The hosts file is a rather vulnerable place in the Windows operating system. This file becomes the number one target for almost all viruses and Trojans that manage to infect a computer.
The task of this file is to store a list of domains and their corresponding ip-addresses. The operating system uses this list to convert domains to IP addresses and vice versa.
Every time you enter the address of the site you need in the address bar of the browser, a request is made to convert the domain to an ip address. Now this conversion is performed by a service called DNS. But, at the dawn of the development of the Internet, the hosts file was the only way to associate a symbolic name (domain) with a specific ip-address.
Even now, this file has a direct effect on the translation of symbolic names. If you add an entry to the hosts file that will associate the ip address with the domain, then such an entry will work fine. This is exactly what developers of viruses, trojans and other malicious programs use.
As for the file structure, the hosts file is a plain text file with no extension. That is, this file is not called hosts.txt, but simply hosts. To edit it, you can use the usual text editor Notepad (Notepad).

The standard hosts file consists of several lines that begin with the "#" character. Such lines are ignored by the operating system and are simply comments.
Also in the standard hosts file there is an entry "127.0.0.1 localhost". This entry means that when you access the symbolic name localhost, you will be accessing your own computer.
Fraud with the hosts file
There are two classic ways to benefit from making changes to the hosts file. Firstly, it can be used to block access to sites and servers of anti-virus programs.
For example, after infecting a computer, a virus addsthe following entry in the hosts file: "127.0.0.1 kaspersky.com". When you try to open the kaspersky.com website, the operating system will connect to the IP address 127.0.0.1. Naturally, this is the wrong ip-address. This leads to access to this site is completely blocked.As a result, the user of the infected computer cannot download antivirus or anti-virus database updates.
In addition, virus developers can use another trick. By adding entries to the hosts file, they can redirect users to a fake site.
For example, after infecting a computer, the virus adds the following entry to the hosts file: “90.80.70.60 vkontakte.ru”. Where "90.80.70.60" is the ip address of the attacker's server. As a result, when trying to access a well-known site, the user gets to a site that looks exactly the same, but is located on someone else's server. As a result of such actions, fraudsters can get logins, passwords and other personal information of the user.
So in case of any suspicion of a virus infection or site spoofing, the first thing to do is to check the HOSTS file.
The malware masks modification of the hosts file in the following way:
To make it difficult to detect lines added by a virus, they are written to the end of the file.
After a vast empty area formed as a result of repeated line feeds;
After that, the original hosts file is assigned the Hidden attribute (by default, hidden files and folders are not visible);
A fake hosts file is created, which, unlike the real hosts file (which has no extension), has a .txt extension (by default, extensions are not displayed for registered file types):

Where is the hosts file
Depending on the version of the Windows operating system, the hosts file can be located in different folders. For example, if you use Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows 8, the file is located in the folderWINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\

On Windows NT and Windows 2000 operating systems, this file is located in the folder WINNT\system32\drivers\etc\
Editing the hosts file
You can edit the file hosts and in Notepad, delete unnecessary lines, or add your own.
In order to edit the hosts file, you need to start notepad in Administrator mode, and then open the file C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts.
How to clean the hosts file
So, point by point.
Click "Start".

Choose "All programs".
Then select the item "Standard".
Click on Notepad right mouse button and select "Run as administrator".
In the Notepad window that opens, select the File menu, then the item "Open..."
In the window that opens, select "Computer" on the left side of the window. 
Then open the disk WITH:.
Windows directory. 
system32 directory. 
The drivers directory. 
directory etc. 
When you open the etc directory, you will have an empty directory. In the lower right corner of the window, select "All files".
Select the hosts file and click the button "Open".
Check for the necessary content: at the beginning there are explanatory comments from Microsoft about what this file is and how to use it. Then some examples of how to enter various commands are given. All this, simple text and it does not carry any functions! Let's skip it and get to the end. The teams themselves should go next. Unlike comments (i.e. plain text), they must begin not with "#" sign, and with specific numbers, denoting the ip address.
Malicious commands can be any commands that appear in your hosts file after the following lines:
- On Windows XP: 127.0.0.1 localhost
- On Windows Vista: ::1 localhost
- On Windows 7/8: # ::1 localhost
As you can see, the host files in different operating systems are slightly different.
In order not to clean up anything superfluous, you need to know how commands are decrypted. There is nothing complicated here. At the start of each command is digital ip address, then (separated by a space) the letter associated with it Domain name, and after it there may be a small a comment after the "#" sign.
Remember!
All commands starting from numbers 127.0.0.1(with the exception of, 127.0.0.1 localhos t) block access to various websites and Internet services. To which ones, see in the next column after these numbers.
Teams that start with any other numbers ip addresses, redirect(make a redirect) to fraudulent sites instead of the official ones. Which sites have been replaced by fraudulent ones, also look in each column after these numbers.
Thus, it will not be difficult to guess which commands in your hosts file are malicious! If something is still not clear - look at the screenshot below.

Take note of this moment. Many virus commands can be hidden far at the very bottom of the file by cunning Internet intruders, so be sure to scroll the slider all the way down!

After you do the "cleanup", don't forget to save all changes ( "File" --> "Save"). If you opened the hosts file from the Notepad program itself, when saving changes, in the column "File type" be sure to select an option "All files", otherwise notepad will only do it instead of saving in the hosts file text copy of hosts.txt, which is not a system file and does not perform any functions!

After a successful save, do not forget to restart your computer.
How to block websites in hosts
So, the hosts file is already open and you can see that it is built in the form of a regular text document.
At the beginning, you will see comments (plain text that does not carry any functionality) starting with the symbol "#" . They may be followed by some functional commands prescribed by the system.
But we don't need them. We skip them and get to the very end of the document. We make a retreat. And now, here, it is already possible to prescribe the commands we need!

When finished working with the file, open the File menu, select the item "Save".
To understand how to correctly enter web resource blocking commands, you need to know that each PC has its own so-called. loopback address A that sends any request back to itself. For any computer running Windows, Linux or Mac systems, this address is always the same - 127.0.0.1 . Here, with the help of just this ip-address, you can block any request to an unwanted site so that it is directed not to the requested resource, but to to the local computer.
This command in hosts is written as follows: " 127.0.0.1 blocked domain name ". Here, real examples: 127.0.0.1 mega-porno.ru, 127.0.0.1 odnoklassniki.ru, 127.0.0.1 vk.com etc.

That's all. Now access to all unwanted sites is securely blocked. The main thing after the changes made is to resave the hosts file! See above for detailed instructions.
Restoring the hosts file after a virus infection
As already mentioned, today a large number of malicious programs use the file hosts to block access to websites of popular portals or social networks. Often, instead of blocking sites, malware redirects the user to pages that look like popular resources (social networks, mail services, etc.), where an inattentive user enters credentials, which thus get to attackers.
If the file contains entries like 127.0.0.1 odnoklassniki.ru 127.0.0.1 vkontakte.ru or the addresses of your sites that you cannot access, then first check your computer for "malware", and then restore the file hosts
Many hacked users are interested in where they can download the hosts file. However, you do not need to search and download the original hosts file at all. You can fix it yourself, for this you need to open it with a text editor and delete everything except the line except "127.0.0.1 localhost". This will unblock access to all sites and update the antivirus.
Let's take a closer look at the process of restoring the hosts file:
1. Open the folder where this file is located. In order not to wander through the directories for a long time in search of the desired folder, you can use a little trick. Press key combination Windows+R to open the menu "Run". In the window that opens, enter the command "%systemroot%\system32\drivers\etc"and click OK.
2. After that, a folder will open in front of you in which the hosts file lies.
3. Next, you need to make a backup copy of the current file. In case something goes wrong. If the hosts file exists, just rename it to hosts.old. If the hosts file is not in this folder at all, then this item can be skipped.
4.Create a new empty hosts file. To do this, right-click in the etc folder and select"Create a text document"
5. When the file is created, it must be renamed to hosts. When renaming, a window will appear in which there will be a warning that the file will be saved without an extension. Close the warning window by clicking the OK button.
6. After the new hosts file has been created, it can be edited. To do this, open the file with Notepad.
7. Depending on the version of the operating system, the contents of the standard hosts file may differ.
This is how all, without exception, "clean" hosts files should look like. 


Note!
- For Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, add "127.0.0.1localhost"
- Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7 and Windows 8 need to add two lines: "127.0.0.1 localhost" and "::1 localhost"
If you ever find missing or, conversely, extra entries in such a file, it is better to delete them as soon as possible. Especially if they are not made by you or without your consent. Most likely, this is the result of the work of viruses!
Restoring the default hosts file in Windows 7: Copy the following text to a file.
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host # localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
Save and close the file.
The hosts file is the file that is responsible for the correct operation of your web browsers. It matches IP addresses with domain names. It depends on his work which sites and how they will open. Therefore, this file often becomes the target of virus programs that block the work of browsers.
Where is this file located, and how to restore it after damage in Win 7, we will consider further.
On Windows 7, this file is located at the following location: C: WINDOWS SYSTEM32 DRIVERS ETC. To access it, just enter this path in the address bar and press Enter.

Mostly this file is hidden, so before that you should enable the view of hidden files. To do this, in the Windows window menu "Tools" - "Folder Options" - select the "View" tab and put the switch in front of "Show hidden files and folders" in it.

Next, the hosts file needs to be edited. We open it with Notepad and remove all unnecessary. By default, this file should look like this.
Save it and restart your computer. It should be remembered that if extraneous entries appear in this file, then you must definitely check your operating system for viruses and delete them. If this is not done, then virus programs will again block the work of your browsers.
The hosts file is located along the path C:WindowsSystem32Driversetchosts (if C is the system drive). You can open it with regular notepad. If you have not made changes to the hosts file, then the following will be written there:
hosts file in Windows XP:
#
#
#space.
#
#
# For example:
#
127.0.0.1 localhost
hosts file in Windows Vista:
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost
hosts file in Windows 7:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2006 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
hosts file in Windows 8
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
As you can see, regardless of the version, the host file does not differ much, but if a virus "worked" on the hosts file, various sites and IP-shniks can be added there. For example:
127.0.0.1 ftp.kasperskylab.ru
127.0.0.1 ids.kaspersky-labs.com
127.0.0.1 vk.com
127.0.0.1 drweb.com
Such additions to the file prevent you from accessing the specified sites.
1.2.3.4 ftp.kasperskylab.ru
1.2.3.4 ids.kaspersky-labs.com
1.2.3.4 vk.com
1.2.3.4 drweb.com
Such additions to the file when opening the specified sites will redirect you to other sites, possibly infected with viruses (IP-1.2.3.4- are fictitious).
If you find that the hosts file has changed, you need to fix it. In Windows XP, the file is simply opened in notepad, the necessary changes are made and saved (you must be logged in as an administrator). On other versions (Windows Vista, 7, 8) you need to give permission to modify the file. To do this, open the folder containing hosts C:WindowsSystem32Driversetc (if C is a system drive). Right click on hosts and select "Properties".
Select the "Security" tab, then select the user under which you work on the computer / laptop (in this example, it is pk-help.com) and click the "Change" button. The "Permissions for the "hosts" group" window will open, select the user again and assign full rights to the file, click "OK", in the "Properties: hosts" window, also "OK".
After that, open hosts with Notepad and return the file to its original state, when finished, save the changes.
This file is a system file and is located in the system disk partition in the WindowsSystem32driversetc folder. In its format, this is a plain text file named hosts, but without the name extension. It consists of text lines and can be edited by any text editor. Each of its lines can be either a comment (in which case its first character is #) or a match specification that has a format.
There must be one or more spaces between the address and the name. For example, the line 102.54.81.91 rh.com associates the host rh.com with its address 102.54.81.91. During its installation, Windows 7 generates the standard content of this document, which looks like: How to restore hosts Sometimes a situation may arise when you need to restore the initial state of this file. It can occur either after its accidental deletion or distortion, or as a result of exposure to malware.
It should be said right away that administrator rights are required to access this file (including when restoring it). Its content can be generated manually in a text editor or downloaded from the Internet. Editing hosts Of course, in order to edit hosts, you need to have administrator rights. You can edit it with any text editor. As an example, we use the standard Notepad, which is always installed in Windows 7.
You can start it in two ways - from the command line and by directly calling Notepad: Starting Notepad from the command line. You need to execute "Start" - "Accessories" - "Command Prompt" (right-click - "Run as administrator"). A command prompt window will open, in which you need to type notepad C:WindowsSystem32driversetchhosts. A Notepad window will appear with the contents of the file. Direct call to Notepad.
You need to follow the path indicated for the command line case, only instead of "Command line" you need to specify "Notepad". An empty notepad window will appear. Through the menu item "File" you need to get to the etc folder and open it. If it does not show the hosts name, then it must be entered manually in the "File name" field at the bottom of the Notepad window. After any changes to this document, be sure to reboot, otherwise its new content will not be known to Windows 7, since it becomes known only during the reboot.
Benefits and harms of changing hosts Useful changes to this file can be considered, for example, the following: Setting the correspondence between the IP address and the domain in order to speed up access to the site by bypassing the DNS server. Changes to block access to a particular site, such as blocking Windows Authentication or the availability of software updates.
To do this, 127.0.0.1 is specified as the IP address, which the operating system perceives as an appeal to this computer, and not to a real site. Changes to "advertise" this computer as a local server, since the DNS service does not know anything about it. Of course, for this, the IP address must be static. Hosts is the main target for most malware. There are two main, one might say "classic" ways to modify this file, which are used by attackers in order to benefit from it.
These changes are: Blocking access to anti-virus program servers so that the computer cannot download such a program or virus syndrome database updates. For example, if a string like “127.0.0.1 esetnod32.ru” appears in hosts as a result of exposure to a virus or trojan, then any attempts to enter a site with this antivirus will be blocked. Substitution of the real address of the site, registered on the DNS server, with a fake one.
Suppose a malicious application that has penetrated a computer writes the line “91.81.71.61 vk.com” in this file, where the computer address of the author of this program is specified. This is done in order to ensure that attempts to access everyone's favorite site lead to an attacker accessing the server, the interface of which completely repeats its real counterpart, but is used to collect confidential information about site users, for example, their logins and passwords.
Therefore, if there is any suspicion of the presence of viruses in the system, you should first of all check the status of this file, which is why many antivirus programs tirelessly monitor its status and notify the user of any attempts to change it.
Where is the hosts file located?
The hosts file is located in the folder with the Windows operating system, usually it is the "C" drive on the user's computer.
The path to the hosts file will be:
C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts
You can manually follow this path, or directly open the folder with the host file, using a special command.
For quick access to the file, press the key combination "Windows" + "R" on the keyboard. This will open the Run window. In the "Open" field, enter either the path to the file (see above), or one of these commands:
%systemroot%system32driversetc
%WinDir%System32DriversEtc
Then click on the "OK" button.
hosts file in folder
This file does not have an extension, but it can be opened and edited with any text editor.
Default contents of the hosts file
On the Windows operating system, the "hosts" file has the following standard content:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
This file is similar in content to Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10 operating systems.
All entries that start with the pound sign # and continue to the end of the line are largely irrelevant to Windows, as they are comments. These comments explain what this file is for.
It says here that the hosts file is for mapping IP addresses to site names. Entries in the hosts file will need to be made according to certain rules: each entry must begin on a new line, the IP address is written first, and then the site name after at least one space. Further after the pound sign (#), it will be possible to write a comment to the entry inserted into the file.
These comments do not affect the operation of the computer in any way, you can even delete all these entries, leaving only an empty file.
You can download the standard hosts file from here to install it on your computer. It can be used to replace the modified file if you don't want to edit the hosts file on your computer yourself.
What to pay attention to
If this file on your computer is no different from this standard file, then this means that there are no problems on your computer that could arise due to modification of this file by malware.
Pay special attention to the contents of the file after these lines:
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
Additional entries can be inserted into the host file, which are added here by some programs.
For example, in this image, you can see that Unchecky has added some entries to the default contents of the hosts file. Between the commented lines, additional entries have been inserted to perform certain actions. This was done so that during the process of installing programs on my computer, this utility would cut off unwanted software.
Added entries
There may be additional lines, of this type: first a “set of numbers”, and then after a space, “site name”, added in order, for example, to disable ads in the Skype program, or block access to some site.
If you yourself did not add anything to the hosts file, and do not use the program mentioned in this article (Unchecky), then you can safely remove incomprehensible entries from the host file.
Why change the hosts file?
The hosts file is modified in order to block access to a specific resource on the Internet, or in order to redirect the user to another site.
Typically, malicious code is initially executed after a program downloaded from the Internet is launched. At this point, changes are automatically made to the properties of the browser shortcut, and quite often additional lines are added to the hosts file.
To block a site (for example, the VKontakte site), lines of the following type are entered:
127.0.0.1 vk.com
For some sites, two variants of the site name can be entered with or without "www", or without this abbreviation.
You yourself can block unwanted sites on your computer by adding an entry like this to the host file:
127.0.0.1 site_name
In this entry, the IP address (127.0.0.1) is the address on your computer's network. Next comes the name of the site that you need to block (for example, pikabu.ru).
As a result, after entering the name of the site, you will see a blank page from your computer, although the name of this web page will be written in the address bar of the browser. This site will be blocked on your computer.
When using a redirect, after entering the name of the desired site, a completely different site will be opened in the user's browser, usually a web page with advertising, or a fake page of a popular resource.
To redirect to another site, entries like this are added to the host file:
157.15.215.69 site_name
First comes a set of numbers - the IP address (I wrote random numbers here for an example), and then, after the space, the name of the site will be written in Latin letters, for example, vk.com or ok.ru.
The scheme of this method is something like this: bad people deliberately create a fake (fake) site, with a dedicated IP address (otherwise this method will not work). Next, an infected application gets onto the user's computer, after launching which changes are made in the hosts file.
As a result, when a user types the name of a popular site in the browser's address bar, instead of the desired site, it is redirected to a completely different site. This could be a fake social network page designed to steal user's personal data, or a site with intrusive ads. Very often, from such a fake site, there are redirects (redirects) to many other specially created pages with advertising.
How to edit the hosts file
You can change the contents of the host file yourself by editing it with a text editor. One of the easiest ways to be able to modify a file is to open the hosts file in Notepad by opening the program as an administrator.
To do this, create a shortcut to the Notepad utility on the Desktop, or run the application in standard programs that are located in the Start menu. To start, first right-click on the program shortcut, and then select "Run as administrator" from the context menu. This will open the Notepad text editor window.
C:WindowsSystem32driversetc
After opening the "etc" folder, you will not see the "hosts" file, as the Explorer will display text files. Select the "All Files" setting. After that, the hosts file will be displayed in this folder. You can now open the hosts file in Notepad to edit it.
After finishing editing, save the changes in the hosts file. Please note that the file type when saving must be: "All files".
In the event that the malicious program has changed entries in the hosts file, you can replace the modified file with a standard one, or edit the contents of this file by removing unnecessary entries from there.
How to open and edit the hosts file?
The hosts file can be opened using standard Windows Notepad.
This is probably the most interesting part of the article.
First of all, you need to understand why change this file at all? Yes, in order to deny access to certain sites. Thus, by changing this file and adding the site address to it, the user will not be able to access it through any browser.
In order to modify the hosts file, it is advisable to open it as an administrator (How to run a file or program as an administrator) by right-clicking on the file and selecting "Run as administrator". Or open Notepad in this way and open the file in it.
For quick action, you can simply click the Start button and select Run (win + r) (What to do if there is no Run in Start) and enter in the line:
notepad %windir%system32driversetchchosts
how to open hosts file
This will open the file in Notepad.
In order to block access to the site (suppose it will be test.ru), you just need to add a line with this site to the very bottom:
127.0.0.1 test.ru
As a result, the file will have the following content:
# Copyright (c) 1993-1999 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# This HOSTS file created by Dr.Web Anti-rootkit API
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
127.0.0.1 test.ru
Each new site that you want to block, you need to start on a new line and write, not forgetting the local IP address 127.0.0.1
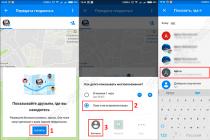
Also, to edit the hosts file, there is a HOSTS EDITOR program, which you can download and read the description from the official website.
The principle of her work is that she helps to edit the hosts file.
From the screen below, the principle of its operation is clear, everything is done in a couple of clicks. Adding is done by clicking on +.
how to edit the hosts file
After editing, do not forget to click on the save button (2 "Save changes" button to the left of the "+" button).
You can also change this file for good purposes, for example, speed up the loading of the site.
How it works?
When you enter the site, you see its domain name, which has letters. But all sites on the Internet have an IP address, and the names are already assigned using DNS. I will not go into the details of this process, the article is not about that. But here you need to know that the hosts file has priority when accessing sites, and only after it is a DNS request.
In order to speed up the loading of the site, you need to know its IP address and domain.
The IP address of a site can be found using various services, such as this or this.
Domain is the name of the site.
For example, let's speed up the loading of this site on which you are reading an article by explicitly specifying the IP address and domain for the file.
Then the added line will be:
91.218.228.14 vindavoz.ru
This speeds up the loading of the page in a couple of seconds, and sometimes it can give access if you cannot access the site using standard means.
You can also redirect to another site using the hosts file.
To do this, you need to know the IP address of the site and its domain (as in the case described above), then the added line will be like this:
91.218.228.14 test.ru
And now, after entering the site test.ru into the address bar of the browser, you will be redirected to the site specified in the IP address. In this case, to the site vindavoz.ru.
If you want to clean the hosts file, you can do it by simply deleting the content and pasting the original text into it, from the description above (under the spoilers).
Some nuances in the hosts file:
Always make sure you have a scroll bar on the side and always scroll down the window. this is due to the fact that some viruses are registered in the area hidden outside the window.
In some cases, usually if you can't save the file, you need to log in with an Administrator account.
Sometimes, due to viruses, this file may be hidden. Read the article Hidden files and folders.
In the two methods described (redirection and acceleration), the desired result may not be obtained. The fact is that several sites can be located on one IP address, this is especially true for external IP addresses that provide services.
Due to the fact that viruses love this file, its attributes can be changed to Hidden and Read-only.
Check the file attributes if you cannot save the hosts file.
Thus, you can easily and free of charge block access to sites in Windows by editing the hosts file
 Hello everyone As I understand it, your situation is not quite simple, right? Do you need to open the hosts file in Windows 10, but not just open, but open as administrator? Here the guys are not so simple .. In short, guys, yes, I thought that everything is not so simple here, but do you know why I thought so? Because I thought that you need to do this, that they say, in order to open the hosts file as an administrator, you first need to run the program as an administrator, so that later you can open the hosts file itself! But I don’t know where this idea came from, in short, I’ll say right away that you can do without this crap, everything is easier ...
Hello everyone As I understand it, your situation is not quite simple, right? Do you need to open the hosts file in Windows 10, but not just open, but open as administrator? Here the guys are not so simple .. In short, guys, yes, I thought that everything is not so simple here, but do you know why I thought so? Because I thought that you need to do this, that they say, in order to open the hosts file as an administrator, you first need to run the program as an administrator, so that later you can open the hosts file itself! But I don’t know where this idea came from, in short, I’ll say right away that you can do without this crap, everything is easier ...
But why is this hosts file needed at all? Viruses often write their entries in this file. In short, the file itself is needed in order to manually match the IP address and the name of a site. The fact is that every site on the Internet, it has a name. But this name, this is done in order to be convenient for us personally. And there is also such as the IP address of the server where the site is located. Well, but there can be several sites on the server, then what? In general, I mean here not just a server, but exactly the server on which the site lies and to which the site name is attached. Well, in short, it doesn't matter. It is important for you to know that every site on the Internet has both just the name dot ru (for example) and also just an IP address, which if you type in the address bar of your browser, the effect will be the same as if you typed the site address.
Well, guys, viruses often write some nonsense to the hosts file so that you actually get not to a real site, but to some kind of fake one. They do it there, they write the address of their server IP and then they write the name of the site. Then you write the name of this site in the browser and get to the server that is specified in the hosts file, that is, the redirect goes, well, I think you understand what I mean
So guys, stop talking, in general, I'm sorry that I wrote a little off topic, well, that is, on the topic, but not quite. In short, so that you open the hosts file as an administrator in Windows 10, then you need to open the Task Manager, for this, right-click on the taskbar and select this item there:

Then in the dispatcher itself, at the very top, in the left corner there will be something like File, so you click it and select the Run a new task item:

Then you will see a small window Create a task, there you need to check the box Create a task with administrator rights and then where Open, then write the path to the file there:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts

Then you will see a window, well, they say how to open the hosts file, you need to open it with notepad, so here you double-click on Notepad:

After that, a file will open in notepad, in short, something like this file will open for you:

By the way, this is the content of the file by default, well, that is, what goes in the newly installed Windows 10. Well, guys, the file has opened, great, now I'll write something here (this is for a test) and close the file. Here I wrote the word test here:

Then I closed the hosts file, well, I clicked on the cross, the following message appeared, then I clicked the Save button:

And all the guys, I had no mistakes! So what does that mean? And this only means that the changes made to the hosts file have been saved! That is, everything works. But you may also have such a situation that the changes will not be saved, but instead you are prompted to save the hosts file, in general, I mean that this window will appear:

But you ran it with administrator rights, what kind of joke is this, huh? Guys, the joke is that it can be such a mess that your hosts file is read-only, well, that is, there is such an attribute, this is done for security purposes, so to speak. What to do in this case, how to remove this attribute? It's very simple, go to the folder where the hosts file is located, for this you can hold down the Win + R buttons, the Run window will appear, you write the following command there, well, that is, such an address:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc

Well, click OK. Then you will open a folder where the hosts file will be located, right-click on it, and then select Properties from the menu:

Well, then the Properties window will appear, it is in this window that the Read Only attribute can be checked, well, look at the checkmark:

That is, if it is, then remove it and try to open the hosts file again as an administrator, well, I already wrote above how to open it.
Another thing I'll write to you, here's how to clear the hosts file, you know? Here you just need to know one iron rule, look, remember that everything that does not start with a pound sign, well, that is, not with a # sign, then all this is already being recorded, so to speak. Anything that starts with a # sign is a comment. Well, and most importantly, in a clean hosts file, that is, in the one that is only in the installed Windows, then there is nothing there except comments! That is, in a clean hosts file, there should be nothing but comments, that is, lines that begin with #! Thinking about something, want to be 100% sure that the hosts file is clean? No problem. To clear the hosts file completely, in general, so completely, one hundred percent, then simply DELETE EVERYTHING IS INSIDE IT. Delete it all, save it and that's it. The hosts file is clean, even without comments. This is real, I’m not inventing anything for you here, if you do this, then your hosts file will be cleared for sure
It would be possible to finish already, but guys, I want to show you one more way how to open the hosts file as an administrator in Windows 10. Well, why not? Maybe this particular method will be more convenient for you, don’t worry, I won’t write much. So look, right-click on the Start icon, select Command Prompt (Administrator) from the menu, this item:

Then you may see such a window, or it may not appear, it's such a simple type of security, in general, if anything, then click here Yes:

A black window will appear, well, this is the command line, here you write in this window such as:
START C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
By the way, you can simply copy this line and then right-click in the black window and it will automatically be inserted. Well, so, here you put the command:

Then press the enter button, after which a window will appear where you need to double-click on Notepad:

And then the hosts file will open, there you can delete something, that is, make changes, and after that if you close it, then there should be no error. Everything must be clear
Well, that's all the guys on this, I really hope that everything was clear to you here, but if something is wrong, then you'll be sorry. Good luck in life and that everything is fine with you, all the best
08.01.2017The note will discuss the "long-suffering" system file hosts, which often gets from network "malware" that has leaked onto the computer. hosts does not have an extension, but in fact it is a plain text file and the built-in Notepad (Notepad) is enough to edit it. The purpose of the file is to store a list of domains and their corresponding IP-addresses. This is the list that the browser first accesses after entering, say, a domain name in the address bar Yandex.ru to find out that it matches the address 77.88.21.11 .

Now imagine that a malicious program has changed the hosts"ipishnik" Yandex.ru to the address of the "weedy" site she needs. Now every time after a character set in the browser Yandex.ru you will be on some xxx.com. Of course, this disgrace must be quickly stopped, for which you will have to turn directly to the file hosts. In the article I will voice a guaranteed way to do this, because. in latest versions Windows the developer has strengthened the security of the OS, which in practice has made life difficult for users: the desired folder may not be visible or the file itself cannot be edited.

So, to bring hosts in the "divine" view should be opened Notepad as administrator. To do this, go to the menu "Start" → next, " All programs" → "Standard" → click the right mouse button on Notebook and select from the context menu "Run as administrator ".
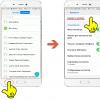
In the top panel that appears, click " File " → "Open" → in the address bar, specify the path to the desired folder - C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc . If the folder is empty, in the line "File name" we write hosts and click " Open(next screenshot).

The contents of the file can be compared with the original in Windows 7 and, in case of discrepancies, copy to yourself.
# Copyright (c) 1993-2006 Microsoft Corp. # # This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows. # # This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each # entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should # be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name. # The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one # space. # # Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual # lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol. # # For example: # # 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server # 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host # localhost name resolution is handle within DNS itself. # 127.0.0.1localhost
In principle, only one entry can be left − 127.0.0.1 localhost or even leave nothing - in any case, this is better than disgrace as in the screenshot below (a real example of an editorial hosts virus villain).

As you can see, the "malware" has blocked anti-virus software updates and access to social networking sites. In order to prevent the situation from happening again, it is recommended to protect the file with the " Only reading"by clicking on hosts right click → " Properties" → on the first tab "General", check the box next to the corresponding attribute.

About what else useful can be done with the system file hosts I will tell in our .
Not every user of the Windows operating system can find, know how to open and how to save the hosts file with changes. This article shows an example of how this can be done in Windows 7. In Windows XP, this file is located in the same place, I hope that in Windows Vista and Windows 8 it has not changed its location. It's just that I've never worked in whist and I'm not going to install windows 8 yet, so try to find and change it yourself. I hope that the way to open and make changes also remain similar to Windows 7.
And so the file hosts in the system is located in the system folder Windows, which is located on the "C" drive, unless, of course, you installed the system on another drive. In the Windows folder look for the folder "system 32", then folder drivers, then a folder "etc", here is the file you are looking for.
If you did not find it, then do some actions, obviously the parameter is set in the settings "Do not show hidden files, folders and drives".
Open folder "Computer", press the key Alt, an additional menu will appear in which you need to select "Tools", "Folder Options". A small window will open with folder options. In chapter "View" point to be noted "Show hidden files, folders and drives". Next, click "OK" and try again to look into the "etc" folder. The file must be in place.
Now the question arises: "How or with what to open it?", because the extension of this file is not known. It turns out that everything is very simple, you can open this file using notepad. To do this, double-click on the file name, an additional window will open with programs to open it, from which you need to select "Notepad" and click OK.
A text document will open with the following content:
This is where you will make changes. All entries below the lines with the first "#" sign indicate blocked addresses and Internet sites.
Let's experiment by blocking access to the VKontakte website. To do this, add the following to the file:
The site is now closed. In a similar way, you can restrict access to other sites that for some reason you do not want to view or, for example, you want to hide pornographic sites from children.
Now close notepad and try to open the VKontakte website.
That does not work? Naturally, because access to it is closed. To open access, do the opposite, remove the line with the specified site from the hosts file. Don't forget to save your changes.
1. If you are a complete teapot, then first think a few times before changing something, or don’t touch anything at all, but contact a specialist who can help you. If you still decide to make changes yourself, then in case of any problems, blame yourself. With this file jokes are bad.
2. If you really want to try it, at least make a copy of the file before making changes by copying it to another location. If something goes wrong, it will be possible to move the copy of the file back to the folder with the original file, with the consent to replace it.
3. If you did not make a copy of the file and after your self-confidence, the computer began to act naughty, try to find an identical file on the Internet, download it and replace it with your own, or delete all lines in the hosts file up to the lines with the “#” sign. Don't forget to save.
4. Before each attempt to make any changes or settings, first think about whether it is really necessary and how much you want it!