Microsoft Corporation, starting with Windows Vista, has changed the security policy of its systems with respect to the local network. The operating system seemed new, somehow too complex, and therefore many could not figure out how to open access to files on the computer. Today we will analyze how this is done using the example of Windows 8.1, but Vista and 7 have a similar system, and the difference is not fundamental. The local area network can also be used for subsequent creation , which will unite all multimedia devices of the house or apartment, or to share files with your phone or tablet.
In my opinion, this is very convenient when, without additional movements, you can play a movie from a computer, laptop or even a phone on a large TV screen or listen to your favorite music from a phone, on a speaker system without connecting additional wires, although this is already necessary ... But let's move on to setting up a local network.
Video instruction is available by link.
Step-by-step instruction
- For normal functioning of a local network, all computers on this network must be in the same workgroup; for a home network, let's take MSHOME. To install it, we need to go along the following path: open the "Control Panel" - "System and Security" - "System" (you can also right-click on the "Computer" shortcut on the desktop and select "Properties" or the key combination "" ). In the window that opens, in the left column, select "Additional system parameters".

- In the window that opens, go to the "Computer name" tab and press the "Change" button. A dialog box opens in which we need to record a new working group. We register MSHOME (all in capital letters) and click OK. We close the system parameters by pressing the OK button and restart the computer.

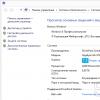
- Further, it is advisable to configure a permanent IP for both computers. To do this, go to the "Control Panel" - "Network and Internet" - "Network and Sharing Center" - on the left side of the "Change adapter settings" window - select the network card, right-click and click "Properties".

- Before performing this step, read the notes below the screenshot. Select "Internet Protocol version 4" and click "Properties", fill in as shown in the picture.

P.S. If your local network is organized through a router with a DHCP server enabled - the IP address, the Default gateway and DNS Server can be left in automatic mode. This action must be done if you have two computers connected directly or DHCP is disabled on the router.
P.P.S. The value of the IP address must be different on computers within the same local network. That is, we specify IP 192.168.0.7 for this computer, and 192.168.0.8 for the next one.
- At this point, we begin to work with the folders that we will share on the network. I will tell you on the example of one folder, but you can open access to the entire local disk in a similar scenario.
First, we need to share the folder. It should be borne in mind that if the network is not limited to two computers (for example, some providers (Beeline) conduct the Internet in apartments on the basis of one large local network), it makes sense not to give the right to change the contents of the folder; if you are sure of the computers included in the local network, feel free to give "Full Control". So, open the properties of the folder we need, for this we right-click on the folder and select "Properties", open the "Access" tab and click the "Advanced settings ..." button.
- In the window that opens, put a checkmark "Share this folder", press the "Permissions" button and give the necessary rights to the folder; since this is an example, I give full access to the folder, but you put it at your discretion. That's what I did:

- Click OK to accept the changes, also click OK in the "Advanced Sharing Settings" window, then in the folder properties go to the "Security" section and click the "Change" button.

Next, we need to configure the visibility of the computer within the local network. To do this, go to the "Control Panel" - "Network and Internet" - "Network and Sharing Center" - on the left side of the window, select "Change advanced sharing options" and we will open profiles of sharing options. Here your task is that in all profiles you must enable "network discovery" and "file and printer sharing" and "sharing so that network users can read and write files in shared folders", as well as Disable Password Protected Sharing. We press to save changes.



Hello friends! I went to my mail today, and decided to check the spam folder (I haven't checked it for a couple of months already)... I found a couple of necessary letters, among which there is a question from a reader (visitor) of the site. The question was submitted using the contact form and got into spam.
As a rule, I do not answer questions by e-mail, but I do it on the website, or on our ... Well, also in the VKontakte group. But the question was very interesting and very well written.(and not in a nutshell, as is usually the case)... And the topic is very relevant.
Dmitriy (that's the name of the author) sent it back on December 9 (and today is already December 24)... It is a pity that I did not notice earlier. I thought that this situation (like Dmitry's) worries many now, and decided to publish this question on the site and try to give an answer to it.
I hope Dmitry will not mind.
Security issue when connecting to open Wi-Fi
Hello, Sergey.
I read your article and comments to it.
The situation is this, I use the MTS connection, but the quality of the connection is such that it is a very slow Internet, which also disappears from time to time (connection breaks, etc.), unreliable in general. At the same time, I can see several Wi-Fi networks, almost all of them are password-protected, some are open (but they don’t let the Internet, and I don’t know what you can use there), and there is an open network where you do not need to enter a password and lets go to the Internet. Most likely, this is someone's home Internet, someone from the residents of the house, but I'm not 100% sure, of course.
And it seems to me that he left the access open deliberately (there are people who do this, like they don't mind, let people use it)... At least he could have closed access, but he still hasn't done so and it seems he is not going to. In such a situation, I continue to use the MTS connection and, if necessary, sometimes connect to an open Wi-Fi.
And my question is simple. What can the owner of this Wi-Fi do on my computer and maybe I won't even see it?
- First, whether he can see the passwords that I enter somewhere. I was told that if you log in to any site through https, then the password cannot be seen and stolen, is this really so? Or is it better not to risk it?
- Secondly, are they visible to him if I am simultaneously connected via the MTS-connection? I check my mail and some important sites (pay something) I log in through the MTS connection, but there have already been cases when I just forgot to disconnect from Wi-Fi by connecting to the MTS connection at the same time. And now I also don't quite understand how the traffic goes in this case and whether it was possible to steal passwords?
- And finally, the biggest questions I have about what the owner of this Wi-Fi can look at on my computer, can he open any files, can he delete them, copy himself, etc. And how can you protect yourself from this ? Those. I kind of clicked on the disks that are on the computer (C, D, F) and there is no public access to them, but I don’t understand this at all. Maybe there is access to some folders or files on the table. How do you know what a stranger can see?
Also, I faced the fact that his computer now began to appear right next to my folders (I have Windows 8.1 Pro). Those. you click on the conductor, you look, and there you can see some other's folder (computer) and it generally amazes me nedecko, it feels like I was hacked and a stranger is climbing on my laptop. First, in the section “This computer”, where Explorer shows all the disks that it has, and the folders of these disks, it appeared (ie its folder).
And then, too, there below in the explorer in the section "Net" besides the name of my laptop, another computer began to appear! Stunned.
Now, as I write this, it is not yet. (not connected to me, apparently, but later it will probably appear again, and Wi-Fi is open), but if you click on this section ("Network"), then the tab appears "Computer" (while there is only mine) and just below "Network infrastructure", and it contains "Network router" – Debian Router... If you click on this Debian Router, then by the IP address in the browser, a site opens with various information, in which I still do not understand much. Earlier, when I log on to Wi-Fi, this was not the case.
But I think that now since this person is setting up something there, I will see his computer in my explorer regularly (when he goes online) and this gives me security concerns, i.e. since I do not know what files he can see on my computer, download, delete them, etc., etc.
In addition, in "Windows Firewall" there is a section "Private networks", and there is a signature "Connected"!
And there is an inscription "Active private networks" and next to it is the name of its Wi-Fi (or, probably, the same name of this Wi-Fi owner's computer).
Those. it turns out that he has already tuned in to my computer and is actively connected to it sometimes, right?
In general, tell me what to do in such a situation? Is it worth using this Wi-Fi, not paying attention that someone is connected to my laptop (or maybe even something is looking at him) may even actually move in that direction to establish interaction (through computers and not only maybe even) with the owner of the Wi-Fi or it is better not to connect to this Wi-Fi in order to avoid the above problems (fears that he sees my files and can do something with them or with my computer).
At the same time, I am ready to replenish his Internet account. (i.e. not free to use it), since the quality of the MTS connection does not satisfy me, and its Wi-Fi is caught just fine. In general, I'm ready to pay for high-quality Wi-Fi access, if some company gave it officially.
Thank you. Dmitriy.
Let's try to figure it out [answer]
I'll probably start with the main thing, and then I'll try to answer all the questions. In this particular case, I do not think that this open Wi-Fi network was created by some “hacker”. If only because the number of potential victims is not very large (only neighboring apartments)... Better places can be found for such a business.
Yes, and in a networked environment (on Dmitry's computer) computers of other users appear that are connected to this network. If this network had been set up by some "hacker", then he would hardly have set fire to his computer. Although, of course, I cannot say 100% of this, no one can.
Now, let's move on to more detailed points.
About the security of passwords and authorization on sites
Not so long ago, I wrote an article on this very issue. In it, I talked about security when connecting via public Wi-Fi networks. The network to which Dmitry connects is also to some extent public.
I would still advise Dmitry to use this network through a VPN connection. Not necessarily through a paid service, you can find free VPNs as well. But this is only advice, and Dmitry will be calmer this way.
As far as the connection via https is concerned, yes, this protocol is well secured. But, unfortunately, not all sites use it. And there is no 100% protection, we must always remember this.
Can a neighbor see your passwords if you are connected to his router? No, just like that, never. Even if this is some kind of super user, he will have to work very hard to intercept your authorization on some site (if at all possible) especially if you are using a VPN connection and the channel is encrypted using https.
Connection via Wi-Fi and via MTS modem
Dmitry, most likely, when you have a Wi-Fi connection and a modem (at the same time), then the Internet is used via Wi-Fi. I don’t know for sure, true, but it’s not so important, based on what I wrote above.
But, if you feel so calmer, then disconnect from Wi-Fi and do serious operations via a modem from MTS.
File security when connecting to someone else's Wi-Fi
As for the security of files that are on the computer, which in turn is connected to open Wi-Fi, everything is a little simpler and clearer here.
It is probably worth starting with the fact that the computer, or rather the operating system, is designed for the computer to connect to open networks in public places. And assume that the owner of the Wi-Fi router (to which you connected), maybe just getting access to files on your computer is stupid. Well, you must agree.
Of course, there is protection, there are appropriate settings, and so on.
Dmitry has Windows 8.1, unfortunately I now do not have access to this operating system, therefore, I cannot show it for sure. But I will show it using Windows 7 as an example. I advise that for the network to which you are connected, set the status Public (I just don't know exactly how to do this in Windows 8.1).
You need to go to “ Network and Sharing Center " (Control Panel - Network Control Center ...)... The network you are connected to should be displayed there. Below, under it should be written which network it belongs to. If there is a public (or something like that), then everything is fine, let it be so.
If there Home is then click on it and select Public network.

Perhaps, just when you first connected to this network, you indicated that this is a home network.
But then you tell me, what if the network was in the “Home network” status, access to my files was open? No, you won't be able to access your files just like that.
If only because password-protected sharing is enabled by default. And even if it were disabled, then access would only be open to the folder Are common (if you haven't shared other folders / drives)... And as a rule there is nothing in it.
For complete reassurance, I propose to go to the "Network and Sharing Center" and on the left select "Change advanced sharing options".

And check the settings for both profiles: General and Home or work... Depending on what status you have set for a particular network, such parameters will be applied.
Make sure password protected sharing is enabled. You can turn off file and printer sharing. But, when you need it, then remember this, otherwise there may be problems with access.
Accessing your files is not easy, even if you are connected to the same network. But, do not forget about hacks and so on. Again, there is no 100% protection.
Some more nuances
Dmitry wrote that in the explorer, in the "Network" section, he sees other people's computers, and this worries him very much. The fact that computers appear there does not mean that you have been broken. On the contrary, it most likely means that the user whose computer you see is not very experienced.
If more computers appear there, then it is most likely that someone else will connect to the same network. And you most likely cannot get access to these computers.
Also, Dmitry wrote that a router (Debian Router) is visible on the Network Infrastructure page. It's just as normal. And if you click on it, the router settings open (most likely at 192.168.1.1)... This again speaks of the illiteracy of the owner of this router. Access to the settings is not closed (but necessary). You can go in and put them a password on Wi-Fi 🙂.
The firewall most likely simply says that you are connected to the network, well, its name is indicated. There is currently no way to see exactly this on Windows 8.1.
Afterword
Specifically, according to the situation that arose with Dmitry: I think that this is just a network of an inexperienced user who simply does not know and does not want to understand this. Or for example: a specialist set up a router, and then the settings on the router went off (this happens), and the network was left without a password.
The network of most likely one of your neighbors (if the signal is good)... You can try to find it. Knock on the door and say: "Is this your net ...?" 🙂 well, or come up with a more original way.
Many thanks to Dmitry for this question!
Best wishes!
More on the site:
Is it safe to use an open Wi-Fi network? Can they access my computer over Wi-Fi? [question from reader] updated: December 24, 2013 by the author: admin
Kivshenko Alexey, 1880
This article provides an overview five options for solving the problem of organizing access to corporate network services from the Internet. The review provides an analysis of options for safety and feasibility, which will help to understand the essence of the issue, refresh and systematize their knowledge for both novice specialists and more experienced ones. The materials of the article can be used to substantiate your design decisions.
When considering options, take the network where you want to publish as an example:
- Corporate mail server (Web-mail).
- Corporate Terminal Server (RDP).
- Extranet service for contractors (Web-API).
Option 1. Flat network
In this variant, all nodes of the corporate network are contained in one common network for all ("Internal network"), within which communication between them is not limited. The network is connected to the Internet through an edge router / firewall (hereinafter - IFW).Access of nodes to the Internet is carried out through NAT, and access to services from the Internet through Port forwarding.
Pros of the option:
- Minimum requirements for functionality IFW(can be done on almost any, even a home router).
- Minimum requirements for the knowledge of the specialist who implements the option.
- The minimum level of security. In the event of a breach, in which the Intruder gains control over one of the servers published on the Internet, all other nodes and communication channels of the corporate network become available to him for further attack.
Such a network can be compared to a company where staff and customers are in one common room (open space)

hrmaximum.ru
Option 2. DMZ
To eliminate the previously mentioned drawback, network nodes accessible from the Internet are placed in a specially dedicated segment - the demilitarized zone (DMZ). The DMZ is organized using firewalls that separate it from the Internet ( IFW) and from the internal network ( DFW).
In this case, the rules for filtering firewalls are as follows:
- From the internal network, you can initiate connections to the DMZ and to the WAN (Wide Area Network).
- You can initiate connections to the WAN from the DMZ.
- From the WAN, you can initiate connections to the DMZ.
- Initiating connections from the WAN and DMZ to the internal network is prohibited.

Pros of the option:
- Increased network security from hacking of individual services. Even if one of the servers is compromised, the Intruder will not be able to access resources located on the internal network (for example, network printers, video surveillance systems, etc.).
- Moving servers to the DMZ alone does not increase their security.
- An additional ME is required to separate the DMZ from the internal network.
This variant of the network architecture is similar to the organization of the work and client areas in a company, where clients can be located only in the client area, and the staff can be in both the client and work areas. The DMZ segment is exactly the analogue of the client zone.

autobam.ru
Option 3. Separation of services into Front-End and Back-End
As noted earlier, placing a server in the DMZ does not in any way improve the security of the service itself. One of the options for correcting the situation is to divide the service functionality into two parts: Front-End and Back-End. Moreover, each part is located on a separate server, between which network interaction is organized. Front-End servers that implement the functionality of interacting with clients on the Internet are placed in the DMZ, and the Back-End servers that implement the rest of the functionality are left in the internal network. For interaction between them on DFW create rules to allow initiation of Front-End to Back-End connections.
As an example, consider a corporate email service that serves clients both from within the network and from the Internet. Clients from the inside use POP3 / SMTP, while clients from the Internet use a Web interface. Usually, at the stage of implementation, companies choose the simplest way to deploy a service and put all its components on one server. Then, as the need to ensure information security is realized, the functionality of the service is divided into parts, and the part that is responsible for servicing clients from the Internet (Front-End) is transferred to a separate server that interacts over the network with the server that implements the remaining functionality (Back -End). In this case, the Front-End is placed in the DMZ, and the Back-End remains in the internal segment. For communication between Front-End and Back-End on DFW create a rule allowing initiation of connections from Front-End to Back-End.
Pros of the option:
- In general, attacks directed against the protected service can "stumble" over the Front-End, which will neutralize or significantly reduce possible damage. For example, attacks such as TCP SYN Flood or slow http read aimed at a service will result in the Front-End server being unavailable, while the Back-End will continue to function normally and serve users.
- In general, the Back-End server may not have access to the Internet, which, if hacked (for example, by locally running malicious code), will make it difficult to remotely manage it from the Internet.
- Front-End is well suited for hosting an application-level firewall (such as a Web application firewall) or an intrusion prevention system (IPS, such as snort).
- For communication between Front-End and Back-End on DFW a rule is created that allows initiating a connection from the DMZ to the internal network, which creates threats associated with the use of this rule by other hosts in the DMZ (for example, through the implementation of IP spoofing attacks, ARP poisoning, etc.)
- Not all services can be divided into Front-End and Back-End.
- The company must implement business processes for updating the firewall rules.
- The company must implement protection mechanisms against attacks from Intruders who gain access to the server in the DMZ.
- In real life, even without dividing servers into Front-End and Back-End servers from the DMZ, it is very often necessary to access servers located in the internal network, therefore, the indicated disadvantages of this option will also be true for the previous considered option.
- If we consider the protection of applications running through the Web interface, then even if the server does not support the separation of functions between the Front-End and Back-End, the use of an http reverse proxy server (for example, nginx) as a Front-End will minimize the risks associated with attacks for denial of service. For example, SYN flood attacks can make the http reverse proxy unavailable while the Back-End continues to work.
This option is essentially similar to a work organization in which assistant secretaries are used for highly loaded workers. Then Back-End will be an analogue of a loaded employee, and Front-End will be an analogue of a secretary.

mln.kz
Option 4. Secured DMZ
The DMZ is the portion of the network that is accessible from the Internet and, as a result, is most at risk of host compromise. The design of the DMZ and the approaches used in it should provide maximum survivability in conditions when the Intruder gained control of one of the nodes in the DMZ. As possible attacks, consider attacks that affect almost all information systems operating with default settings:Defending Against DHCP Attacks
Despite the fact that DHCP is designed to automate the configuration of IP addresses for workstations, in some companies there are cases when IP addresses for servers are issued via DHCP, but this is rather bad practice. Therefore, in order to protect against Rogue DHCP Server, DHCP starvation, it is recommended to completely deactivate DHCP in the DMZ.Protection against MAC flood attacks
To protect against MAC flood, the switch ports are configured to limit the maximum intensity of broadcast traffic (since usually broadcast traffic is generated during these attacks). Attacks involving specific (unicast) network addresses will be blocked by MAC filtering, which we discussed earlier.Protection against UDP flood attacks
Protection against this type of attack is performed in the same way as against MAC flood, except that filtering is carried out at the IP level (L3).Protecting against TCP SYN flood attacks
To protect against this attack, the following options are possible:- Host protection with TCP SYN Cookie technology.
- Firewall protection (assuming the DMZ is subnetted) by limiting the amount of traffic that contains TCP SYN requests.
Protection against attacks on network services and web applications
There is no universal solution to this problem, but it is an established practice to implement software vulnerability management processes (identification, patching, etc., for example), as well as the use of intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS / IPS).Protection against attacks to bypass authentication means
As in the previous case, there is no universal solution to this problem.Usually, in the case of a large number of unsuccessful authorization attempts, accounts are blocked to avoid brute force authentication data (for example, a password). But this approach is quite controversial, and here's why.
First, the Intruder can brute-force authentication information with an intensity that does not lead to account blocking (there are cases when a password was brute-force within several months with an interval of several tens of minutes between attempts).
Secondly, this feature can be used for denial of service attacks, in which the Intruder will deliberately make a large number of authorization attempts in order to block accounts.
The most effective option against attacks of this class will be the use of IDS / IPS systems, which, when attempts to brute-force passwords are detected, will block not the account, but the source from which this brute-force comes from (for example, block the IP address of the Intruder).
The final list of protective measures for this option:
- The DMZ is divided into IP subnets based on a separate subnet for each host.
- IP addresses are assigned manually by administrators. DHCP is not used.
- On the network interfaces to which the DMZ hosts are connected, MAC and IP filtering are activated, restrictions on the intensity of broadcast traffic and traffic containing TCP SYN requests.
- Auto-negotiation of port types is disabled on the switches, the use of native VLAN is prohibited.
- The TCP SYN Cookie is configured on DMZ hosts and servers on the internal network to which these hosts connect.
- Vulnerability management is implemented on the DMZ hosts (and preferably the rest of the network).
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems IDS / IPS are being implemented in the DMZ segment.
- High degree of security.
- Increased requirements for the functionality of the equipment.
- Labor costs in implementation and support.
If earlier we compared DMZ with a client area equipped with sofas and ottomans, then a protected DMZ will look more like an armored cash desk.

valmax.com.ua
Option 5. Back connect
The protection measures considered in the previous version were based on the fact that the network had a device (switch / router / firewall) capable of implementing them. But in practice, for example, when using virtual infrastructure (virtual switches often have very limited capabilities), such a device may not exist.Under these conditions, many of the previously considered attacks become available to the Intruder, the most dangerous of which will be:
- attacks allowing to intercept and modify traffic (ARP Poisoning, CAM table overflow + TCP session hijacking, etc.);
- attacks related to the exploitation of vulnerabilities of internal network servers to which connections can be initiated from the DMZ (which is possible by bypassing filtering rules DFW due to IP and MAC spoofing).
Thus, we are faced with the task of protecting the servers of the internal network from the attacks of the Intruder both from the DMZ and from the internal network (infection of the automated workplace with a Trojan can be interpreted as the actions of the Intruder from the internal network).
The approach proposed below is aimed at reducing the number of channels through which the Intruder can attack servers, and there are at least two such channels. The first is the rule on DFW, allowing access to the server on the internal network from the DMZ (even with limited IP addresses), and the second is the network port open on the server, on which connection requests are expected.
You can close these channels if the internal network server will itself build connections to the server in the DMZ and will do this using cryptographically protected network protocols. Then there will be no open port, no rule on DFW.
But the problem is that ordinary server services do not know how to work in this way, and to implement this approach, you need to use network tunneling, implemented, for example, using SSH or VPN, and already within the tunnels allow connections from the server in the DMZ to the server on the internal network ...
The general scheme of operation of this option is as follows:
- An SSH / VPN server is installed on a server in the DMZ, and an SSH / VPN client is installed on a server in the internal network.
- The internal network server initiates the building of the network tunnel to the server in the DMZ. The tunnel is built with mutual authentication of the client and server.
- The server from the DMZ, within the framework of the constructed tunnel, initiates a connection to the server in the internal network, through which the protected data is transmitted.
- A local firewall is configured on the internal network server to filter traffic passing through the tunnel.

Using this option in practice has shown that it is convenient to build network tunnels using OpenVPN, since it has the following important properties:
- Cross-platform. You can organize communication on servers with different operating systems.
- Ability to build tunnels with mutual client and server authentication.
- The ability to use certified cryptography.
Pros of the option:
- Architectural reduction of the number of attack vectors on the protected server of the internal network.
- Ensuring security in the absence of filtering network traffic.
- Protecting data transmitted over the network from unauthorized viewing and modification.
- The ability to selectively increase the level of security of services.
- The possibility of implementing a two-circuit protection system, where the first circuit is provided using firewalling, and the second is organized on the basis of this option.
- The implementation and maintenance of this protection option requires additional labor costs.
- Incompatibility with Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS / IPS).
- Additional computing load on the servers.
The main point of this option is that a trusted person establishes a connection with a non-trusted person, which is similar to a situation when, when issuing loans, the Banks themselves call back a potential borrower in order to verify the data. Add tags
Every year, the competition in the field of trade becomes more and more due to the fact that many are striving to open their own store and shopping center. Retail chains are gaining more and more popularity - these are 2 or more retail outlets that have one owner, sell goods with a similar assortment, they have a single procurement and sales service, they are decorated in the same style. 
Combining stores into a common network is one of the most effective ways to develop trade. This is confirmed by both Russian and world experience in the field of sales.
Benefits of creating retail chains
The main advantages are:
- due to a wider territorial segment, goods can be placed, changing the space;
- you can change the assortment of goods, as well as sell it at lower prices, which corresponds to the demand of consumers;
- when buying goods in large quantities, there is an opportunity to significantly save thanks to discounts and reduced transport costs;
- the management of the retail network is always centralized and at a high level, the employees are mostly qualified specialists, due to which many shortcomings in the work that an ordinary store has in excess are eliminated;
- you can improve the efficiency of care by diversifying different types of activities;
- the cost of the cost of goods is reduced, since there is no need to stimulate sales and purchase advertising;
- an online store can combine both wholesale and retail networks;
- each individual store belonging to the same chain has a certain freedom, thanks to which it is possible to act independently, taking into account the preferences of local buyers.
 Now in all developed countries it is retail chains that make up the majority of the entire retail space, the rest account for about 4% of the total market. In Russia, retail chains now account for 20-30% of the total market, but there is a tendency towards the development of retail chains. A chain that includes more than 19 stores or supermarkets is considered a retail chain. According to experts, the most effective is such a retail network, which will include at least 21 stores. The most widespread retail chains are in Moscow, where they account for approximately 45% of the total number of retail outlets.
Now in all developed countries it is retail chains that make up the majority of the entire retail space, the rest account for about 4% of the total market. In Russia, retail chains now account for 20-30% of the total market, but there is a tendency towards the development of retail chains. A chain that includes more than 19 stores or supermarkets is considered a retail chain. According to experts, the most effective is such a retail network, which will include at least 21 stores. The most widespread retail chains are in Moscow, where they account for approximately 45% of the total number of retail outlets.
Back to the table of contents
The structure of the trading network and the conditions for its creation
In general, a retail chain is considered to be several trading enterprises that are located in different territories, they have a common goal related to the sale of goods and customer service, they are under the control of one management. This is a single trade link, thanks to which the needs of customers in certain goods are satisfied. When a trading network is operating, the population has the opportunity to conveniently, quickly, without spending a lot of time, to purchase the necessary goods and services that are freely available, in the required quantity, not far from work or place of residence.
The characteristics of the retail chain are:
- the ratio of the number of chain stores engaged in the trade of food and non-food products;
- the share of one network in the total number of all trade enterprises;
- the proportion of stores that sell specialized goods in the total number of outlets;
- the various forms of sale and the various methods of service that are used;
- the number of retail and non-retail space in the store, their ratio to each other;
- opening hours of a store located in a certain retail space;
- the ratio of the total area of the store to that of its territory, which is located in the outbuildings and built-in premises;
- the number of stores that have refrigeration equipment and sell perishable goods;
- determination of the average area per store.
When studying retail trade using the main characteristics of the classification, it is necessary to obtain information about the quality, importance and relative value, the impact of external factors and the organization of trade in a particular enterprise.
To open a retail network, you must:

Each store in the chain has a modern look, a strictly defined assortment of goods, a specific size of sales area, pre-planned methods and forms of service. All stores use only advanced technologies related to doing business, as well as modern premises.
Back to the table of contents
How to create your own chain of stores correctly
If you organize your business correctly, then having a store is very profitable. You can get even more profit if you open a chain of stores, especially if they are located in different cities. Using some tricks, you can open it without much effort and without incurring material costs.
 At the initial stage, it is necessary:
At the initial stage, it is necessary:
- draw up a business plan;
- register an enterprise and obtain permits;
- choose premises;
- negotiate with suppliers;
- recruit employees for work;
- take care of advertising.
Operating procedure

Back to the table of contents
Rules for opening a chain store
With even a small start-up capital and no experience in entrepreneurship, it is possible to open a chain store. To open your own retail outlet, you can conclude a franchise agreement, based on an existing business plan, according to which many enterprises are already working, bringing a stable income.
Store opening rules
In America, about 50% of all stores operate under the franchise. Franchising means a partial transfer of rights for the use of a brand and a business plan, for which the franchisor receives a certain, pre-agreed payment or a certain percentage of the profit. This is the lease of a brand or trademark from its owner.
 The indisputable advantages in order to open a chain store are: the use of an already promoted brand, the supply of only high-quality products, no need to spend money on advertising, a small level of entrepreneurial risk.
The indisputable advantages in order to open a chain store are: the use of an already promoted brand, the supply of only high-quality products, no need to spend money on advertising, a small level of entrepreneurial risk.
To open a chain store that will generate a regular income, the first step is to choose the most successful company in the area in which it is supposed to work. It doesn't matter if it is clothing, household appliances or the official representation of any brand, the main thing is that there are attractive franchise conditions and a short period for which the business will pay off.
Here we will look at information on how to become an Internet provider, what equipment is needed for this, and what is generally needed.
To a large number of very different people, and even to some businessmen, the scheme of organizing the activities of an Internet provider may seem very complicated and confusing from a technical point of view. Therefore, the number of entrepreneurs who have entered the telecommunications market is not that large. But everything is not as difficult as it seems at first. If you do not look at the organization of an Internet provider as a complex technical system, but as a business, then everything comes down to three simple points.
Necessary equipment
We present to you the minimum list of the equipment that you need to organize the provider:
- Web server;
- Mail servers (can be combined with web servers on small systems);
- FTP servers (usually combined with web servers);
- Identity and terminal server;
- Master server;
- Secondary servers;
- News servers (optional);
- Servers for development and control;
- Registration server (for online registration, optional);
- Settlement server (option);
- Typical server (on large systems);
- Router;
- Protection against unauthorized hacking of the system;
- Network switches;
- Equipment racks;
- Cables, tools and control equipment;
- Remote access server;
- Administrative panel and printer;
- Uninterruptible power supplies (at least 1 hour supply);
- Cabinets, racks, etc .;
- Spare parts.
All the main costs you will have are associated with the equipment. It will take from 2-3 million rubles to buy it at the lowest prices and quantity (for a small Internet provider). It will be very important for you to seek advice from specialists, because they will help you avoid wrong and unnecessary purchases.
How to become an Internet provider - organizational and legal part
So, consider the information on how to become a provider in terms of organizing this business.
Registration
Internet service - just like every other type of business, should be headed only by a legal entity. Therefore, the first step is to register a "Limited Liability Company" and obtain all the necessary documents for the Internet provider. The process of registering a "Limited Liability Company" can take from five to thirty calendar days, and the time for registering a legal entity is about five calendar days. Upon receipt of all registration documents for an Internet provider, it is mandatory to obtain a seal and open your account at a bank institution. The time spent on opening an account depends primarily on the bank that you have chosen, and varies from two days, up to several weeks. Do not forget - for operations on servicing a bank account, you will need copies of constituent documents, copies of documents on state registration, and a certificate of tax registration.
The approximate cost is about 15 800 rubles. This amount includes:
- State duty for registration of a Limited Liability Company - 4000 rubles;
- The minimum amount of the authorized capital is 10,000 rubles;
- Notarized copy of the certificate - 100 rubles;
- A notarized copy of the charter of an Internet provider - 500 rubles;
- A notarized copy of the memorandum of association - 1,200 rubles.
Licensing
After completing all the work of the first stage, you should start more "fine-tuning" your business. To legalize the activities of our Internet provider, compulsory communication licenses are required, since it is a communication operator.
List of licenses:
- Telematic services license;
- License for data transmission, excluding data transmission for voice purposes.
Additional licenses may also be needed for an Internet provider, but this is only when you intend to provide services not only for clients' access to the Internet, but also others, such as IP telephony, hosting, data backup, cable TV and others. You can deal with the registration of licenses for an Internet provider yourself, but if you do not have enough experience in this area, you should contact a consulting company for help - this will give you the opportunity to save unnecessary costs and amount of valuable time. The time that will be spent at this stage can vary from ten to forty-five days. It will take two to three days to check, and submit all the necessary papers to Roskomnadzor, and up to forty-five days, according to the law, your application will be considered.
The approximate cost will leave about 28,000 rubles. This bag includes:
- State fee for obtaining two licenses - 12,000 rubles;
- Provision of services by a consulting company - from 16,000 to 20,000 rubles;
After receiving all the necessary licenses and documents, the Internet provider must begin to provide communication services, this is our final point.
Final part
After the license review time has expired, and having received a positive answer, we will proceed to the final stage. To finalize the status of an Internet provider, you need to create a project for a communication center and submit it to Roskomnadzor for examination. For a project to successfully pass the examination, it must meet a large number of criteria. These criteria concern both the project itself and the designers, and the technical equipment of the unit. The Internet provider's software must be exclusively licensed, and have all the certificates of conformity in the Svyaz Certification System, special attention is paid to TM and PD servers, Billing and channel technology. After successfully passing the expert assessment at FSUE MIR IT., Commissioning is carried out. The stage of technical preparation of the equipment is the longest. Depending on the amount of work, the design of the site can take from two weeks to three months, and the expert assessment of the project in the IT WORLD can take from a month to a year.
Stages of acceptance of a communication center into operation:
- Notification of "Roskomnadzor" about the beginning of the construction of a communication facility;
- Collection of all necessary documents, in accordance with Order 113;
- Notification of "Rossvyaznadzor" about the completion of construction, with a petition to appoint a representative of RSN to the selection committee;
- Consideration of documents by the RSN inspector, and check of PD and TM nodes;
- Obtaining a permit for operation.
The approximate cost is 70,000 rubles. This amount includes:
- Site design - 35,000 rubles;
- Expert assessment at the FGBU Center IT WORLD. - is from 30% of the design cost.
- Commissioning - 30,000 rubles.