When computers first appeared and began to gain momentum in popularity, they were autonomous and functioned independently of each other. With the increase in the number of machines, it became necessary for them to work together.
In a sense, this is due to the activities of users, which took place within the framework of one document. To solve this problem, the use of global and local networks began. Their creation led to the need to manage this process and perform all sorts of tasks. The network administration has assumed these responsibilities.
Main functions of network administration
According to international standards, network administration has the following functions:
Failure management (search, correct identification, as well as troubleshooting and malfunctions in the operation of a specific network);
configuration management (configuration of system components, including their location, network addresses, setting the parameters of network operating systems, etc.);
accounting of network operation (consists of registration and subsequent control over the resources and network devices used);
performance management (provision of statistical data on network performance for a certain period of time);
security management (access control is performed and the integrity of all data is maintained).
Various sets of presented functions are embodied in products by manufacturers of networking tools. With regard to performance management, it is carried out to minimize the cost of resources, energy and in order to plan resources for further needs.
Responsibilities of the system administrator
Administration of computer networks is carried out under the control and guidance of the system administrator, who must perform the following tasks:
Check the health of databases;
control the smooth operation of local networks;
ensure the protection of data and their integrity;
to protect the network from illegal access;
regulate the access rights of local network users to network resources;
back up data;
use the best programming techniques to make full use of available tools as well as network resources;
keep special journals on the network;
conduct training for local network users;
control the software used;
monitor the improvement of the local computer network;
develop network access rights;
suspend illegal modification of the software for the network.
In addition, the system administrator is responsible for informing the employees of a particular enterprise or organization about the weaknesses of the network administration system and the likely ways of illegal access to it.
Features and criteria for planning systems
Before installing a computer network, you need to find answers to the following questions:
1. What tasks is it called upon to solve, what functions to perform?
2. How will the computer network be built?
3. How many and what devices will be present in the network?
4. What programs for network administration will be involved?
5. At what level is the organization's security policy, where systems will be installed and so on.
After answering these questions, you can create a system of criteria for a specific computer network. It will include the following items:
1. Preparation, control and testing of programs used on a daily basis in the network.
2. Control over the performance, as well as the health of the computers involved in the work.
3. Preliminary preparation of system recovery processes in the presence of errors or failures.
4. Ensuring that further installation of the new system does not negatively impact the network.
To achieve all of these goals, it is necessary to engage in the training of staff and users.
Remote administration software
When the need arises to control the system outside the organization, remote network administration is used. For this purpose, it is necessary to use special software that makes it possible to control the system and remote access using the Internet in real time. These programs are able to provide almost complete control over the remote components of the local network, as well as each computer separately.
This allows you to remotely control the desktop of each computer on the network, copy or delete various files, work with programs and applications, and more. Today, there are many programs known for performing remote access. They all differ in their protocol and interface. The latter is capable of having a console or visual character. Notable programs include Windows Remote Desktop, UltraVNC, Apple Remote Desktop, Remote Office Manager and others.
Categories of networks A network is a collection of different hardware, software, and communication tools responsible for the efficient allocation of information resources. All of them are conventionally divided into three categories:
Local;
global;
urban.
Global networks are able to provide interaction, as well as the exchange of information between users located at a remote distance from each other. During the operation of these networks, slight delays in the transmission of information may occur. The reason for this is the relatively low speed of this process. The length of global computer networks can reach thousands of kilometers. Urban networks operate at a shorter distance, therefore, they provide information transfer at medium and high speeds.
They slow down the data a little, like global ones, but they are not capable of transmitting it over long distances. The length of these computer networks is limited and ranges from several kilometers to several hundred kilometers. The local network guarantees the highest data transfer rate. As a rule, it is located inside one or more buildings. As for its length, it is no more than one kilometer. Often, a local area network is provided for one specific organization or enterprise.
Data transmission mechanisms in various networks
The mechanism of data transmission in global and local networks is different. Global computer networks are primarily about connectivity. In other words, before starting the transfer of data between two users, it is necessary to establish a connection between them in advance. In local computer systems, completely different methods are involved that do not require preliminary communication. In this case, the data is sent to the addressee without receiving confirmation of his readiness.
In addition to different speeds, there are other differences between certain categories of networks. When we mean local area networks, here each device is equipped with its own network adapter that connects it to other computers. For similar purposes in urban networks, special switching devices are used. As for the wide area networks, they use routers with high power. They are linked by communication channels.
Network infrastructure
A computer network includes components that can be easily combined into separate groups. Thus, they are as follows:
1. Active network equipment.
2. Cable system.
3. Means of communication.
4. Network applications.
5. Network protocols.
6. Network services.
Each of the presented groups has its own subgroups and additional components. All devices connected to a specific network are designed to transmit data in accordance with an algorithm. It must be understood by other devices that are included in the system.
Network administration tasks
Network administration involves working with a specific system at various levels. If there are complex corporate networks, administration is designed to solve the following tasks:
Network planning (as you know, the installation of the system and the installation of all its components, as a rule, are performed by the appropriate specialists, therefore the network administrator often has to change the system, including removing or adding individual elements to it);
configuring network nodes (administration of local networks in this case works with active network equipment, as a rule, it is a network printer);
setting up network services (a complex network can have an extensive set of network services, including network infrastructure, directories, files in print, as well as access to databases, etc.);
troubleshooting (network administrators have the ability to find all possible malfunctions, including problems with the router, as well as failures in the settings of network protocols and services).
installation of network protocols (in this case, this includes such work as planning and further configuring network protocols, testing and identifying the optimal configuration);
search for ways to increase the efficiency of the network (this can include the search for bottlenecks that need to be replaced by the corresponding equipment);
monitoring network nodes, as well as network traffic;
ensuring data protection (backup, development of a security policy for personal information of users, the use of secure communication, etc.).
It is also worth noting that all the tasks mentioned above must be performed in parallel and comprehensively.
Administration of security means Administration of security means involves working simultaneously in several directions, which include:
1. Dissemination of relevant information required for the operation of security tools.
2. Collecting and analyzing information about the operation of security mechanisms (in this case, the administration of local networks consists of working with the security management information base).
At the same time, the administrator has the following tasks:
Generation and redistribution of keys;
configuring, as well as managing access to the network;
managing encryption using appropriate crypto parameters;
configuring and managing traffic and routing.
In addition, the system administrator must distribute the data to users. This information is required to ensure successful authentication. This data includes passwords, keys, and more.
Protecting your system from viruses and malware
Microsoft Windows has a dedicated Information Assurance Center that is responsible for protecting the system from viruses and malicious software. Also, the operating system is capable of performing the functions of protection against hacking, as well as automatic updating of its data. However, the system administrator is required to perform additional tasks, the purpose of which is to ensure the security of the computer network. Here are the main tasks:
Access to the computer using all kinds of device IDs;
setting a ban on writing data to removable drives;
encryption of removable media and so on.
Network administration is actions that are aimed at ensuring the security policy, reliability, and availability of information resources of the network. For this purpose, appropriate software and hardware are used. As for the system administrator, he has many responsibilities and tasks.
At the beginning of their history, all computers were autonomous and operated separately from each other. With the increase in the number of machines, it became necessary to work together. In particular, this concerned the work of users on one document. The solution to this problem was the use of global and local networks. The construction of networks made it necessary to manage this process, as well as to perform various tasks. Network administration took over these functions.
Basic network administration functions
According to international standards, network administration has the following functions:
- Failure management. This includes finding, correctly identifying and fixing all problems and failures in the operation of a particular network.
- Configuration management. We are talking about the configuration of system components, including their location, network addresses, network operating systems, etc.
- Accounting for network operation. Computer network administration includes registration and subsequent control over the resources and network devices used.
- Performance management. It is about providing statistical information about network performance for a specified period of time. This is done in order to minimize the cost of resources and energy, as well as to plan resources for future needs.
- Security management. The function is responsible for controlling access and maintaining the integrity of all data.

Different sets of these functions are embodied in the products of developers of tools for networks.
Responsibilities of the system administrator
Administration of computer networks is carried out under the control and guidance of the system administrator, who has the following tasks:
Checking the health of databases.
- Control over the smooth operation of local networks.
- Protecting data and ensuring its integrity.
- Protecting the network from illegal access.
- Adjustment of access rights of local network users to network resources.
- information.
- Use programming best practices to make full use of available tools and network resources.
- Keeping special journals on the network.
- Implementation of training for local network users.
- Control over the software used.
- Control over the improvement of the local computer network.
- Development of access rights to the network.
- Suspension of illegal modification of software for the network.

The system administrator is also responsible for informing the employees of a particular enterprise or organization about the weak points of the network administration system and possible ways of illegal access to it.
Features and criteria for planning systems
Before installing a computer network, you need to find answers to the following questions:
- What tasks will the system solve and what functions will the system perform?
- How will the computer network be built? (its type, routing, etc.)
- How many and which computers will be present on the network?
- What programs for network administration will be used?
- What is the organization's security policy, where will the systems be installed, etc.

Answers to these questions will allow you to create a system of criteria for a specific computer network, which will include the following points:
- Preparation, control and testing of programs that will be used on a daily basis in the network.
- Control over the performance and health of the computers used.
- Preliminary preparation of system recovery procedures in case of errors or failures.
- Control that the subsequent installation of a new system will not have a negative impact on the network.
For all these purposes, staff and users need to be trained.
Remote administration software
If it is necessary to control the system outside the organization, remote network administration is used. For these purposes, special software is used that allows control over the system and remote access via the Internet in real time. Such programs provide almost complete control over remote elements of the local network and each computer separately. This makes it possible to remotely control the desktop of each computer on the network, copy or delete different files, work with programs and applications, etc.

There are a huge number of programs for remote access. All programs differ in their protocol and interface. As for the latter, the interface can be console or visual. Common and popular programs are, for example, Windows Remote Desktop, UltraVNC, Apple Remote Desktop, Remote Office Manager, etc.
Categories of networks
A network is a collection of various hardware, software, and communication tools that are responsible for the efficient allocation of information resources. All networks can be divided into three categories:
- Local.
- Global.
- Urban.
Global networks provide interaction and data exchange between users who are located at great distances from each other. During the operation of such networks, small delays in the transmission of information may appear, which is caused by the relatively low data transfer rate. The length of global computer networks can reach thousands of kilometers.
Urban networks operate in a smaller area, so they provide information at medium and high speeds. They do not slow down data as much as global ones, but they cannot transmit information over long distances. The length of such computer networks ranges from several kilometers to several hundred kilometers.
The local network provides the fastest speed Usually the local network is located inside one or several buildings, and its length is no more than one kilometer. Most often, a local network is built for one specific organization or enterprise.
Data transmission mechanisms in different networks
The method of transferring information in global and local networks is different. Global computer networks are primarily connection-oriented, i.e. before starting data transfer between two users, you must first establish a connection between them. Local computer systems use other methods that do not require prior communication. In this case, information is sent to the user without receiving confirmation of his readiness.

In addition to the difference in speed, there are other differences between the indicated categories of networks. If we are talking about local networks, then here each computer has its own network adapter that connects it to the rest of the computers. For the same purposes in urban networks, special switching devices are used, while global networks use powerful routers that are interconnected by communication channels.
Network infrastructure
A computer network consists of components that can be combined into separate groups:
- Active network equipment.
- Cable system.
- Communication means.
- Network applications.
- Network protocols.
- Network services.
Each of these levels has its own sublevels and additional components. All devices that connect to an existing network must transmit data in accordance with an algorithm that will be understood by other devices in the system.
Network administration tasks
Network administration foresees working with a particular system at a variety of levels. In the presence of complex corporate networks, the administration faces the following tasks:
- Network planning. Despite the fact that the installation of the system and the installation of all components are usually carried out by the appropriate specialists, the network administrator quite often has to change the system, in particular, remove or add individual components to it.
- Configuring network nodes. In this case, the administration of local networks foresees working with an active one, most often with a network printer.
- Configuring network services. A complex network can have an extensive set of network services, which include network infrastructure, directories, files in print, database access, etc.
- Troubleshooting. Network administration foresees the ability to troubleshoot all possible problems, ranging from problems with the router, and ending with problems in the settings of network protocols and services.
- Network protocol settings. This includes activities such as planning and then configuring network protocols, testing them, and determining the optimal configuration.
- Finding ways to improve the efficiency of the network. In particular, we are talking about finding bottlenecks that require replacement of the corresponding equipment.
- Monitoring of network nodes and network traffic.
- Ensuring the protection of information. This includes backing up data, developing a security policy for user accounts, using secure communications, etc.
All of these tasks should be performed in parallel and comprehensively.
Security Administration
Security administration envisions work in several directions:
- Dissemination of relevant information necessary for the operation of security tools.
- Collection and analysis of data on the functioning of security mechanisms.
Administration of local networks in this case includes work with the security management infobase. The duties of the adnimistar in this matter include the following tasks:
- Generation and redistribution of keys.
- Configuring and managing network access.
- Management of encryption using appropriate crypto parameters.
- Configuring and managing traffic and routing.
The system administrator should also distribute information to users that is necessary for successful authentication (passwords, keys, etc.).

Protecting your system from malware
Microsoft Windows has a special Information Assurance Center that is responsible for protecting the system from malicious software. In addition, the operating system also has anti-tampering features and automatic updates of all data. Despite this, the system administrator is required to perform additional tasks aimed at protecting the computer network:
- Access to the computer using different device IDs.
- Setting a ban on writing information to removable disks.
- Encryption of removable media, etc.
Network administration is actions aimed at implementing the security policy, reliability and availability of information resources of the network. For these purposes, the appropriate software is used and a number of responsibilities and tasks are declared on the system administrator.
Ais tickets
1Administration. The ratio of system and network administration 2
2Administration. Network Administration 4
3Administration. System Administration 5
4Administration. IT service management. Challenges and prospects 7
5ITSM, Resolving Issues, Need for Use 9
6ITIL, communication with ITSM 10
7 ITIL Benefits and Potential Challenges 11
8 ITIL Library Books 12
9ITIL, provision of services 13
10ITIL, service support 15
11Other ITIL books. Certification 16
12 Standards, Theories and Methodologies 17
13ITPM, composition, differences 18
14ITPM for enterprises. IRM - ITPM 19 Idea Guide
15 Tivolli Enterprise Architecture 20
16TMF (Tivoli Management Framework) 21
17Tivoli. Main disciplines of management and control applications. Deploy software 22
18Tivoli. Main disciplines of management and control applications. Making Networks and Systems Available 23
19Tivoli. Main disciplines of management and control applications. Process automation. Security of information resources 24
20Tivoli. Service Desk (3 applications) 25
21Tivoli. Information Infrastructure Management (GEM), Application Management 26
Administration. The ratio of system and network administration
AdministrationThe purpose
The history of system administration goes back several decades. Due to the host-terminal architecture that dominated the 1980s, the organization of the administrative software was also centralized. In the 90s, the rapid spread of the client-server architecture led to dramatic changes: instead of monitoring a homogeneous environment, the administrator had to solve many problems: accounting for resource allocation, license control, load redistribution, etc.
From the point of view of the tasks being solved, when mainframes prevailed, their administration could be attributed to the category system administration... With the advent of distributed architecture, management tasks were limited to overseeing the functioning of individual components. System administration includes:
Solving problem situations
Resource management
Configuration management
Performance monitoring
Data management
Network administration arose when administrators had the ability to control the image of the entire network. For some time, network administration began to be viewed as the main concern of IS administrators, which did not quite correspond to the logic of the functioning of the CIS. the network is just an infrastructure. Network administration includes:
Monitoring the operation of network equipment
General network management
When the number of distributed applications exceeded a certain threshold, the process of integrating system and network administration was inevitable. Network administration came to be seen as a component of system administration, and the network as one of the managed resources.
Administration. Network administration
Administration Are control procedures that regulate some or part of the processes. These processes include work planning, construction, operation and support of an effective IT infrastructure integrated into the overall architecture of the information system. The purpose administration is the achievement of such parameters of the functioning of the IS that would meet the needs of users.
Network administration includes:
Monitoring the operation of network equipment- monitoring of individual network devices, setting and changing their configuration, eliminating failures. Also called reactive control.
General network management- monitoring network traffic, identifying trends in its change and analyzing events to anticipate network problems. It uses a single view of the network for the purposes of making changes to the network, accounting for network resources, managing IP addresses, filtering packets. Also called preventive administration.
The most common architecture is manager-agent. The manager is launched on the control console and constantly interacts with agents on the network devices. Agents collect local data on the parameters of the network device.
Now a three-tier scheme is used: part of the control is delegated to the most important network nodes. The nodes are installed with manager programs, which, through their own network of agents, control the operation of devices, and they themselves are agents of the central manager. Local and central managers only interact when needed.
The networking software industry is divided into three parts:
Network Management Platforms
Management applications from network hardware manufacturers
Third party software aimed at solving narrow problems of network administration
Introduction ............................................................................................................... 3
Defining the network infrastructure ............................................... ...................... 5
Network Administration ................................................ ................................ 7
Monitoring ................................................. .................................................. ..... 13
Conclusion................................................. .................................................. ....... eighteen
List of used literature ............................................... .................. twenty
In our age of computer technology, no company can do without the use of computers. And if there are several computers, then they, as a rule, are combined into a local area network (LAN).
A computer network is a system of interconnected computers, as well as, possibly, other devices called nodes (workstations) of the network. All computers on the network are connected to each other and can exchange information.
As a result of combining computers into a network, opportunities arise:
Increasing the speed of information message transmission
Rapid exchange of information between users
Expansion of the list of services provided to users by combining significant computing power in a network with a wide range of various software and peripheral equipment.
Using distributed resources (printers, scanners, CD-ROMs, etc.).
Having structured information and efficiently finding the data you need
Networks offer tremendous benefits that cannot be achieved with computers alone. Among them:
Sharing processor resources. By dividing processor resources, it is possible to use computing power for the simultaneous processing of data by all stations in the network.
Data separation. Data sharing allows you to manage databases from any workstations that need information.
Shared Internet access. LAN allows you to provide access to the Internet for all its clients using only one access channel.
Sharing resources. A LAN allows you to economically use expensive resources (printers, plotters, etc.) and access them from all connected workstations.
Multimedia capabilities. Modern high-speed technologies make it possible to transmit audio and video information in real time, which allows video conferencing and network communication without leaving the workplace.
LANs have found wide application in computer-aided design and technological preparation of production systems, production control systems and technological complexes, in office systems, on-board control systems, etc. LAN is an effective way to build complex management systems for various production departments.
Defining the network infrastructure
A network infrastructure is a collection of physical and logical components that provide connectivity, security, routing, management, access, and other required network properties.
Most often, the network infrastructure is determined by the project, but much is determined by external circumstances and "inheritance". For example, connecting to the Internet requires supporting technologies such as TCP / IP. Other network parameters, such as the physical layout of the main elements, are determined during the design, and then are inherited by later versions of the network.
The physical infrastructure of a network means its topology, that is, the physical structure of the network with all its equipment: cables, routers, switches, bridges, hubs, servers and nodes. Physical infrastructure also includes transport technologies: Ethernet, 802.11b, public switched telephone network (PSTN), ATM - collectively, they determine how communication is carried out at the level of physical connections.
The logical network infrastructure consists of all the set of software elements that are used for communication, control and security of network nodes, and provides communication between computers using communication channels defined in the physical topology. Examples of logical network infrastructure elements include Domain Name System (DNS), network protocols such as TCP / IP, network clients such as Client Service for NetWare, and network services such as Quality of Service Packet Scheduler (QoS).
Maintaining, administering and managing the logical infrastructure of an existing network requires in-depth knowledge of many network technologies. A network administrator, even in a small organization, must be able to create different types of network connections, install and configure the required network protocols, be familiar with manual and automatic addressing and name resolution methods, and finally troubleshoot communication, addressing, access, security, and name resolution issues. In medium and large networks, administrators have more complex tasks: setting up dial-up remote access and virtual private networks (VPN); Create, configure, and troubleshoot interfaces and routing tables Creation, maintenance and troubleshooting of the public key security subsystem; serving mixed networks with different operating systems, including Microsoft Windows, UNIX and Nowell NetWare.
Network administration.
Modern corporate information systems, by their nature, are always distributed systems. User workstations, application servers, database servers, and other network nodes are spread over a large area. In a large company, offices and sites are connected by various types of communications using various technologies and network devices. The main task of the network administrator is to ensure reliable, uninterrupted, productive and secure operation of this entire complex system.
We will consider a network as a set of software, hardware and communication tools that ensure the efficient allocation of computing resources. All networks can be roughly divided into 3 categories:
local networks (LAN, Local Area Network);
global networks (WAN, Wide Area Network);
city networks (MAN, Metropolitan Area Network).
Global networks make it possible to organize interaction between subscribers over long distances. These networks operate at relatively low speeds and can introduce significant delays in the transmission of information. The length of global networks can be thousands of kilometers. Therefore, they are somehow integrated with national-scale networks.
Urban networks allow communication in smaller territorial entities and operate at medium to high speeds. They slow down data transfer less than global ones, but they cannot provide high-speed communication over long distances. The length of urban networks ranges from several kilometers to tens and hundreds of kilometers.
Local networks provide the highest speed of information exchange between computers. A typical local area network takes up space in one building. The length of local networks is about one kilometer. Their main purpose is to bring together users (usually the same company or organization) to work together.
Data transmission mechanisms in local and global networks differ significantly. Global networks are connection-oriented - before the start of data transmission, a connection (session) is established between subscribers. In local networks, methods are used that do not require preliminary connection establishment - a packet with data is sent without confirmation of the recipient's readiness for exchange.
In addition to the difference in data transfer rates, there are other differences between these categories of networks. In local networks, each computer has a network adapter that connects it to the transmission medium. Metropolitan area networks contain active switching devices, and wide area networks are usually made up of groups of powerful packet routers connected by links. In addition, networks can be private or public.
The network infrastructure is built from various components, which can be conditionally divided into the following levels:
1. cable system and means of communication;
2. active network equipment;
3. network protocols;
4. network services;
5. network applications.
Each of these levels can be composed of different sublevels and components. For example, cable systems can be built on the basis of coaxial cable ("thick" or thin "), twisted pair (shielded and unshielded), fiber. Active network equipment includes such types of devices as repeaters (repeaters), bridges, hubs, switches, routers A rich set of network protocols can be used in a corporate network: TCP / IP, SPX / IPX, NetBEUI, AppleTalk, etc.
The basis of the network is the so-called network services (or services). The basic set of network services for any corporate network consists of the following services:
Network infrastructure services DNS, DHCP, WINS;
File and Print Services;
Directory services (e.g. Novell NDS, MS Active Directory);
Messaging services;
Database access services.
The highest level of network functioning is network applications.
The network makes it easy for a wide variety of computer systems to interact with each other thanks to standardized communication methods that hide the variety of networks and machines from the user.
All devices operating in the same network must communicate in the same language - transmit data in accordance with a well-known algorithm in a format that will be understood by other devices. Standards are a key factor in network interconnection.
network administrator - a specialist responsible for the normal operation and use of network resources. In more detail, then administration information systems includes the following goals:- Installation and configuration of the network. Support for its further performance.
- Monitoring. System planning.
- Installation and configuration of hardware devices.
- Installing software.
- Archiving (backup) information.
- User creation and management.
- Installation and control of protection.
Here is a summary of the network administrator's job responsibilities:
- Installs network software on servers and workstations.
- Configures the system on the server.
- Provides software integration on file servers, database management system servers and workstations.
- Maintains the working state of the server software.
- Registers users, assigns IDs and passwords.
- Teaches users how to work in the network, maintain archives; answers users' questions related to working in the network; draws up instructions for working with the network software and brings them to the attention of users.
- Monitors the use of network resources.
- Organizes access to local and global networks.
- Sets limits for users by:
- using a workstation or server;
- time;
- degree of resource use.
- Provides timely backup and backup of data.
- Turns to technical personnel when troubleshooting network equipment.
- Participates in the restoration of system performance in case of failures and failure of network equipment.
- Detects errors of users and network software and restores system performance.
- Monitors the network, develops proposals for the development of network infrastructure.
- Provides:
- network security (protection against unauthorized access to information, viewing or changing system files and data);
- security of interconnection.
- Prepares proposals for the modernization and purchase of network equipment.
- Carries out control over the installation of equipment by specialists of third-party organizations.
- Informs his line manager about cases of abuse of the network and the measures taken.
- Keeps a log of system information, other technical documentation.
- ………………………………………………………………………………………………
User groups - what are they and why?
All network users are divided into groups according to their authority. Each group can be responsible for performing certain tasks. It is possible to define the rights of user groups in such a way that users have all the rights they need to perform their functions, but nothing more. Only one user, the administrator (supervisor) of the network, should have full all rights. He has all the rights, including the ability to create user groups and determine the rights that they have.
Users can be members of several groups at the same time. You can, for example, create a new directory and allow access to it for all network users at once. In this case, you will have to change access rights not for all users (there may be several dozen of them), but only for one group, which is much easier. It makes sense for each laboratory or department to create its own user group. If you have users who require additional rights (for example, access rights to some directories or network printers), create the appropriate user groups and grant them these rights.
If there are many workstations on the network that are located in different rooms and belong to different departments or laboratories, it makes sense to create a group of network administrators. The rights of multiple network administrators are determined by the system administrator. Do not give network administrators all system administrator rights. It is quite enough if in each department or laboratory there will be one or two administrators who have management rights only for users working in this department or laboratory. If the department or laboratory has a network printer or any other network resources, the administrator must have rights to manage these devices. However, there is no need at all for the administrator of one laboratory to be able to manage a network printer belonging to another laboratory. At the same time, users should have the minimum access rights to the server disks necessary for normal operation.
Thus, it is obvious that the creation of user groups is relevant only in large computer networks. If the network is small, then one person can handle issues such as adding new users, access control there is no point in creating groups of administrators and regular users to server drives, network printers and other network resources.
Creating a user group
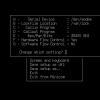
We start the server on the virtual machine. Let's get a command mmc and add to the console the equipment we will work with - DNS, DHCP, AD Users and Computers... This requires the command Console-Add or Remove Snap-in-Add(fig.55.1.
Rice. 55.1.
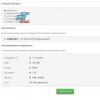
Now in AD right click and run the command Create-Group(fig.55.2 and (fig.55.3).

Rice. 55.2.
Security group assigns access rights to network resources (administers). Distribution group cannot administer, she is engaged in sending messages. Domain local can contain a user of any domain in the forest, but this group can be administered only in the domain in which the group was created. The global can contain users from the domain in which it was created, but they can be administered by anyone