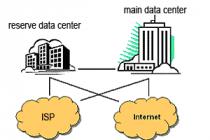
The development of any electronic device is accompanied by physical or mathematical modeling. Physical modeling is associated with high material costs, since it requires the manufacture of models and their laborious research. Physical modeling is often impossible due to the extreme complexity of the device, for example, in the design of large and very large integrated circuits. In this case, they resort to mathematical modeling using the means and methods of computer technology.
For example, the well-known P-CAD package contains a block of logical modeling of digital devices, but for beginners, including students, it presents significant difficulties in mastering. No less difficulties are encountered when using the DesignLab system. As the analysis of the state of the circuit modeling software has shown, at the stage of the initial development of computer-aided design methods and at the stages of exploration and research it is advisable to consider the possibility of using the following programs such as Electronics Workbench - EWB.
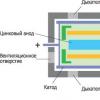
The circuit simulation system Electronics Workbench is designed to simulate and analyze electrical circuits in Fig. 1. It is correct to say: the Electronics Workbench system for modeling and analyzing electrical circuits, but for brevity, hereinafter, we will call it a program.
The Electronics Workbench program allows simulating analog, digital and digital-to-analog circuits of a high degree of complexity. The libraries available in the program include a large set of widely used electronic components. It is possible to connect and create new component libraries.

Component parameters can be changed over a wide range of values. Simple components are described by a set of parameters, the values of which can be changed directly from the keyboard, active elements - by a model, which is a set of parameters and describes a specific element or its ideal representation.
The model is selected from the list of component libraries, the model parameters can also be changed by the user. A wide range of instruments allows you to measure various quantities, set input influences, and build graphs. All devices are depicted as close to real as possible, so working with them is simple and convenient.
The simulation results can be output to a printer or imported into a text or graphic editor for further processing. Electronics Workbench software is compatible with P-SPICE software, that is, it provides the ability to export and import diagrams and measurement results in its various versions.
The main advantages of the program
Saving time Working in a real laboratory requires a lot of time to prepare an experiment. Now, with the advent of the Electronics Workbench, the electronic lab is always at hand, making the study of electrical circuits more accessible. Measurement reliability
In nature, there are no two completely identical elements, that is, all real elements have a wide range of values, which leads to errors in the course of the experiment. In Electronics Workbench, all elements are described by strictly set parameters, therefore, each time during the experiment, the result will be repeated, determined only by the parameters of the elements and the calculation algorithm.
Convenient Measurements Learning is impossible without errors, and errors in a real laboratory are sometimes very expensive for the experimenter. Working with the Electronics Workbench, the experimenter is insured against accidental electric shock, and the devices will not fail due to an incorrectly assembled circuit. Thanks to this program, the user has at his disposal such a wide range of devices that will hardly be available in real life.
Thus, you always have a unique opportunity to plan and carry out a wide range of studies of electronic circuits with a minimum amount of time. Graphic capabilities Complex circuits take up a lot of space, while trying to make the image denser, which often leads to errors in connecting conductors to circuit elements. Electronics Workbench allows you to place the circuit in such a way that all the connections of the elements and at the same time the entire circuit are clearly visible.
The intuitiveness and simplicity of the interface makes the program accessible to anyone familiar with the basics of using Windows. P-SPICE Compatibility The Electronics Workbench software is based on standard SPICE software elements. This allows you to export various models of elements and carry out processing of the results using the additional capabilities of different versions of the P-SPICE program.
Components and Experiments
The program component libraries include passive elements, transistors, controlled sources, controlled switches, hybrid elements, indicators, logic elements, trigger devices, digital and analog elements, special combinational and sequential circuits.
Active elements can be represented by models of both ideal and real elements. It is also possible to create your own models of elements and add them to the libraries of elements. The program uses a large set of instruments for measurements: ammeter, voltmeter, oscilloscope, multimeter, Bode plotter (plotter of frequency characteristics of circuits), function generator, word generator, logic analyzer and logic converter.
Circuit Analysis Electronics Workbench can analyze both AC and DC circuits. DC analysis determines the operating point of the circuit in steady state operation. The results of this analysis are not reflected in the instruments, they are used for further circuit analysis. AC analysis uses the results of DC analysis to generate linearized models of nonlinear components.
Analysis of circuits in the AC mode can be carried out in both the time and frequency domains. The program also allows you to analyze digital-to-analog and digital circuits. In Electronics Workbench, you can investigate the transients when the circuits are affected by input signals of various shapes.
Analysis operations:
Electronics Workbench allows you to build circuits of varying degrees of complexity using the following operations:
... selection of elements and devices from libraries,
... moving elements and diagrams to any place of the working field,
... rotation of elements and groups of elements by angles divisible by 90 degrees,
... copying, pasting or deleting elements, groups of elements, fragments of schemes and whole schemes,
... color change of conductors,
... color highlighting of the outlines of circuits for a more convenient perception,
... simultaneous connection of several measuring instruments and observation of their readings on the monitor screen,
... assigning a symbol to an element,
... changing the parameters of elements in a wide range. All operations are performed using the mouse and keyboard. Control only from the keyboard is not possible.
By configuring the devices, you can:
... change the instrument scales depending on the measurement range,
... set the operating mode of the device,
... set the type of input influences on the circuit (direct and harmonic currents and voltages, triangular and rectangular pulses).
The graphic capabilities of the program allow:
... simultaneously observe several curves on the graph,
... display curves on graphs in different colors,
... measure the coordinates of points on the graph,
... import data into a graphics editor, which allows you to make the necessary transformations of the picture and output it to the printer.
Electronics Workbench allows using the results obtained in the P-SPICE and PCB programs, as well as transferring the results from the Electronics Workbench to these programs. You can insert a diagram or its fragment into a text editor and print explanations or notes on the operation of the diagram in it.
Working with Electronics Workbench
Electronics Workbench software is designed to simulate and analyze electronic circuits. The capabilities of Electronics Workbench v.5 are roughly equivalent to those of MicroCap and allow you to perform work from the simplest experiments to statistical modeling experiments.
When creating a schematic, the Electronics Workbench allows you to:
-select elements and devices from libraries,
Move elements and diagrams to any place in the working area,
Rotate elements and their groups by angles in multiples of 90 degrees,
Copy, paste or delete elements, fragments of circuits,
Change the colors of the conductors,
Highlight the outline of the schemes,
Connect several measuring devices at the same time and observe their readings on the monitor screen,
- assign symbols to elements,
Change parameters of elements.
By changing the device settings, you can:
- change the instrument scales depending on the measurement range,
Set the operating mode of the device,
Set the type of input influences on the circuit (direct or harmonic currents or voltages, triangular or rectangular pulses).
Insert a diagram or its fragment into a text editor, in which an explanation of the diagram's operation is printed.
Electronics Workbench components
After launching WEWB32, the menu bar and component bar appear on the screen.
The component panel consists of icons of the component fields, and the component field - of the symbolic images of the components.
Clicking on the component icon opens the field corresponding to this icon.
Following are some of the elements from the component fields:
Basic (basic components)

Connecting knot
The node is used to connect conductors and create control points.
Resistor
Resistor resistance can be specified as a number in Ohm, kOhm, MOhm
Capacitor
the capacitance of the capacitor is set by a number indicating the dimension (pF, nF, μF, mF, F).
Key
Key operated by key. Such keys can be closed or opened using controlled keys on the keyboard. (The name of the control key can be entered from the keyboard in the dialog box that appears after double-clicking on the key image.)
Sources

Earth
The "Ground" component has zero voltage and serves as a reference point for the potentials.
DC voltage source 12V
EMF of a constant voltage source is indicated by a number indicating the dimension (from μV to kV)
DC power supply 1A
The DC source current is specified by a number with an indication of the dimension (from μA to kA)
AC voltage source 220 V / 50 Hz

The rms value (root-mean-sguare-RMS) of the source voltage is given by a number with an indication of the dimension (from μV to kV). It is possible to set the frequency and start phase.
AC source 1 A / 1 Hz

The effective value of the source current is specified by a number with the indicated dimension (from μA to kA). It is possible to set the frequency and start phase.
Clock generator 1000 Hz / 50%

The generator generates a periodic sequence of rectangular pulses. Pulse amplitude, duty cycle and pulse repetition rate can be adjusted.
Indicators

The simplest instruments are a voltmeter and an ammeter. They automatically change the measurement range. Several such devices can be used simultaneously in one circuit.
Voltmeter

A voltmeter is used to measure AC or DC voltage. The bold side of the rectangle corresponds to the negative terminal.
Double-clicking on the voltmeter image opens a dialog box for changing the voltmeter parameters:
-values of internal resistance (default 1MΩ),
- the type of measured voltage (DC-constant, AC-variable).
When measuring alternating sinusoidal voltage (AC), the voltmeter shows the rms value
Ammeter
![]()
An ammeter is used to measure AC or DC current. The bold side of the rectangle corresponds to the negative terminal.
Double-clicking on the ammeter image opens a dialog box for changing the ammeter parameters
Internal resistance values (default 1mOhm),
Type of measured voltage (DC-constant, AC-variable).
When measuring alternating sinusoidal voltage (AC), the ammeter shows the rms value
Instruments

1 .Functional generator
The generator is an ideal voltage source producing sinusoidal, triangular or rectangular waveforms. The middle terminal of the generator, when connected to the circuit, provides a common reference point for the amplitude of the AC voltage. To read the voltage relative to zero, this terminal is grounded. The extreme left and right pins are used to feed a signal to the circuit. The voltage at the right terminal changes in the positive direction relative to the common terminal, at the left terminal in the negative direction.
When you double-click on the generator image, an enlarged image of the generator opens, where you can set:
- the form of the output signal,
- the frequency of the output voltage (Frequency),
- Duty cycle,
- the amplitude of the output voltage (Amplitude),
- constant component of the output voltage (Offset).

2. Oscilloscope
The oscilloscope image has four input terminals
- upper right clamp - common,
- lower right - synchronization input,
- the bottom left and right terminals represent the Channel A and Channel B inputs, respectively.
Double-clicking on the oscilloscope thumbnail image opens an image of a simple oscilloscope model on which you can install
- the location of the axes along which the signal is deposited,
- the required scale of the scan along the axes,
- offset of the origin along the axes,
- capacitive input (AC button) or potential input (DC button) of the channel,
- synchronization mode (internal or external).

The Trigger field is used to determine when the sweep starts on the oscilloscope screen. The buttons in the Edge row set the moment when the oscillogram is triggered by the rising or falling edge of the pulse at the synchronization input. The Level field allows you to set the level above which the sweep starts.
Auto, А, В, Ext buttons set the synchronization modes
-Auto - automatic start of the sweep when the circuit is turned on. When the beam reaches the end of the screen, the waveform is recorded from the beginning of the screen,
-A - the triggering signal is the signal arriving at the input A,
-B - the triggering signal is the signal arriving at the input B,
-Ext - External launch. In this case, the trigger signal is the signal applied to the sync input.
Pressing the EXPAND button on a simple scope model opens the expanded scope model. In contrast to the simple model, there are three information boards on which the measurement results are displayed. In addition, a scroll bar is located directly under the screen, allowing you to observe any time interval from the moment of switching on to the moment of switching off the circuit.

On the oscilloscope screen there are two cursors (red and blue), designated 1 and 2, with which you can measure instantaneous voltage values at any point in the oscillogram. To do this, the cursors are dragged with the mouse to the required position (with the mouse, they grab the triangles at the top of the cursor).
The coordinates of the points of intersection of the first cursor with the oscillograms are displayed on the left panel, the coordinates of the second cursor on the middle panel. The right panel displays the values of the differences between the corresponding coordinates of the first and second cursors.
The Reduce button takes you to a simple oscilloscope model.
3. Plotter (Bode plotter)
Used to build amplitude-frequency (AFC) and phase-frequency<ФЧХ) характеристик схемы.
The plotter measures the ratio of signal amplitudes at two points in the circuit and the phase shift between them. For measurements, the plotter generates its own frequency spectrum, the range of which can be set during instrument setup. The frequency of any AC source in the circuit under study is ignored, but the circuit must include some AC source.
The plotter has four terminals: two input (IN) and two output (OUT). The left pins of the IN and OUT inputs are connected to the test points, and the right pins of the IN and OUT inputs are grounded.
When you double-click on the plotter image, its enlarged image will open.

The MAGNITUDE button is pressed to obtain the frequency response, the PHASE button - to obtain the phase response.
The VERTICAL panel sets:
-initial (I) value of the parameter of the vertical axis,
-final (F) value of the parameter of the vertical axis
- type of vertical axis scale - logarithmic (LOG) or linear (LIN).
The HORIZONTAL panel is configured in the same way.
When receiving the frequency response along the vertical axis, the voltage ratio is plotted:
-in a linear scale from 0 to 10E9;
-in a logarithmic scale from - 200 dB to 200 dB.
When the phase response is obtained, the degrees from -720 degrees to +720 degrees are plotted along the vertical axis.
The horizontal axis is always the frequency in Hz or in derived units.
The cursor is located at the beginning of the horizontal scale. The coordinates of the point of movement of the cursor with the graph are displayed on the information fields at the bottom right.

Modeling circuits
The investigated circuit is assembled on the working field using a mouse and keyboard.
When building and editing circuits, the following operations are performed:
-selection of a component from a library of components;
-allocation of an object;
-movement of the object;
-copying objects;
-deleting objects;
-connection of circuit components by conductors;
-setting component values;
-connection of measuring devices.
After building the circuit and connecting the devices, the analysis of the circuit's operation begins after pressing the switch in the upper right corner of the program window (while the moments of circuit time are shown in the lower left corner of the screen).
Pressing the switch again will terminate the circuit.
You can pause the circuit by pressing the F9 key on the keyboard; pressing F9 again restarts the circuit (a similar result can be achieved by pressing the Pause button located under the switch.)
The choice of the component necessary for the construction of the circuit is made after the selection of the component field containing the required element. This element is grabbed by the mouse and moved to the working area.
Selection of an object. When selecting a component, left-click on it. In this case, the component turns red. (You can remove the selection by clicking anywhere in the working area.)
Moving an object. To move an object, select it, set the mouse pointer over the object and, keeping the left mouse button pressed, drag the object.
The object can be rotated. To do this, the object must first be selected, then right-click and select the required operation
-Rotate (rotate 90 degrees),
-Flip vertical (vertical flip),
-Flip horizontal
Objects are copied using the Soru command from the Edit menu. The object must be selected before copying. When the command is executed, the selected object is copied to the clipboard. To paste the contents of the buffer into the working field, select the Paste command from the Edit menu
Removing objects. Selected objects can be deleted with the Delete command.
Connecting circuit components with conductors. To connect the components with wires, you need to move the mouse pointer over the component pin (a black dot will appear on the pin). While holding down the left mouse button, move the mouse pointer to the component pin you want to connect to, and release the mouse button. The component leads are connected with a conductor.
The color of the conductor can be changed by double-clicking on the conductor with the mouse and selecting the desired color from the window that appears.
Removing a conductor. If for any reason a conductor needs to be deleted, you must move the mouse pointer to the component output (a black dot should appear). Pressing the left mouse button, move it to an empty place in the working area and release the mouse button. The explorer will disappear.
Parameter values are set in the component properties dialog box, which is opened by double-clicking on the component's image (Value tab).
Each component can be named (Label Tab)
Connecting devices. To connect the device to the circuit, you need to drag the device from the toolbar to the working field with the mouse and connect the device leads to the points under study. Some devices need to be grounded or their readings will be incorrect.
An expanded view of the device appears when you double-click on the thumbnail image.
Exercise: Assemble the voltage divider circuit shown in the figure.
- Apply a sinusoidal voltage with a frequency of 3 kHz and an amplitude of 5 V to the input of the circuit from the function generator,
-Connect the same signal to channel A of the oscilloscope,
-Connect channel B of the oscilloscope to the divider output,
- highlight the conductors of channel A and channel B with different colors,
-Turn on the circuit, if necessary change the settings of the measuring instruments,
-Go to the advanced oscilloscope model. Using the cursor and the left bulletin board, measure the amplitude value of the output signal.
-Additionally connect voltmeters to the input and output and turn on the circuit again.
Get the correct voltmeter readings.

Word generator
A reduced image of the word generator is displayed on the diagram
![]()
Bits of the generated word are fed in parallel to 16 outputs at the bottom of the generator.
The clock output (bottom right) is supplied with a sequence of clock pulses with a specified frequency.
The sync input is used to provide a sync pulse from an external source.
Double click to open the extended generator image

The left side of the generator contains 16-bit words, specified in hexadecimal code. Each code combination is entered using the keyboard. The number of the edited cell (from 0 to 03FF, i.e. from 0 to 2047) is highlighted in the Edit window. In the process of generator operation, the Address section displays the address of the current cell (Current), the initial cell (Initial) and the final cell (Final). Code combinations issued to 16 outputs (at the bottom of the generator) are indicated in ASCII code and binary code (Binary).
The generator can operate in stepping, cyclic and continuous modes.
-The Step button switches the generator to step-by-step mode;
- Burst button - in cyclic mode (all words are sent to the generator output once sequentially;
-Button Cycle - in continuous mode. To interrupt continuous operation, press the Cycle button again.
The Trigger panel determines the moment of the generator start (Internal - internal synchronization, External - external synchronization when data is ready.)
External synchronization mode is used when the DUT can acknowledge (acknowledge) the receipt of data. In this case, a signal from the Data ready terminal is sent to the device along with the code combination, and the DUT must issue a data acquisition signal, which must be connected to the Trigger terminal of the word generator. This signal also makes the next start of the generator.
The Breakpoint button interrupts the generator in the specified cell. To do this, select the desired cell with the cursor, and then press the Breakpoint button
The Pattern button opens a menu with which you can
Clear buffer - erase the contents of all cells,
Open - load code combinations from a file with the .dp extension.
Save - save all combinations typed on the screen to a file;
Up counter - fill the screen buffer with code combinations, starting from 0 in the zero cell and then adding one in each subsequent cell;
Down counter - fill the screen buffer with code combinations, starting with FFFF in the zero cell and then decreasing by 1 in each subsequent cell;
Shift right - fill every four cells with combinations of 8000-4000-2000-1000 with their shift in the next four cells to the right;
Shift left is the same, but shifted to the left.
Logic analyzer
A reduced image of the logic analyzer is displayed on the circuit
The logic analyzer is connected to the circuit using the pins on the left side. Signals can be observed simultaneously at 16 points in the circuit. The analyzer is equipped with two cross-hairs, which allows to obtain readings of time intervals T1, T2, T2-T1, as well as a horizontal scroll bar

The Clock block has terminals for connecting a conventional External and Selective Qualifier trigger sources, the parameters of which can be set using the menu invoked by the Set button.
Triggering can be done on the rising edge (Positive) or the falling (Negative) edge of the trigger signal using an External or Internal source. In the Clock qualifier window, you can set the value of the logical signal (0.1 or x) at which the analyzer starts.
External synchronization can be performed by a combination of logic levels applied to the analyzer channel inputs.
MySQL Workbench is a software product created for database design. A catalog of tools for operating and modeling the database is available. The tool is characterized by high performance.
The use of the software is recommended for a complex transition. Saved processes, foreign keys are displayed in the tables. An integrated shell is supported to enable scripting. First of all, the program is a design tool for a clear graphical presentation. In the presence of an editor that allows you to correct requests with subsequent sending through the server. The accepted responses are presented in the form of tables. When the view is rendered, the user can still make edits.
Free download the full Russian version of MySQL Workbench from the official website without registration and SMS.
System requirements
- Supported OS: Windows 10, Vista, 8.1, XP, 7, 8
- Bit depth: 64 bit, 32 bit, x86
A web developer grows with the projects he creates and develops. With the growth of projects, the complexity of the software part increases, the amount of data processed by it inevitably increases, as well as data schema complexity... Communication with other web providers shows that MySQL databases are very popular among us, and for managing them - the well-known PHPMyAdmin... Moving from small projects to large ones, from cms to frameworks, many, like me, remain faithful to MySQL. However, for the design of a complex database with a large number of tables and relationships, PHPMyAdmin's capabilities are sorely lacking. So I decided to write a review MySQL Workbench is a wonderful free desktop program for working with MySQL.
In the first part of the review, I will talk about the very basics of working with the program, so you can use this article as beginner's guide. The second part will be devoted to using the Workbench in battle when working with a remote server. In it I will give the basic instructions and recommendations for configuring server connection and synchronization with it.
MySQL Workbench- a tool for visual database design that integrates the design, modeling, creation and operation of databases into a single seamless environment for the MySQL database system.
I must say that the program is really great. It allows you to quickly and happily throw project data schemas, design entities and relationships between them, painlessly implement changes into the scheme and just as quickly and painlessly synchronize it with a remote server. A graphic editor EER diagrams, resembling funny cockroaches, allows you to see the general picture of the data model and enjoy its lightness and elegance :) After the first try, this tool becomes an indispensable assistant in the battle arsenal of a web programmer.
Download MySQL Workbench
The MySQL Workbench distribution is available on this page. The most recent version of the program at the time of this writing is Version 6.1... Before downloading, you need to select one of the following platforms:
- Microsoft Windows (MSI Installer and ZIP archive available)
- Ubuntu Linux
- Fedora
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux / Oracle Linux
- Mac OS X
After choosing a platform, you are prompted to register or log in to Oracle. If you don't want to, there is a link at the bottom. "No thanks, just start my download"- click on it;)
Beginning of work
The start screen of the program reflects the main directions of its functionality - the design of database models and their administration:

At the top of the screen there is a list of connections to MySQL servers of your projects, and a list of recently opened data models is at the bottom of the screen. Work usually starts with create data schema or loading existing structure into MySQL Workbench... Let's get to work!
Creating and editing a data model
To add a model, click the plus sign next to the heading "Models" or select "File → New Model" (Ctrl + N):

On this screen, enter the name of the database, select the default encoding and, if necessary, fill in the comment field. You can start creating tables.
Adding and editing a table
The list of project databases and the list of tables within the database will be located in the tab "Physical Schemas". To create a table, double click on "+ Add Table":

A convenient interface will open for editing the list of fields and their properties. Here we can set the field name, data type, as well as set various attributes for the fields: assign a field primary key (PK), mark it Not Null (NN), binary (BIN), unique (UQ) and others, set for the field auto-increment (AI) and default value.
Index management
You can add, delete and edit table indexes in the tab "Indexes" table management interface:

Enter the name of the index, select its type, then check the boxes in the required order to mark the list of fields participating in this index. The order of the fields will correspond to the order in which the checkboxes were ticked. In this example, I have added a unique index to the field username.
Relationships between tables
Setting foreign keys and linking tables is only possible for tables InnoDB(This storage system is selected by default). To manage relationships, each table has a tab "Foreign Keys":

To add a connection, open the tab "Foreign Keys" child table, enter the name of the foreign key and select parent table... Further in the middle of the tab in the graph Column select the key field from the child table, and in the column Referenced Column- the corresponding field from the parent table (the type of fields must match). When creating foreign keys corresponding indexes are automatically created in the child table.
In chapter "Foreign Key Options" customize the behavior of the foreign key when changing the corresponding field (ON UPDATE) and removing (ON DELETE) parent record:
- RESTRICT- throw an error when changing / deleting a parent record
- CASCADE- update foreign key when parent record changes, delete child record when parent is deleted
- SET NULL- set foreign key value NULL when changing / deleting a parent (unacceptable for fields that have the flag set NOT NULL!)
- NO ACTION- do nothing, but in fact the effect is similar to RESTRICT
In the above example, I added to the child table UserProfile foreign key to link to parent table User... When editing a field userId and deleting items from the table User similar changes will automatically happen to related records from the table UserProfile.
When creating a project, you often need to add start data to the database. These can be root categories, admin users, etc. There is a tab for this in the MySQL Workbench table management "Inserts":

As you can see from the example, if you need to apply some MySQL function to the data before writing to the database, this is done using the syntax \ func functionName ("data"), for example, \ func md5 ("password").
Creating an EER diagram (entity-relationship diagram)
An EER diagram editor is available in MySQL Workbench to represent data schemas, entities and their relationships in graphical form. To create a diagram at the top of the database management screen, double-click on the icon "+ Add Diagram":

In its interface, you can create and edit tables, add links of various types between them. To add an existing table in the diagram to the diagram, simply drag it from the panel "Catalog Tree".

To export the data schema to a graphic file, select "File → Export" and then one of the options (PNG, SVG, PDF, PostScript File).
Import existing data schema (from SQL dump)
If we already have a data schema, it can be easily imported into MySQL Workbench for further work. To import a model from a SQL file, select "File → Import → Reverse Engineer MySQL Create Script ...", after which we select the required SQL file and press "Execute>"

MySQL Workbench also provides for the import and synchronization of the data model with a remote server. To do this, you need to create connecting remote access to MySQL, which I will talk about in the continuation of this review.
A demo project from the article is available for download at this link. I wish you success and beautiful cockroach schemes!
How do I create a MySQL database structure? How do I create MySQL tables? MySQL Workbench database creation software!
How to create a MySQL database structure using MySQL Workbench
Want to create your own database, but are you tired of creating tables and relationships between them using SQL? Use the free software MySQL Workbench, which was created to visually create databases.
MySQL Workbench allows you to model a MySQL database using a visual representation of tables. This eliminates the need to painstakingly describe the structure of the database, in SQL, MySQL Workbench will generate the code for you! You can download the program for free on the website: http://www.mysql.com/downloads/workbench, you can download both the installation version and the one that only requires unpacking (available systems include: Windows, Ubuntu Linux, Fedora, Mac OS X).
How to use the program to create a MySQL database?
Open MySQL Workbench, select File -> New Model, or press CTRL + N. The database modeling area is displayed in the image below:
The first thing you need to do is create a table with attributes - so click on the Add Table button.

Fill in the appropriate fields: table name, attributes (remember that one of them must be the master key - indicated by the checkbox, PK "primary key".).

When you create tables, you have to think about how they will relate to each other.
If you have filled in all the tables, click on the "Add Diagram" button to define the relationships between the subjects.

You will see a window similar to the one below, showing the created table in the Chart Workspace.

My database structure will not be correct, as here I am only showing how to model the database structure. Therefore, you can expand tables in the work area.

Now combine the table in order to form a relationship.
Suppose they look like this:
Book, can belong to one reader
The reader may borrow several books
Typically, three options are used to create a log (1: 1, 1 for many, and many to many):
Thus, we create connections as shown in the figure:

If you double click on the relationship, you can set more options.

When you are done creating the structure, you can create the SQL database simply by importing it. To do this, select the File menu -> Export -> and select the desired option, the data is mainly tables, and users (if any). The file I created is shown below.