10.07.2018
With all the transparency of tariffs, this operator, like all others, has various paid services. GPRS Internet: how to disable content on Tele2 for which funds are regularly deducted? Let's see what can be done.
What is GPRS content
And so, the content supplied by Tele2 GPRS, what is it? In short, this is the content of any service that we receive using GPRS.
These include:
- Images.
- Music.
- Movies.
- Jokes.
- Audiobooks.
- Books in text formats.
- Horoscopes
- Exchange rates
- News from various fields, etc.
Such Internet content can be provided both for money and free of charge; connected for a billing period with or without auto-renewal. An example is the Tele2-theme service. Within its framework, you get almost all types of content from those listed above. Part can be obtained for free, and for everything else a monthly fee will be charged (daily or for each request). We found out about GPRS what it is, let's see on the phone, how to disable it on Tele2?
Briefly on the topic
What is GPRS traffic and how to disable it in Tele2:
1. This is paid or free content (news, pictures, horoscopes, music, etc.) obtained through an Internet connection.
2. Disconnected by command *152*0# , if we are talking about Tele2-theme, by USSD code *189# and through the settings in the smartphone.
How to disable GPRS content
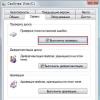
Before thinking about how to disable GPRS on Tele2, you first need to determine where exactly the funds go. The main problem with using such content is that it is not displayed in any way in the personal account on the operator’s website, and in connected services as well. That is, we (or our children, without asking) activated something paid and forgot, the subscription fee continues to be charged, and this is discovered after a decrease in money in the account becomes noticeable. To make sure that these write-offs occur exactly as a payment for GPRS content, you need to order itemization by number. The easiest way to do this is via the Internet, in your personal account on the operator's website. Here's how to do it:
- Sign in app or
- Open the "Expenses" section
- Click "Details"
- In the window that opens, enter your email address and click "Receive"



You can find out more information about how to locate a Tele2 subscriber


If you made such a request and received a notification that the service is not activated, but the money continues to be debited, you should check for other paid subscriptions. To do this, we again use the USSD command, but already * 189 # . The response SMS will list all the services for which money is debited + instructions on how to disable them. You can read more about this in our other article.


Please note that connected internet content does not appear in the "Services" section of the site. Disabling GPRS Internet Tele2 in your account will not work, there is no such functionality. Therefore, you can check what exactly is activated for you only in the above ways. Is there - read the answer in another article on the site.
How to disable GPRS traffic
The measure, of course, is radical, but in some cases it is indispensable. For example, if the number is used by a child or a very elderly person. The first can connect too much, and the second Internet content is completely unnecessary, and the risk of activating paid subscriptions is completely useless. You can do it in one of the following ways.
- Call to 611 .
- Visiting the Tele2 office (you must have a passport with you).



Important! It should be remembered that when accessing the network via wired Internet or Wi-Fi, content activation will be available. Therefore, this moment should also be controlled. Wi-Fi, for example, is also turned off through the settings section, the "Connections" item. And if you want to know if there is, follow the link and read the answer to this question.
An article about the principle of operation and the concept of GPRS and GPS systems, and their use in cellular communication/
Navigation
A cell phone is a mini - radio transmitting - radio receiving station that provides full-fledged radio communication without interference. A cell phone is the center of Internet technologies that provides system access to the World Wide Web.
Mobile phone - mini - radio station
GPS technology used in mobile communications, is a network of global determination of an object with reference to the terrain, using space satellites, which performs digital data transmission.

Military object identification technologies used in the GPS system
The GPRS system is a technology that allows a cellular subscriber to exchange messages and calls with subscribers of other devices via this network, external networks and the Internet.

Use of the GPRS system for civil objects
Transceiver channel of the system
The cell phone subscriber has own channel, consisting of a modem in a mobile device. The GPRS system has its own communication channel. The adjustment of both channels, relative to each other, makes it possible to exchange and transmit data.

Mobile phone communication channel, modem
Data transmission takes place in the mode of services of the telecom operator to which this subscriber belongs.
System Capabilities
- instant internet access
- the ability to connect gadgets to the Internet: smartphones, tablets, laptops
- billing for actual Internet access, namely, for the amount of information sent or received

GPRS System Capabilities
Connecting the system on a personal phone
Several ways:
- connection in the "default" mode from your phone operator
- manual connection
- connection through the service of a cellular operator by phone
- connection via communication center given operator
Connection in the "default" mode from the operator does not require solving problems and any actions for the subscriber.
Manual connection is required for phones where the manufacturers did not take into account the automatic configuration of the system. Connecting through the service of a cellular operator involves a call to a specific number of this operator. Information about the phone number can be found on the operator's website, contact a representative of the service center there, get a package of settings from him in automatic mode, to your phone. If the procedure does not work, you can manually configure the system, at the prompt of a service center specialist.

Ways to connect the GPRS system to a mobile phone
Phones of service - operator centers for connecting the system
- MTS - call by number 0876 or any text message to the number 1234
- Megaphone - call by number 0500 or text message (number 1 ) per number 5049
- Beeline - call by number 0880 , saving sent settings when using a password "1234"
- Tele 2 - - call the number 679
All operators, except MegaFon, provide the ability to order GPRS settings via Personal Area on the operator's website. To do this, fill in information about the phone model, operating system, and your number, in the order - online. A phone in which there are several cards, a settings package is sent to each card. The last way to connect GPRS is to contact the communication salon for help.

Service - mobile operator center
The difference between GPS and GPRS
GPS is a satellite communication system for determining coordinates, location on the map, speed of movement, object. The owner and operating organization is the US Department of Defense. The system is available to ordinary subscribers, if they have a navigation device or a mobile phone with a GPS receiver.
GPRS is an internal GPS system, a transmitter that sends data to cellular subscribers, connects them with gadgets, the Internet, and other devices.
The difference is that GPS is for identifying an object, GPRS is a data radio transmission system when connected to the Internet.

Collaboration of two GPRS and GPS systems
GPS refers to military technologies, GPRS is not related to the militaristic sense of determining objects and the parameters of their location.
The meaning and principle of operation of individual systems is significantly different. However, their tandem provides huge opportunities for a civilian cellular subscriber.
Video: Setting up GPRS
What is GPRS
Beginners often confuse GPS and GPRS. Sometimes they also confuse the first two terms with RFID, but for this, you definitely need to deprive yourself of sweets. To avoid confusion, let's still clarify this issue. Today we will find out what the mysterious term GPRS means, which is colloquially pronounced as "ZhPRS", but quite colloquially ... however, I will not be able to pronounce it on the radio, because I will be fired immediately. So, the abbreviation GPRS stands for and translates as "packet data transmission over a radio channel." GPRS is, as it were, an add-on to the GSM standard, according to which our familiar mobile phones work. To implement GPRS, a mobile operator requires installation, configuration and ongoing administration of various hardware and software, which together form a special computer-mobile network. However, ordinary users should not worry about all these subtleties. In order to use this technology, they just need to purchase a mobile phone with GPRS support, and I must say that almost everyone supports it. modern phones even the cheapest ones. After that, you need to enable the GPRS service with your operator, if it is suddenly not enabled, and then use GPRS in the tail and in the mane, if there is such a need. What gives GPRS on a regular mobile phone-smartphone? The ability to access the Internet and connect to the relevant services: Internet pages, news channels, and so on and so forth. "Wait," you say. That's right, you can! But only when you connect to WAP through a regular connection (CSD), then your phone is busy, and you pay for this connection in almost the same way as for a regular conversation on a mobile phone - that is, wild money! And GPRS is a technology that allows you to transfer data over parallel channels that practically do not interfere with normal communication. In this regard, you do not pay for the time you work on the Internet, which is very painful for any wallet, but only for traffic - that is, for the transferred files (I note, just in case, that opening a web page already means downloading files - text and page design). Moreover, this fee, compared to the payment for calls, is very small: about 10-20 cents per megabyte of data. Thus, your mobile phone can be connected to GPRS all the time - it practically does not interfere with incoming and outgoing calls, and if you do not download anything, then money from your account is not spent.
Mobile Internet is one of the most popular services among subscribers of various mobile operators. This is related to the fact that modern man it is difficult to do without the Internet: communication with friends and loved ones through instant messengers, social networks, data transfer - personal files, documents and presentations for work, etc. Thus, in order to always stay in touch and keep abreast of news and latest events, subscribers configure their gadgets (tablet PCs, mobile phones) to connect to the global network .
Also, for the mobile Internet service, cellular operators offer a whole line of specialized options. In this article, we will talk about how to perform GPRS settings on the Megafon number, what tariffs apply to the Internet service, how they can be reduced by connecting profitable options.
general description
Before talking about how it is carried out on mobile gadgets, you should bring general description Moreover, GPRS settings - what is it. This term refers to an add-on in the GSM network, which is necessary to connect to the Internet. Initially, on earlier models cell phones, the Internet speed could theoretically reach 171.2 Kbps. Now such figures may seem ridiculous to Internet users. After all, many telecom operators allow you to use 4G Internet, which is not much different in speed from wired. Under the GPRS settings (what it is, it was indicated earlier) means standard installation settings for mobile internet.

Internet service connection
On the SIM card of the Megafon operator, as, indeed, on the number of any other telecom operator, the Internet service is connected by default and is included in the basic services. Therefore, the question of how to connect GPRS on Megafon is not entirely correct, because this GSM network setting is already included in the operator's services. All that the subscriber needs to do is to configure the device. However, if not planned with mobile device Internet sessions, then the Internet service can be turned off completely to avoid unplanned expenses. In addition, you can refuse to use it by deactivating mobile data on the device itself. Modern gadgets make it easy to manage its condition.
How to get GPRS settings on the Megafon number?
Most modern cellular operators allow you to protect the client from unnecessary manipulations: after installing a SIM card in the device slot, the settings are made automatically, after registering on the network. In some situations, human intervention may be required if the machine cannot be set up automatically. What can the client do? First, you can always request via automatic system"Megaphone" settings. They will arrive as a text message and all the subscriber has to do is save them to their phone. alternative this method will become manual on the device.

Setting Internet Options
For the number of the Megafon operator, GPRS settings can be requested by sending one in the text of the message to number 5049. If after a while the message with the parameters does not arrive, then it makes sense to contact the operator (by free phone 0500). So, if nevertheless the parameters were received in the message, then they need to be saved (or applied) in the phone (tablet). Then you should reboot the device and you can start using the Internet.
GPRS ("Megafon" is considered as an operator) can also be done manually. To do this, go to General settings operating system gadget, select the "Cellular" section and go to the "Access Points (APN)" item (section names may vary). Then, in the form that opens, you need to create a new access point, giving it an arbitrary name. Next, you must specify the APN - in the case of Megafon, this is Internet. The rest of the parameters can be left blank, as well as the username and password. If your gadget does not accept empty fields and requires you to specify a username and password, then both fields should be written - gdata. No further action is required. The setting must be saved.

Contacting a communication salon
As a rule, the measures described earlier make it quite easy to deal with the issue of setting up the Internet on the card of the Megafon operator. GPRS settings can be saved from a message sent automatically by the operator's service, or manually entered by the client. But what if all these actions did not lead to success, and you still can’t use the Internet? The office staff can help you resolve this issue. It is enough to contact the Megafon department with your gadget and explain what exactly the difficulty arises with. Owners of Chinese phone models may be denied assistance.

Internet cost
Mobile Internet GPRS ("Megafon" - operator) has a fixed fee - 9.90 rubles per megabyte of data. For active use of the Internet, it is recommended to connect unlimited Internet options or use tariff plans that already include certain traffic. Among the additional options that can be connected over the tariff plan, one can single out the package that is minimal in cost and traffic volume - XS (70 megabytes is provided to the client per day for a subscription fee of 7 rubles). The maximum package is L - 36 gigabytes of traffic per subscriber is allocated every month. payment of 890 rubles per month.
The subscriber can choose any package that he thinks best suits his needs. At the same time, it will be possible to reconnect the option if, for example, the volume of traffic on it turned out to be insufficient for you, or, conversely, you cannot use the limit, which is calculated for one month. Please note that the rest of the traffic is not transferred to a new billing period. Thus, there is no need to save on traffic, especially since it is possible to extend it if it has been completely used up. More information about the conditions for connecting options and their cost in relation to your region can be clarified on the operator's website, specifying the region in advance.

GPRS roaming Megafon
Using the Internet in roaming, and especially in international, is quite unprofitable. When traveling abroad, in order to save money, it is recommended to purchase local SIM cards or use wireless internet. For trips around Russia, you can use any of the options (except XS) - S / M / L - the set amount of traffic can be spent while in any region of the country. Also, to optimize the cost of Internet services in roaming, the services "Internet abroad" and "Internet within Russia" can be used. You can find out the terms of provision for your region on the official website of the operator.

For those who want to protect themselves and exclude the possibility of connecting to the Internet abroad, you can set a ban on the use of Internet roaming. You can do this in the following way:
- By dialing the ban *105*746# (in the future it can be removed so that you can use the Internet again).
- By calling the operator at the free support line number - 0500 (the specialist will send to your phone, after specifying the model of the device, automatic settings in SMS).
- By contacting the Megafon salon (employees will help you correctly set up the service on a smartphone or tablet).
- Using the functionality of a personal account.
Conclusion
In this article, we talked about how you can set up the Internet in various ways, on what financial conditions data is transmitted via Megafon GPRS channels, what options can be used to optimize costs, subject to active use, etc. Please note that the cost of communication services is given for the Moscow region, you can clarify the tariffs for your region on the operator's website or by contacting the contact center.
General Packet Radio Services technology.
Answering the question of what GPRS is and why it is needed, let's dwell on some aspects of the operation of GSM networks. We will not go into unnecessary technical details and will try to tell everything intelligibly.
1. How does GPRS work?
With a normal connection, both for conversation and for data transmission, a GSM subscriber is allocated a radio channel (more precisely, a part of the radio channel) with a bandwidth of 9.6 Kbps. Such a low speed seriously limits the possibilities of using GSM networks, for example, it concerns working with the Internet. (For comparison: when connecting to the Internet using a modem, the speed of information exchange can ideally reach 52 Kbps.) But when the GSM standard was developed, the need for data transmission was small, and they did not concentrate on solving the problem.
All existing difficulties associated with high-speed information exchange will disappear with the advent of third generation networks (3G). However, 3G is tomorrow ( approx. edit: this article was written in 2006), and you need to transmit data today in networks that have received daily distribution, GSM. GPRS technology allows you to modify communications with minimal costs (although we are still talking about millions of dollars).
The principle of operation of GPRS is based on the fact that the radio channel is divided into intervals (timeslots, we will call them slots). At each moment of time, a part of the slots remains free, which means that they can be used for data transfer. This opportunity is exploited by GPRS. An ordinary GSM phone always uses one slot, while GPRS devices use several at once, which significantly speeds up data transfer. The throughput of a single slot can be from 9.5 to 21.4 Kbps depending on the coding scheme. The theoretical speed limit in GPRS is 171.2 Kbps. According to the provided speed (the number of simultaneously occupied slots), all GPRS devices are divided into 12 classes (MultiSlot Class). The first generation devices are capable of exchanging information at speeds up to 40.3 Kbps.
Handsets are also classified according to another criterion - in the order of working with data and voice (GPRS Class). Class A devices allow you to simultaneously transmit information and conduct a conversation. Class B also works in both voice and data mode, but does not allow you to do this at the same time (mobile phones of this class are currently on the market). Class C supports either voice or data.
GPRS places higher demands on cellular network. For data transmission, resources that are not occupied by conversations are used. Voice traffic has priority, so if the network is congested, then GPRS does not work. Accordingly, the network reserves can be judged by the data transfer rate.
Test laboratory PC Magazine / RE investigated new GPRS data transmission services provided by Beeline GSM network.
Theoretically, as mentioned above, GPRS provides data rates up to 171.2 Kbps (8 channels of 21.4 Kbps per channel, using the CS4 coding scheme). In practice, the speed, of course, is less, when using the CS2 coding scheme implemented in the current terminals, the data transfer rate in one channel is 13.4 Kbps, while existing phones can occupy only three or four channels for receiving data (plus one - for transmission).
One of the problems that has significantly delayed the deployment of GPRS networks is the insufficient number of GPRS phones. When developing finished devices, designers faced the problem of increased power consumption; since the terminal works with several channels, the transmitter power must be higher, and therefore more consumption. Despite the fact that the GPRS architecture provides for the possibility of solving this problem (for example, the terminal does not spend energy scanning the air over a given frequency range, tracking only signaling channels, through which information is transmitted, on which channels this particular terminal needs to wait for data), the problem nutrition turned out to be quite serious. Today it is more or less solved, but relatively mass production of GPRS phones is expected only in autumn. At the time of testing, there was only one phone on sale - Motorola T260 (maximum speed 40.2 kbps).
Exploring GPRS services in the Beeline GSM network (while the network is in trial operation mode). First, it was planned to evaluate the quality of services based on a set of special scenarios that simulate the actions of an average cellular Internet user (browsing e-mail, Web, working with ICQ, FTP, etc.), when working with a laptop and different models handheld PCs (Psion netBook, Palm IIIxe and HP Jornada 548). In the course of the research, no noticeable problems were found when setting up the connection of hand-held PCs and laptops with GPRS, at least there are no more of them than when working with a conventional cell phone. Everything is as always - the "profiles" of the modem and the "connection" are created and the information provided by the operator is entered into them (IP addresses DNS servers and quality of service management parameters). To connect to the GPRS network, you need to “call”, using standard system tools, to the “pseudo-phone” number * 99 #.
While any quantitative estimates do not make sense. The nominal communication speed in the BeeLine GSM network, according to company representatives, is 15-20 Kbps. Practice has shown that this is the peak speed, as a rule, in reality it is much less. In the Beeline GSM network today, voice traffic has a higher priority than GPRS services, and therefore the “average communication speed” parameter is small, which indicates the quality of communication, there is too much variation in values. In general, Web pages are loaded at approximately the same speed as when working with the GSM network, however, from the user’s point of view, this happens a little differently - if the page is slowly but surely “pumped” in the GSM network, then when working with GPRS , as a rule, there is a pause (speed 3-4 bytes / s), then a "peak" (15-20 kbps), a "peevsite" is loaded, then a pause again. As a result, the process takes approximately the same time as when working with GSM (we measured the "loading" time of the www.pcmag.ru page, taking some measures to compensate for the influence of graphic images posted on other Web sites).
It should be noted the strange behavior of the network when working with FTP servers - if the test file has a length of more than 1 KB, then the chances of copying are sharply reduced. At the same time, an attempt to “download” a file using the http protocol will certainly be successful. An almost similar picture is observed when working with e-mail (letters larger than 1 KB are transmitted quickly, while larger ones “freeze”). What explains this effect is not clear; it is quite possible that these are manifestations of the "exploratory" nature of the GPRS network. After the start of commercial operation, this problem can be investigated in more detail.
From the user's point of view, there are few preferences in GPRS. Before, the paid pause (20-60 s) disappears when connecting to the traditional "cellular Internet" (currently the user is registering on the network). An “instant” connection makes work much more comfortable, and a simple calculation shows that by connecting to the cellular Internet twice a day (for example, checking mail, watching the news, etc.), you can save 20-60 minutes per month. airtime. Another plus is the principle of "per megabyte" payment, the dependence on a factor not controlled by the user - time - disappears.
It is too early to draw final conclusions, because the main thing is unknown - the prices (during the trial operation, until September 20, GPRS services are provided free of charge). However, at first glance, the technology looks promising.
2. A look at GPRS technology from the inside.
One of the significant shortcomings of GSM cellular communication networks today is the low data transfer rate (maximum 9.6 kbit / s). And the organization of this process itself is far from perfect - one voice channel is allocated to the subscriber for data transmission, and billing is carried out based on the connection time (and in terms of tariffs, it differs little from voice channels).
For high-speed data transmission via existing GSM networks, GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) was developed. It should be noted that in addition to increasing the speed (the maximum is 171.2 Kbps, but more on that below), the new system involves a different payment scheme for data transmission services - when using GPRS, calculations will be made in proportion to the amount of information transmitted, and not the time spent online. In addition, the introduction of GPRS will contribute to a more economical and rational distribution of the radio frequency resource: without going into technical details, we can say that data “packets” are supposed to be transmitted simultaneously over many channels (it is in the simultaneous use of several channels that the speed gain lies) in pauses between speech transmissions. And only in pauses - voice traffic has unconditional priority over data, so the speed of information transfer is determined not only by the capabilities of network and subscriber equipment, but also by network load. I emphasize that in GPRS, not a single channel is completely engaged in data transmission - and this is the main qualitative difference new technology from those currently in use. Just imagine - you can always have a green ICQ chamomile on your laptop without loading the network with it, and pay in proportion to the volume of received and sent messages.
Of course, the GPRS developers have made every effort to ensure that the installation new system“over” the existing GSM networks turned out to be as less burdensome (and ruinous, which is important) for operators as possible. Let's take a closer look at what new units and connections are emerging in the overall architecture of a GSM cellular system with the introduction of GPRS, and then discuss user equipment capable of working with high-speed packet data.
2.1 GPRS from inside.
Refinement of the GSM network for the provision of high-speed GPRS data transmission services can be divided into two forms - software and hardware. If we talk about software, then it requires either replacement or updating almost everywhere - from HLR-VLR registries to BTS base stations. In particular, a multi-user access mode to time frames of GSM channels is introduced, and in HLR, for example, a new Mobile Station Multislot Capability parameter appears (the number of channels that a subscriber's mobile phone can simultaneously work with, but more on that below).
Rice. 1 Structural diagram of the GPRS network.
The core of the GPRS system (GPRS Core Network) consists (Fig. 3.1) of two main blocks - SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node - GPRS support node) and GGPRS (Gateway GPRS Support Node - GPRS gateway node). Let's take a closer look at their functions.
SGSN is, roughly speaking, the brain of the system in question. In some way, SGSN can be called an analogue of MSC - a GSM network switch. Appeared in the same way as MSC, SGSN, there may be more than one in the system - in this case, each node is responsible for its own section of the network. For example, Motorola's SGSN has the following characteristics: each node supports the transmission of up to 2000 packets per second, simultaneously controls up to 10,000 online users. In total, there can be up to 18 Motorola SGSNs in the system.
The purpose of the GGSN can be understood from its name - roughly speaking, it is a gateway between the cellular network (more precisely, its part for GPRS data transmission) and external information highways (Internet, corporate intranets, other GPRS systems, etc.). The main task of the GGSN, therefore, is the routing (routing) of data going from and to the subscriber through the SGSN. The secondary functions of the GGSN are data addressing, dynamic issuance of IP addresses, as well as tracking information about external networks and own subscribers (including billing of services).
Note that the GPRS system has good scalability - when new subscribers appear, the operator can increase the number of SGSNs, and when the total traffic escalates, add new GGSNs to the system. Inside the core of the GPRS system (between SGSN and GGSN), data is transmitted using a special tunnel protocol GTP (GPRS Tunneling Protocol).
Another component of the GPRS system is the PCU (Packet Control Unit). PCU docking with controller base stations BSC and is responsible for directing data traffic directly from the BSC to the SGSN.
In the future (when the system is oriented towards Mobile Internet) it is possible to add a special node - IGSN (Internet GPRS Support Node - Internet support node).
The OMC-R / G (Operation and Maintenance Center - Radio / GSN - control and maintenance center for the radio / GPRS node: not shown in the figure) is responsible for the management and control of the GPRS system. This is the so-called interface between the system and its personnel.
Before starting to work with GPRS, the mobile station, as in the usual case of voice transmission, must register in the system. As already mentioned, registration (or, more precisely, “attachment” to the network) of users is handled by SGSN. In case of successful completion of all procedures (checking the availability of the requested service and copying the necessary user data from the HLR to the SGSN), the subscriber is issued a P-TMSI (Packet Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity - a temporary mobile subscriber number for packet data), similar to the TMSI, which is assigned mobile phone for voice transmission (by the way, if the subscriber terminal belongs to class A, then both TMSI and P-TMSI are allocated to it during registration).
To quickly route information to a mobile subscriber, the GPRS system needs data about its location relative to the network, and with greater accuracy than in the case of voice traffic transmission (let me remind you that HLR and VLR store the Location Area (LA) number in which the subscriber is located). But imagine how the service traffic in the cellular network and the energy consumption of the mobile device will increase if the phone informs the system every time it moves from one cell to another! To find a compromise between the volume of signaling traffic in the GPRS network and the need to know the location of the subscriber with high accuracy, the terminals are divided into three classes:
· IDLE (idle). Your phone is offline or out of network coverage. Obviously, the system does not track the movement of such subscribers.
STANDBY (standby mode). The machine is registered (attached) to the GPRS system, but for a long time(determined by a special timer) does not work with data transfer. The location of STANDBY subscribers is known up to RA (Routing Area). RA is smaller than LA (each LA is divided into several RAs, but, however, RA is larger than a cell and consists of several elementary cells).
· READY (readiness). The subscriber terminal is registered in the system and is in active operation. The coordinates of phones that are in READY mode are known to the system (or rather, SGSN) with an accuracy of a cell. According to this ideology, terminals in STANDBY mode, when moving from one RA to another, send a special signal to the SGSN about changing the routing area (routing area update request). If the new and old RAs are controlled by the same SGSN, then the RA change will only update the entry in the SGSN. If the subscriber moves into the coverage area of the new SGSN, then the new SGSN requests information about the user from the old one, and the MSC, VLR, HLR and GGSN are notified of the SGSN change. When a GPRS phone moves to another LA, the SGSN sends a message to the corresponding VLR to change the location record of the subscriber.
The situation with data routing in case of GPRS-subscriber roaming is interesting. In this case, two options, or, more appropriately, scenarios, are possible. In both cases, the SGSN is used by the guest (VSGSN - Visited SGSN), but the GGSN can be used either by the guest (VGGSN - Visited GGSN) or home (HGGSN - Home GGSN). In the latter case, a GPRS backbone must exist between the home and guest operators (InterPLMN GPRS BackBone - a GPRS line between different mobile networks) to transfer traffic between HGGSN and mobile subscriber. In addition, there is a need for a BG (Border Gateway) on both sides in order to protect networks from outside attacks.
It should be noted that important parameter, as Qo (Quality of Service - quality of service). Obviously, real-time video conferencing and sending by e-mail have different requirements, such as delays in the path of data packets. Therefore, there are several Qo classes in GPRS, which are divided according to the following criteria:
· Required priority (there is a high, medium and low data priority);
· Reliability (divided into three classes according to the number of possible errors of various kinds, lost packets, etc.);
· Delays (delays of information outside the GPRS network are not taken into account);
Quantitative characteristics (peak and average speed);
The Qo class is selected individually for each new data transfer session.
In addition to Qo, the characteristics of the data transmission session include the protocol type (PDP type - Packet Data Protocol type) the PDP address issued to the mobile station (the issuance of addresses can be both static and dynamic), as well as the GGSN address with which work is in progress. The "profile" of the session (in the English literature, the designation "PDP context" is accepted) is recorded in the phone, as well as in the SGSN and GGSN serving it. Multiple data transfer profiles can be supported at the same time for each user.
Broadly speaking, packet data transmission provides two modes of "connections":
1. PTP (Point-To-Point);
2. PTM (Point-To-Multipoint).
Broadcast mode PTM, in turn, is divided into two classes:
1. PTM-M (PTM-Multicast) - transmission necessary information to all users located in a certain geographical area;
2. PTM-G (PTM-Group Call) - data is sent to a specific group of users.
Support for multipoint PTM information transmission is expected in future GPRS specifications.
Therefore, the main characteristics of the GPRS protocol are the efficient use of radio and network resources, as well as fully transparent support for the IP protocol. GPRS optimizes the use of network and radio resources. The GPRS protocol uses the radio resource only when it is really required to receive or transmit data. Using packet technology, this protocol allows applications to use network resources only when user applications have data to send over the network. Thus, the protocol is adapted to the uneven nature of user application traffic.
One more important characteristic GPRS is to provide immediate connection and high bandwidth. Applications based on standard communication protocols such as IP and X.25 are supported. To support data applications, the GPRS protocol uses several new network nodes, in addition to the network nodes used in the GSM PLMN. These nodes are responsible for traffic routing and implementation of other exchange functions with external packet switching networks, subscriber search, cell selection, roaming, and many other functions necessary to ensure the operation of the cellular network. In addition, GPRS uses the GSM SMS and GSM MM protocols (the latter is called GMM in GPRS).
2.2 GPRS outside subscriber devices.
Let's talk now about GPRS client equipment. Unfortunately or fortunately, but to work with a packet data system, you must have a special phone that is compatible with GPRS. More strictly speaking, GPRS terminals are divided into three classes:
1. Class A devices are able to simultaneously work with both voice and data transmission (they, technically speaking, have the ability to function both in circuit switched mode and in packet switched mode). - we are talking about simultaneous operation in different modes);
2. Class B devices can carry out either voice or data transmission, but not both;
3. Class C devices only support data transmission and cannot be used for voice communications. As a rule, these are various kinds of computer boards for providing wireless access to data.
It should be noted that the maximum data transfer rate is determined, first of all, by the number of channels with which the user terminal can simultaneously work. One channel provides data transfer at speeds up to 13.4 Kbps.
The French company SAGEM was one of the first manufacturers to introduce GPRS-compatible phones. The Sagem MC-850 model, which was presented at the Geneva TELECOM-99 exhibition, belongs to class B and has one data transmission channel and three for reception, and a slightly more modern Sagem MW-959, brought to the public at CEBIT-2000, already includes four channels for incoming traffic (there is still one channel for transmission, the device class has not changed either). Thus, the maximum data reception rate using the Sagem MW-959 phone is 53.6 Kbps, and the maximum transmission rate is 13.4 Kbps.
Conclusion. This year 2002 is expected to see an avalanche-like, so to speak, introduction of GPRS all over the world. The next step from GSM to third-generation UMTS (Universal Mobile Telephone System) networks is EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution - loosely translated as “data transmission at an increased speed”), which allows information to be transferred at speeds up to 384 Kbps over eight GSM channels (48 Kbps per channel). To implement EDGE over GPRS, operators will need to replace BTS base station hardware, and users will need to purchase EDGE-enabled handsets. Although at the moment I personally find it difficult to imagine what a subscriber of the GSM cellular network should do in order to lack the speed of 170 Kbps offered by GPRS.
2.2.1 What does GPRS technology give the subscriber?
GPRS will introduce fundamentally new services that were not available before. First of all, this is mobile access to Internet resources with a speed that satisfies the consumer, instant connection and a very favorable billing system. For example, when browsing a WEB page using the GPRS system, we can study the content as much as we need, since we pay only for the received information and do not pay for the time spent on the Internet (without transmitting data, we do not occupy network channels) . With the introduction of time-based payment on fixed telephone lines, tariffs for Internet access from a mobile GPRS phone will be even more competitive.
GPRS technology will allow you to quickly transfer and receive large amounts of data, video images, MP3 music files and other multimedia information.
For those subscribers who have already appreciated the convenience of using phones with a WAP browser, the introduction of GPRS technology means almost instant loading of WAP pages on the phone screen and a more favorable billing system.
For corporate users The GPRS system can serve as an excellent tool to provide employees with safe and fast access to corporate networks enterprises, to mail, information servers, remote databases. In this case, it will be possible to gain access to corporate networks even if the subscriber is in the network of another GSM operator with which GPRS roaming is organized.
GPRS technology can be used in telemetry systems: the device can be connected all the time without occupying a separate channel. Such a service may be required by bank security services to connect ATMs in other areas, including industrial ones.
3. Trends in the development of demand for GPRS. Prospects for the development of services.
After describing the benefits of GPRS, it is hardly necessary to substantiate the assertion that while a number of GSM operators consider GPRS only as a transitional step to 3G systems, others, especially those who are not going to apply for 3G licenses and do not hope to receive such licenses, see GPRS as a long-term solution to the predicted explosion in wireless data communications, comparable to what can be provided by leading implementation. However, for those who intend to implement 3G systems, the additional equipment required to support GPRS will be a good basis for supporting data traffic in W-CDMA systems.
GPRS infrastructure development, which is actively pursued by Alcatel, Ericsson, Lucent, Motorola, Nokia, Nortel and Siemens, is moving forward by leaps and bounds. GPRS system exams, conducted jointly with operators, made it possible to make the first GPRS data call on a live GSM network as early as November 1999. Since then, although the initial impetus for GPRS development came from major European GSM operators, more operators from other regions, especially Asia Pacific, have reported GPRS exams.
The supply of subscriber terminals (ie GPRS phones), as in the case of WAP, was late in comparison with infrastructure development. Successful launches of GPRS networks in commercial operation will be blurred due to the lack of suitable phones in mass quantities. As of early March 2000, only a few cell phone manufacturers have demonstrated prototype GPRS equipment, and none of them could give exact dates for their commercial production.
After the mass appearance of various models of GPRS telephones on the market, GPRS services will be gradually reoriented to the mass consumer, and the development of GPRS will follow a combined scenario that takes into account the interests of both corporate clients, and the mass consumer with a development trend towards the demands of the latter.