a request from a program or operating system. For conventional hard drives, this figure is in the range of 10-19 ms (milliseconds) and significantly affects the responsiveness of the system and the speed of copying small files. SSD drives, due to the absence of moving parts, have access speeds up to 100 times higher. Therefore, this parameter is usually not focused on, any SSD provides an incredibly high access speed. Nevertheless, higher quality models can have access times of the order of 0.1 ms, and the most budgetary ones can have 0.4 ms. The difference in access time by 4 times does not speak in favor of budget SSDs. With this parameter, manufacturers of budget SSDs can also be cunning and indicate the theoretical value under ideal conditions.
You can find out the real speed characteristics of SSD drives from tests on the most reputable technical portals. You can download a file with links to them at the end of the article in the "" section.
5. Types of memory and SSD resource
Modern SSD drives use several types of memory - MLС, TLC and 3D NAND (V-NAND).
MLC is the most popular type of memory for SSD drives with an optimal price / speed / durability ratio and an estimated resource of 3000-5000 rewriting cycles.
TLC is a cheaper type of memory found in budget SSDs, with a rewrite resource of about 1000 cycles.
3D NAND is a modern fast memory developed by Samsung with the highest rewriting capacity. Fits into more expensive Samsung SSD models.
There is a myth that SSD drives wear out very quickly. Therefore, you need to choose models with the maximum possible resource and use all sorts of tricks in the operating system settings to extend SSD services disk, otherwise it will quickly work out its resource and fail.
In fact, the resource of modern SSDs matters only when they are installed in servers, where the disks are worn out around the clock. In such conditions, due to the colossal number of rewriting cycles, SSDs really serve an order of magnitude less than their older brothers - mechanical hard drives. But we already know that in computers ordinary users the number of write operations that cause wear and tear is 20 times lower than read operations. Therefore, even with a relatively heavy load, the resource of any modern SSD will allow it to work for 10 or more years.
Despite the fact that the data on rapid wear is highly exaggerated, it is not worth buying an SSD based on the cheapest TLC memory, since the savings will be insignificant. Today the most the best option there will be an SSD disk with MLC memory. And the actual lifespan of an SSD disk will depend more on the quality of production and. Pay more attention to the brand and the warranty period.
6. Clipboard
The clipboard (cache) based on DDR3 memory speeds up the performance of the SSD disk, but makes it somewhat more expensive. For every 1 GB of SSD storage, there must be 1 MB of DDR3 cache. Thus, an SSD with a volume of 120-128 GB must have 128 MB DDR3, 240-256 GB - 256 MB DDR3, 500-512 GB - 512 MB DDR3, 960-1024 GB - 1024 MB DDR3.
Some models have older DDR2 memory caches, but this does not significantly affect performance.
7. Protection against de-energizing
It is desirable that a disk with DDR3 cache memory has Power Protection, which is usually based on tantalum capacitors and allows data to be saved from the buffer to memory chips in the event of a power outage of the SSD. But if you have a source uninterruptible power supply(UPS, UPS), the power failure protection is negligible.
SSDs without DDR3 cache do not require additional protection from blackout.
8. SSD controllers
There are many controllers for SSD drives. The most popular brands include Intel, Samsung, Marvell, SandForce, Phison, JMicron, Silicon Motion, Indilinx (OCZ, Toshiba).
The best SSD drives are built on Intel, Samsung, Marvell controllers. In the middle class, the more popular SandForce controllers and the younger Phison controllers are more popular. Inexpensive SSD models are often content with older budget JMicron controllers and younger Silicon Motion controllers. Indilinx made fairly reliable controllers and was bought out by OCZ and then Toshiba for use in their mid-range SSDs.
But each manufacturer has both cheaper and more expensive controllers. Therefore, you need to navigate by specific model controller, an overview of which is easy to find on the Internet.
Most of the controllers in entry and mid-range SSDs are 4-channel. Top SSD models are equipped with faster and more modern 8-channel controllers. But don't bother too much with controller models, it's not always easy to figure it out. Focus primarily on the brand, the declared characteristics of the SSD drive and real tests of a specific model, which often also consider the advantages and disadvantages of the installed controller and other electronic filling of the SSD.
In addition to the read / write speed, the controller also depends on the support of various technologies designed to improve the operation of the SSD disk.
9. Supported technologies and TRIM function
An SSD drive, depending on the model and the controller installed in it, can support various technologies designed to improve its performance. Many manufacturers design their proprietary technologies to deliver more marketing value than actual value to users. I will not list them, this information is in the descriptions of specific models.
The most important feature that any modern SSD should support is TRIM (garbage collection). Her job is as follows. An SSD can only write data to free memory locations. As long as there are enough free cells, the SSD disk writes data to them. As soon as there are few free cells, the SSD needs to clear cells, data from which are no longer needed (the file has been deleted). An SSD without TRIM support clears these cells just before new data is written, which significantly increases the write operation time. It turns out that as the disk fills up, the write speed degrades. An SSD with TRIM support, having received a notification from the operating system about the deletion of data, also marks the cells in which they were unused, but clears them not before writing new data, but in advance in free time (when the disk is not used very actively). This is called garbage collection. As a result, the write speed is always kept at the highest possible level.
10. SSD hidden area
Each SSD has a fairly large amount of memory in a hidden (inaccessible to the user) area. These cells are used instead of failing ones, due to which the volume of the disk is not lost over time and the safety of the data that is previously transferred by the disk from the “sick” cells to the “healthy” ones is ensured.
In high-quality SSDs, this hidden volume can be up to 30% of the declared disk size. Some manufacturers, in order to save money and gain a competitive advantage, make the hidden disk volume less (up to 10%), and more available to the user. Thanks to this, the user gets more available volume for the same money.
But there is another negative side to this manufacturer's trick. The fact is that the hidden area is used not only as an inviolable reserve, but also for the TRIM function. Too small amount of the hidden area leads to insufficient memory required for background data transfer (garbage cleaning) and the speed of the SSD disk with high occupancy (80-90%) degrades greatly, sometimes several times. This is the price of the "free" additional volume and that is why high-quality SSD drives have a large hidden area.
The TRIM function must be supported by the operating system. All versions starting from Windows 7 support the TRIM function.
11. SSD manufacturers
The best manufacturer of SSD drives is Intel, but their cost is very high and they are used mainly in the corporate sector for mission-critical systems and servers.
The next leader in terms of technology is Samsung. Their SSDs cost on average higher than all the others, but they are of impeccable quality, reliability and speed.
The SSD brands Crucial, Plextor (a Samsung trademark) and SanDisk were recognized as the best in terms of price / quality ratio.
Also, as a compromise option in terms of price / quality, you can consider the SSD of the proven Corsair brand and A-DATA.
I do not recommend purchasing Kingston-branded SSDs, since most of them do not meet the declared characteristics and their speed degrades as they fill up. But this manufacturer also has SSDs from the top-end HyperX series, which are of higher quality and can be considered as an alternative to top-end expensive brands.
In general, budget and unpopular brands - like a lottery, may or may not be lucky. Therefore, I recommend that you refuse to purchase them if possible. And on the model of the recommended brands it is still better to look for reviews, since "there is a hole in the old woman too." Let me remind you that links to reviews of SSD drives are in the file, which can be downloaded in the "" section.
12. SSD Form Factor and Interface
The most popular today are 2.5 ″ form factor SSDs with a SATA3 (6 Gb / s) interface connector.

Such an SSD can be installed in a computer or laptop. Motherboard or the laptop must have a SATA3 (6Gb / s) or SATA2 (3Gb / s) connector. Correct work when connected to the first version of SATA (1.5 Gb / s) is possible but not guaranteed.
When connected to the SATA2 connector, the read / write speed of the SSD will be capped at around 280MB / s. But you will still get a significant performance boost over a conventional hard disk drive (HDD).

Plus, the access time, which is 100 times lower than that of the HDD, will not go anywhere, which will also significantly increase the responsiveness of the system and programs.
The more compact SSD form factor is mSATA, which is based on the SATA bus but has a different connector.

The use of such an SSD is justified in ultra-compact computers, laptops and mobile devices (tablets) with an mSATA connector, in which it is impossible or undesirable to install a conventional SSD.
Another more compact SSD form factor is M.2. This connector replaces mSATA, but is based on the faster PCI-E bus.

The motherboard, laptop or mobile device (tablet) must also have an appropriate connector.
Well, another type of SSD is presented in the form of a PCI-E expansion card.

Such SSDs have a very high speed (3-10 times higher than SSD with SATA3 interface), but they are much more expensive and therefore are used mainly in very demanding professional tasks.
13. Body material
An SSD enclosure is usually made of plastic or aluminum. It is believed that aluminum is better because it has a higher thermal conductivity. But since the SSD does not heat up significantly, this does not really matter and may not be taken into account when choosing a model.
14. Package contents
If you are purchasing an SSD for a computer and the case does not have mounts for 2.5 ″ drives, then pay attention to the presence of a mounting frame in the kit.

Most SSDs do not come with a mounting frame or even screws. But the included screw mount can be purchased separately.
The presence of a mount shouldn't be a weighty criterion when choosing an SSD, but sometimes a better SSD bundled with a mount can be purchased for the same money as a budget SSD with a separate mount.
15. Setting up filters in the online store
- Go to the "SSD drives" section on the seller's website.
- Select the recommended manufacturers (Crucial, Plextor, Samsung, SanDisk), you can also consider Corsair and A-DATA.
- Select the size you want (120-128, 240-256 GB).
- Sort the sample by price.
- Browse SSDs starting with the cheaper ones.
- Choose several models suitable for the price and speed (from 450/350 Mb / s).
- Search online for their reviews and buy the best model.
Thus, you will get an SSD disk that is optimal in terms of volume and speed, meeting high quality criteria, at the lowest possible cost.
16. Links
SSD Samsung MZ-76E250BW
SSD A-Data Ultimate SU650 240GB
SSD A-Data Ultimate SU650 120GB
Solid State Drives (SSDs) are new and fast and are a good alternative to HDDs, but do you need one? Read on to see how we demystified the SSD. Over the past few years, there has been a noticeable increase in SSD production volumes and a decline in prices (although of course you cannot compare prices in this way between SSDs and traditional hard drives).
What is SSD? In what ways will you benefit from purchasing an SSD drive? What needs to be done differently with an SSD? Read on to find out all about solid state drives.
What is Solid State Drive?
You might find it hard to believe, but solid state drives are actually pretty old technology. Solid state drives have been around for decades in various forms, the earliest being based on random access memory and were quite expensive, and only appeared in ultra-high-end and super computers. In the 1990s, flash drives made the first SSD, but they were again too expensive for the consumer market and barely visible outside the specialized computing circles. Throughout the 2000s, flash memory prices continued to fall, and by the end of the decade, consumer solid state drives had entered the personal computer market.
So what exactly is a solid state drive? Here you must first highlight what a traditional hard disk drive (HDD) is. A hard drive is a set of ferromagnetic-coated metal plates that rotate on a spindle. Writing to the surface of the magnetic platters is done by a tiny mechanical handle (drive lever) with a very thin tip (head). The data is retained by changing the polarity of the magnetic bits on the surface of the platters. This, of course, is a little more complicated, but suffice it to say that everything is done here by analogy with an automatic turntable, his hand is looking for a track on the record, and the drive handle and the hard disk heads are also looking for data. When you want to write or read data from magnetic hard disks, the platters rotate, the hand searches and finds the data. It is the same mechanical process as it is digital.
In contrast, SSDs have no moving parts. Although the scales are different, and the storage area on the HDD is significantly larger, the SSD has much more in common with a simple portable flash drive than with a mechanical one. hard disk(and, of course, much more than ever with a tape recorder!) The vast majority of solid state drives on the market are NAND flash, a type of non-volatile memory that does not require electricity to store data (unlike RAM in your computer, which loses its saved data as soon as the power is turned off). NAND memory also provides a significant speed boost far more than mechanical hard drives, since the time wasted when the platters are spinning and not looking for data is removed from the equation.
Comparing Solid State Drives to Traditional Hard Drives
It is always good to know what solid state drives are, but it is even more useful to compare them with traditional ones. hard drives which you have been using for many years. Let's take a look at a few key differences in a point-to-point comparison.
Spin Time: SSDs do not have a "spin" time; the drive has no moving parts. Hard drives have different spin times (usually a few seconds); when you hear the click-whirrrrrr for a minute or two when you boot your computer or access infrequently used files, you always hear the hard drive spinning.
Access time and data latency: Solid-state drives find data very quickly and are typically 80-100 times faster than hard drives; skipping mechanical rotating plates and searching for data, so they can access the data almost instantly. Quick search for data on hard drives prevents the physical movement of the armature and the rotation of the plates.
Noise: SSDs are silent; no moving parts means no noise. Hard drives range from fairly quiet to very strong sound levels.
Reliability: Selected manufacturing issues aside (bad drives, firmware, issues, etc.) SSDs come out ahead in terms of physical reliability. The vast majority of hard drive failures are due to mechanical damage; at some point after tens of thousands of hours of operation, the mechanical drive simply wears out. In terms of the read / write cycle of hard drives is limited.
On the other hand, solid state drives have a limited number of write cycles. This limited number of write cycles is a major condemnation of solid state drives, but the reality is that the average computer user is unlikely to be able to do many read / write cycles on an SSD. Intel companies The X25-M, for example, can handle 20 GB of data for 5 years without interruption. How often do you erase and write 20GB of data on your primary drive on a daily basis?
In addition, SSD drives can continue to be used; when NAND modules have reached the end of their write cycles, they become read-only. The disk then reads the data from the bad sector and overwrites it to the new part of the disk. Apart from lightning or a catastrophic design flaw, the failure of an SSD is more like “old age, why does it hurt in my bones!” Rather than a sharp “boom! bearings in the HDD! ” and stop it. You will have enough time for Reserve copy your data and to purchase a new disc.
Power Consumption: SSD drives consume 30-60% less power than traditional hard drives. The savings of 6 or 10 watts might not seem like a lot, but within a year or two on a heavily used car, it all converges.
Cost: SSDs aren't cheap. Traditional hard drive prices have dropped by about five cents per gigabyte of data. SSDs are much cheaper than they were 10-20 years ago (when they were limited to special computer systems), but they are still quite expensive. Depending on the size and model, you can expect to pay anywhere between $ 1.25- $ 2.00 per GB.
Caring for your solid state SSD drive
In operating system management, saving data, and interacting with your computer, the only difference that you will notice is how end user, in time SSD work disk is the speed boost. When it comes to taking care of your drive, there are a few rules that are critical.
Do not defragment the disk. Defragmentation is useless for an SSD and will shorten its lifespan. Defragmentation is a technique that finds chunks of files and optimizes them by placing them on hard disk platters to reduce seek time and disk wear and tear. SSDs have no platters and have nearly instant seek times. Defragmenting them eats up more write cycles. Defragmentation is disabled for SSDs by default in Windows 7.
Disable Indexing Services: If your OS has any search - added tool such as indexing service, disable it. The read times on an SSD are fast, which you don't really need to create an index on a file and the actual disk indexing and index writes will be slow on an SSD.
Your OS must support clipping. The TRIM command allows your OS to talk to the SSD and tell it which blocks are no longer in use. With this command, performance on SSDs will rapidly degrade. This post supports the TRIM command for Windows 7, Mac OS x 10.6.6+ and Linux with kernel 2.6.33+. And registry hacks and additional programs exist to modify earlier OS versions such as Windows XP to semi-support the TRIM command. Your SSD should be paired with a modern OS for maximum performance.
Leave part of the disk empty. Check the specs for your device, most manufacturers recommend keeping 10-20% blank. This empty space assists the alignment algorithm (they transfer data through the modules' NAND memory to minimize overall wear on the drive and ensure long drive life and optimal performance). If you leave too little space, the alignment algorithms over time will lead to premature wear on the disk.
Media to Drive 2: SSDs are expensive, so it doesn't make sense to store your massive media files on your expensive SSD. You can pick up traditional 1TB hard drives, and use a large additional disk(if possible) for storing large and static files (for example, movies, music collections and other multimedia files).
Invest in Memory: Compared to the cost of SSDs, RAM is cheap. The more RAM you have installed, the fewer write cycles to disk will be. You will be able to extend the life of your expensive SSD by ensuring that you have adequate RAM installed in your system.
Is a solid state drive for me?
At this point you have a history lesson, point by point comparison, and some tips to keep your SSD in top shape, but do you need an SSD? Check all that apply and prepare for the following:
- Nearly Instant Load Time: You can go from cold boot to web browsing in seconds with an SSD; you could often get into this window in more than a minute with a traditional hard drive.
- You want quick access for general apps and games: we've said this many times before, but SSDs are super fast.
- You want a quieter, less power hungry computer: As highlighted above, SSDs are silent and consume significantly less power.
- You will be able to use two drives, one for the OS and one for files: if you only store a few family photos and a CD-Rip or two, you will need a more affordable traditional HDD for storing large files.
- You are willing to pay a sizable amount for an SSD: this is the largest amount per gigabyte to date, but at the same time the performance gain is huge at 3000%.
- If your list looks more complete than empty and you want speed while working, then SSD is for you!