Siemens (symbol: Cm, S) SI unit of measurement of electrical conductivity, reciprocal of ohm. Before World War II (in the USSR until the 1960s), the Siemens was a unit of electrical resistance corresponding to resistance ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Becquerel. Becquerel (symbol: Bq, Bq) is a measure of the activity of a radioactive source in the International System of Units (SI). One becquerel is defined as the activity of the source, in ... ... Wikipedia
Candela (designation: cd, cd) is one of the seven basic units of the SI system, equal to the intensity of light emitted in a given direction by a source of monochromatic radiation with a frequency of 540 1012 hertz, the energy intensity of which is in this ... ... Wikipedia
Sievert (symbol: Sv, Sv) is a unit of measurement of effective and equivalent doses of ionizing radiation in the International System of Units (SI), has been used since 1979. 1 sievert is the amount of energy absorbed by a kilogram ... ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Newton. Newton (symbol: N) is a unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). Accepted international name newton (symbol: N). Newton is a derived unit. Based on the second ... ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Siemens. Siemens (Russian designation: См; international designation: S) is a unit of measurement of electrical conductivity in the International System of Units (SI), the reciprocal of ohm. Through others ... ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Pascal (meanings). Pascal (symbol: Pa, international: Pa) is a unit of pressure (mechanical stress) in the International System of Units (SI). Pascal is equal to pressure ... ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Tesla. Tesla (Russian designation: Tl; international designation: T) is a unit of measurement of the magnetic field induction in the International System of Units (SI), numerically equal to the induction of such ... ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Gray. Gray (symbol: Gy, Gy) is a unit of measurement of the absorbed dose of ionizing radiation in the International System of Units (SI). The absorbed dose is equal to one gray if as a result ... ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Weber. Weber (symbol: Wb, Wb) is a unit of measurement of magnetic flux in the SI system. By definition, a change in magnetic flux through a closed loop at a rate of one weber per second induces ... ... Wikipedia
The concept of frequency and period of a periodic signal. Units. (10+)
The frequency and period of the signal. Concept. Units
The material is an explanation and addition to the article:
Units of measurement of physical quantities in radio electronics
Units of measurement and ratios of physical quantities used in radio engineering.
Periodic processes are often encountered in nature. This means that some parameter characterizing the process changes according to a periodic law, that is, the equality is true:
Definition of frequency and period
F(t) = F(t + T) (relation 1), where t is time, F(t) is the value of the parameter at time t, and T is some constant.
It is clear that if the previous equality is true, then this is also true:
F(t) = F(t + 2T) So, if T is the minimum value of the constant for which relation 1 holds, then we will call T period
In radio electronics, we study the strength of current and voltage, so that periodic signals will be considered signals for voltage or current in which the ratio 1 is true.
Unfortunately, errors occur periodically in articles, they are corrected, articles are supplemented, developed, new ones are being prepared. Subscribe to the news to stay informed.
If something is not clear, be sure to ask!
Ask a Question. Article discussion.
More articles
Field effect transistor, CMOS chip, operational amplifier. Installation, at...
How to solder a field effect transistor or CMOS chip ...
The mode of continuous / discontinuous (intermittent) current through the indus...
Comparison of continuous and discontinuous current modes. Online calculation for step-up, ...
Signals are mathematical (arithmetic) operations. Addition, summation...
Schemes for performing arithmetic operations on signals. Summation, subtraction...
How does a step-up stabilized voltage converter work. Where is he at...
How it works is a transformerless power supply. Description...
Formation of an arbitrary / adjustable output voltage using...
Adjustment, setting the output voltage of a specialized integrated circuit ...
The language for its designation is the abbreviation "Hz", in the English language the designation Hz is used for these purposes. At the same time, according to the rules of the SI system, if the abbreviated name of this unit is used, it follows with, and if the full name is used in the text, then with lowercase.
Origin of the term
The unit of frequency, adopted in the modern SI system, got its name in 1930, when the International Electrotechnical Commission adopted the corresponding decision. It was associated with the desire to perpetuate the memory of the famous German scientist Heinrich Hertz, who made a great contribution to the development of this science, in particular, in the field of electrodynamics research.Term meaning
Hertz is used to measure the frequency of oscillations of any kind, so the scope of its use is very wide. So, for example, in the number of hertz it is customary to measure sound frequencies, the beating of the human heart, fluctuations in the electromagnetic field and other movements that repeat with a certain frequency. So, for example, the frequency of a human heart in a calm state is about 1 Hz.Meaningfully, the unit in this dimension is interpreted as the number of vibrations made by the analyzed object during one second. In this case, experts say that the oscillation frequency is 1 hertz. Accordingly, a greater number of oscillations per second corresponds to a greater number of these units. Thus, from a formal point of view, the value denoted as hertz is the reciprocal of the second.
Significant frequencies are usually called high, insignificant - low. Examples of high and low frequencies are sound vibrations of varying intensity. So, for example, frequencies in the range from 16 to 70 Hz form the so-called bass, that is, very low sounds, and frequencies in the range from 0 to 16 Hz are completely indistinguishable to the human ear. The highest sounds that a person can hear lie in the range from 10 to 20 thousand hertz, and sounds with a higher frequency belong to the category of ultrasounds, that is, those that a person is not able to hear.
To designate large values of frequencies, special prefixes are added to the designation "hertz", designed to make the use of this unit more convenient. Moreover, such prefixes are standard for the SI system, that is, they are used with other physical quantities. So, a thousand hertz is called "kilohertz", a million hertz - "megahertz", a billion hertz - "gigahertz".
In the article, you will learn what sound is, what is its lethal volume level, as well as the speed in air and other environments. We will also talk about frequency, encoding and sound quality.
We will also consider sampling, formats and sound power. But first, let's define music as ordered sound - the opposite of the disordered, chaotic sound we perceive as noise.
- These are sound waves that are formed as a result of fluctuations and changes in the atmosphere, as well as objects around us.

Even when talking, you hear your interlocutor because he affects the air. Also, when you play a musical instrument, whether you beat a drum or pull a string, you produce vibrations of a certain frequency, which in the surrounding air produces sound waves.
Sound waves are ordered And chaotic. When they are ordered and periodic (repeated after a certain period of time), we hear a certain frequency or pitch.
That is, we can define frequency as the number of repetitions of an event in a given period of time. Thus, when sound waves are chaotic, we perceive them as noise.
But when the waves are ordered and repeat periodically, then we can measure them by the number of repeating cycles per second.
Audio sampling rate
The audio sample rate is the number of measurements of the signal level in 1 second. Hertz (Hz) or Hertz (Hz) is a scientific unit of measurement that determines the number of repetitions of an event per second. This is the unit we will be using!
 Audio sampling rate
Audio sampling rate Probably, you have often seen such an abbreviation - Hz or Hz. For example, in equalizer plugins. In them, the units of measurement are hertz and kilohertz (that is, 1000 Hz).
Normally, a person hears sound waves from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz (or 20 kHz). Anything less than 20 Hz is infrasound. Anything over 20 kHz is ultrasound.
Let me open the equalizer plugin and show you what it looks like. You are probably familiar with these numbers.
 sound frequencies
sound frequencies With an equalizer, you can attenuate or boost specific frequencies within the human audible range.
Small example!
Here I have a recording of a sound wave that was generated at 1000 Hz (or 1 kHz). If we zoom in and look at its shape, we will see that it is regular and repetitive (periodic).
 Repetitive (periodic) sound wave
Repetitive (periodic) sound wave In one second, a thousand repeating cycles occur here. For comparison, let's look at a sound wave that we perceive as noise.
 Disordered sound
Disordered sound There is no specific repeating frequency. There is also no specific tone or pitch. The sound wave is not ordered. If we look at the shape of this wave, we will see that there is nothing repetitive or periodic in it.
Let's move on to the richer part of the wave. We zoom in and see that it is not constant.
 Unordered wave when scaled
Unordered wave when scaled Due to the lack of cyclicity, we are not able to hear any specific frequency in this wave. Therefore, we perceive it as noise.
Deadly sound level
I want to mention a little about the lethal level of sound for a person. It originates from 180 dB and higher.

It should be said right away that according to regulatory standards, a safe noise level is considered to be no more than 55 dB (decibels) during the day and 40 dB at night. Even with prolonged exposure to hearing, this level will not cause harm.
| Sound volume levels | ||
|---|---|---|
| (dB) | Definition | A source |
| 0 | Not sound at all | |
| 5 | Almost inaudible | |
| 10 | Almost inaudible | Quiet rustle of leaves |
| 15 | barely audible | rustle of leaves |
| 20 — 25 | barely audible | Whispers of a person at a distance of 1 meter |
| 30 | Quiet | The ticking of the wall clock permissible maximum according to the norms for residential premises at night from 23 to 7 hours) |
| 35 | Quite audible | Muted conversation |
| 40 | Quite audible | common speech ( norm for residential premises during the day from 7 a.m. to 11 p.m.) |
| 45 | Quite audible | Talk |
| 50 | clearly audible | Typewriter |
| 55 | clearly audible | Talk ( European standard for class A office space) |
| 60 | (norm for offices) | |
| 65 | Loud talk (1m) | |
| 70 | Loud talk (1m) | |
| 75 | Scream and laugh (1m) | |
| 80 | Very noisy | Scream, a motorcycle with a silencer |
| 85 | Very noisy | Loud scream, motorcycle with silencer |
| 90 | Very noisy | Loud screams, freight railcar (7m) |
| 95 | Very noisy | Subway car (7 meters outside or inside the car) |
| 100 | Extremely noisy | Orchestra, thunder ( according to European standards, this is the maximum allowable sound pressure for headphones) |
| 105 | Extremely noisy | In old planes |
| 110 | Extremely noisy | Helicopter |
| 115 | Extremely noisy | Sandblaster (1m) |
| 120-125 | almost unbearable | Jackhammer |
| 130 | pain threshold | Airplane at the start |
| 135 — 140 | Contusion | Jet plane taking off |
| 145 | Contusion | rocket launch |
| 150 — 155 | Contusion, injury | |
| 160 | shock, trauma | Shock wave from a supersonic aircraft |
| 165+ | Rupture of eardrums and lungs | |
| 180+ | Death | |
Speed of sound in km per hour and meters per second
The speed of sound is the speed of propagation of waves in a medium. Below I give a table of propagation speeds in various media.

The speed of sound in air is much less than in solid media. The speed of sound in water is much higher than in air. It is 1430 m / s. As a result, propagation is faster and audibility is much further.
Sound power is the energy that is transmitted by a sound wave through the surface in question per unit of time. Measured in (W). There is an instantaneous value and an average (over a period of time).

Let's continue with the definitions from the music theory section!
Pitch and note
Height is a musical term that means almost the same thing as frequency. The exception is that it does not have a unit of measurement. Instead of defining sound by the number of cycles per second in the range of 20 - 20,000 Hz, we designate certain frequency values in Latin letters.
Musical instruments produce regularly shaped periodic sound waves, which we call tones or notes.
That is, in other words, it is a kind of snapshot of a periodic sound wave of a certain frequency. The pitch of this note tells us how high or low the note is. At the same time, lower notes have longer waves. And tall, shorter.
Let's look at a 1 kHz sound wave. Now I'll zoom in and you'll see how far apart the cycles are.
 Sound wave at 1 kHz
Sound wave at 1 kHz Now let's look at a 500 Hz wave. Here the frequency is 2 times less and the distance between cycles is greater.
 Sound wave at 500 Hz
Sound wave at 500 Hz Now let's take a wave of 80 Hz. It will be even wider and the height is much lower.
 Sound at 80 Hz
Sound at 80 Hz We see the relationship between the pitch of a sound and its waveform.
Each musical note is based on one fundamental frequency (fundamental). But in addition to tone in music, it also consists of additional resonant frequencies or overtones.
Let me show you another example!
Below is a wave at 440 Hz. It is the standard in the world of music for tuning instruments. It corresponds to the note la.
 Pure sound wave at 440 Hz
Pure sound wave at 440 Hz We hear only the fundamental tone (pure sound wave). If we zoom in, we will see that it is periodic.
Now let's look at a wave of the same frequency, but played on the piano.
 Periodic piano sound
Periodic piano sound Look, it is also periodic. But it has small additions and nuances. All of them together give us an idea of how the piano sounds. But besides this, overtones are also determined by the fact that some notes will have a greater affinity for a given note than others.
For example, you can play a tighter note, but an octave higher. It will sound completely different. However, it will be related to the previous note. That is, it is the same note, only played an octave higher.
Such a relationship of two notes in different octaves is due to the presence of overtones. They are constantly present and determine how closely or distantly certain notes are related to each other.
Parameters whose values are expressed in hertz can be found in the technical specifications of various devices: computer components, radios, measuring equipment - wherever alternating electrical signals flow. Nevertheless, not everyone can answer the question of what is measured in hertz without hesitation.
Hertz (Hz) is a derived SI unit used to express the frequency of periodic, that is, repeating after a certain period of time, processes. The numerical value of this value means the number of realizations of the specified process per second, which can be mathematically written as 1 Hz=1/s=s -1 . In hertz, you can quantify the frequency of phenomena of any physical nature, whether it is a change in the current in a household electrical network, contractions of the heart muscle, swing oscillations, the occurrence of impulses or the propagation of sound waves.
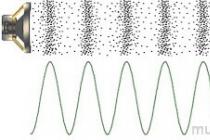
The easiest way to understand the meaning of the unit of measure in question is by the example of sinusoidal dependences of signals on time. The picture shows graphs of sound vibrations of different frequencies. In the first figure, for a period equal to a second, one maximum value of the wave occurs, and in the second - ten. That is, the appearance of the same states of process parameters in the latter case occurs ten times more often - with a frequency of 10 Hz.
Data transmission in communication systems, propagation of sound waves and many other processes can be characterized by frequencies several orders of magnitude greater than 1 Hz. Therefore, with this unit of measurement, standard SI prefixes are used, denoting multiples (1 kHz \u003d 10 3 Hz, 1 MHz \u003d 10 6 Hz and others).
In addition to the hertz, there is another unit of measurement that corresponds to 1 / s or s -1 - becquerel. Unlike the first one, which serves to describe periodic signals, this value characterizes the activity of sources of radioactive decay, which is a random process.
Here are some interesting facts on the topic of the article.
- The approximate frequency range of sounds audible to humans is from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Moreover, with age, the upper limit shifts downward - most people gradually lose the ability to perceive high sounds.
- In Russia and European countries, the frequency of alternating current in power networks is 50 Hz, in the USA, Canada - 60 Hz, and in Japan, depending on the region, this network parameter can be equal to both 50 and 60 Hz.
- The heart of a healthy person who does not experience significant physical exertion beats at a frequency of approximately 1 Hz.
- The FM broadcasting range is from 87.5 to 108 MHz, the frequency of electromagnetic waves generated for cooking and heating food in a microwave oven is 2450 MHz.