Between multiple computers is a tricky business that involves many devices. This process itself is quite complex, so it will be problematic to consider it all. Therefore, you can learn within the framework of the article only about one device necessary for reliable transmission of information, namely, about the adapter. What is it? What is the functionality of this device and why is it needed? Does it fully cope with its tasks or are auxiliary devices used?
What is a network adapter?
This is a peripheral device that directly interacts with the data transmission medium. This process can be carried out directly or through other switching equipment. An adapter is a device that solves the problems of secure exchange of binary data, which are represented by the corresponding electromagnetic signals. Like any controller in a computer, it works under the control of the appropriate operating system driver. In the very first local networks, an adapter is a device that established the interaction of different computers. They directly interacted with each other. Now, it is usually provided that between the network adapters there is some kind of communication device (bridge, hub, router or switch), which is assigned the functions of data flow control.
The functionality of this device

There are five main functions of the network adapter. This:
- To arrange the transmitted information in the form of a frame having a certain format.
- Synchronize bits, bytes and frames for stable reception of information transmitted from another point.
- Get access to the data transmission medium.
- Encode a bit-frame with a sequence of electrical signals necessary for it during data preparation for transmission and decode during reception, for example, in Windows 7. Network adapters can usually work with all popular protocols.
- The device converts information from serial to parallel and vice versa to simplify signal synchronization.
It seems to be not very much, but thanks to these functions, data can be transferred in huge quantities.
Classification
Network adapters are distinguished based on their type and the width of the internal data bus that is used in the computer:
- EISA;
Also, classification can be carried out on the basis of network technology, which are represented by FDDI, Token Ring, Ethernet and many others. Usually, one model supports only one of them, although it uses different means of data transmission. If this function is not supported, then converters and transceivers are used. This leads to a more complex design. But such examples are now quite rare, and most of them are old models that are five or ten years old.
Conclusion

For communication between different computers within even a local network, only one network adapter is rarely used. This is a complex device, which, for greater security of transmitted data, is rarely used alone. If you want to get acquainted with a schematic device, you need to stock up on scientific and technical literature, as well as one sample that you don’t mind disassembling and seeing what is designed in it and how (this applies to those who want to fully master their computer). It should be noted that it does not matter which operating system to work with. A network adapter for Windows 7, XP or Linux in general will work the same way. There is only one small feature - another software firmware will be needed. But setting up the shell is a matter of minutes.
Network adapter (with network interface card NIC – Network Interface Card) is a physical interface or connection between a computer and a mono channel, i.e. serves to connect servers and workstations to the physical environment.
Network interface cards (boards) are installed on desktop and laptop PCs. They are used to communicate with other devices on the local network. There is a whole range of network cards for various PCs that have specific performance requirements. They are characterized by data transfer speed and network connection methods.
Network adapter:
· Prepares computer data for transmission over the cable.
· Sends data to another computer.
· Receives data from the network and transfers it to the computer.
Considering simply the way networked PCs receive and transmit data, modern network cards (network adapters) play an active role in improving performance, prioritizing critical traffic (transmitted / received information), and monitoring network traffic. In addition, they support features such as remote activation from a central workstation or remote reconfiguration, greatly saving administrators of ever-growing networks time and effort.
Network cards, together with their driver, implement the physical and link layers of the algorithmic structure of the network. Appropriate drivers are used to communicate with the protocols of the upper layers of the COS. More precisely, in a network operating system, the adapter/driver pair performs only the functions of the physical and MAC- levels while LLC-level is usually implemented by an operating system module that is common to all drivers and network adapters. Actually, this is how it should be in accordance with the protocol stack model IEEE 802. For example, in OS Windows NT level LLC implemented in the module NDIS, common to all network adapter drivers, regardless of which technology the driver supports.
The network adapter, together with the driver, performs two operations: transfer And reception frame.
Frame transmission from a computer to a cable consists of the steps listed below (some may be missing, depending on the coding methods adopted).
Frame reception data LLC through an interlayer interface along with address information MAC- level. Usually, interaction between protocols inside a computer occurs through buffers located in RAM.
Data to transfer to the network are placed in these buffers by higher-level protocols that retrieve them from disk memory or from the file cache using the I / O subsystem of the operating system.
- Data framing MAC - layer, in which encapsulated (nested) frame LLC(with flags 01111110 dropped). Filling in the destination and source addresses, calculating the checksum.
- Formation of code symbols when using 4V/5V type redundant codes.
- Scrambling codes to obtain a more uniform spectrum of signals. This stage is not used in all protocols - for example, 10 Mbps Ethernet technology does without it.
One of the effective methods to reduce the impact of burst errors is interleaving or mixing (English - interleaving). The data, before being transmitted over the communication channel, is rearranged in a given order, and the original order is restored in the receiving part, i.e. deinterleaving is performed. In this case, a burst error that occurred in the communication channel turns into a set of single errors dispersed in time, which are easier to detect and correct using error-correcting codes.
term scrambling in the MPEG-2 standard, it is called changing the characteristics of a data stream (video, audio or other information) in order to prevent unauthorized receipt of this information in an undistorted form. Descrambling is the reverse operation, i.e. reversal of data flow characteristics.
Scrambling is the encryption of a data stream, as a result of which it looks like a stream of random bits. The sequences of bits in the original data array, both regular and irregular, are reversibly destroyed, so that the probabilities of the occurrence of a logical one and a logical zero in each subsequent bit position of the stream are the same and do not depend on the prehistory. As applied to telecommunication systems, scrambling increases the reliability of synchronization of devices connected to opposite sides of the communication line, and reduces the level of interference radiated to adjacent lines of a multicore cable. There is another area of application of scramblers - the protection of transmitted information from unauthorized access; however, this area is not considered here.
Scrambling can also be used as a way to increase transmission efficiency and confidentiality in digital mobile communication systems.
The scrambler is installed on the transmitting side. It adds the original binary sequence with the pseudo-random sequence modulo 2. The descrambler is installed on the receiving side and restores the original sequence. The scrambler and descrambler are implemented as a feedback shift register.
Issuing signals to the cable in accordance with the accepted line code - Manchester, NRZI, MLT-3 and so on.
Receiving a frame from a cable to the computer includes the following steps.
Receiving from the cable signals that encode the bit stream.
Isolation of signals against the background of noise. This operation can be performed by various specialized chips or DSP signal processors. As a result, a certain bit sequence is formed in the adapter's receiver, with a high degree of probability coinciding with the one that was sent by the transmitter.
If the data was scrambled before being sent to the cable, then it is passed through the descrambler, after which the code symbols sent by the transmitter are restored in the adapter.
Frame checksum check. If it is incorrect, then the frame is discarded, and the corresponding error code is transmitted to the LLC protocol through the interlayer interface upwards. If the checksum is correct, then MAC- frame retrieved frame LLC and is transmitted through the interlayer interface upward, to the protocol LLC. Frame LLC is placed in the RAM buffer.
The distribution of responsibilities between the network adapter and its driver is not defined by standards, so each manufacturer decides this issue on its own. Typically, network adapters are divided into adapters for client computers And server adapters. In adapters for client computers, much of the work is offloaded to the driver, thereby making the adapter simpler and cheaper. The disadvantage of this approach is the high degree of loading of the computer's central processor with routine work on transferring frames from the computer's RAM to the network. The central processor is forced to do this work instead of performing user application tasks. Therefore, adapters designed for servers usually have their own processors, which do most of the work of transferring frames from RAM to the network and vice versa.
As an example of the classification of adapters, we use the approach of the company 3Com, which has a reputation as a leader in Ethernet adapters. Firm 3Com believes that Ethernet network adapters have gone through three generations in their development.
First generation adapters were performed on discrete logic microcircuits, as a result of which they had low reliability. They had buffer memory for only one frame, which led to poor performance of the adapter, since all frames were transmitted from the computer to the network or from the network to the computer sequentially. In addition, the configuration of the first generation adapter was done manually, using jumpers. Each type of adapter used its own driver, and the interface between the driver and the network operating system was not standardized.
In network second generation adapters to improve performance began to apply the method of multi-frame buffering. In this case, the next frame is loaded from the computer's memory into the adapter's buffer simultaneously with the transfer of the previous frame to the network. In receive mode, after the adapter has fully received one frame, it can begin to transfer this frame from the buffer to the computer's memory at the same time as receiving another frame from the network. Second-generation network adapters make extensive use of highly integrated chips, which improves the reliability of the adapters. In addition, the drivers for these adapters are based on standard specifications. Second generation adapters usually come with drivers that work as standard. NDIS(Network Driver Interface Specification) developed by 3Com And Microsoft and approved IBM, as well as in the standard ODI(open driver interface) developed by Novell.
In network third generation adapters (to them the company 3Com refers its adapters to the family Ether Link III) a conveyor scheme for processing frames is implemented. It lies in the fact that the processes of receiving a frame from the computer's RAM and transmitting it to the network are combined in time. Thus, after receiving the first few bytes of the frame, their transmission begins. This significantly (by 25-55%) increases the performance of the chain RAM- adapter - physical channel - adapter - RAM. Such a scheme is very sensitive to the transmission start threshold, that is, to the number of frame bytes that are loaded into the adapter's buffer before transmission to the network begins. The third generation network adapter self-tunes this parameter by analyzing the operating environment, as well as by calculating, without the participation of a network administrator. Self-tuning provides the best possible performance for a particular combination of the performance of the computer's internal bus, its interrupt system, and its direct memory access system.
Third generation adapters based on specialized integrated circuits (ASIC), which improves the performance and reliability of the adapter while reducing its cost. 3Com named its Frame Pipelining Technology Parallel Tasking, other companies have also implemented similar schemes in their adapters. Improving the performance of the "adapter-memory" link is very important for improving the performance of the network as a whole, since the performance of a complex frame processing route, including, for example, hubs, switches, routers, global links, etc., is always determined by the performance of the slowest element this route. Therefore, if the network adapter of the server or client computer is slow, no fast switches will be able to speed up the network.
Network adapters produced today can be attributed to fourth generation . These adapters must include ASIC, which performs the functions MAC- level, as well as a large number of high-level functions. The set of such functions may include support for a remote monitoring agent RMON, frame prioritization scheme, computer remote control functions, etc. In server versions of adapters, it is almost necessary to have a powerful processor that offloads the central processor. An example of a fourth-generation network adapter is the company's 3Com - Fast Ether Link XL 10/100.
Separate remote LAN equipment (computers, peripheral equipment, other networks) can be connected via modems and communication lines (telephone, radio, satellite). Network adapter communication with network software is carried out by network adapter drivers. It is thanks to the driver that the computer may not know any hardware features of the adapter (its addresses, rules for exchanging with it, its characteristics). The driver unifies, makes the interaction of high-level software with any adapter of this class uniform. The network drivers supplied with the network adapters allow network programs to work equally with cards from different vendors and even cards from different LANs (Ethernet, Arcnet, Token-Ring, etc.). If we talk about the standard OSI model, then drivers, as a rule, perform the functions of the link layer, although sometimes they also implement some of the functions of the network layer (Fig. 3.2). For example, drivers form a packet to be transmitted in the adapter's buffer memory, read a packet that came over the network from this memory, issue a transmission command, and inform the computer about packet reception.
Rice. 5.1. Network adapter driver functions in the OSI model
The quality of writing a driver program largely determines the efficiency of the network as a whole. Even with the best performance of a network adapter, a low-quality driver can drastically degrade network traffic.
Before you purchase an adapter card, you should check the Hardware Compatibility List ( Hardware Compatibility List, HCL), which is published by all manufacturers of network operating systems. The choice there is quite large (for example, for Microsoft Windows Server the list includes over a hundred network adapter drivers). If the list HCL some type of adapter is not included, you'd better not buy it. The generalized structure of the network card is shown in Figure 5.2.

Rice. 5.2. Generalized structure of a network card
The network card is available in a design IBM PC and connects to a free slot on the computer.
Scheme for generating physical signals performs amplification and conversion of signals to the form in which they are transmitted over the physical medium, for example, to the Manchester 2 code.
Network processor, together with network ROM, perform protocol transformations of the received and transmitted information in accordance with the protocols of the physical and link layers.
Buffer RAM serves to buffer received and transmitted frames.
Scheme of interfacing with the system bus serves to organize an interface with the PC system bus.
There are a number of parameters characterizing the network card:
– bit depth (8, 16 and 32 bits);
– network buffer size;
– throughput;
– supported SOS;
– the type of mono channel being used.
Bit depth determines the length of the words that the frame processes. Obviously, the higher the bit depth, the higher the performance of the card.
Network buffer size is in the aisles from 8 to 128 KB. The larger the buffer size, the higher the resistance of the network card to overloads in conditions of intense network traffic. It should be noted that there are network cards in which there is no network buffer; in this case, the direct memory access (DMA) mechanism is used and the network buffer is organized directly in the computer's memory.
Bandwidth A network card is characterized, as a rule, by its maximum bandwidth, which determines the maximum stream of bytes that can be skipped in the mode of reading (writing) information from the file server. Throughput ranges from 300 KB/s for small files (1 KB) to 1100 KB/s for large files (100 KB).
Supported SOS. Each NIC supports multiple SOCs. The wider the list of SOSs supported by the card, the higher the possibility of building heterogeneous (using different operating systems) LANs.
The type of mono channel being used. Each NIC works with one or more types of mono channels. The most common mono channels are Ethernet, Token Ring, Arcnet, FDDI.
Returning to the structure of the network adapter, you can clarify the composition and functions of the components of the structure :
· Memory , a place where the card temporarily stores messages that are waiting to be sent.
· Cable connections And connectors allow network cables to physically connect to the card. This card has a connector RJ-45 And AUI And BNC connector.
· CPU completes the final conversion of messages into signals that can be transferred to the line and the first level of messages enters it.
| · Bus connector is where the card plugs into the computer's expansion slots. · Jumpers or DIP switches is used to manage network card settings, and will vary depending on your computer and network. The design of network adapters is focused on specific network signal transmission methods, the type of computer bus and the network transmission medium. To implement a network connection, four components are needed: 1. connector, corresponding to the network transmission medium; 2. transceiver; 3. controller, supporting MAC sublayer of the OSI link layer ; 4. firmware to manage the protocol. Connectors and framing circuits are designed for a particular type of communication medium (eg, coax, twisted pair, fiber, or wireless). Some NICs are made with multiple connectors and can therefore be used in a variety of environments. Combined adapters are most often made with outputs for coaxial and twisted pair. These adapters are shipped with software drivers or firmware appropriate for the media type. Software and hardware (firmware) means are programs stored on a chip, such as read-only memory (ROM). In addition, some drivers may recognize the type of media connected to the network adapter and the appropriate driver will be installed automatically. On some operating systems, such as Windows 2000 and Windows XP, hardware drivers, including network drivers, may be signed. Signed Driver contains some kind of digital signature that ensures that the driver has been checked for compatibility with the operating system, that the driver being installed will not replace a more recent version, and that the driver is free of bugs or viruses. Practice 4-1 will show you how to determine if a network adapter driver is signed on Windows 2000 and Windows XP Professional systems. Note: A combo adapter can support two or more signal media, but it requires only one media to be connected at a time for it to work properly. The cable connector is connected to the transceiver (transceiver), which can be either external or built into the network adapter. A transceiver is a device that transmits and receives signals over a communication cable. In computers, servers, and network equipment, the transceiver is most often built into the interface board. In some cases, usually older network equipment, the transceiver is external to the adapter and a drop cable is used to connect it to the adapter. A transceiver drop cable is needed only when the transceiver is external to the network adapter. It should not be used if the transceiver is built into the adapter board. The purpose of the MAC controller block. The overall task of the MAC controller block and the firmware is to correctly pack the source and destination addresses (the physical addresses of the transmitting and receiving network adapters), the transmitted data, and the checksum. The MAC controller operates on the MAC sublayer of the OSI link layer and formats frames. In addition, the controller block functions at the LLC sublevel of the same level and performs the following tasks: Ø initiates a communication channel between two nodes; Ø ensures the integrity of the channel and reliable data transmission; Ø Ensures that the network adapters on both communication nodes maintain a pause equal to 9.6 µs between receiving one frame and transmitting the next, so that both adapters have a small margin of time to correctly switch between receiving and transmitting modes. The MAC controller unit and firmware are configured for a specific network technology, for example: Ø Ethernet; Ø Fast Ethernet; Ø Gigabit Ethernet; Ø 10 Gigabit Ethernet; Ø Token Ring; Ø Fast Token Ring; Ø FDDI; ØATM. Signaling Modes Some network adapters can support multiple technologies such as Ethernet and Fast Ethernet, making it easy to upgrade your network to high-speed data transfer. In addition, many adapters can operate in both half-duplex and full-duplex modes. Half-duplex mode of operation prevents the network adapter and network equipment from transmitting and receiving data at the same time. full duplex(full-duplex), or just duplex the mode provides for the possibility of simultaneous transmission and reception, which is possible due to data buffering in the network adapter. To this end, the adapter is provided with a memory for temporary storage of information that is not being processed at the moment. Tip: Before configuring an adapter for half-duplex or full-duplex operation, determine the settings for the communication device to which the adapter is connected. For example, if a computer with an adapter is connected to a switch port and that port is configured for half-duplex operation, then the network adapter must be configured for the same mode. If the operating modes of the adapter and the communication device are not consistent, then they will not be able to communicate with each other. Wireless network adapters The wireless adapter provides data transfer in one of two modes. One mode is a dedicated, peer-to-peer interaction with another wireless adapter. Another Mode is interaction with an access point (place), for example, with a wireless bridge. If you are working with a wireless access point, then it is not advisable to also use dedicated wireless communications, as they will not work stably in the presence of an access point. 802.11b-compliant wireless adapters on the market are typically rated at 1, 2, 10, and 11 Mbps. Some manufacturers also offer 802.11a compatible wireless adapters that transfer data at speeds up to 54 Mbps. Wireless adapters do not always operate at their highest possible speed, they "negotiate" the speed that is most appropriate for current conditions, and this takes into account the load of the peer computers or access point. Tip: A fast network adapter in a computer or network device will be fully loaded unless the computer has a fast processor (such as a high-end Pentium, Itanium, or RISC processor) that can provide the required performance of the adapter. Network adapters and buses Network adapters must match the type of bus used in the computer. Tire - it is a computer highway through which information is transmitted to the processor and peripherals connected to the computer. The following are the main types of buses in workstations and servers: ü Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) - legacy expansion bus design that supports 8-bit and 16-bit data transfer at 8 MB/s; u Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA) a newer ISA-based bus design capable of transferring 32-bit data. EISA allows the use of bus mastering - a process that reduces the load on the CPU when performing I / O; u Microchannel Architecture (MCA) - 32-bit bus design used in legacy IBM computers; u Peripheral Computer Interface (PCI) - modern bus design providing 32-bit and 64-bit data transfer. PCI uses the idea of a local bus, which allows different buses for network interfaces and for disk drives; u SPARC Bus (SBUS) - a dedicated bus designed for Sun Microsystems SPARC workstations; u NuBus- a specialized 96-pin bus used in Apple computers (from Macintosh II to Macintosh Performa); u Universal Serial Bus (USB) - a bus standard that allows any type of device (such as keyboards, cameras, pointing devices, telephones, and tape drives) to be connected to a single computer bus port; u VESA local bus (VL-bus) – bus used on some 80486 computers to transfer 32-bit data between the network adapter and the CPU. This bus is not used on Pentium-compatible computers, where it has been replaced by the PCI bus. Choosing a Network Adapter Each network adapter has a decisive effect on the effectiveness of network communications. When purchasing an adapter, consider the following points. · Is the network adapter used for a host computer, a server, or a workstation? Host and server adapters are often used to connect to a network at 100 Mbps or higher to improve overall performance. These types of adapters require a fast system bus (such as PCI). The requirement for high performance for workstation network adapters is determined by the applications that run on them. · What network environment and network access method are used? Each environment and access method requires different network adapters (for example, token ring networks, Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, etc.). · Who produces this adapter model? Buy only high-quality network adapters from renowned manufacturers and use the fastest expansion slots for adapters (such as PCI slots). · What type of bus is used in the computer or network equipment? Check if the network adapter fits the existing bus expansion slots. What operating system is installed on the computer? Any network adapter requires a driver that is compatible with your system (eg Windows 2000, Windows XP, etc.). · What data transmission mode is used in the network - half duplex or full duplex? Network adapters must work in both modes, this provides the ability to change or upgrade the network. · If the adapter is designed for specific cases (for example, for FDDI), how does it connect to the network? FDDI adapters can use either single or dual connections. In addition, in some cases, adapters are used that do not have a built-in transceiver; in this case, the transceiver must be purchased separately. One of the best ways to prevent network problems is to purchase high performance network adapters for all stations connected to the network. It's also important to buy adapters from manufacturers that regularly update adapter drivers to fix potential problems and improve performance. Many network adapter manufacturers have Web sites where you can download the latest drivers for free. Tip: One network bottleneck is the server's network adapter, which can be slow and require an upgrade (for example, replacing an EISA bus adapter with a PCI adapter). Another bottleneck might be a server with a fast network adapter but a relatively "weak" processor. In both cases, it will appear to users that the network is slow, although the real problem lies with an insufficiently powerful network adapter or server processes. Setting up the network board. The process of setting up a network should begin with the installation of a network card, and this can be done both during the installation of the operating system itself, and later, during operation. If the network adapters are plug-and-play, the operating system automatically recognizes the installed network card at boot and configures it. However, there is a certain chance that the configuration will have to be done manually. In this case, you need to open a DOS window and run the configuration program for the purchased card (for example, diag or lanset). Then open the "Control Panel" and double click on the "Add Hardware" icon. This will launch the Add Hardware Wizard. By clicking on the "Next" button, go to a dialog box where Windows 95 will prompt you to automatically search for new installed devices. It's a good idea to let the operating system recognize the hardware itself. If she succeeds, then she will not have to manually enter information about the device. If Windows 95 could not recognize the network adapter, then you will have to manually install and configure it. After clicking on the "Next" button, a dialog box will be displayed in which you must specify the type of device to be installed by double-clicking on the line " Network boards". As a result, the following dialog box will open, in which you must select the manufacturer and model of the network card from the list provided. The choice is made by clicking on the corresponding line in the list. After selecting the network card, Windows 95 displays a dialog box in which the parameters of the installed card are indicated. Type and the amount of information displayed depends on the type of card.If the network card is recognized in automatic mode, then the parameters displayed in the dialog box are set by Windows 95. If the system does not recognize the network card, then the default values are assigned, which quite often leads to conflicts with other devices.In this case, you need to change the settings to eliminate conflicts.After that, the system installs the software necessary for the operation of the network card.You can use the standard driver available on the Windows 9x distribution disk.If one is missing or for some reason does not suit you, use the driver on the diskette supplied with the adapter (button " Install from disk"). Handling the computer The first step in installing the network card: turn around and disconnect the computer. CAUTION: Before installing the network card, turn around the computer and unplug it. Working on a computer that is still connected may result in an emergency that (Animation) After disconnecting all cables from the computer, remove the cover First, remove a few screws from the back cover of the computer (Animation) network card The components of your computer are: · CD-ROM driver. Plays CDs. · hard disk. Stores programs and data. The content may be enlarged or reduced. · Motherboard, contains the CPU, memory, and other hardware required for a computer. · CPU. The brain of the computer where the processes are carried out. · Expansion slot. This is where boards like the network adapter plug in. · Power supply / Fan. Provides voltage to all internal components and cools the system. · Memory. High-speed short-term memory. All information in memory is erased when the computer is turned off without being saved to disk. Installation The card can be installed in one of the expansion slots. Make sure the card is firmly in place. Take the cover and put it back in place. (Animation) |
Types of LAN Links (physical media)
Information transfer medium those communication lines (or communication channels) are called, through which information is exchanged between computers.
The vast majority of computer networks (especially local ones) use wired or cable communication channels, although there are also wireless networks that are now increasingly used, especially in portable computers.
Information in local networks is most often transmitted in a serial code, that is, bit by bit. This transfer is slower and more complicated than using parallel code. However, it should be taken into account that with faster parallel transmission (through several cables at the same time), the number of connecting cables increases by a factor equal to the number of bits of the parallel code (for example, 8 times with an 8-bit code). This is not at all a trifle, as it might seem at first glance. With significant distances between network subscribers, the cost of a cable is quite comparable to the cost of computers and may even exceed it. In addition, it is much easier to lay one cable (less often two multidirectional ones) than 8, 16 or 32. Finding damage and repairing the cable will also be much cheaper.
But that is not all. Transmission over long distances with any type of cable requires complex transmitting and receiving equipment, since it is necessary to generate a strong signal at the transmitting end and detect a weak signal at the receiving end. With serial transmission, this requires only one transmitter and one receiver. With parallel, the number of required transmitters and receivers increases in proportion to the bit depth of the parallel code used. In this regard, even if a network of insignificant length (on the order of ten meters) is being developed, serial transmission is most often chosen. In addition, with parallel transmission it is extremely important that the lengths of the individual cables are exactly equal to each other. Otherwise, as a result of passing through cables of different lengths, a time shift is formed between the signals at the receiving end, which can lead to malfunctions or even to the complete inoperability of the network. For example, at a transmission rate of 100 Mbps and a bit duration of 10 ns, this time shift should not exceed 5-10 ns. This amount of shift gives a difference in cable lengths of 1-2 meters. With a cable length of 1000 meters, this is 0.1-0.2%. It should be noted that some high-speed local networks still use parallel transmission over 2-4 cables, which allows using cheaper cables with a lower bandwidth at a given transmission speed. But the permissible cable length does not exceed hundreds of meters. An example is the 100BASE-T4 segment of a Fast Ethernet network.
The industry produces a huge number of types of cables, for example, only one largest cable company Belden offers more than 2000 of their names. But all cables can be divided into three large groups:
- electrical (copper) cables based on twisted pairs of wires (twisted pair), which are divided into shielded (shielded twisted pair, STP) and unshielded (unshielded twisted pair, UTP);
- electrical (copper) coaxial cables (coaxial cable);
- fiber optic cables (fiber optic).
Each type of cable has its own advantages and disadvantages, so when choosing it is necessary to take into account both the features of the task being solved and the features of a particular network, including the topology used. We can single out the following main parameters of cables, which are fundamentally important for the use
26. 03.2017
Blog of Dmitry Vassiyarov.
Network card or network adapter what is it?
Hello dear visitors.
Today we will talk about another piece of iron, and more specifically about what a network card is. Do you work at an enterprise where a corporate connection between computers is established? Then you should learn more about the network adapter, since it is he who serves as a link between office computers.
Getting to know each other better
Not with me, but with a network card, of course :).
In English, it is called "network interface controller / card" (NIC), that is, "controller or network interface card." Also, according to the technology that is used in the operation of the device, it has another name - an Ethernet adapter.
So that you understand its essence, I will decipher the first word: “ether” is translated as “ether”, and network is “network, chain”. The concept itself means a family of packet data transmission technologies among computer networks.
The network card is designed to create local networks between computers and/or connect them to the Internet. In other words, you will not connect to the Internet without it.
Recently, communication has been organized using a special cable - an eight-core twisted pair cable equipped with an "8P8C" connector, that is, it has 8 conductors in the same number of places for them.
Connect such a pair to a modern network and a new model card, and you will get speeds from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps (Gigabit). This is, of course, if your ISP gives you such a speed.

This technology is called Gigabit Ethernet, which is now relatively popular. Among its main competitors are fiber optics, Docsis (connecting computers using a television cable) and DSL technology (using a telephone cable).
Also, the connection can be made using the 15-pin AUI connector of the transceiver for a thick coaxial cable or a BNC connector for the same cable, only thin.
Types of network cards
The main criterion by which Ethernet adapters are distinguished is their way of connecting to a computer:

Main settings
Thinking about buying a network card? When choosing, consider not only the types of cables and interface, but also the following characteristics:
- Bit depth (bus bandwidth). It comes in 8, 16, 32 and 64 bits. In ordinary computers, as a rule, a 32-bit device is installed, and in server computers - the maximum amount. Do you have an old computer and operating system? Then, perhaps, it is worth looking at 16 or even 8-bit boards.
- Controller microcircuit (chip). The most reliable are third-generation adapters based on integrated circuits (ASICs). High-quality chipsets are now produced by realtek, intel, broadcom, etc.
- Transfer rate. It starts at 10 Mbps and can go up to 100 Gbps. But don't go after the highest score. Since not all providers will be able to give you maximum speed. Or rather, they may not exist at all.
What card is in your computer?
Can't you answer this question? Then let's find out now. We go along the path Start - Control Panel - Device Manager (in case you have Windows). You can find it in the menu System and Security - System. Among the devices available on your computer, find the one you need.

In principle, I think I wrote everything in detail.
You now have a basic knowledge of what a network card is.
Come back to me for new information.
See you soon, and don't forget to subscribe for updates.
There are two main types of network: wireless and wired. Network adapters can be used with both types of network. At the same time, there are more network adapters for wireless networks, since there are more varieties of such networks.
A computer with an adapter can be connected to a network using a cable. For wired networks, the device is a USB key with a dedicated port for an Ethernet cable. This cable can connect, for example, a router and an adapter.
The adapter may come with software, but most modern operating systems recognize the USB adapter and find the necessary drivers for it to work.
But most often, a network adapter means a device for wireless networks. Such adapters are popular due to their mobility. They allow the computer to join a nearby wireless network.
The wireless network adapter looks like a memory card or flash drive. It's a small USB device with a warning light to indicate it's charged and ready to use. When it is connected to a computer, it scans the Internet channels of local providers and informs the computer software about the presence of networks. The computer, in turn, shows these networks to the user. In order for the computer to connect to the network of interest, just click on its name and enter the password, if required. The next time you turn on your computer, it will automatically connect to this network.
In many modern computers, wireless network adapters are already integrated into the machine. They are microchips.
Finally, there are network adapters, which are purely software. They simulate the functions of a network card. They are called "virtual network adapters".
Why Network Adapters Are Necessary
Most laptops have a built-in wi-fi card or wireless network card. But sometimes this card doesn't work. This is especially true when wireless networking standards change to a new and faster connection protocol. Then old cards that support outdated protocols will not work with a router that supports the new standard.
When buying a new network adapter, you should pay attention to the protocol it supports. This small and necessary device can be found in any Hi-Tech store.
When the internal network card does not support the new standard, a new network card can become an alternative to the network card. It's fairly easy to replace on a desktop computer. But in laptops and laptops, this is much more difficult to do. In such cases, it is more convenient to use a network adapter.
Sources:
- Can't setup network with 1394 adapter
You can develop several schemes for networking computers so that they all get access to the Internet using one single account. When it comes to two laptops, it is most reasonable to use a wireless communication channel.
Instruction
Select a mobile computer that will be connected to the Internet via a network cable. This laptop will act as a router when creating a local network. Connect the provider's cable to the selected mobile computer and set up an Internet connection. At this point, do not change the settings for this connection.
Check the activity of the Wi-Fi network adapter of the first mobile computer. Open the Control Panel and select the "Network and Internet" submenu. Go to the Network and Sharing Center. Open the Manage Wireless Networks menu. Click the "Add" button in the menu that opens. From the options offered, select "Create a computer-to-computer network" and click the "Next" button in the next window.
Fill in all the fields of the menu that appears. Specify an arbitrary network name and select any suitable security type. Enter your password and remember it. Activate the "Save settings for this network" function by checking the box next to the corresponding inscription. Click the "Next" button and close the program window.
Open the menu that displays a list of active . Right-click on the Internet connection icon and select "Properties". Open the "Access" menu. Activate Internet Sharing for networked computers. In the next field, enter the wireless network you created. Save the settings for this menu.
Turn on the second laptop. Start searching for available Wi-Fi networks after turning on the wireless adapter. Connect to the newly created network. If after that the second mobile computer did not get access to the Internet, then set the wireless adapter of the first laptop to a static IP address. Enter its value in the "Default Gateway" and "Preferred DNS Server" fields, opening the TCP / IP protocol settings of the adapter of the second laptop.
Related videos
Adapters are called devices and devices that are completely different from each other in design. One thing unites them: they coordinate with each other two objects of one kind or another that are not directly compatible with each other.
Older people will remember that adapters are sometimes called pickups used in turntables. In those years when gramophones and gramophones were widespread, many of their owners wanted to listen to records through amplifiers without changing the entire apparatus. To match the existing gramophone or gramophone with an amplifier, an adapter was placed on it. Later, when the players began to be equipped with piezoelectric or electromagnetic heads initially, they almost stopped calling pickups adapters. For the same reason, adapters are still called pickups for guitars and other musical instruments, especially those in whose design they were not originally provided. Tools equipped with them are called adapters. Power supplies made in cases that look like enlarged power plugs are also called adapters. They match low-voltage, but sometimes high-current load inputs with high-voltage lighting networks, consuming little current from it. Anyone who knows that power is equal to the product of current and voltage will understand that this does not contradict the law of conservation of energy. Also, any kind of adapters are called adapters. Some of them are designed to coordinate electrical connectors of various designs, while others are used as part of hydraulic, pneumatic, mechanical and other systems. Sometimes even fasteners carry this name. What about the video card installed in your computer? You have probably heard how it is sometimes called a video adapter. And rightly so, because you cannot directly connect the monitor to the motherboard - only through a video adapter. The only exceptions are boards with built-in video subsystems. True, modern video cards do not quite fit this, since they are separate computing systems, sometimes competing in performance with the computers they are installed in. A telephone adapter is an electromagnetic device that acts similarly to the musical instrument adapter already discussed above. It allows you to coordinate the speaker, located in the handset of the telephone, with a voice recorder or hearing aid. If an old device is used, the telephone adapter can pick up an alternating magnetic field not from the sound emitter, but from the conversation node transformer.
Related videos
Adapter is an ambiguous word that refers to a variety of accessories for technical devices. How to use the adapter depends on what it is intended for.

Instruction
Mains adapter - a power supply unit structurally integrated with a mains plug. The output voltage of this device must correspond to that for which the load is designed, and the maximum allowable output current must not be less than the load consumed. Also pay attention to the type of plug and the polarity of the voltage on its contacts. For cylindrical plugs, the polarity is often marked on the adapter and on the load - they must match. Do not plug heavy power supplies directly into loose outlets, use extension cords.
To install a memory card of one format into a device designed for cards of another format, use an adapter consisting of two connectors connected by wires. There is nothing electronic in it. Today, the most common adapters for installing Micro SD cards in devices designed for full-size SD cards. Insert the card into the adapter, and then the adapter with it into the device, and everything will work just like with a full-sized SD card.
Adapters for interfacing different types of connectors are also called adapters. Such an accessory is useful, for example, for connecting a VGA monitor to a video card with a DVI output, if analog signals are output to it. You can also use the appropriate adapter to connect headphones with a 3.5mm plug to a device with a 6.3mm jack, or vice versa. Choose such an adapter correctly: to connect stereo headphones to a stereo output, it must be a three-pin, and to connect a mono microphone to a mono input, it can be either two- or three-pin.
Power plug adapters allow plugs with thick pins to be plugged into outlets with small diameter holes. Please note that many of them start to overheat at a current of more than 4 A. Do not use them in conjunction with powerful devices, especially for a long time. Also remember that the device when using such an adapter remains ungrounded.
An adapter is also called an expansion card that is installed in a motherboard slot. Today, almost all peripherals are integrated into the motherboard or performed as external devices connected via USB. The exception is video adapters, and then only powerful ones. If you do not need significant GPU performance, use the video adapter built into the motherboard. And if you cannot do without a separate video card, do not forget to periodically carry out its prevention: lubricate the fan, clean the heatsink, change the thermal paste.
Another type of device called adapters is pickups. They are divided into guitar and intended for use in turntables for vinyl records. In both cases, select the correct amplifier input for connecting the adapter. It must have an input impedance close to the output impedance of the amplifier, and be designed for an amplitude close to that developed by the adapter. Sometimes the matching of the amplitude-frequency characteristics (AFC) is also required. If there is no suitable input on the amplifier, then the signal amplitude must either be reduced by an external attenuator (if the input sensitivity is excessive), or increased using an external pre-amplifier (if the input sensitivity is insufficient).
note
Many types of adapters can only be installed and removed when all devices are de-energized.
Windows 7 supports the vast majority of network cards. Moreover, most modern network equipment is sharpened specifically for Windows, with all the ensuing problems, because Windows is not famous for its stability. However, Microsoft promptly solves most of the problems that arise with network equipment, honor and praise to them, but those that inevitably arise will be analyzed in detail in this article.
First of all: in order to expand the potential range of tasks that a client computer performs on a network, there is a need to change the basic parameters of a network card.
Here are examples of such tasks:

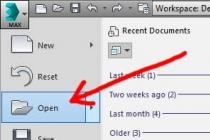
How to see a list of available network adapters (network connections) in Windows 7?
The list of available devices on Windows 7 can be seen in two ways:

The second method starts by opening the "Device Manager" using the "Run" window:

Enabling the network card, including using the BIOS
Read the instructions for all BIOS versions in the article -
On laptops, turning the network interface on and off is done by pressing a keyboard shortcut, on desktop computers, through the BIOS menu.

To enable the wireless network adapter on laptops, there is a Fn + F12 combination, although some manufacturers make a special key for this function.

Installing a network driver on Windows 7, including without the Internet
Since the network adapter is equivalent to the Internet, its absence makes it very difficult to download the driver for the network card. The issue is resolved by pre-recording drivers on media.
- Drivers are downloaded and written to a flash drive, CD, etc.
- The media is connected to the PC.
- After that, the "Device Manager" opens, using the "Run" window (called by pressing the "Win + R" keys), in which the "devmgmt.msc" command is entered.

- There is a section "Sound, game and video devices", subsection "Unknown device", which is not yet installed. You need to start installing drivers for an unknown device (future network adapter) after selecting it with the right mouse button and selecting it in the "Properties" drop-down menu.

- Click the left mouse button - "Update".

- Manual setting is selected.

- The path to the driver media is written or indicated.

- Finally, the installation begins. It takes no more than a couple of minutes.
The network card without drivers in the "Device Manager" was in the "Unknown Devices" section. After the update, it takes its rightful place - in the "Network Adapters".

Video - How to install a network adapter driver without access to the Internet
Setting up a network connection in Windows 7
Although Internet Service Providers prefer to configure their customers' network equipment themselves, sometimes more advanced configuration is required. This is typical for computers with multiple adapters.
For this:
- Go to the context menu "Start", open the "Control Panel".

- In the "View" category, set the value to "Category", find and open the "Network and Internet" section.

- Click on the "Network and Sharing Center" link.

- Click on the "Change adapter settings" link.

- Right-click on the network connection shortcut, select "Properties".

- Check the box "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)", click on the "Properties" button.

- Check the box "Use the following IP address", fill in the fields with data.

On a note! The fields and "Main gateway" are in the agreement with the Internet provider, the remaining fields contain the same values for all users.
Video - The computer does not see the network adapter
How to view and change network card settings (IP, Mac, and more) in Windows 7?

It is easy to see the adapter parameters and its MAC address thanks to system programs.
For this:

How to reset all network driver settings?
If you want to completely roll back all settings to their original level, then do the following:


Is it possible to create two network cards?
Many users are thinking about getting a second network card. Physically, there are no problems here: most laptops and computers support a second network card. But there are exceptions, as well as damaged slots, as well as netbooks and tablet computers. In this situation, you need to use a virtual board that distributes Internet traffic no worse than a physical one.
The ability to install such a virtual card is in the Windows system itself:
- In the "Start" menu, type "manager" in the field, open "Device Manager".

- In the "Device Manager" click on the "Network adapters" section, select "Actions" in the top menu, and from the drop-down menu - "Install an old device".

- The installation wizard will open. You need to select the manual option to access the list of drivers for all devices.

- Scroll through the categories, select "Network adapters", click "Next".

- Then click on the "Micrsoft" item, add "Micrsoft loopback adapter" or "Microsoft Loopback Adapter", which will then appear in the network connections window.


- Confirm. The network adapter should now appear in Network Connections.


Complete reset of network drivers
If your Internet is down or most of the Internet pages are not opening, then resetting all parameters and the TCP / IP stack can be an excellent solution to this problem.

Disable network card
To disable the network adapter, the best remedy is to use the most standard and convenient Windows tool for maintaining all such equipment - this is the device manager. Do the following:

In this case, the shutdown will occur immediately, it will not even be necessary to reboot the OS.
Important! After the adapter is disconnected, the Internet connection will be cut off along with it and there will be a disconnection from the local network. Therefore, it is recommended to finish all your business on the Internet in a timely manner before turning off the network card.
The network adapter does not have valid IP settings
A common problem for Windows 7 users is when there are problems accessing the Internet and the Network Diagnostics tool gives a message that the network adapter does not have valid IP settings.

In this case, you can first try to reset the router. If you have a wired connection, then disable and then re-enable your network-connection in the network connections menu. If this does not help, then you can proceed to the next steps.
Step 1. Renew your IP address - this is the easiest method, although not always helpful in this case. To do this, open Command Prompt (as administrator) and enter the following commands:

Check again if the error is still displayed? If yes, then let's move on.
Step 2 You can try to reset the network settings, namely the IP protocols. It is recommended to reset the TCP/IP protocol stack to factory settings in the most acute cases, when problems occur as a result of malware, etc. To do this, open a command prompt in administrator mode and type:

Network card settings crash
When setting up a network, users may encounter the following situation: when the IP address, gateway, DNS are manually entered - the prescribed parameters are not saved, but reset to factory settings, and thus it becomes impossible to change network settings from automatically receiving addresses from the router. One of the common reasons for this is the incorrect removal of an antivirus that has firewall functions.

What should be done:
- Reset the TCP/IP protocol stack to factory settings (see how to do this earlier in the article).
- Reboot.
If this does not help, then do the following:

After that, the problem should be resolved.
What to do if there are problems with the network card?
Many plug-in network adapters, due to their vulnerability to electricity, can temporarily fail during periods of severe thunderstorms, or power outages in a building. In most cases, difficulties manifest themselves in situations with wired equipment, since multi-storey buildings have long cable routes laid by Internet providers in places not quite intended for this, next to telephone and television cables and high voltage wires. High humidity, dampness and low temperature in this area - all this has an extremely negative effect on the insulation of wires, so breakdowns appear in them. .

Sometimes also, in more rare cases, breakdowns occur due to emergencies such as a major thunderstorm. Network adapters often burn out, or users begin to experience difficulty logging into the network. In this case, the equipment will function, but there may be no connection to the Internet during such periods.
Unfortunately, this problem can only be solved by purchasing another network adapter model. For a desktop computer, it complies with the PCI standard, for a laptop - USB and PCMCIA.

It is also not recommended to include a network cable in the router, and then connect a computer to it, because even if the router breaks down, its replacement will be relatively inexpensive compared to replacing the network card built into the computer (or even the entire motherboard).
Windows 7 does not see network adapter

When the integrated network equipment is not shown in either the Network Connections window or the Device Manager, and is not even reflected in the Unknown Devices section (which would be due to the lack of drivers), then something is most likely wrong with it physically. It is quite possible that some transistors burned out on the network card board, or a chip flew off - in this case it is more expedient to buy a new card.
Video - How to set up a wired network card on Windows 7