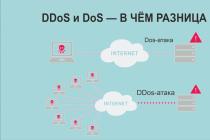
Everyone has long been accustomed to the fact that Russia does not have its own production of smartphones - we simply do not make them. However, there are many brands on the market that call themselves Russian, selling smartphones that are not collected from us. The resource has found out how relations are built between domestic companies and Asian factories.
Android is a mobile OS that is very tolerant of the gadgets it is installed on. Any company can order a newly assembled smartphone from China, put its version of the platform on it, stick an emblem with its logo and release it on the shelves of salons cellular... How did this development model affect the smartphone market in Russia, why do domestic companies persuade the Chinese to improve the product, and why Yota Devices had difficulty finding a manufacturer for the famous YotaPhone.
Copy paste
The Black brick scheme has been effectively working in Russia for more than three years. In 2012, the domestic company Explay ordered a noname copy in China Samsung Galaxy S2, branded for herself, set the price tag 2 times less (10,000 rubles versus 20) and came to success. The dual-sync, the bright screen (Super AMOLED Plus) and the similar design made this device a hit. During that year, Explay's revenue grew by 80%, and by the end of 2013 - by another 40%. So many companies that call themselves Russian: they brand Chinese gadgets with their logo, russify the interface and put them on the shelves.

However, there are also some nuances here. Often, devices brought from Asia are positioned not as replicas of hit models, but as unique solutions. Three slots for sim cards, four slots for sim cards (the first in Russia - at teXet), huge batteries (up to 5000 mAh), TV tuners, projectors and others. useful functions are not in demand among A-brands, but they flicker in smartphones coming out of the conveyor belt of Chinese factories. A person who follows Asian hits will easily find “twins” of Russian models and find a price markup (usually by 1.5–2 times), but this is not surprising: you have to pay money for the transportation of smartphones and firmware in Russian.
The Silicon Valley Experience
The teXet company (Alkotel electronic systems) was opened in St. Petersburg 11 years ago. Initially, affordable DECT phones, players and navigators were produced under this brand, but then smartphones with tablets began to appear. “Apple ushered in the tablet era by offering the highest level of devices to the market. price segment... We are trying to take our share in this trend by releasing inexpensive products, "said Alkotel CEO Alexander Korolkov. By the fall of 2014, the share of iPad in Russia decreased by a third: this space was occupied by budget gadgets, many of which are domestic.

“We are a Russian company, our headquarters are located in St. Petersburg. We do not want to dump and import "gray" devices in order to increase market share: our business idea is no different from the one used in Silicon Valley. Product development is carried out in our company, production - in Southeast Asia. It's easier and cheaper that way, ”Korolkov continues. Under "product development" should be understood, first of all, software, but despite this, teXet is already a recognizable brand in Russia, so its smartphones will in any case be more popular than their Chinese counterparts.
In this regard, the Highscreen brand had a harder time: in the first year (2011) "Vobis Computer" sold only 20-30 thousand imported gadgets. For the sake of increasing the share and profit, it was decided to make smartphones exclusive: now Chinese factories for Highscreen produce products that differ from standard ones. For example, inexpensive devices with bright and different to the touch covers (glossy - for girls, matte - for men). So Android gadgets under the Highscreen brand also became in demand.

Now the company's share is 2.8% of the Russian market, and only Fly and Explay are higher among the B-brands (according to Vobis Computer). “At the same time, Fly has the same share of the money as ours, because their smartphones are cheaper, and Explay is almost not engaged in the refinement of smartphones,” Highscreen representatives assure.
"Everyone should have a smartphone"
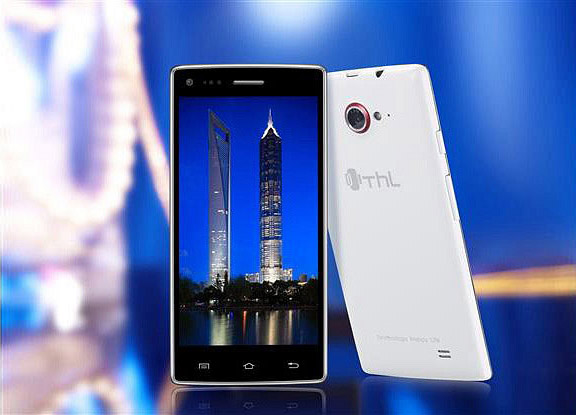
However, negotiating with Chinese suppliers is a time consuming process that sometimes takes months. The young DNS brand (the devices are sold in the chain of stores of the same name) brought ThL W11 Monkey King smartphones to Russia, but with important changes. For example, the back, home and options keys for the DNS order are printed more clearly, support has been added fast charging, and instead of the usual protective glass Corning Gorilla Glass 3 is used with a thickness of 0.7 millimeters. The last point is the most curious: the sealed glass is aimed at reducing the defect that is still found in Asian smartphones. To reduce the number of returns, it is more efficient to negotiate and slightly increase the cost of each item than to issue returns and carry out endless examinations for those whose "original" glass cracked on the very first day.

Sometimes entering the Russian market means going from a supplier to an independent brand. This was the case with SenseIt: earlier this company brought "miniphones" for "Megafon", and now it produces indestructible smartphones and phones with its own logo. Absolutely identical to the Chinese among them can not be found: SenseIt carefully approaches design issues.
“Any Russian consumer needs to be able to afford a smartphone,” says Eduard Vaschenko, head of Explay. According to him, the most important thing for a new brand is to occupy a niche free from competitors. In 2010, Explay was the first to make a navigator with both GPS and Glonass, then (also among the first) opened three-SIM phones for Russians, and in March 2014 it was a pioneer among those who installed a set by default on their smartphones. Yandex.Kit applications. True, after 8 months it was abandoned due to claims from Google, and in May 2015, the Kit project froze altogether.
"Nobody believed in us"
The most resonant and most Russian smartphone on the market is YotaPhone 2. Development of the first gadget with two screens began back in 2011: Yota Devices chose four important characteristics (slim body, two displays, fast internet, long-term work without recharging), created a layout and started looking for a manufacturer. “At first, no one wanted to talk to us at all - no one believed in us, because we were a small company with some kind of incomprehensible device,” recalls Vladislav Martynov, CEO of Yota Devices.

The order was accepted only in Suzhou: the head of this plant, Yao Xiao Tong, made a bet on Yotafon, as he once did on BlackBerry. The first generation of YotaPhone came out largely experimental, the second - mature and refined, but with an overpriced: in a crisis people are not ready to give 35-40 thousand rubles for a gadget that does not have the A-brand logo on it. By the end of May this year, Yota Devices had sold 144,000 smartphones out of 150,000 that belonged to the first batch.
“The global market is equal for all players, therefore such small companies as Yota Devices are on a par with others. A-brands have priority support from vendors of chipsets / components, and already built sales channels, and clear marketing, ”says Evgeny Kozlov, who previously developed smartphones for Fly. But Yota Devices is not giving up. The plans include the third generation YotaPhone and its own tablet with an additional screen in electronic ink.
Five main Russian smartphones
YotaPhone 2
Price - 36 thousand rubles
The second YotaPhone first appeared at the Barcelona exhibition MWC 2015. There it was remembered for its attractive case and sounded characteristics: they were much more interesting than the first version. The gadget received two touch screens (5-inch - Full-HD, 4.7-inch - qHD on electronic ink), Snapdragon 800 chipset, 2 GB random access memory and an 8 megapixel camera.
Now the device receives updates regularly operating system: for example, one of them improved the performance of the camera. The main convenience when using YotaPhone 2 is the auxiliary screen, which does not get tired of the eyes when reading. Additional advantage- autonomy: for those who often use an economical black and white display, the smartphone lives much longer without an outlet.
TeXet iX-maxi
Price - 9-10 thousand rubles
Frank iPhone copy 6, which can be mistaken for the original if you look at the smartphone from the other end of the subway car. Outwardly, everything is similar (there is only an apple on the back panel), but the characteristics are lame: the screen is qHD, the processor is Chinese MediaTek, the battery is 5 hours of talk time, the operating system is Android.

But the RAM is the same as in the iPhone - 1 GB. However, for the OS from Google, a gigabyte is not enough for a long time.
SenseIt R390 +
Price - 13 thousand rubles
This smartphone can be confused with a walkie-talkie, but a harsh design is necessary for full protection according to the IP68 standard. The waterproof device weighs over 200 grams, runs on Android 4.2, shoots HD video and is indifferent to any falls.

For those who go on long journeys, there is a second SIM card slot and a 2400 mAh battery: such a capacity can be easily stretched for two days.
Explay tornado
Price - 4.5 thousand rubles
A bright (five body colors) anti-crisis smartphone with support for three (!) SIM cards, a 4.5-inch IPS-screen (ppi - 218), a MediaTek quad-core chip and 512 MB of RAM. A 1550 mAh battery guarantees one day of operation, and a slot for a memory card (its 4 GB here) turns a budget device into a media center.

The main plus of this device is the price: the Tornado costs less than $ 100, which is great.
Highscreen ICE 2
Price - 13 thousand rubles
"Vobis" computer "tried to make a noticeable smartphone, and ICE 2 really suits this role - on the shelves it stands out with a shiny glossy body and a window on the back panel. The 4.7-inch screen with HD resolution falls into the "retina" category (ppi - above 300), the 13-megapixel camera takes more or less decent pictures, and the 8-core MediaTek processor (frequency - 1.7 GHz) and 2 GB RAM eliminates slowdowns.

The additional display on the rear panel resembles an external screen of a clamshell in functionality: it displays the time and service information (charge, calls, tracks in the player).
Russian smartphone manufacturers
The Russian market for smartphones and tablets is flooded with B-brands, inexpensive gadgets under little-known brands. In the past few years, several domestic companies have set up their production: distributors of equipment "Vobis Russia" (brand Highscreen), "Expley" (brand Explay), " Electronic systems"Alkotel" "(teXet brand), as well as cellular operators Megafon and MTS. B-brands retail much less than A-brands (Apple, Samsung). As a rule, they have a very simple filling, and manufacturers practically do not spend on their promotion.
According to GfK, B-brand manufacturers in the first nine months of 2013 occupied 17.5% of the market. One of Explay models was even named "Best Gadget of 2013" in the tablet category on the Hi-Tech Mail.ru portal.
There are several dozen B-brands in Russia. The best dynamics in terms of sales growth was shown by the brands Explay, Megafon and Highscreen: they grew 24, 18 and five times, respectively. The largest B-brand "Megafon" occupies only 2.6% of the smartphone market. For comparison: the leader Samsung has 24.4%.
In the tablet category, B-brands are also showing growth. According to Euroset, in the first nine months of 2013, the Cypriot brand, created by immigrants from Belarus, Prestigio increased its share from 4% to 10%. At the rate general director Prestigio companies in the CIS and Eastern Europe by Yuri Antoshkin, the largest players among Russian tablet manufacturers - DNS (produced by the network of the same name) and teXet - have a market share of 7% and 5%, respectively. For comparison: according to Euroset, in the first nine months of 2013, iPad occupied 19% of the market, and Samsung - 25%. Moreover, compared to the same period last year, Apple products have reduced their share by 7%.
What explains the growth in sales of B-brands?
Firstly, they are cheap, and when buying a gadget, many consumers first of all pay attention to the price. Of course, B-brands do not offer any unique developments, they copy the main technical characteristics of the market leaders and are produced in Chinese factories.
Another reason is that B-brands have managed to interest many retail chain owners. Retailers' markup for A-brands is 5-7%, and for second-tier brands - no less than 20%. "In the coming years, the total share of B-brands in Russia may become more than 50%, this is a real prospect," says Anton Spiridonov, editor-in-chief of the Hi-Tech Mail.ru portal.
It seems that many consumers have already ceased to perceive the smartphone as a status purchase, the value of brands has been falling lately. The brands of the "second echelon" skillfully take advantage of the current situation.
5.6 thousand rubles was the average price of a smartphone in the Russian market in 2013, according to the Euroset company. Over the year, it decreased by 10% due to the growth in sales of budget devices
In 1994, the first President of Russia Boris Yeltsin, by his decree, gives 12 June state significance - Day of adoption of the Declaration of State Sovereignty of Russia. The word "sovereignty" in the minds of many is associated with "independence", and the masses begin to call this holiday simply - Independence Day. But from what or from whom? We weren't dependent anyway. Therefore, in 2002, at the state level, the holiday was renamed, and it begins to be called briefly and succinctly - the Day of Russia.
Russia Day- a symbol of national unity and common responsibility for the present and future of our Motherland. Therefore, "Svyaznoy", based on the specifics of its work, proposes to talk about domestic manufacturers of mobile electronics and portable technology.
Explay - striving for new things

Explay Crystal - a window to the world
One area where Explay is second to none is multi-SIM mobile phones. Last summer a troika burst into the market like a whirlwind Explay phones- B200, B240, Q230, the main feature of which was the support of not even two, but three SIM cards at once. They burst in, looked around and secured a foothold. Over the year, the company's portfolio has already numbered about two dozen different phones, including the spectacular and original Explay Crystal, the first phone with a transparent display. Yeah, almost like the one that the engineering genius Tony Stark from the movie "Iron Man", only simpler.
Various concepts, engineering designs, prototypes and similar projects with transparent displays have appeared with enviable regularity over the past five years, probably. Some of them even succeeded. For example, a company Sony ericsson released in 2009 Xperia phone Pureness. For about 45 thousand rubles.
And now - Explay Crystal. It really has a transparent display that really lets light through. And at the same time, the phone makes no claims to show-off or superintelligence. This is a trendy phone available to everyone. Design is the main feature of the model, and inside it is a simple multimedia dialer with traditional Explay support for two SIM-cards. But you can look through it!
Gresso - you can't forbid living luxuriously
If Explay products are aimed at the mass consumer and offer functional technology at an affordable price, then the strategy of the Gresso company is exactly the opposite. Gresso produces exclusive high-tech items of the "luxury" class.
The Gresso company was founded in 2005. And in 2007, Gresso created its first collection - the Avantgarde luxury phone. It is the only phone carved out of 200-year-old African ebony. In that collection, much was done for the first time, for example, a telephone keypad with Roman numerals, a magnetic Smart Lock to fix the battery compartment. Precision turning technology was used in the manufacture of the phone's function keys, which made it possible to achieve high precision and impeccable shape of every detail. Forbes magazine named Gresso Avantgarde in the top ten most expensive mobile phones the world.

Gresso pandora
In 2008, the company introduced a collection of Enigma and Pandora USB sticks. Enigma is the world's first 192GB flash drive, and Pandora is the only luxury device with a fingerprint reader. The collection was crafted from 200-year-old ebony and adorned with a scattering of gorgeous colored diamonds set in yellow or white gold.
The history of Gresso's glorious victories on the "luxury" battlefield does not end there - every year the company finds something to surprise the most discerning and demanding customers. Gresso's price tag can cause cloudy eyes, but what is money? In vain. True, you can buy a lot with them.

Gresso enigma
Gresso Luxor World Time - keeping pace with the times
Gresso Luxor World Time is the world's first phone with a world time function, designed specifically for business people living in the rhythm of the planet.
A unique feature of Gresso Luxor World Time is six independent Swiss watch movements, mounted in the back cover of the phone, with a power reserve of 10 years. This watch shows the time in five major business centers of the world: Tokyo, Moscow, Paris, London and New York.
The case of the Gresso Luxor World Time is made of an ultra-strong and ultra-light titanium alloy specially developed for Gresso. At the final stage, it is covered with high-tech ceramics. Another borrowing from the watchmaking industry is the polished steel bezel with a black PVD coating on the front. On the back panel there is a finish made of genuine Italian leather.
Two hand-polished 97-carat anti-reflective sapphire crystals frame the display and the elegant Roman numeral dial on the back.
Each function key is made of sapphire monocrystal, hand-polished with a diamond tool.
Gresso Luxor World Time is not just a phone. This is a revolutionary Gresso solution in the mobile industry, inspired by the Swiss tradition of high watchmaking.
3Q - triple quality
3Q is a company founded in 2006 as a manufacturer of external hard drives and external optical drives CD / DVD / BD. Why Q is three at once is not very clear, but most likely it is quality multiplied by three. Or three times "ku!" and crimson pants. Officials are not covered in this regard.
Over the past six years, the company's assortment has expanded significantly, and today it includes tablet computers, media players, nettops, netbooks and laptops, external hard drives, external optical drives, card readers, network storage devices (NAS), solid state drives(SSD), universal power adapters, external batteries and pen batteries, as well as bags and stands for mobile computers.
The first 3Q netbooks and notebooks appeared in 2009, and at the end of 2010 the company announced the start of production of the Surf tablet computers. The name was not chosen by chance: on the one hand, it symbolizes boards for riding waves, and on the other, lightweight wearable computers that are used mainly for viewing Internet content, that is, surfing the net.
For the new 2012, the company began selling the flagship model of a tablet computer on Android version 3.2 - 3Q TS1005B, back cover and the ends of which are trimmed with leather. And on April 5, 2012, Russian journalists were shown the 3Q TS1010C - the first tablet computer based on the Nvidia Tegra 3 processor from Russian company.
3Q actively cooperates with Intel, Nvidia and Microsoft and is one of the few companies in Russia supplying computers with a pre-installed MeeGo operating system.
3Q Adroit OE1501NH Notebook - Qoo Style!
The 3Q Adroit OE1501NH notebook is the lightest and most affordable model in the Adroit 1500 family, built on the modern Intel mobile platform. This laptop is aimed at users who are primarily interested in efficiently solving typical office and home tasks that are not associated with resource-intensive 3D games.
With the outward simplicity of a laptop, you can find more than one "highlight" in it. For example, high-speed USB port 3.0, which allows you to transfer large files from compatible media to HDD 3Q Adroit OE1501NH and vice versa.
The USB 3.0 specification raises the maximum data transfer rate to 4.8 Gbps - orders of magnitude more than the 480 Mbps that USB 2.0 can provide. Thus, the transfer speed increases from 60 Mb / s to 600 Mb / s and allows you to transfer 1 TB of data (and this is a huge amount of information) not in 8-10 hours, but in 40-60 minutes.
In addition to USB 3.0, the laptop is equipped with an HDMI port (which is rarely found in a budget model), a Bluetooth module and a gigabit Ethernet port (as opposed to the more common but outdated 100 megabit one).
RoverComputers - Godfather
Speaking about Russian manufacturers of portable electronics, one cannot ignore RoverComputers, which was founded already in 1991 (however, then it did not yet have the word Rover in its name).
RoverComputers is the so-called umbrella brand because it combines several product lines at once: RoverBook laptops, RoverPads, RoverPC smartphones, RoverMedia MP3 players, RoverBox multimedia consoles, RoverMate digital accessories and RoverSkan LCD monitors.
![]()
The monumentality of the company is confirmed by the fact that the first laptop was released on the basis of 486 Intel processor... 1995 was the year of the birth of the Russian laptop and forever entered the history of the domestic high-tech market.
RoverBook laptops have become a landmark product of the company and over twenty years of existence have received more than a hundred awards, several times became the leader in the sales rating in Russia and twice the owner of the Brand of the Year / EFFIE award.
In September 2010, RoverComputers opens the RoverPad Tablet PC business. Their the lineup constantly expanding following the development of technology, devices keep pace with the times and are equipped with advanced technologies. All RoverPad tablets run on the popular Android operating system, newest versions which are installed on new RoverPad models.
At the end of 2011, RoverComputers launched a new project called Detvore. Within the framework of this project - the release of branded electronics for children. The products are created based on the images of media heroes well known to children. For example, MP3 players with images of popular Soyuzmultfilm characters or cameras with the popular Hello Kitty. The goal of the project is to create “smart toys” for the all-round development of children.

Tablet RoverPad 3W T71D - the fourth "Android" in action
Novelty from RoverPad runs the latest operating room Android systems 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich and equipped with a Cortex A8 processor with clock frequency one gigahertz and 3D accelerator. For gamers, there is great news - the 3D accelerator is great for overclocking the work. graphics applications(read - games) and the speed at which the RoverPad 3W T71D flies, allows you to fully enjoy your favorite games.
The tablet is equipped with a bright seven-inch capacitive display with a resolution of 800x480 pixels, supporting multi-touch technology, so that you can operate the device with several fingers at once.
The creators of the tablet made sure that it was as convenient as possible to use. So, the built-in mini-USB connector allows you to connect external devices, for example, a keyboard, 3G modem and much more, so you can work with your tablet as with a regular home computer or laptop.
Built-in four gigabytes of tablet memory can be easily expanded with microSD cards... So you no longer have to think about which application to install and which one to uninstall for lack of free space.
The RoverPad 3W T71D is a compact and lightweight device with tremendous potential.
The four described companies are not even a drop in the ocean, but an asterisk in the vast universe of Russian manufacturers of mobile electronics and portable technology. But we hope that by touching on this topic, we managed to awaken interest to look around, look at our phone, tablet, camera and ask ourselves if there are Russians in his pedigree. And smile, experiencing a sense of pride for ours, if any.
So, we put on a robe, put on shoe covers and a hat, set off on a journey to the inside of a Chinese economic miracle.

First work shift - 8 am
All workers are divided into teams of 10-20 people, they have their own commander, who is a little god in charge of his people. The structure completely copies the army - there are no strong and weak. Achievements are judged solely by how the entire team has done their job. As a work plan, a certain number of actions are set for each person - that is, formally, you can make your own thousand details and be free. In practice, the conveyor for assembling phones is designed in such a way that the production depends not only on your work, but also on what your comrades do - they give you parts of the phone after their manipulations. This deceptive maneuver serves to increase labor productivity, if the team can mobilize all workers, then their productivity will increase - but no one can leave the workplace separately.
This is another part of the story that is often forgotten or overlooked. In Asia, historically, there are prerequisites for each nationality to create classes within - in India these are the Kshatriya stories remembered in the school course, as well as untouchables and others, in Japan there is a modern caste system of belonging to one or another corporation or company. In China, factories have adopted approximately the same approach, but here the unit of the universe is a working team. An individual worker is a cog in a large machine who is not too interested in this machine and should not influence it, his task is only to be a part of the whole. An absolutely army approach, in which a specific worker cannot prove himself in any way, is the task of the collective - that is, the brigade. It is safe to say that on the social ladder, factory workers are somewhere at the very bottom. Sometimes the smartest, those who can organize the work of other workers, turn out to be foremen, a kind of sergeants of the working world. It is not the speed of a particular person that is valued here, but how quickly the team manages its work. Individuality fades into the background.
The normal working day starts at 8 am. At this time, workers come to the workshops, which are located on several floors, and are being built together with the foreman. Each team appears at the time strictly allotted to it - the gap between their exit is about 5 minutes, this is done in order not to create a crush. Therefore, the time 8 o'clock can be regarded as a certain conditional milestone - the factory works around the clock, but on the night shift, if there is no force majeure, the number of workers is less.
Sleep is the most valuable thing a Chinese worker has, and he treasures it very much - the one who does not get enough sleep threatens the well-being of his comrades. The workload of the entire team may suffer, which means that the working day will turn from 10 hours to 11 hours, or even more. By law, the maximum working day is 10.5 hours. The best crews manage 9.5 hours, but most do 10 hours. Gaining half an hour of time is given at the cost of great effort, people become squeezed out like lemons, they only have the strength to get to bed. And the factory leadership can raise output for the Stakhanovists by forcing others to work in the same way. Everyone is well aware of this, so they try to fit into typical rates- only sometimes, in connection with some festivities, the brigades can accelerate.
It is curious that it is customary here to celebrate birthdays or other events of workers. The dining room has separate rooms with round tables and the ability to seat one team. It costs nothing to occupy such a room, the same food is served as for everyone, but people can celebrate something of their own in an intimate setting. It somehow reminds me of everyday life in the army, where your unit becomes everything for you - exactly the same role for a brigade in a Chinese factory - it should become a home for the worker.
The transition from one brigade to another is possible, sometimes it happens, but this is not encouraged - it is easier to work with those whom you know well. The foreman is not at all a white-handed, he works on an equal basis with the others, although he has some privileges. Curiously, the foreman has to master more operations in order to train newcomers if no one else can do it.
The Chinese factory is a sweatshop where workers work hard. In the morning they have no time for breakfast, so at 11 o'clock there is what is called lunch. In fact, this is the first meal of the day for most workers. The second meal takes place after 3-4 o'clock in the afternoon, the ritual of taking workers out of the workshop is repeated.


The foreman leads everyone through a metal detector, and workers can also be searched on special pedestals in search of parts that they could take out. From the point of view of theft, each factory seeks to protect itself and creates conditions under which it is impossible or extremely difficult to endure something. In some factories, a paranoid level of secrecy is introduced, when not only players, telephones or something else are prohibited inside the production, but the finished product is closed in opaque boxes, which are moved to other workshops.




There is a little secret with which you can determine how serious measures are taken at the factory to ensure the safety of production and what is happening on it. You just need to look at whether the girls who are behind the assembly line have headphones. Having your own players clearly means that there is an opportunity to bring something of your own and take it back. As a rule, this is not possible in most industries.
Let's go back to the standard food for a Chinese worker. The two meals that take place in the factory are almost all the food a worker consumes during the day. There is a small shop on the territory of the factory with a very modest selection of cookies, sweets and other nonsense to kill the worm. The diet isn't full of variety, and if you look into your dorm room, you'll find foods such as tea, concentrated juices, soda, cookies, and chocolate. Families can cook food, but they do it almost exclusively because of the children who do not eat in the factory cafeteria.
The scarcity of food ten years ago was fantastic, I'm not sure what they fed in concentration camps. Some factories amazed me with the lack of not just a balanced diet, it was a cup of rice and some vegetables with tea. This sight always made an impression on the Europeans, but did not touch the Chinese themselves - they explained this by the fact that in the villages the food of their workers was even more scarce. There is no reason not to believe these people, I think that it was so. But even then, there were no emaciated people at the factories, those who gave the impression of sick or infirm. It is possible that the reason for this lies in the Chinese organization of labor - as soon as the worker stops fulfilling his quota, he is refused and he is forced to leave the factory. A crude but highly effective system that is focused only on results. About any social protection of workers, which would allow them to pay money when their work deteriorates, no. The most that a Chinese worker can count on is payments from production if he gets a disability due to the fault of the factory. The amount of such payments is very small and cannot in any way cover the lack of work or ensure a decent standard of living.
Another interesting question is the size of the pension in China and why the villagers are so eager to go to factories. The explanation should be sought in the fact that in China there are no pensions for peasants and rural residents, there are none at all. Government officials have a pension; a prerequisite is work for at least 15 years. The law also states that at enterprises, including private ones, employees must receive a pension upon reaching a certain length of service. The size of this pension ranges from 750 to 1200 yuan (3,800-6,000 rubles). As a rule, it is very difficult to fulfill all the conditions for receiving a pension. But this is an additional incentive to connect your life with the factory, since the pension guarantees life in old age. Historically, in China, parents relied on children to support them in old age - the more children, the better the parents lived. The state program "one family - one child" brought a time bomb under this concept; parents of children born since 1980 can no longer count on support - one child is not able to feed two adults. The alternative is to work for the state, which, like a vacuum cleaner, picks up the most gifted and capable children, or, in the absence of education, a trip to factories. This is state regulation of the economy, which de facto creates and enlarges classes - employees and workers.
Sometimes I come across reports about how Chinese workers live, or discussions about their difficult working conditions, as well as life. Some Western publications call it slave labor, which, of course, is not. But the fact that in China the state has created all the conditions for the country's residents to be busy is beyond doubt. There is segregation in the country based on the qualities of people, and those who do not want to work have no place in this social structure - most people have to work to provide themselves with food. Much and hard.
The working class in China is not privileged; on the contrary, they are the people on whose shoulders the economic miracle is built, and they are one of its constituent parts. Cheap labor of workers, multiplied by a long working day, gigantic output and low wages, create the economy of this fairy tale.
Conveyor - Japanese version of production
Each factory fights for greater production efficiency, it is not about a multiple increase in product yields, but about percentages. Factory managers are willing and quick to adapt innovations that take place in manufacturing, especially if they are not costly.
Usually the conveyor on which the phone is assembled is a straight line with assembly tables. On each such table, a certain operation is done - first the board is inserted, then other parts are mounted, and so on. At the end of the conveyor, there is a primary inspection of the resulting product or semi-finished product, at some stages there is a quality check (both instrumental and eyes). In Europe, in such factories, you can see chairs, and tables are low, adapted for seated people. In Asia, all industries, or almost all, are for standing people (imagine 10 hours on their feet, in almost one position and at a narrow table? This explains the fatigue of people after the shift). The choice in favor of people standing during production is explained by physiology - the pressure does not drop, the concentration on details is higher and longer. The payback for this is more time for rest, sleep. For factories, this is beneficial in that the workers do not have time for walks or something else, they either sleep or work.
























At the Oppo factory, a slightly different type of conveyor was used, it is not delivered in one line, but with the letter P. This innovation was applied in Japan about a year ago, as they say, this option allows you to save space and speed up work by the same percent. Workers stand on the inside of the letter P and pass blanks to each other.
The Oppo factory employs 1,700 people on a day shift, with 40 conveyors that assemble telephones. The plant is capable of producing up to 50,000 devices per day, but the actual production volume is slightly less, it is regulated by the night shift, which is not so numerous.
The conveyors described above are typical for any factory, whether it is located in China or any other corner of the world. In fact, we can say that most of the devices are assembled by hand, and this applies equally to both Oppo phones and Apple iPhone coming out of the Foxconn factories. The share of manual labor in each apparatus remains maximum, and the idea of ordinary people that all this is assembled by robots is as far from the truth as the number of such industries (they exist, but almost never produce goods for the mass market, the cost is too high, cheaper to use working hands).
Full-cycle factories also have their own SMT lines, where boards for phones are assembled. Almost always, when they want to talk about the fact that production is modern and innovative, they show an SMT line as a picture, on which machines lined up in a row string small parts onto a board, picking them up from bobbins. Robots skillfully and efficiently assemble boards, which then undergo primary quality control.
The cost of one SMT line for the production of boards for phones is about $ 10-12 million. There are five such lines at the Oppo factory, it is planned to buy two new ones with improved equipment. In fact, for each production, the maximum production volume depends not only on the number of workers and assembly lines, but on the number of SMT lines. Usually the ratio is 1 to 5, that is, five conveyors with workers are opened per SMT-line. This clearly shows the difference in the performance of machines and humans.










The economics of production and conveyors are approximately the same for all companies, that is, here we can say that the equipment differs, the cost of labor and the thoroughness of intermediate testing at all stages of assembly. But the main difference in price between different factories lies in other aspects of the work, we will talk about them.
Testing of components and finished products
If in the shops an experienced eye can see many things, evaluate the quality of work organization, roughly estimate the cost of a product, then he will not be able to identify the main thing - how good or bad the final product is. Quality control is responsible for this, and it is not concentrated in production facilities, it is a separate laboratory. In factories where quality is given the main role, there are two laboratories - one is engaged in testing its own, finished product, and the second checks all purchased components, plus considers components from new suppliers. In the case of Oppo, there are both labs. On test benches there were models that have not yet been officially announced, so I cannot show you all the instruments and machines for testing. But in general terms I will tell you what is happening outside the walls of these rooms. Let's start with the component testing laboratory.

Each factory independently purchases a variety of components - from plastic and screws to stickers on phone screens, displays, material for printed circuit boards... It takes two hundred items to assemble one phone, and the performance and quality of the final product can directly depend on any of the components. Therefore, input quality control is very important, and it starts with the simplest tests - the weight and size of the components. The supplier has specifications to which he makes, for example, screws. They must be of a certain size, weight and color. All this is checked for each batch that is delivered to the plant - a spot check takes place here. If the supplier is new or the component has never been delivered before, then the check is carried out on all possible machines - resistance to aggressive environments, humidity, strength characteristics, and so on. Whether a component passes these tests or not depends on whether the factory will buy it or not. Components of several companies are often tested at the same time and the best ones are selected.
In the photo below, you can see how the laboratory tests the oleophobic coating of the display by a drop of liquid placed on it.

This laboratory has X-ray machines to detect hidden defects in small parts, circuit boards, and so on. That is, it is a full-fledged quality control of all components. Accessories, such as headphones, are tested in the same way. After testing, they are cut so that they do not fall into the manufactured products by mistake; weighty bags with cut off ears and connectors can be found in different places.



There is a separate room with test tables for cameras, modules are tested here - even before they are installed in phones, you can also check the final devices and how the software works.
The laboratory looks shabby, it is not brand new, which better than any words says that life is in full swing in it and work is constantly going on. This is one of the most interesting places in the factory. As a rule, outsiders are not allowed into these laboratories, since the equipment does not make a stunning impression, moreover, it is very difficult to explain its wear and tear, and such explanations can be taken as excuses.
Several times I was unlucky enough to get on press tours to factories, where we were taken to specially created production facilities, in particular, they demonstrated perfectly clean laboratories of input quality. When I asked how long ago the laboratory was built, I found the answers very amusing - a year ago, several years. Such laboratories cannot always be tidy - they are clean, but the wear and tear of the equipment, scratches on it arise due to the fact that it is used. But if they do not use it, then nothing of this is there.
In the test laboratory, where ready-made phones are tested, there are several rooms, each of which is designed to test devices in different conditions. I'll start with the climate laboratory, which has large metal cabinets - a certain temperature and humidity can be created inside each such cabinet, this is an imitation of different climatic zones.



Phones can be inside either on or off. Separate installation responsible for the artificial aging of materials, this is, perhaps, the place from which they are trying to get away quickly, because they do not want to give out their know-how. By and large, an aging setting is a combination of machines that simulate climatic conditions - UV light is usually added to humidity and temperature and, possibly, something else. It is the testing technique that is the secret - it is important to achieve the real effect of aging in the shortest possible time, which allows you to change the technological process and avoid problems in the future. European engineers treat such attitudes as shamanism, and condemn them, quite sensibly noting that they are not certified, are a product tied exclusively to Chinese realities and do not have one hundred percent guaranteed result... There is no harm from them, but a definite benefit can still be traced. I wouldn't be surprised if the Chinese end up creating something through trial and error that works and guarantees a result. So far, this direction can be perceived as promising, but by no means the main one.
For phones with an IP / IPX protection level, there are cameras in which the devices are flooded with water from different angles (the most interesting thing in such cameras is the wipers, which clean the glass from water from the inside so that you can see the device).
Household use and the durability of the apparatus are tested on other devices. The mechanical strength of the screen is tested by metal balls that fall on it from a certain height. I did not dare to put my phone under this torture machine, although I understood that it had passed exactly the same tests and should withstand everything here. Psychologically, this is the safest test a manufacturer can show - a heavy metal ball falls on the screen and leaves no traces on it.




An automatic machine works to abrade the surface with jeans put on the handles, a phone in a pocket, and the fabric rubs against the body. Approximately several hundred thousand times. In general, when I talk about tests for strength or abrasion, one must understand that they pass 100-300 thousand repetitions. This is an automaton that checks the number of clicks on the screen in different places, and a device that takes a picture of a magazine page, immediately erases the picture and takes pictures again - this is how the resource of the camera is checked.
In another machine, the phone is clamped in two legs, and they begin to twist it in different directions, trying to bend it. Nearby, the machine polishes the plastic surface with different materials - cloth, denim, leather and others. It is also a test for surface abrasion under various conditions.
Measured bangs are heard from another row, about ten telephones are raised by 10 centimeters on suction cups and then dropped on the metal surface of the machine. Then the suction cups come down again, and everything is repeated. This happens a hundred thousand times, and the phone must pass all the tests.
There is a separate radio laboratory, where they check how the radio module of the phone works. An artificial hand, worth 2,500 euros, holds the phone, and inside the sealed chamber is tested for all frequencies. There are two such cameras at the Oppo factory, unnamed Chinese manufacturers or small factories do not have them at all, this is too expensive.






A short afterword, or to be continued
If in the first part of the report from China we talked about the place of factories in the state, about what they are, how propaganda works in production, then in this part we were able to look behind the curtains of production and see production workshops, as well as laboratories for example one pretty good factory. Behind the scenes, there was a story about the highest paid employees of the factory, the role of design and why there are so many different shells for Android and what kind of human factories are doing this in China. The third part of the report will be devoted to this. Don't miss it. I also hope that after this material, the question of why one device costs one hundred dollars, and another three hundred, and whether this is only a fee for the brand, will not arise. This report shows what affects the cost of the final product and what such rigorous testing brings, besides price increases.
It just so happened in the world that every state, every nationality or region, has a trait or peculiarity inherent only to it. For example, the Germans are famous for the production of their quality cars, which have earned the trust of millions of people around the world. China, Korea, Japan and other eastern regions traditionally produce 90% of all technology and electronic devices. Indeed, if you look at the market for computers, tablets, smartphones and other digital technology, then the vast majority of companies are from the East. This is due to the presence of cheap labor in these regions and the proximity of natural resources. More than 70, and maybe more, percent of all home appliances are produced in China and its neighbors. Some users mistrust such manufacturers. And then they start looking for manufacturers from European countries or from the United States. However, for people with a Russian passport and residence permit, one should not look at the horizon, looking for a high-quality European brand, because there are quite a few successful and trustworthy Russian companies that can offer their fellow countrymen decent and high-quality devices. Yes, yes, this fact is quite deliberately surprising. Who would have thought that they also produce good smartphones and tablets with which you are not ashamed to be in the circle of geek friends. There are not many such companies, but they exist, and I would like to introduce you to several of them, and at the same time tell you about their devices.
It's better to start with the company. Highscreen as the most successful and outstanding. The firm began its active development back in 2009 and now belongs to the Russian company Vobis Computer. Initially, Highscreen ordered smartphones from Chinese manufacturers, slightly changed their design and Android interface, and sold them under its own brand. The company's smartphones are notable for their low price, good workmanship and build quality. The most notable model in recent years has become a smartphone Highscreen Boost 2. It is notable for the fact that it became famous as the longest-playing smartphone in the world. The device can work up to 2 weeks from one battery charge. The set includes batteries for 3000 and 6000 mAh. The company even applied to the Guinness Book of Records. Also, the Russians have a very good line of Zera smartphones and new flagship Highscreen Thor, running on eight cores of the Mediatek processor.
Another domestic company that deserves special attention is the Russian OEM supplier Explay. This company was founded back in 2005 and did not immediately enter the mobile phone market, but was engaged in the sale of navigation equipment, music players, headphones and other digital equipment. Since 2009, the company has been among the top five mobile phone suppliers, focusing more on the budget market. There are many smartphones in their lineup with two SIM cards. From the latest devices, the Explay Fresh smartphone can be distinguished. The device has decent for a budget employee technical characteristics- good IPS-display with a diagonal of 5 inches, quad-core Mediatek processor, support for two SIM cards. Pleased with the variety of body colors, and as a shell on top of Android 4.2, the native Yandex.Shell interface is installed.
Many have heard of such a brand as Texet, but few know that it is also domestic. Relatively domestic, because products for the brand are produced by another Chinese company. The company's office is based in St. Petersburg, it was founded in 2004, and besides inexpensive smartphones also produces navigators, portable radios, players, e-books and tablets. The first mobile phone was released relatively recently - in 2010. The company's lineup has a lot of devices with different screen diagonals, up to 5.2 inches. There is also a smartphone for 4 SIM cards and a line of protected smartphones for athletes, builders, hunters, fishermen, and the military.
It is impossible not to say a few good words about the truly Russian manufacturer of smartphones - the company Yota Devices... The company is quite young, was founded in 2011 and is widely known for the production of high-tech LTE subscriber equipment. In December 2013, the company introduced its first YotaPhone smartphone. The device became the world's first dual-display phone. The first is not particularly impressive - a usual 4.3-inch IPS-matrix with a resolution of 1280 by 720 pixels, but the second is more interesting - it is located in the place where the cover and the manufacturer's logo are usually located. The second display is made using Eink technology, in other words, the same as in the readers. The rest of the characteristics are at the level of smartphones at the beginning of 2013, but the manufacturer at the start of sales asked for about 20,000 Russian rubles for a smartphone. The device has not become as popular as the manufacturers wanted, but the release of the second version of the smartphone is expected soon, which will cost less and offer users more interesting features.