IN Lately MediaTek processors make serious competition to their counterparts manufactured by Qualcomm. We present to your attention the results of testing direct competitors in the Geekbench and GFXBench applications.
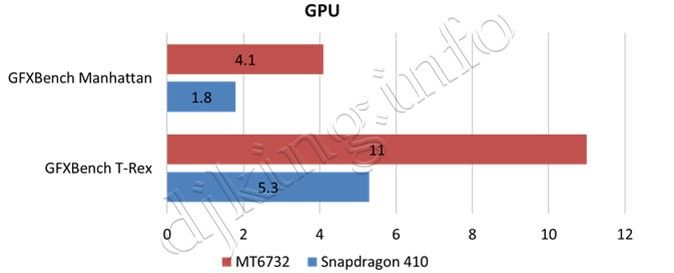
First, let's compare the performance of the junior line of chips from both manufacturers. So, vs Snapdragon 410.
Characteristics:
- MT6732: 28nm process, 4-core Cortex A53, 2-core GPU Mali-T760
- Snapdragon 410: 28nm process, 4-core Cortex A53, Adreno 306 GPU
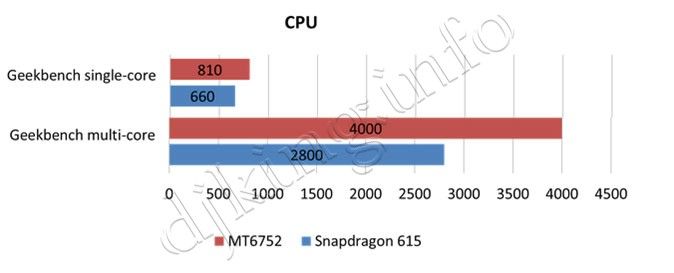
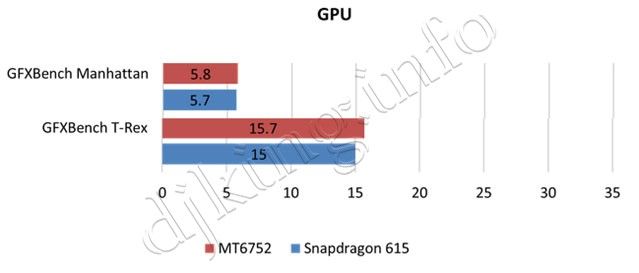
Compete in the middle class vs Snapdragon 615.
Characteristics:
- MT6752: 28nm process, 8-core Cortex A53, 2-core GPU Mali-T760
- Snapdragon 615: 28nm process, 8-core Cortex A53, Adreno 405 GPU
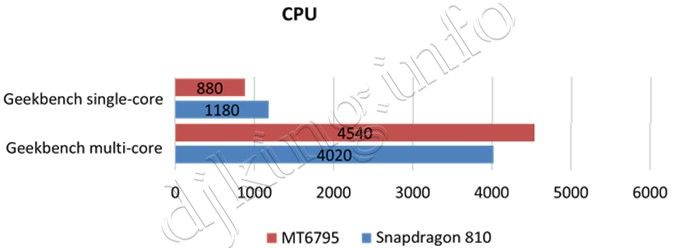
Finally, top-class processors: vs Snapdragon 810
Characteristics:
- MT6795: 28nm process, 8-core Cortex A53, G6200 GPU with dual-channel LPDDR3 @ 900MHz
- Snapdragon 810: 20nm process technology, 4-core Cortex A57 + 4-core Cortex A53, Adreno 430 GPU with dual-channel LPDDR4

What do we see from the test results?
In the lower end, MediaTek is ahead of Qualcomm in both CPU and GPU tests.
In the mid-range, the MediaTek MT6752 has a marginal lead in graphics and single-core CPU benchmarks, but is well ahead of the competition in the multi-core CPU test.
Finally, in the top segment, MediaTek MT6795 only performs best in the multi-core CPU test. In single-core, we see the opposite situation: Snapdragon 810 is faster than its rival. And in graphics tests, the situation for MTK is quite depressing: the processor from Qualcomm is 2-3 times faster than its competitor.
If you believe the statements of Qualcomm executives that, then this processor has every chance of success in future flagship devices. However, traditionally will use the strategy of more low prices, so we are sure that she will not be left without large orders.
MediaTek has shared details about the MT6797 mobile chipset, comparing it to the Qualcomm Snapdragon 810 chip. The novelty is also called Helio 20. The Chinese firm claims that the roots of this branding grow from the Greek word Helios, behind which the Greek god of the sun is hidden.
So, MediaTek built the MT6797 Helio 20 based on 20nm process technology - the same as in the case of the Snapdragon 810.
The chipset turned to a three-cluster configuration of ten (!) cores. This set includes two ARM Cortex-A72 cores running at 2.3 to 2.5 GHz, four Cortex-A53 cores at 2.0 GHz, and four Cortex-A53 cores at 1.4 GHz. This division is focused on serving the most high-load tasks, middle and simple level issues, respectively.
As you can see, Cortex-A57, currently the strongest, is not included in Helio 20. This is due to the fact that manufacturers are not too happy with the design implementation of this core due to its relative bulkiness and increased heat dissipation.
Although the Cortex-A72 cores are ahead of the Cortex-A57 in terms of computing power, the issue of bandwidth is also important. random access memory. For some reason, the MT6797 is still relying on 933MHz LPDDR3 chips instead of the faster 1600MHz LPDDR4 that the Snapdragon 810 professes.
Again, you need to deal with heat dissipation, and the choice in favor of the design 20-nm standards is somewhat strange. Yes, it was possible to declare a technological process on a scale of 16 or even 14 nm, but it cannot yet be put into mass production. This is important given that the MT6797 should be ready to fly.
The video graphics component of the Helio 20 looks decent, but the ARM Mali-T880MP4, running at 700 MHz, cannot yet cope with screen resolutions greater than 2560 by 1600 pixels. In comparison, the Adreno 430 inside the Snapdragon 810 is able to handle 3840x2160 displays.
Photo and video capabilities have received due attention. In addition to the fact that the crystal has enough power to interact with 25-megapixel sensors, support for slow-motion video recording and 3D frame capture is announced. Of course, videos can be both recorded and played back in 2K/4K format, and with support for HDR mode.
But in terms of cellular 4G communication, the MT6797 Helio 20 let us down: it integrates an LTE Category 6 modem - the Snapdragon 810 has this component at the LTE Category 9 level. such high-speed cellular Internet coverage.
Be that as it may, if MediaTek puts a price tag available for manufacturers on the MT6797 Helio 20 mobile devices, this chipset is destined to become a bestseller. Well, Qualcomm will have to come up with something. In any case, competition is always useful.
The first commercial products based on the crystal should appear in late autumn - early winter.
Weibo illustrative material
Qualcomm's Snapdragon 625 (MSM8953) processor began appearing in smartphones back in the middle of this year. And at first we saw it in devices costing $300 and more ( samsung galaxy c7, Asus Zenfone 3, Lenovo Moto Z Play, etc.), and towards the end of the year it appeared in smartphones in a more affordable segment (Nubia Z11 Mini S) and even in the budget Xiaomi Redmi 4 Pro. The secret of the Snapdragon 625's success is its excellent combination of performance and energy efficiency, as it is the second Qualcomm chip after the flagship Snapdragon 820 to be built using the 14nm process technology.
As for Qualcomm's main competitor, which is MediaTek, a chip similar in characteristics appeared only towards the end of the year. The Helio P20 (MT6757) processor, like the Snapdragon 625, is also designed for mid-range smartphones. price segment. It is made according to the 16 nm process technology, becoming the first such modern and energy-efficient processor in the MediaTek line, and has a performance level comparable to its opponent.
Therefore, a quite reasonable question arose: “Which processor is better, Helio P20 or Snapdragon 625, and which solution should be preferred when choosing a smartphone?” And to answer it, we need to compare these two processors in terms of characteristics, test them in benchmarks and check how much they heat up during operation.
Specifications Snapdragon 625 (MSM8953)
- 8 Cortex-A53 cores operating at up to 2.0 GHz;
- GPU Adreno 506;
- Modem X9 LTE (300/150Mbps);
- Support for LPDDR3 933 MHz memory modules;
- Support for eMMC 5.1 / SD 3.0 drives;
- Support for camera sensors up to 24 MP, video [email protected] ;
- Support fast charging QC3.0.
Specifications Helio P20 (MT6757)
- 4x Cortex-A53 @1.65GHz + 4x Cortex A-53 @2.35GHz;
- GPU Mali-T880 MP2, 900 MHz;
- LTE R11 modem (300/50Mbps);
- Support for LPDDR3933 MHz and LPDDR4X 1600 MHz memory modules;
- Support for eMMC 5.1 drives;
- Support for camera sensors up to 24 MP, video [email protected];
- Support fast charging PE 3.0.
As you can see, the specifications of Helio P20 and Snapdragon 625 are very close. The chip from MediaTek has an advantage in maximum frequency cores and support for faster and more energy-efficient RAM modules, but there is also a weak point in the face of the video accelerator.
To understand the whole picture, you need to test both of these processors in benchmarks. And we will compare using the example of Xiaomi Redmi 4 and Meizu M3X (Meilan X) smartphones.

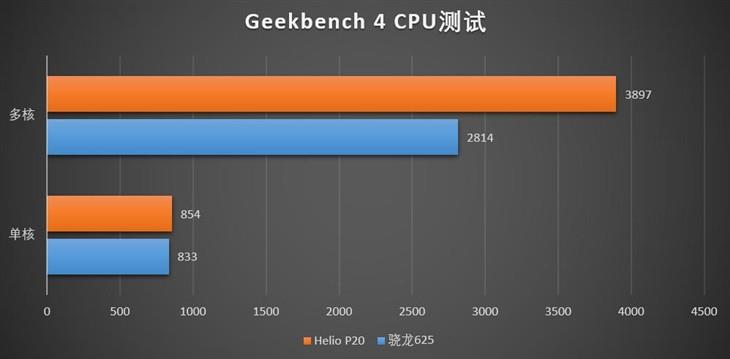
In the AnTuTu benchmark, the Snapdragon 625 processor scored about 62 thousand points, while the Helio P20 showed almost 66 thousand points in the same place.
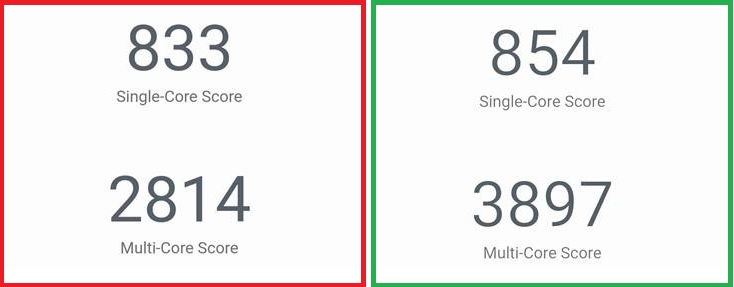
In the GeekBench 4 benchmark in single-core mode, the results of both rivals were almost the same, but in multi-core mode, Helio P20 outperformed its rival by almost a third. At the same time, as expected, the Snapdragon 625 performed better in graphics test, although not by much - by 13%.
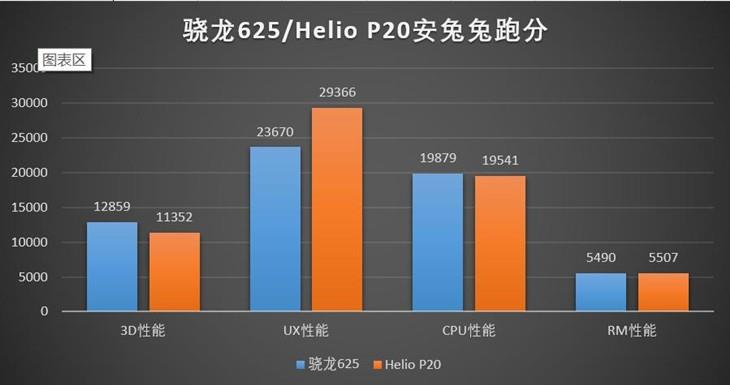
When performing normal tasks, Helio P20 uses a bunch of 4 cores with a clock speed of 1.65 GHz, while Snapdragon 625 uses all 8 cores, but little by little. And when performing complex tasks, both chips use all their cores at maximum frequency. In other words, the algorithms Snapdragon processors 625 and Helio P20 are different depending on the load level, but it is impossible to say unequivocally which one is more energy efficient. This best solutions in terms of energy efficiency for each of the chipmakers, and in the end, everything will come down to optimizing the end device.
And what about the heating of these processors? The measurements showed that both the Helio P20 and the Snapdragon 625 perform just fine in heat control. During testing, none of the smartphones did not heat up above 35 degrees Celsius, which is a very good result. Of course, the designs of the tested smartphones and their cooling systems also played a role here. But in general, the end result was the same.

Thus, we cannot answer unambiguously which of the processors is better. Snapdragon 625 is a little better for those who like to play graphics-demanding games on their smartphone, though not at maximum settings, if we talk about games like WoT. Not at maximum settings, you can also play on a smartphone with Helio P20. And with everyday tasks, both Helio P20 and Snapdragon 625 will cope with a bang, having a good start for this for a couple of years ahead.
And summing up this article, we can finally say that MediaTek managed to release a more or less equivalent product to the Qualcomm processor, albeit only in the mid-range and mid-budget segment. Let's hope this trend continues. And we have every reason to count on this, because the Helio X30 with PowerVR graphics, which will debut in early 2017, should compete on equal terms with the flagship Snapdragon 820 and 821. True, then the Snapdragon 835 will be released and Qualcomm will again go into the lead ....
In contact with
We are closely considering modern chipsets in smartphones that are in the price range of 5000-8000 rubles. The range includes: MediaTek MT6737T, MT6753, Helio p10 and MT6750, Qualcomm Snapdragon 410, 425, 430, 435 and 615.
This price range also includes the Hi Silicon Kirin 620 and Samsung Exynos Republic Act 3475 third party manufacturers Huawei and Samsung do not sell their chipsets as separate platforms, there is very little information. The review will be made separately if I receive responses to the relevant requests made.
Menu
410
Qualcomm Snapdragon 410 contains a CPU of 4 cores with the usual ARM Cortex A-53 architecture. 32 and 64-bit operating modes are supported. The cores operate at the lower "official" frequency of 1.2 GHz and do not differ from those previously reviewed in MediaTek MT6737. As the study will show, it is no different from those in 425, 430 and 435 (8 pieces in the last two), they are all made using the "old" 28-nm process (like all today's chipsets).
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 410 GPU is represented by Adreno 306, which does not differ in performance from Adreno 305. But it has added the ability to display an image on the screen up to 1900x1200 pixels and image transmission using Miracast™ inHD 720 p. In all other respects: All the same 450 MHz, all the same OpenGl ES 3.0, OpenCL 1.1 and DirectX 9.3. Needless to say, the gaming capabilities of the chipset are extremely small?
425
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 425 contains the same cluster of 4 ARM Cortex A-53 cores. The difference from the cores in the 410th comes down to a slightly higher operating frequency - 1.4 GHz (against 1.2).
Adreno 308 is a GPU companion. Significant differences from the notorious 305th: Added hardware support for Qualcomm TruPalette ™ technology (image adjustment by juiciness, brightness, etc.) and Qualcomm EcoPix ™ (it is not important for smartphones, it is used when manufacturing and setting up smart billboards based on this chipset). There is very little information on this GPU, but you involuntarily come to the conclusion that the difference between Adreno 305, 306 and 308 comes down only to the “weighting” of the 305th additional features without affecting its performance in any way. At the same time, as if ashamed of its own brainchild, Qualcomm forgets to specify the version of DirectX (apparently the former 9.3), but does not forget to indicate the relatively current version of OpenGL ES 3.0. Among other things, support for displays up to 1080p and the claimed reduction in power consumption. Some sources claim that Adreno 308 operates at a frequency of 500 MHz (against 450 for its predecessors), but this could not be verified.
430
Snapdragon 430 CPU is Qualcomm's first budget chipset with 8 Cortex A-53 cores. They operate at the upper limit of the nominal frequency of 1.4 GHz. As practice shows, the performance increase compared to 4-core counterparts is still the same 30% (a directly bewitched figure). Alas, miracles do not happen, most Android applications still use 1-2 threads. But 8 cores contribute to the smooth operation of the smartphone with a large number of running applications. But when you start the application immediately after rebooting the smartphone, you will not feel any special advantages from “8 cores”.
The Adreno 505 GPU found in the Snapdragon 430 and 435 runs at 450 MHz. This is quite a modern video processor that supports libraries and image processing technologies OpenGL ES 3.1, OpenCL 2.0 full, DirectX 11.2, HW Tessellation and Geometry Shading. Compared to the bottom benchmark of the Adreno 305, the 505 is more than doubling gaming performance. You can easily verify this by looking at dozens of game tests (as I did). This chipset is already suitable for gaming at medium-high graphics settings in most applications. Screens up to 1920x1200 pixels are supported.
435
CPU Snapdragon 435 is no different from the same in the 430th. All the stories about the "overclocked version" turned out to be untenable. The difference between the chipsets is different, but more on that below.
GPU Adreno 505, as in the 430th. With the same frequency of 450 Mhz, with all the ensuing consequences.
615
The 615th can be called a controversial chipset, on which Qualcomm engineers experimented. Two clusters of 4 Cortex A-53 cores operate at frequencies of 1.5 and 1.0 GHz, respectively. In "processor-dependent" tests and applications, the Snapdragon 615 will be quite a bit behind its "younger brothers" 430 and 435.
GPU Adreno 405, oddly enough, is more productive than the 505th (In 3DMark + 22%). Maybe this is a renamed video processor from the older 8xx segment? Like Adreno 330? This is evidenced by the support for screens up to 2560 × 1600 pixels and a frequency of 550 MHz. Supported libraries include OpenGL ES 3.1, DirectX 11.2, OpenCL Full Profile, tessellation, and geometry shading. Of all the Qualcomms we've reviewed, the 615 is the most suitable for gaming.
МТ6737T
Instead of a thousand words, the MT6737T differs from the MT6737 only in the clock frequency of a cluster of 4 Cortex A-53 cores increased to 1.5 GHz (against 1.3 GHz).
The MT6737T GPU is represented by the Mali-T720 MP2 video processor running at 600 MHz. And, despite its “two-headedness”, it is still equal to Adreno 305/306, “winning” only slightly slowed down Adreno 304. Mali-T720 MP2 is in Intel Atom x3-C3440, Exynos 3475 and other budget devices. At the same time, optimists from MediaTek promise support for screens up to 1920x1080 pixels. Needless to say, buying a device with such a screen and this chipset is a bad idea?
MT6753
CPU MT6753 is represented by two clusters of 4 Cortex A-53 cores. One cluster operates at a frequency of 1.3 GHz, the second at a frequency of 1.5 GHz. Their simultaneous work at MediaTek was called "MediaTek Core Pilot". The MT6753 uses "Core Pilot" version 1.0. I did not find any difference with the standard ARM capabilities “Heterogeneous Multi-Processing” (Cortex A-53 standard of 2013), the situation is from the category of “we plowed with an ox”. We can also safely say that the performance of the MT6753 CPU is equal to the Qualcomm Snapdragon 430-435 CPU.
The single-core Mali-T720 is used as the GPU. The declared support for FullHD-screens is puzzling. Whatever one may say, Mali-T720 in this configuration is much inferior to Adreno 505 and 405 in Snapdragon 430, 435 and 615. This means that you won’t be able to play normal games with such a chipset.
Helio P10
CPU Helio P10, which bears the second name MT8785 (for tablets) is 8 cores in two clusters of 4 Cortex A53 cores, operating at frequencies of 2.0 and 1.2 GHz. If this gives an advantage over 1.3 and 1.5 GHz in the MT6753, then you won’t be able to see the difference with the 8 cores of 1.4 GHz in the Snapdragon 430/435.
GPU Helio P10 is his forte, relative to MT6753. ARM Mali-T860 MP2, running at 700 MHz, is approximately equal to Adreno 505, but inferior to Adreno 405 by 20-22% (In 3DMark). Devices with this chipset can be recommended as "gaming", most games in 2016-2017 will run without a hitch on medium-high graphics settings.
MT6750
Released later than all the contestants, Mediatek MT6750 is a "stripped down" version of the Helio P10.
Judge for yourself: the CPUs are the same 4x4 Cortex A-53, the cluster frequency is reduced to 1.0 and 1.5 GHz. GPU Mali -T860 MP2 runs at 520 MHz (versus 700 in P10). As a result, the CPU is weaker than those in 430 and 435, and the GPU is only slightly ahead of Adreno 305, 306 and 308, very much behind Adreno 505 and 405.
410
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 410 uses LPDDR2 and 3 type RAM with a frequency of 533 MHz, work with drives is carried out according to the JEDEC E.MMC 4.5 standard (up to 200 MB / s on the bus). The old man shows typical averages. Starting with the next chipsets, we will no longer see LPDDR2 RAM, Qualcomm completely abandoned it. Memory cards are supported by any of the existing ones on the market, I think it makes no sense to return to them. As before, any restrictions on the size of memory cards can be deliberately introduced by the smartphone developer, at the software level, in order to build their “flagship-not flagship” line.
425
In Qualcomm Snapdragon 425, the RAM operates at a frequency of 667 MHz, the drive works according to the E.MMC 5.1 standard (up to 400 MB/s via the bus). According to these parameters, the chipset seems to be "hanging" between the old and the new generation of Qualcomm.
430 and 435
Qualcomm Snapdragon 430 and 435 work with LPDDR3 RAM at 800 MHz, reminiscent of the flagships of the first generation of the 800 series. About the JEDEC standards in the official specifications of the new Qualcomm forgot, so let's hope for the best.
615
Snapdragon 615 uses LPDDR3 RAM at 800 MHz, we can still see how it works with drives (the chipset came out up to 430/435), it runs according to the E.MMC 4.51 standard (up to 200 MB / s).
The new Snapdragon 430 and 435 pleasantly surprised us with “high-speed” RAM in the budget segment.
Mt6737T
MT6737T will please with significantly overclocked RAM relative to its predecessor MT6737, the frequency of which is 733 MHz, against 640 MHz. But everything is spoiled by support for LPDDR2 memory. We have already talked about the manufacturer's desire to save money and supply a slower and cheaper LPDDR2, which at a maximum frequency of 533 MHz is twice as inferior to LPDDR3 at a frequency of 800 MHz. Communication with the drive is carried out using a completely modern E.MMC 5.0, with backward compatibility with previous standards such as 4.5 at a speed of 26 MB / s (via the bus). I specifically write about this again, because there is still no trust in specific Chinese smartphone manufacturers.
MT6753
MediaTek does not list RAM and ROM in MT6753. Therefore, there will be no information, as well as fortune-telling on the coffee grounds of Wikipedia and other unreliable sources.
Helio P10
Helio P10 pleases with the frequency of RAM 933 MHz and its type LPDDR3. The data transfer rate on the bus in the drive is carried out according to the E.MMC 5.1 standard (up to 400 MB/s).
MT6750
MT6750, as befits a stripped-down "flagship of the middle segment", uses LPDDR3 RAM at a frequency of 667 MHz (against 933 MHz in P10). Hence its modest performance in gaming tests and lagging behind 430/435 on all fronts. The drive will work according to the E.MMC 5.1 standard (up to 400 MB / s), unless the manufacturer of a particular smartphone saves on it.
410
Unlike the Snapdragon 210, the Snapdragon 410 specifications do not mention the use of Qualcomm's proprietary X-series LTE Global Mode modem, they simply indicate "Integrated 4G LTE Global Mode modem". Modems of the "X" series are the pride of Qualcomm and just like that they would not remain silent. This can only be said by attracting the developments of an unknown contractor. However, supported: LTE FDD, LTE TDD, WCDMA (3C-HSDPA, DC-HSUPA), CDMA1x, EV-DO Rev. B, TD-SCDMA and GSM/EDGE. LTE Cat 4 150 Mbps download and 50 Mbps upload. VoLTE services, HD voice, native video calling, RCS, support for LTE on two SIM cards (DSDS).
Navigation features are presented GPS support, GLONASS and BeiDou. If you don’t see them in the official specifications of Qualcomm, don’t be alarmed, starting from the 410th they are not listed separately, they have moved to the Location section and are hiding in the “Qualcomm® IZat™ location technology Gen8C”. The fact is that Qualcomm does not make a fundamental difference between receiving a navigation signal from a satellite, connecting to WiFi router and receiving an LTE signal. All incoming radio signals of any kind pass through a multi-stage amplifier and modem.
There are also VoLTE, HD voice, native video calling, RCS, support for LTE on two SIM cards (DSDS).
Opportunities wireless connections Wi-Fi 802.11n (2.4GHz) and BT 4.1 are also available for data transfer. This is the weakest part in the Snapdragon 410.
425
Snapdragon 425 contains "Integrated X6 LTE modem with Snapdragon All Mode", which supports all the above standards and types of communication, including navigation. A distinctive feature of the X6 is the transmission of information over the LTE channel (Cat 4) at a speed of 75 Mbps, instead of the standard 50 Mbps.
Wireless data connections are represented by Wi-Fi 802.11ac (with support (MU-MIMO, what it is recommended to study for yourself, so too much text) and BT4.1 + BLE.
430
The Snapdragon 430 boasts an "Integrated X6 LTE modem" that provides all the necessary communication protocols.
435
So we got to the difference between the Snapdragon 430 and 435. And this difference is very significant, since the Qualcomm X9 proprietary modem was placed in the Snapdragon 435, with support for LTE Cat 7 for downloading (300 MB / s, up to 4 channels simultaneously, 57 Mbps) and Cat 13 characteristics for sending information (150 Mbps on two channels simultaneously up to 75 Mbps).
Services, navigation and wireless connectivity remain the same as in the 430th.
615
The Snapdragon 615 unfortunately does not include a modem from QuaLcomm's "X" series. However, the integrated 4G LTE modem is very similar to the one in the Snapdragon 410 and, in principle, will provide the user with decent communication and transmission over the LTE Cat 4 channel (150/50 Mbps download / upload).
Of particular interest is WiFi connection, carried out using technology from Qualcomm VIVE 1-stream 802.11n / ac. What are streamers and amateurs virtual reality and so they know, but those who do not know, sorry, the text is already too much.
MT6737T
Traditionally for budget MTKs, MT6737T supports CDMA2000, EDGE, FDD/TDD LTE, HSPA+, TD-SCDMA. As before, compared to Qualcomm, CDMA 2000 support is exclusive to Chinese chipsets. LTE operates within the standard CAT 4 150/50 Mbit/s download/upload.
The set is complemented by Wi-Fi a / b / g / n and an unknown variety of Bluetooth.
MT6753
All communication indicators are similar to MT6737T. And you know what's the funniest thing? You will not find information about the hardware support for navigation in the MT6753 anywhere. The manufacturer does not provide this information. And even the most advanced technical sites do not have such information. They just shut her up. Let's not lead each other by the nose, hush up or invent. The logic is simple - if it is not indicated on the official website, then there is no such support in this chipset. This does not negate the possibility of desoldering satellite receivers separately on motherboard and support for working with them at the software level.
Helio P10
In the description of this chipset, for the first time we see a kind of MediaTek Cat 6 modem, together with which the MT6300 power stabilization chip works, optimizing power consumption and preventing the chipset from overheating under load. "MediaTek Cat 6" can work with the usual Chinese set (including CDMA 2000), the data transfer rate for LTE Cat 6 is 300/50 Mbps download / send.
From navigation all systems are supported: GPS, Glonass, Beidou and Galileo.
Wireless data connections are represented by Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, of unknown origins and capabilities.
MT6750
As befits a stub from Helio P10, MT6750 repeats all the advantages and disadvantages of the parent with regards to communication.
The middle-younger segment of the Qualcomm Snapdragon 4xx boasts well-established Crystal clear voice calls technology (all but Snapdragon 410 and 615). Good sound.
The sound in MediaTek is very much dependent on the specific manufacturer. Owners of smartphones like Meizu M5S and HOMTOM HT20 Pro initially stand in unequal conditions. And, the less the smartphone costs, the less you will hear and you will be heard.
Qualcomm chipsets, namely 430 and 435, turned out to be the most balanced in terms of price and features, as always. Do not agree? Write about it and we'll discuss it.
Competition among processor manufacturers leads not only to direct attempts to make their product the best on the market, but also to the use of marketing tricks, successfully raising the reputation of a certain brand and at the same time discrediting others.The prevailing stereotypes do not always correspond to the truth, which is why it is especially important to dispel some myths regarding mobile processors.
To a question " Which mobile processor is better?” must be approached in detail.
Of course, we do not choose a smartphone solely because of the processor, other stuffing is no less important. However, without a competent layout of the chipset and other components, even the most top-end and productive mobile processor can literally be useless.
We hope that our excursion into the world of processors and their manufacturers will be useful for you.
Terminology
Usually the concepts "processor" and "chipset" are perceived as synonyms, but this is not entirely true. Modern mobile processors are part of SoC(System on Chip), on which other elements are located.
Outwardly, the chipset is similar to old-style processors, but at its core, the chipset is a platform for placing components, some of which are responsible for graphics, sound, orientation in space, etc. The processor itself is just one of the components.
For example, schematically the chipset Snapdragon 820 looks like this:
Which processor is better?
The answer to this question will logically differ for different categories of users.
Some users want to get the most out of their smartphone, using the device not only as a dialer, but also as a game center. Cunning marketers have found a loophole how to attract the attention of just such an active type of user and at the same time save money - equip a smartphone with a 4-, 8-core processor, but with minimum clock frequency.
In this case, not an expert in the field mobile phones sees a tasty line in the specifications about an 8-core processor and considers the device to be very productive by default. But in fact, a 4-core processor with high clocked cores will easily outperform some lower clocked 8-core processors.
But knowledge in the field of processor frequency does not guarantee correct selection gadget.
Hidden Features
There are hidden characteristics, about which information is sometimes very difficult to find.
Important is technological process on which the processor is executed. Roughly speaking, the technical process is an indicator of the size of transistors, of which the processor consists of millions. Accordingly, than less this indicator, more they can be placed on a crystal and so faster stuffing works. The process technology is measured in nm (nanometers).
At the moment, the most common process technology is 32nm. Some flagships, which are planned to be released in the next few years, will receive processors with a much lower technical process.
In particular, the processor is being prepared for release MediaTekHelio X30, the undoubted advantage of which will be the use of TSMC's 10nm FinFET process.
Besides, Helio X30 equipped top cores, in particular, two ARM Artemis cores (2.8 GHz) are installed, which have already been dubbed the main rivals of Qualcomm's Kryo cores. The chipset also includes the well-known four Cortex-A53 cores (2.2GHz) and the same number of Cortex-A35 (2GHz).
The first devices with this processor will be presented only at the beginning of 2017.
But this is just reference point, not 100% evidence of processor performance.
Specifications: de jure and de facto
A case in point is the iPhone 6, which received 2-core Apple A8 clocked 1.4GHz. Do not forget about another important factor - RAM. With its insufficient amount, even the top-end processor will obviously not be able to fully prove itself.And in the case of the iPhone 6, only 1GB ram. Modest numbers, right?
Especially against the background of many Chinese devices, it is an order of magnitude cheaper and with more attractive performance - for example, Xiaomi Mi3, who received Quad-core Snapdragon 800 clocked cores 1.7GHz And 2GB RAM it seems much “tastier” than the apple set in the paragraph above.
The myth about the importance of numbers in specifications will quickly dispel, one has only to try both smartphones “in action”. The secret lies in optimization.
Apple's software optimization is much better than Android devices, where the emphasis is on the attractiveness of numbers.
You should also be careful with the amount of RAM. The newer the firmware installed on the smartphone, the more voracious it will be. For example, starting from android versions 4.2.X, the minimum amount of RAM to ensure stable operation is 1GB, but already for Android 4.4.X, the starting value of RAM for full operation has increased to 2GB.
But even if the user carefully studied the number of cores, they clock frequency, technical process, the ratio of the processor and the rest of the filling, appreciated the optimization, etc. there is such a factor as peculiarities each processor.
We will talk about the individuality of some chipsets a little later, but for now, here is a list of top processor manufacturers:
Qualcomm- a company that deservedly received the title of one of the best processor manufacturers, however, the cost of chipsets from this company is usually overpriced compared to the pricing policy of other brands.
MediaTek- main Qualcomm competitor. Initially, the company focused production on the production of processors for budget smartphones, but at the moment the situation has changed - just remember the line of processors Helio. Strong advantage of the company - much more affordable prices on processors than Qualcomm.
Intel. The company's success in the field of mobile processors is an order of magnitude more modest than in the production of processors for computers. For mobile devices, the company launched the Atom line, which was distributed mainly to devices from Lenovo. There are a number of other smartphones hiding under their hood Intel Atom, but their number is so small that it hardly makes sense to talk about this series of processors as a serious contender for the two companies described above.
Samsung- a company that produces a fairly successful line of processors Exynos. But as with Intel, Exynos is installed on a small number of phones (mostly smartphones of its own production).
nVidia- the least known manufacturer of processors. Produced series of processors Tegra not in demand and installed on a very narrow range of gadgets. An attempt to enter the international market was made in 2012, when the manufacturer released a 4-core Tegra 3. But a serious flaw soon became apparent: severe overheating.
The most interesting is the confrontation Qualcomm And MediaTek. And for right choice smartphone, you need to know some of the features of the processors produced by these two giants.
Snapdragon 820- Qualcomm's sensational "hot" processor. The “hot” novelty was installed on a variety of smartphones - Xiaomi Mi5 Pro, Leagoo Elite Pro, Doogee F7, Elephone P9000, Meizu MX6, LG G5, etc.
Similar to the situation with Tegra 3, users are faced with severe overheating of their pets. Remarkably, the 820th Snapdragon was released as a replacement for the 810th, which is also prone to overheating.
This failure provided an opportunity for other manufacturers to prove themselves. In particular, one of the main competitors of the Snapdragon 820 is Exynos 8890. An interesting decision was made regarding the Samsung Galaxy S7 and S7 edge. Smartphones are released in two versions: for residents of China and the United States, a version with Snapdragon 820, and for the domestic market and Europe, a variant with branded Exynos 8890.
AnTuTu scores show leadership in terms of performance Snapdragon 820.
But in multi-core mode Geekbench shows superiority Exynos 8890 .
Purchase price Snapdragon 820 is $ 70, which greatly affects the final price of the smartphone. Can be purchased for much less Helio X20($30), the performance of which is almost the same as that of the 820th processor from Qualcomm. Naturally, devices running MediaTek Helio X20 will be much more affordable.
That is why users should be careful when buying a device and objectively evaluate the ultimate goals of using the device: if your priorities do not include spending time with toys, then it makes a lot of sense to pay attention to smartphones with a MediaTek processor. Performed especially well MT6753.
However, MediaTek is gradually getting rid of the reputation of a brand that produces chipsets exclusively for state employees - the above mentioned Helio X30 direct evidence of this.
A few words about synthetic tests
The point is that the test results AnTuTu- just a rough estimate of performance, but not an accurate representation of reality.
The results of the same device often change after a firmware change. Also, an important role is played by the optimization of the hardware and software of the smartphone.
Often, manufacturers try to cheat and artificially wind up the values in the tests. In 2013, a scandal broke out regarding deception Samsung in AnTuTu results. The company's engineers came up with a trick: when you start AnTuTu GPU Samsung S4 automatically switched to high-frequency mode (from 480 to 532 MHz), which is why the results increased.
In the same year, allegations of dishonest results went to the company Intel. Some analysts agreed that AnTuTu is optimized for Intel Atom, so the results in this test will be somewhat overstated.
It makes sense to compare AnTuTu virtual parrots exclusively within the same platform. For cross-platform comparison, there are other applications, the most popular of which are Geekbench And GFXbench. In any case, you need to understand that the results obtained only approximately reflect the capabilities of the smartphone.
Conclusion
To the choice of the most optimal smartphone it is necessary to approach it comprehensively, relying not only on tasty numbers, but also understanding what is really behind them and whether it is worth the money.
It makes no sense to overpay for a top-end multi-core processor if it will be used only for basic functions. But you should not rely on luck that a mediocre chipset will master top toys.
Command b ad-android wishes you only successful and pleasant shopping!
Stay with us ahead many interesting.