Vulnerability management is the identification, assessment, classification and selection of a solution to remediate vulnerabilities. Vulnerability management is based on vulnerability information repositories, one of which is the Prospective Monitoring Vulnerability Management System.
Our solution controls the appearance of information about vulnerabilities in operating systems (Windows, Linux / Unix-based), office and application software, hardware software, information security tools.
Data sources
The Vulnerability Management System database of the Prospective Monitoring software is automatically updated from the following sources:
- Information Security Threats Databank (BDU BI) FSTEC of Russia.
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD) NIST.
- Red Hat Bugzilla.
- Debian Security Bug Tracker.
- CentOS Mailing List.
We also use an automated method to replenish our vulnerability database. We have developed a web page crawler and unstructured data parser, which every day analyze more than a hundred different foreign and Russian sources for a number of keywords - groups in social networks, blogs, microblogs, media dedicated to information technology and information security. If these tools find something that matches the search criteria, the analyst manually checks the information and enters the vulnerability database.
Control software vulnerabilities
Using the Vulnerability Management System, developers can monitor the presence and status of detected vulnerabilities in third-party components of their software.
For example, in Hewlett Packard Enterprise's Secure Software Developer Life Cycle (SSDLC) model, third-party library control is central.
Our system monitors for vulnerabilities in parallel versions / builds of one software product.
It works like this:
1. The developer gives us a list of third-party libraries and components that are used in the product.
2. We check daily:
b. whether there are methods to eliminate previously discovered vulnerabilities.
3. We notify the developer if the status or scoring of a vulnerability has changed in accordance with the specified role model. This means that different development teams of the same company will receive alerts and see the status of vulnerabilities only for the product they are working on.
The frequency of the Vulnerability Management System alerts is customizable, but if a vulnerability with a CVSS score greater than 7.5 is found, developers will receive immediate alerts.
Integration with ViPNet TIAS
The ViPNet Threat Intelligence Analytics System hardware and software complex automatically detects computer attacks and detects incidents based on information security events received from various sources. The main source of events for ViPNet TIAS is ViPNet IDS, which analyzes incoming and outgoing network traffic using the AM Rules decision rule bases developed by "Perspective Monitoring". Some signatures are written to detect exploitation of vulnerabilities.
If ViPNet TIAS detects an information security incident in which a vulnerability was exploited, then all information related to the vulnerability is automatically entered into the incident card from the CMS, including methods of eliminating or compensating for the negative impact.
The incident management system also helps in the investigation of information security incidents, providing analysts with information about indicators of compromise and potential information infrastructure nodes affected by the incident.
Monitoring of vulnerabilities in information systems
Another use case for the vulnerability management system is on-demand scanning.
The customer independently generates a list of system and application software and components installed on the node (AWP, server, DBMS, PAC SZI, network equipment), using built-in tools or a script developed by us, of system and application software and components, transfers this list to the control system and receives a report on the vulnerabilities detected and periodic notifications about them status.
Differences between the System and common vulnerability scanners:
- Does not require installation of monitoring agents on the nodes.
- It does not create a load on the network, since the very architecture of the solution does not provide for agents and scan servers.
- It does not put a load on the hardware, since the list of components is created by system commands or a lightweight open source script.
- Eliminates the possibility of information leakage. "Prospective monitoring" cannot reliably know anything about the physical and logical location or functional purpose of a node in an information system. The only information that leaves the controlled perimeter of the customer is a txt file with a list of software components. This file is checked for content and uploaded to the CMS by the customer himself.
- For the system to work, we do not need accounts on controlled nodes. Information is collected by the site administrator on his own behalf.
- Safe exchange of information via ViPNet VPN, IPsec or https.
Connection to the Perspective Monitoring vulnerability management service helps the customer to fulfill the ANZ.1 requirement "Identification, analysis of information system vulnerabilities and prompt elimination of newly discovered vulnerabilities" of FSTEC orders No. 17 and 21. Our company is a licensee of FSTEC of Russia for technical protection of confidential information.
Price
The minimum cost is 25,000 rubles per year for 50 nodes connected to the system with a valid contract for connecting to
Another way to look at this problem is that companies need to react quickly when an application has a vulnerability. This requires the IT department to be able to definitively track installed applications, components, and patches using automation and industry standard tools. There are industry efforts to standardize software tags (19770-2), which are XML files installed with an application, component, and / or patch that identify the installed software, and in the case of a component or patch, which application they are part of. Tags have authoritative publisher information, version information, a file listing with the filename, a secure file hash, and size that can be used to confirm that the installed application is on the system and that the binaries have not been modified by a third party. These labels are digitally signed by the publisher.
When a vulnerability is known, IT departments can use their asset management software to immediately identify systems with vulnerable software and can take steps to update systems. Tags can be part of a patch or update that can be used to verify that the patch is installed. In this way, IT departments can use resources such as the NIST National Vulnerability Database as a tool to manage their asset management tools, so that once a vulnerability is submitted by the company to NVD, IT can immediately compare the new vulnerabilities with theirs. by now.
There is a group of companies working through a non-profit organization IEEE / ISTO called TagVault.org (www.tagvault.org) with the US government on a standard implementation of ISO 19770-2 that will enable this level of automation. At some point, these tags corresponding to this implementation are likely to be mandatory for software sold to the US government at some point in the next couple of years.
Therefore, in the end, it is good practice not to post about which applications and specific software versions you are using, but this can be difficult, as stated earlier. You want to make sure you have an accurate, up-to-date software inventory, that it is regularly compared against a list of known vulnerabilities such as NVID from NVD, and that IT can take immediate action to reminder the threat.This is along with the latest detection intrusions, antivirus scans and other methods of blocking the environment, at the very least, it will be very difficult to compromise your environment, and if / when it does, it will not be detected for a long period of time.
At startup intelligent scan Avast will scan your PC for the following types of problems and then suggest solutions.
- Viruses: files containing malicious code that can affect the security and performance of your PC.
- Vulnerable software: programs that require updating that can be used by intruders to access your system.
- Bad Reputation Browser Extensions: Browser extensions that are usually installed without your knowledge and have an impact on system performance.
- Weak passwords: passwords that are used to access more than one Internet account and can be easily hacked or compromised.
- Network Threats: Vulnerabilities in your network that could make it possible for attacks on your network devices and router.
- Performance issues: Objects (unnecessary files and applications, settings problems) that can interfere with the operation of the PC.
- Conflicting antiviruses: Antivirus software installed on your PC with Avast. Having multiple antivirus programs slows down your PC and reduces the effectiveness of antivirus protection.
Note... A separate license may be required to resolve certain issues found during smart scan. Detection of unnecessary problem types can be disabled in.
Solving the problems found
A green check mark next to the scan area indicates that no problems were found with it. A red cross means the scan has identified one or more related problems.
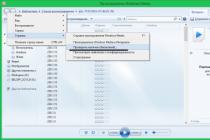
To see specific information about the issues found, click Solve all... Smart Scan shows details of each issue and offers the option to fix it immediately by clicking on Decide, or do it later by pressing Skip this step.
Note... Antivirus scan logs can be seen in the scan history, which can be accessed by selecting Protection Antivirus.
Managing Smart Scan Settings
To change smart scan settings, select Settings General Smart Scan and indicate which of the listed types of problems you want to perform smart scan for.
- Viruses
- Outdated software
- Browser add-ons
- Network Threats
- Compatibility issues
- Performance issues
- Weak passwords
All problem types are enabled by default. To stop checking for a specific issue while performing smart scan, click the slider Included next to the problem type so that it changes state to Turned off.
Click Settings next to the inscription Scanning for viruses to change the scan settings.
Currently, a large number of tools have been developed to automate the search for program vulnerabilities. This article will cover some of them.
Introduction
Static code analysis is software analysis that is performed on the source code of programs and is implemented without actually executing the program under study.
Software often contains various vulnerabilities due to errors in the program code. Errors made during the development of programs, in some situations, lead to a program failure, and, consequently, the normal operation of the program is disrupted: in this case, data changes and corruption, the program or even the system stop, often occurs. Most of the vulnerabilities are associated with incorrect processing of data received from outside, or insufficient verification of them.
To identify vulnerabilities, various tools are used, for example, static analyzers of the program source code, an overview of which is given in this article.
Classification of security vulnerabilities
When the requirement for the correct operation of the program on all possible input data is violated, the appearance of so-called security vulnerabilities becomes possible. Security vulnerabilities can lead to the fact that one program can be used to overcome the security limitations of the entire system as a whole.
Classification of security vulnerabilities depending on software errors:
- Buffer overflow. This vulnerability arises from the lack of control over the out-of-bounds of an array in memory during program execution. When a data packet that is too large overflows a buffer of limited size, the contents of the foreign memory cells are overwritten, and the program crashes and exits. Based on the location of the buffer in the process memory, there are buffer overflows in the stack (stack buffer overflow), heap (heap buffer overflow) and static data area (bss buffer overflow).
- Tainted input vulnerability. Tainted input vulnerabilities can arise when user input is passed without sufficient control to the interpreter of some external language (usually the Unix shell or SQL). In this case, the user can specify the input data in such a way that the launched interpreter will execute a command that is completely different from the one intended by the authors of the vulnerable program.
- Format string vulnerability errors. This type of security vulnerability is a subclass of tainted input vulnerability. It occurs due to insufficient control of parameters when using the format I / O functions printf, fprintf, scanf, etc. of the C standard library. These functions take as one of the parameters a character string that specifies the format for the input or output of subsequent arguments to the function. If the user is able to specify the type of formatting, then this vulnerability can arise as a result of unsuccessful use of string formatting functions.
- Vulnerabilities as a consequence of timing errors (race conditions). Problems associated with multitasking lead to situations called "race conditions": a program that is not designed to run in a multitasking environment may think that, for example, the files it uses in its work cannot be changed by another program. As a result, an attacker who replaces the contents of these working files in time can force the program to perform certain actions.
Of course, besides the listed ones, there are other classes of security vulnerabilities.
Overview of existing analyzers
The following tools are used to detect security vulnerabilities in programs:
- Dynamic debuggers. Tools that allow you to debug a program during its execution.
- Static analyzers (static debuggers). Tools that use information accumulated during the static analysis of a program.
Static analyzers indicate those places in the program where the error may be found. These suspicious code snippets may contain an error or be completely safe.
This article provides an overview of several existing static analyzers. Let's take a closer look at each of them.