Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http:// www. allbest. ru//
Posted on http:// www. allbest. ru//
INTRODUCTION
For many years, information technology has been inextricably linked with business. This is due to the fact that information technology provides opportunities to improve business efficiency. In order to remain competitive, companies need to not only keep up with trends and new technologies, but also apply them. These technologies include cloud computing, which is increasingly gaining popularity in the business world.
Cloud computing is a model for providing ubiquitous and convenient network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be quickly provisioned and released with minimal operating costs or ISP calls. The essence of cloud technology is to provide customers with remote access to services, computing resources and applications over the Internet.
The relevance of this topic is due to the fact that the use of cloud technologies makes it possible to effectively solve business problems. The adoption of cloud technologies is leading to significant changes in the organization, including:
Reduced IT investment
Reduced IT service resources
Productivity increase
Business agility
Disaster recovery
Increased capacity and increased availability
Despite the effectiveness of these technologies, many companies do not use them, preferring other ways to deploy their IT infrastructure. Thus, such companies begin to yield to their competitors, because business efficiency largely depends on the information technology used. Thus, today the question of the use of cloud technologies in business is relevant, since companies need to know and apply the most effective technologies to improve their business processes that affect the profitability of the organization.
The purpose of this work is to identify how effective the use of cloud technologies in business is. To achieve this goal, I need to complete the following tasks:
1. Define cloud technologies, describe their main characteristics, identify the advantages and disadvantages of using cloud technologies in business
2. Determine the opportunities that cloud technologies provide to companies
3. Explore the functions and capabilities of the cloud solution Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud from Kaspersky Lab
4. Evaluate the effectiveness of the application of the investigated cloud solution in small and medium-sized businesses
This work consists of the main and practical parts. The main part contains 3 chapters, which define cloud technologies, describe the deployment and service models of cloud technologies, identify the advantages and disadvantages of using cloud technologies in business. In the practical part of my work, I study the cloud solution Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud and assess the effectiveness of its use in small and medium-sized businesses.
cloud business kaspersky
1. CONCEPT OF CLOUD TECHNOLOGIES
1.1 Definition
Today cloud computing is one of the most popular areas of information technology development. Modern conditions of the information world require the solution of many tasks that can be effectively performed using cloud technologies. Many large global IT companies are using cloud computing, which is a confirmation of the effectiveness of these technologies.
Cloud technologies represent a universal environment for storing and processing information, which combines hardware, licensed software, communication channels, and technical support for users. Cloud technologies also mean the ability to obtain the necessary computing power on demand from the Web. Today, large data centers allow not only storing and processing data in their centers, but also making it possible to create their own virtual data centers. This allows companies not to waste resources building their infrastructure from scratch.
The main feature of cloud technologies is scalability: these technologies do not have a rigid attachment to the hardware platform, there is no attachment to the geographic territory. The use of cloud technologies in companies is aimed at reducing costs and increasing the efficiency of business processes.
Cloud technologies are data processing technologies in which computer resources are provided to the Internet user as an online service. Thanks to this, the user works with cloud services from anywhere and from any device: the main thing is to have access to the Internet. Access to the "cloud" can be obtained not only through the Internet, but also through a local network. In this case, the user's computer is a terminal connected to the Network. Those computers that do cloud computing are "cloud computing". The load between such computers is distributed automatically.
The cloud has three main components:
Cloud computing. Cloud computing refers to the architecture of computer data processing. The cloud architecture enables self-service, scalability, and agile processes. Such an architectural solution replaces fixed costs with variable costs and provides ample opportunities for data analysis.
Cloud platforms. Cloud platforms include tools, software and information models, system software, and other technologies that perform assigned tasks.
Cloud services. Cloud services are models for delivering information services.
The development of cloud technology has a huge impact on business. In order to have an advantage over competitors, companies need to take into account current trends in information technology. Companies using cloud technologies in their business processes reap a number of benefits. Cloud computing is a business process management approach that reduces the complexity of information systems. This is achieved through self-managed cloud computing available on demand within a virtual infrastructure.
Thus, companies have the following advantages from using cloud computing: reduced IT costs, improved service delivery, business agility. The reduction in IT costs is due to the fact that cloud technologies reduce operational and capital costs: thanks to the "cloud", company IT specialists can focus on strategic projects without spending time managing their own data center.
Cloud technology works like this: instead of acquiring, installing and managing their own servers to run applications, companies rent servers (for example, from Microsoft or Google). The user controls these servers over the Internet. The payment includes only the actual use of servers for processing and storing data.
Computing clouds are made up of a huge number of servers that are located in data centers. Data centers provide tens of thousands of applications that are simultaneously used by millions of users simultaneously. Full automation is a prerequisite for efficiently managing an infrastructure of this scale.
Thus, the use of cloud technologies is becoming a trend, and companies need to know about them and apply them effectively to improve business processes.
1.2 Characteristics of cloud technologies
In order for information resources to be cloud-based, they must have the following key properties: high availability and scalability, and be cost-effective for the client. In order to distinguish cloud technologies from other earlier approaches to the provision of hardware and software resources, the following main characteristics of cloud computing are distinguished:
1. Wide network availability
2. Easy scalability, elasticity
3. Ability to monitor
4. Consumption metering
5. Self-service on demand
6. Pooling resources
Wide network availability means that the user has access to software products, resources and services over the network, no matter what device is used. The user can use a personal computer, laptop, tablet, mobile phone or any other terminal device - the main thing is to have access to the network.
Easy scalability consists in connecting (or disconnecting) additional hardware or software devices. This happens without additional delay with the supplier, in automatic mode.
"Clouds" are equipped with a monitoring system that allows you to monitor the stability of work and assess availability.
The following characteristic is especially important for business, because directly affects the monetary resources spent on IT. It is economically advantageous that when using cloud technologies there is consumption accounting. The client does not spend money on resources that are not being used. The resources consumed are recorded (for example, the number of users and transactions, the amount of data storage used), and based on this accounting, the supplier estimates the services provided to the client in monetary terms.
Self-service on demand gives the customer the ability to manage their computing needs. These needs include server time, speed of data access and processing, and the amount of stored data. The customer can exercise such control without direct contact with the service provider.
Finally, resource pooling means that a provider combines resources to serve a large number of consumers into a single pool in order to dynamically distribute capacity among consumers when the demand for capacity is constantly changing. Thus, customers monitor only the basic parameters (data volume, access speed, etc.), while the actual allocation of resources is monitored by the service provider.
2. MODELS OF DEPLOYMENT AND MAINTENANCE OF CLOUD TECHNOLOGIES
2.1 Cloud deployment models
Typically, the following cloud deployment models are distinguished: private, public, and hybrid cloud.
The main models are public cloud and private cloud. The public cloud provides cloud services and resources to a large number of customers using public data centers. The private cloud, on the other hand, provides the organization's own infrastructure. Speaking of the public cloud, it is worth noting that it allows you to translate all relevant costs into operating costs and provides a quick and budgetary launch of an IT solution. With a private cloud, capital investment is maintained while still maintaining complete control of the IT infrastructure.
If we talk in more detail about the private cloud, then it should be noted that a private cloud is an infrastructure that is located within the same organization. The private cloud is designed to meet the needs of internal workforce while providing a high level of data security.
Today, business makes more and more demands on IT technologies. A private cloud allows you to solve problems such as providing a large number of business services and optimizing costs. By deploying a private cloud, the company mitigates information security risks and ensures that IT resources are highly available despite the potential for heavy server utilization.
Speaking of the advantages of a private cloud, the following can be noted:
1. Compared to the public cloud, the company has more opportunities to control the IT infrastructure, because all its components remain on the side of the company.
2. High level of security. This is ensured by the fact that the service is consumed by one organization, so the infrastructure can be optimally tuned to the data protection requirements of this organization.
3. High productivity. It is connected, in particular, with the fact that all operations take place within the framework of internal firewalls and protection of the corporate network perimeter. Thanks to this, data transfer is fast.
4. The implementation of a private cloud increases the agility of the IT department - at any time, he can quickly deploy the desired service. IT professionals only need to "lift" the virtual machine from the template and install the necessary service.
Despite the advantages, private clouds have a number of disadvantages:
1. Significant costs at all stages of the cloud life cycle. The deployment phase requires investment in hardware and software.
In addition, the private cloud needs to be managed, which entails administration and staff costs.
2. Compared to the public cloud, the risks of service or data loss due to physical threats are much more significant.
3. The company may run out of space in the cloud when infrastructure resources may not be enough.
Analyzing the above, we can conclude that the most significant drawback of a private cloud is the need to spend a significant amount of human and material resources for its creation and further operation. This significantly affects the financial condition of the organization.
Moving on to the public cloud, it is worth saying that a public cloud is an infrastructure designed for free use by multiple organizations. This cloud model can be owned by multiple companies. Despite this, the word "public" does not mean that user data is available to absolutely everyone. The public cloud implements security mechanisms to control access. Ease of configuration and low cost are the main benefits of a public cloud deployment. The provider does all the work associated with creating the cloud, and the client only configures the required amount of resources.
In the case of using a public cloud, the consumer uses the infrastructure of a third-party provider, which creates many opportunities for efficient use and reallocation of resources. Public cloud services are simple and efficient to use, as clients need nothing more than a stable Internet connection to access applications.
Speaking about the merits of a public cloud, it is worth noting the following:
1. Simplicity and efficiency of use.
2. Only a stable internet connection is required to access the applications.
3. Using a public cloud makes it possible to reduce IT costs due to the absence of costs for hardware and software.
4. Flexibility and scalability: the public cloud allows you to pay for exactly as many resources as is required at the moment, and adjust this parameter up or down.
5. Reducing the time spent on infrastructure maintenance.
6. The risk of downtime of business processes due to server accidents is eliminated, since the application servers are in the cloud. Virtual servers of providers are most often configured on a powerful physical base and located in large data centers, where the possible downtime is calculated in minutes per year.
7. The use of public clouds and the lack of contact of users with sophisticated computer equipment makes it possible to refuse the services of additional IT specialists.
However, the public cloud model has some disadvantages:
1. The main disadvantage of a public cloud is the lack of opportunities for control by the organization, since the operability of services is completely subordinate to the service provider.
2. Slow speed: the performance of public cloud services directly depends on the stability of the Internet connection, therefore, in some cases, data transfer may be slow. When operating with large amounts of data, public clouds are inferior to private ones in terms of performance.
3. Weak data security is a common feature of public cloud environments. Private cloud protection is an order of magnitude more reliable.
In addition to private and public clouds, there is a hybrid cloud.
Hybrid cloud is a cloud infrastructure deployment model that provides a combination of private and public clouds and combines the benefits of each separately. The combination of these two models allows a company that already has a private cloud to leverage the resources of a public cloud. Thus, the organization has the opportunity, if necessary, to expand its own infrastructure using the computing resources of the public cloud.
Hence, when choosing a hybrid cloud, a company gains the control and security of a private cloud with the scale and benefits of a public cloud.
Features of the hybrid cloud:
1. Expanding the capabilities of the private cloud. Hybrid cloud allows network users to access the applications they need in the private cloud through the public cloud, while the security of the private cloud remains the same.
2. Redistribution of the load. A hybrid cloud allows you to transfer part of the load from a private cloud to a public cloud, if necessary, which provides a high level of performance.
3. Data safety. To increase the level of data security, the hybrid cloud allows, if necessary, to store in encrypted form in the public cloud "backups" from the private cloud.
4. Mobility. Thanks to the ability to organize access to certain applications from the private cloud through the public cloud, it is possible to work with these applications from anywhere in the world with an Internet connection.
2.2 Cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
The cloud computing concept is characterized by service models (layers) that perform specific functions. The cloud provides the following service levels:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Figure 1. Cloud Service Models
Infrastructure as a Service, IaaS is the provision of computing infrastructure as a service based on the concept of cloud computing ?. This service model consists of physical assets - network devices, servers, disks, etc. When interacting with IaaS, the user does not control the underlying infrastructure. It manages data storage, operating system, deployed applications, and networking components.
IaaS removes the need for a company to maintain complex IT infrastructures, data centers, customer and network infrastructures. This helps to reduce the associated capital costs and operating costs.
Platform as a Service, PaaS is an Integrated Delivery? platforms for developing, testing, deploying and maintaining a web application? as a service.
PaaS is a service model where the customer is given the opportunity to use the cloud infrastructure to host the underlying software and then host applications on it. Such a platform includes tools for creating and testing application software. These tools are provided by a cloud provider.
PaaS, as an integrated platform for developing, testing, deploying and maintaining a web application ?, allows the entire list of operations? for developing, testing and deploying a web application? run in one integrated environment. This approach eliminates the expense of maintaining separate environments for each stage of application development.
Does the ability to create source code and share it within the development team significantly improve the productivity of building an application? based on PaaS.
Service as a service, SaaS is an application deployment model that implies the provision of an application to the end user as a service on demand. The SaaS concept makes it possible to use software as a service and do it remotely over the Internet. This allows the client not to buy a software product, but only to temporarily use it when the need arises. In this case, the main advantage of the SaaS model for the customer is that there are no costs associated with installing, updating and maintaining the health of the hardware and software running on it.
The SaaS model is characterized by the following:
the app can be used remotely
payment for the application is charged either as a monthly subscription fee or based on the total volume of transactions
no additional payment is required for application support
regular automatic updates
the application can be used simultaneously by several clients
target audience of SaaS - end consumers.
For a more accurate description of the three service models, Table 1 describes their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages and risks.
Table 1. Service models. Characteristics, advantages, disadvantages and risks
|
Service models |
Specifications |
Advantages |
Disadvantages and risks |
|
|
1. Generally platform independent; 2. Reducing infrastructure costs; 3. Payment upon use; 4. Automatic scaling. |
3. Low threshold of implementation; 4. Smooth scaling. |
1. Efficiency and productivity depend on the service provider; 2. Potentially large long-term costs; 3. Centralization requires new methods of protection and security. |
||
|
1. Uses cloud infrastructure; 2. Provides methods for dynamic project management. |
Smooth deployment of versions. |
Centralization requires new methods of protection and security that ensure that malware cannot exploit vulnerabilities in the software platform. |
||
|
1. User interface; 2. Interaction via API (Application Programming Interface); 3. Semantic compatibility. |
1. Reduced hardware and labor costs; 2. Reducing the risk of losing investments; 3. Regular updates. |
Centralization requires new methods of protection and security that relate to the confidentiality of customer data. |
3. APPLICATION OF CLOUD TECHNOLOGIES IN BUSINESS
3.1 Choosing IT infrastructure for small and medium businesses
The company can choose between the following IT infrastructures:
Self-supported internal IT infrastructure
Managed Services: IT infrastructure functions are transferred to services that are managed by third parties
Cloud IT infrastructure
In the case when the equipment is owned by the company, the company has an IT infrastructure with internal management. When comparing internal and cloud infrastructure, it is worth noting that cloud infrastructure has a significant advantage in terms of financial indicators: when using cloud IT infrastructure, there is no need for capital investments that are necessary to use it.
When using the internal IT infrastructure, the company purchases expensive equipment and pays for the services of the people who maintain this equipment. When one of the servers goes down, the company needs to bear the financial costs of repairing and replacing the hardware.
When outsourcing IT infrastructure functions, the following happens: the organization pays the third party that owns the servers. The company pays for equipment rental and maintenance.
In the event that one of the servers fails, a third party company that provides this service takes care of its repair and replacement. Also, this company takes care that the necessary operating systems are installed on the servers, and manages the network infrastructure in which the servers work.
A comparative analysis of IT infrastructures data can be carried out by considering the following aspects taken into account when choosing an IT infrastructure:
investment
current operating costs
commissioning time
flexibility
personnel qualification requirements
reliability
Investment. The choice of an internal IT infrastructure implies a high capital investment, since the company itself purchases expensive equipment. In the case of managed services, the company has a more modest capital investment: the company needs to pay an initial fee to use third-party equipment. Cloud-based IT infrastructure is a low capital investment: organizations generally do not incur any upfront costs or mandatory fees.
Current operating costs. Ongoing operating costs for back-end infrastructure consist of the cost of wages for the personnel who maintain and operate the equipment and the cost of space provided by the hosting provider, as well as the cost of real estate, energy and utilities.
In the case of managed services, ongoing operating costs vary depending on the terms of the contract. Often, services for using a third-party service can be expensive, but in this case, the company usually knows how much it will have to spend each month. This amount usually does not change. Considering cloud IT infrastructure, it is worth noting that it can be expensive or cheap: it depends on the needs of the company itself. cloud infrastructure implies that the company pays only for the resources and capacities consumed.
Time to put into use. The internal IT infrastructure is characterized by a long time to put a new component into use. This is due to the fact that when using an internal infrastructure, a company wishing to add a new component to its infrastructure must plan this work in advance, place an order for a new component, wait for its delivery and implement it in its data center. When a company uses the services of a third-party service provider, the time it takes to bring a new component to use is generally shorter. such third-party companies are pre-purchased equipment. In the case of a cloud infrastructure, a company can “roll out” a new server in a matter of minutes if the organization decides it needs one.
Flexibility. Internal IT infrastructure is poorly flexible because this kind of infrastructure has severe limitations. It is common for resource demands to increase and there is not enough disk space. The company can eliminate these needs only at the expense of new financial costs. Third party service providers have moderate flexibility. They can offer the company a temporary increase in disk space and resources. Cloud infrastructure is highly flexible. This is that such an infrastructure provides the company with resources as needed. A company may not use resources when it does not need them.
Requirements for the qualifications of personnel. Internal IT infrastructure requires highly qualified personnel. In this case, employees perform the following functions: understand the company's IT infrastructure, maintain and replace equipment, monitor the current state of operating systems, install operating system and software updates. In the case when the company uses the services of a third-party service provider, the requirements for staff qualifications are minimal. All issues related to the IT infrastructure are decided by a third-party company, which is paid for this. When using cloud infrastructure, staffing requirements vary and depend on how and what exactly the company uses.
Reliability. In the case of an internal IT infrastructure, reliability depends on a number of circumstances. Whether the information environment is highly resilient depends primarily on the qualifications of the company's employees and on investment in IT infrastructure. Third party service providers provide high reliability. When comparing third-party service providers with cloud infrastructure, it is worth noting that the latter lacks stability and service level. Thus, the reliability of the cloud infrastructure can be either moderate or high: it largely depends on the service provider.
Based on the above, we can conclude that for small and medium-sized companies, having their own IT infrastructure is not advisable, because this type of infrastructure requires large investments and equipment maintenance costs. The choice of such an infrastructure is justified only if the company cannot store its data on the side from the point of view of confidentiality and security.
Thus, today it is profitable for companies to use the services of service providers or switch to the use of cloud infrastructure.
3.2 Benefits of using cloud technologies in business
Cloud computing has a number of benefits. Next, I will consider each of them.
Availability. Cloud technologies make it possible to access products and services from any computer that has Internet access.
Client computers. When using cloud services, the company does not need to purchase equipment that has a large amount of memory and disks. The use of programs over the Internet does not require a large number of such computers in the company. Also, the company does not need a large number of data carriers, since all programs, services and documents are stored in the "cloud".
Reducing damage from data loss or hardware theft. When data is stored in the cloud, copies of that data are spread across multiple servers, which may be located in different countries. Thus, in the event of theft or equipment failure, the company does not lose valuable data.
Reliability. Data centers are managed by qualified specialists who provide ongoing support for the operation of equipment and services. This fact indicates a fairly high level of reliability and fault tolerance of the system.
Profitability. The company pays only for those services and services that it uses. Cloud technologies make it possible to pay only for the resources actually used.
Rent of resources. The need for computing resources is not constant: at some period of time the company needs additional computing resources, at some period of time they are not necessary, that is, the resources are simply not used. Cloud technologies enable companies to use only the necessary amount of computing resources, thereby reducing the cost of equipment and its maintenance.
Rent of software. Cloud technologies make it possible not to purchase software packages for each employee of the company. Instead, the company buys only the programs it needs in the cloud. Purchased programs are used only by those employees who need these programs for work. It should be noted that the cost of programs that are available over the Internet is lower than their local counterparts for PCs. In the event that the programs are not often used by users, then they can not be bought, but rented with an hourly rate. One of the main advantages of renting software from cloud providers is that the company does not need to spend money and time on updating programs and maintaining them in working order at every workplace.
Service. With the introduction of cloud technologies, physical servers are getting smaller, making it easier and faster to maintain them. Looking at the software, it's worth noting that it's installed and configured in the cloud. It is updated there as well. The company always makes sure that the latest version of the program is being used. In addition, there is no need to spend money on software updates.
Open interfaces. Clouds usually have standard APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for communicating with existing applications and for developing new ones.
Flexibility and scalability. This implies unlimited computing resources (memory, processors, disks, etc.). Cloud technologies are elastic and scalable because resources are allocated and released based on the need for them.
Performance computing. Compared to a conventional PC, the computing power available to cloud users is limited only by the number of remote servers. This means that employees can tackle more complex tasks that require a lot of memory and storage space. In other words, employees have the opportunity to work with a powerful computer without actually acquiring it by the company. Scalability manifests itself in the ability to run a large number of copies of an application on many virtual machines. The number of copies of the application can grow on demand, depending on the workload.
Data storage. Personal computers have a limited amount of memory. When using cloud technologies, the company has the amount of data storage that it needs at a particular moment. There is no risk of running out of memory because cloud technologies provide a huge amount of gigabytes of free space.
Technology for a young company. From a financial point of view, cloud technologies are a viable solution for a young company, because there is no need to purchase various expensive equipment and software, as well as to hire people who will support it.
3.3 Disadvantages of using cloud technologies in business
Despite the large number of advantages, cloud technologies have a number of disadvantages, including:
The need for a permanent connection to the network. Cloud computing almost always requires a constant internet connection. This can cause some inconvenience to the company and affect the continuity of business processes, because if there is no access to the network, then there are no programs or documents. In addition, cloud applications often require a stable and good Internet connection with high bandwidth, which leads to the fact that the programs may run slower than if they were located on-premises instead of in the cloud.
Data security. When choosing a cloud provider, it should be borne in mind that not all third-party providers can be trusted with their data. The company must be sure that the provider provides high-quality cloud services, has been operating in this service market for several years and has a good reputation. Otherwise, the company may be at risk of losing confidential data.
The state on the territory of which the data center is located can have access to any information that is stored in it. For example, in the United States (the country with the largest number of data centers at the moment), a provider company can disclose the fact of transferring confidential information only to its lawyers. This problem is key in the issue of storing confidential information in the cloud, which can be solved in several ways: encrypt information and not store the most valuable information with the provider. One way or another, companies using cloud technologies should consider this point.
The functionality of cloud programs. Not all programs or their properties are available remotely. Today, if we compare the functionality of local and cloud programs, the latter are inferior to the former (for example, Google Docs and Microsoft Excel: the latter has more functions and capabilities).
Cloud provider dependency. There is a risk that the provider may not back up the data and it may be lost. However, this risk is no higher than the risk of employees themselves losing valuable data by losing their device or failing to back up the data on their PC in time.
Thus, there are more advantages to using cloud technologies than disadvantages. Nevertheless, before deciding whether to use cloud computing in its IT infrastructure, a company must correctly build an IT security strategy, taking into account all the risks when using cloud technologies.
4. PRACTICAL PART
4.1 Problem statement
In the main part of the work, the definition of cloud technologies was given, their main characteristics were considered, and the deployment and service models were studied. In addition, the benefits and risks of using cloud technologies were identified. In the practical part of the work, it is necessary to study a specific cloud solution for a business and evaluate its effectiveness.
For the research, I chose the cloud solution Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud from Kaspersky Lab, which ensures the company's information security. The problem of effective information security always remains relevant, since the lack of due attention of the company to the protection of confidential data leads to an increase in the risk of information security incidents that can cause significant damage to the company.
The purpose of the practical part of the work is to determine the effectiveness of using cloud solutions offered for small and medium-sized businesses.
To achieve this goal, you must complete the following tasks:
Explore the capabilities of the cloud solution Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud
Reveal the benefits of this cloud solution
Evaluate the effectiveness of this cloud solution in small and medium-sized businesses
The practical part of the work contains a description of the investigated cloud solution, its capabilities and advantages, as well as an assessment of its effectiveness in small and medium-sized businesses.
4.2 Solving the problem
Today, the number of cyber threats is constantly growing. Corporate data protection, efficient use of time and high IT performance are vital to the success of any business, regardless of size or location. The requirements for information security are similar for companies of any size: protection of confidential data, business continuity, security of working devices. The result of a cyberattack on a poorly protected company can lead to serious consequences:
Loss of valuable data, including information constituting intellectual property
Leak of confidential information about clients and employees
Disruption of business processes, which directly affects the profitability of the business.
Not all companies can hire a qualified full-time IT administrator, let alone an IT security specialist. While large companies have the resources to effectively and efficiently protect their data, small and medium-sized companies often cannot afford to allocate sufficient funds to protect information. According to Kaspersky Lab, small and medium-sized businesses suffer losses from incidents related to information security, but despite this, such companies often do not take effective measures to counter cyber threats. This leads to the fact that it is small and medium-sized businesses that become the target of cybercriminals. lack of due regard to the protection of company data and information. Challenges inherent in small and medium-sized businesses typically include:
limited time for IT security
insufficient resources for the administration of complex solutions small (in comparison with large companies) IT budget
As a result, just such companies, which cannot allocate a large amount of resources for information security, need a software solution that does not require significant time and effort to deploy within the company, is easily managed and does not require additional expensive resources. Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud (hereinafter KES) is just such a product, the main advantage of which is the cloud-based management console. In this cloud solution, access to all the necessary management functions is in the cloud. For small and medium-sized businesses, it is important that Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud is an easy-to-manage product that does not require special technical knowledge. In particular, this is a big plus for small companies, which often cannot have several highly qualified IT specialists on their staff. Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud can be customized to the needs of the client using pre-installed scripts adapted to the standard needs of any company. This includes creating multiple user groups with different access rights, blocking access to entertainment sites, blocking the use of USB drives, associating corporate and mobile devices of users with their accounts, and much more. The choice of available scenarios can be expanded, allowing customers to use different functions depending on the number of employees, the number of offices and the business processes of the company.
4.3 Product Description
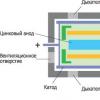
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud is a solution that meets the needs of small and medium-sized businesses by providing reliable protection for personal computers, mobile devices and file servers from the cloud-based management console. Choosing such a solution, the company does not need to purchase additional expensive equipment. Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud allows you to manage your information security system at any time, from any place and device connected to the Internet. This solution makes it possible to protect up to 250 workplaces.
The product is a cloud-based console for centralized management and client applications. To work with the cloud console of Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud, you need an Internet connection and a browser:
Internet Explorer 10.0 or later
Microsoft Edge 13.0 or later
Chrome 36.0 and later
Firefox 35 and later
Safari 8.0 and later.
During operation, Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud uses the following Kaspersky Lab applications:
Kaspersky Endpoint Security 10 for Windows.
Kaspersky Security 10 for Mobile.
The hardware and software requirements of your computer or mobile device match the requirements of the programs and browsers listed above.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud supports the following platforms:
Winsows computers
Windows file servers
Android and iOS mobile devices
Thus, KES is a software solution, the essence of which is the centralized management and protection of devices (PCs, mobile phones, tablets, etc.) of the company's employees.
Fig 2. Architecture of Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud
Key features of Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud include:
centralized installation and updating of Kaspersky Lab applications on PCs and mobile devices of company employees.
manage device settings and protect them using security profiles
managing user data, creating user groups, and assigning rights to users from the cloud.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud has a number of characteristic features:
1. The fastest possible deployment and easy management from the cloud console, flexible cloud administration. The cloud console of Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud is always ready for use. Centralized management is supported from the cloud console, which allows the administrator to manage the protection of the corporate network at any time from any device that has access to the Internet. This is convenient if the company does not have a system administrator who can regularly be present in the office. Thanks to remote protection, the company may not hire a second administrator if the company has several offices, which saves the organization's money. Due to the fact that the console is cloud-based, the company does not need to purchase and maintain additional equipment, which also makes it possible to save financial resources. Initial settings are quick, so it doesn't take much time and effort to deploy Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud.
Fig 3. Remote control of company devices
2. High level of protection for all types of devices. Multilevel protection of all devices used in the company is provided regardless of their territorial location. The main requirement is that the device can access the Internet.
Kaspersky Lab's proven technologies protect Windows-based workstations, laptops and file servers from a variety of threats, including ransomware and other ransomware. Device security is provided at many levels - protecting files from malware, protecting mail servers and Internet traffic. Protection is complemented by such effective laboratory technologies as Firewall, Network Attack Protection and System Monitor. By default, the solution is configured taking into account the recommendations of Kaspersky Lab specialists. The protection functions of Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud devices for Windows-based workstations and file servers, as well as for smartphones and tablets, are presented in Tables 2-3.
Table 2. Protection features for Windows-based workstations and file servers
|
Windows workstations and file servers |
|||
|
Malware protection |
|||
|
Firewall |
|||
|
Web protection |
|||
|
Mail antivirus |
|||
|
System monitoring |
|||
|
Blocking network attacks |
|||
|
Controls |
Web control |
||
|
Device control |
Table 3. Security features for mobile devices
|
Smartphones and tablets |
||||
|
Malware protection |
||||
|
Antiphishing / Safe Browser |
||||
|
Call and SMS filtering |
||||
|
Password settings |
||||
|
Setting up corporate mail |
||||
|
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth control |
||||
|
Built-in camera control |
||||
|
Anti-Theft (Remote Data Lock / Wipe) |
||||
|
IOS function control |
Not available |
3. Centralized management. All security features can be configured and deployed from a single console across all devices - Windows workstations, laptops, file servers and Androis / iOS mobile devices. With a simple and user-friendly interface, the IT security officer can quickly configure policies and apply them to all workplaces.
4. Preset security settings. There are preset settings based on the recommendations of Kaspersky Lab employees. These settings allow you to provide full protection immediately after implementation.
5. A profitable solution for small and medium-sized companies. This solution enables companies to save money by eliminating the need to purchase additional equipment. All company devices can be secured remotely, which eliminates the need to hire additional IT staff. As a result, it simplifies the protection of geographically distributed offices and branches of the company.
The main features of this cloud solution are the following:
1. Control of access to devices and the Internet. Device control tools make it possible to determine which devices are allowed access to the corporate network of the company. At the same time, Web Control allows you to set security policies for the Internet, as well as monitor the use of employees' web resources. The administrator can deny or restrict access to certain websites or categories of websites (for example, social networks).
2. Rapid deployment from the cloud. Since all security functions are managed from the cloud, there is no need to install the management console on a local server. The cloud console is always available on the website https://cloud.kaspersky.com/, which makes it possible to deploy the necessary software directly from the cloud to all company devices (computers, file servers, mobile devices).
3. Simple mobile device management. Mobile device management tools (MDM, master data management) include functions that allow you to determine the parameters for accessing smartphones and tablets to the corporate network, set Wi-Fi and Bluetooth settings, monitor camera use and adjust other parameters. There is no need to purchase a separate management solution to manage iOS devices, as the server for managing iOS devices is already deployed in the cloud.
4. Protection against mobile threats. Modern technologies for ensuring the security of mobile devices from Kaspersky Lab help protect mobile devices from various cyber threats, including ransomware. Anti-phishing tools (a set of technologies used to protect against online fraud and identity theft) protect against theft of confidential information or credentials on fake sites. Unauthorized flashing attempts are immediately detected, and access to the corporate network is blocked for such devices.
5. Protection of valuable data, including on lost devices. If an employee's mobile device is lost or stolen, the administrator can remotely lock the device from the cloud console or delete all corporate data from it, thereby avoiding the loss of important information.
The key functionality of the KES cloud console is presented in table # 4.
Table 4. Cloud Console Functionality
|
Functionality |
Actions available to the administrator |
|
|
User account management |
View user accounts Creating groups of accounts Changing account information Moving accounts between groups Removing accounts Removing groups of accounts |
|
|
User rights management |
Granting Administrator Rights to a User Revoking user administrator rights |
|
|
Device management |
View a list of devices and device properties Connecting Windows devices Connecting mobile devices Sending commands to mobile devices Assigning an owner for a Windows device Removing a device from the device list |
|
|
Security Profile Management |
Creating and configuring a security profile Assigning a security profile to a user account or group of user accounts Deleting a Security Profile |
|
|
File management in the Quarantine section |
Viewing files in the Quarantine section Restoring files in the Quarantine and Backup categories Removing files from the Quarantine section |
|
|
Configuring general settings for Kaspersky Endpoint Security Cloud |
Similar documents
History and development factors of cloud computing. The role of virtualization in the development of cloud technologies. Service models and principles of cloud services. Benefits of the cloud for Internet startups. Application of cloud computing technology in business.
abstract, added 03/18/2015
Implementation of "cloud" technologies in corporate information systems. Application of "cloud" technologies at RUE "Belorusneft". Pre-commissioning, installation and launch of the cloud service, initial configuration and scaling suggestions.
term paper, added 07/24/2014
The history of the emergence of cloud technologies. The essence and objectives of cloud technologies, their classification, advantages and disadvantages. A study of the application of cloud technologies using the example of Google Drive. Comparison of Google Drive with Apple's analogue (iCloud).
term paper, added 12/05/2016
Creation and levels of implementation of cloud computing. Advantages and disadvantages of using cloud technologies in organizing a single information space. Assessment of the importance of criteria by the method of "Pairwise comparison", "Heat maps", "Expert estimates".
thesis, added 04/08/2014
The evolution of cloud services. Characteristics and classification of cloud services. Analysis of the possibilities of cloud services offered for use in small businesses. Analysis of the cost of ownership of a local solution for the automation of accounting.
term paper added on 05/10/2015
Analyze cloud services for business automation and justify the benefits of moving to cloud computing. Types and models of cloud services for business, principles of their operation and characteristics. Business automation tasks on the example of cloud solutions.
thesis, added 09/06/2017
Analysis of the structure and content of the company's marketing plan. The cloud computing market and the possibility of their application. Selection of information sources and presentation of the results. Development of a software tool shell for cloud computing.
thesis, added 11/12/2013
The concept of cloud computing, their advantages and disadvantages; types of clouds. Comparative analysis of the risks of using cloud services in Russia and the EU. Regulators in the field of information security, their concepts, features and regulatory authorities.
term paper added on 05/14/2014
The history of the emergence of computer science. Apple products. Main categories, distinguishing features, levels of cloud services. Characteristics of public and private clouds. Advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing, prospects for their development.
test, added 08/06/2013
The concept of cloud technologies is a convenient environment for storing and processing information that combines hardware, licensed software, communication channels and technical support for users. Disadvantages and advantages of Dropbox.
The Internet has become entrenched in our lives. Many users can no longer imagine their life without a computer. Naturally, technologists are improving every year. And for active users of the global network, such a useful technology as a cloud server has appeared. What it is? What is it for?
Cloud technology is ...
Today it is very common to hear about such a function as cloud computing. The name of such servers comes from the graphic image that is used to denote technologies.
Cloud technology is the ability to access data without installing special applications on the device. Servers provide all the necessary support for users. But whether or not you have to pay for this remote access to data directly depends on the requests.
How are cloud technologies different from conventional ones?
To better explain the difference between conventional technology and cloud storage, consider email as an example. The case when an e-mail client, such as Outlook, is already installed on the user's computer, and all data received by e-mail is saved to the hard drive, is considered a common IT technology. That is, the user himself can dispose of the received files and decide what to do with them. And the mail client will work exactly as long as the computer is running.

But e-mail, which is opened using a browser, is already a cloud technology. That is, the user, without installing anything on the device, can access his email address. Moreover, if something happens to the server that stores all the data, then access to e-mail will be lost.
What do you have to pay for when using the cloud?
Cloud server is not completely free technology. There are times when a user will have to pay to provide a cloud storage service. All servers are divided into three types, which charge fees for different functions.
- IaaS is a cloud model that requires a fee to provide remote storage access. That is, the user only pays for access to the server.
- When using the PaaS cloud, you will have to pay not only for available resources, but also for access to special software for processing data.
- SaaS is a storage that provides access to a whole range of software, for which, of course, you will have to pay a considerable monthly fee.
Positive sides
The use of cloud technologies has a number of advantages, which are quite significant.

It is very beneficial for young businesses to use cloud servers. They will not have to worry about buying their own server equipment, spending money on building a local network, or hiring sysadmins. You just need to choose one of the cloud servers that is ideal in terms of memory size, number of clients and other characteristics, and pay a monthly subscription fee.
Cloud technology is the ability to access the necessary information using a regular browser from anywhere in the world. Operability will no longer concern the client, since it is monitored by those who are paid by the user for the cloud storage. Such systems are in demand among corporate users who need to establish document flow in the enterprise network.
For ordinary users who simply do not want to clog their computer with unnecessary information, there are free cloud servers, which will be quite enough.
Negative moments
Of course, new cloud technologies also have a number of disadvantages.
First, confidential data that is transmitted using cloud storage can be intercepted by hackers. The quality of the internet connection must be very high. If there is an interruption to the Internet, access to data on the "clouds" will be impossible. At the same time, large enterprises still need a system administrator to establish data transmission.

If the client wants to save money and gives preference to a cheaper server, then he will have to face performance problems. Low-cost cloud storage has a poor hardware infrastructure, which regularly breaks down and takes a long time to fix.
If the use of cloud technologies is planned for the long term, then this can be much more expensive than setting up your own local server. Especially if a cloud technology with a wide range of possibilities is chosen for work, such as SaaS.
Cloud storage overview
Cloud technologies are storage facilities that can be divided into three types of service:
- Creation of infrastructure.
- Platform services.
- Software services.
This unit will help with choosing a cloud storage server.
Windows Live SkyDrive is perfect for those who need a lot of data. It allows you to store information up to 25 GB in size. At the same time, there are no restrictions on the file format. However, there are a number of advantages for some types. So, for example, when storing Office documents, you can edit them directly in the browser.

Dropbox is more widespread than Windows Live SkyDrive, although it has much less information at just 2GB. It is enough to install one application per device to have remote access.
There is even a dedicated server for storing music. This is Grooveshark, which is considered one of the most popular cloud storage for music files.
What is hidden behind the same type of abbreviations like XaaS?
Browsing the news of cloud technologies, readers are confronted with different definitions and designations, the meaning of which may not be immediately clear. Not to mention the same type of abbreviations for cloud services, in which even IT specialists are sometimes confused. Therefore, we decided to collect in one place basic definitions, the knowledge of which will help to read materials on the topic of cloud technologies and understand them without being distracted by search engines or Wikipedia.
For convenience, we have divided the terms into several categories, briefly describing the most important in each of them. Of course, not all definitions are given in our article, but even this list will be enough to navigate the world of cloud technologies relatively freely.
Clouds. General terms
Cloud computing — In simple terms, it is a scenario in which the user is given access to computing resources such as servers, networks, storage systems, applications and services over a network, most often over the Internet.
Public cloud — infrastructure that provides the ability to use cloud computing for a wide range of users. Usually owned by a commercial organization.
Private (private) cloud — as the name suggests, it is an infrastructure owned by one organization that allows cloud computing to be used solely for its own purposes.
Hybrid cloud — combines the features of a private and public cloud. With this approach, part of the infrastructure belongs to the client, and part is leased. The connection between the two structures is provided using data transmission technologies.

Hardware part
Data processing center (DPC) — a specialized free-standing building to accommodate various server and network equipment, which is accessed via the Internet. In addition to providing redundancy for power supply and communication channels, such a building necessarily employs qualified personnel who ensure constant monitoring and maintenance of all systems.
Server — a specialized computer used to run applications and services that support the IT infrastructure.
Cluster — several servers connected by communication channels and presented to the user as one hardware resource.
Data storage systems (DSS) — hardware and software solution that allows you to consolidate all disk space within one system. In addition to general fault tolerance and constant monitoring of its own state, storage systems support many useful functions, such as, for example, data replication at the array level.
Replication — the process of copying data in order to synchronize it to one or more objects. Allows you to secure information from loss in the event of equipment failure.
Network switch ( Switch) — a device that allows you to connect several nodes of a computer network. Works at the L2 level of the OSI model.
Network router ( Router) — a device that has several network interfaces and allows data to be transferred between different network segments. The rules on the basis of which the packet transmission will be carried out are configured by the administrator. Works at the L3 level, OSI model.
Virtualization
Virtualization — a technology that allows you to provide computing resources that are abstracted from the hardware and at the same time logically isolated from each other. That is, on one physical server, you can create many virtual ones that will work independently.
Hypervisor — a program that allows you to implement virtualization technology. The hypervisor manages and configures virtual machines, as well as networks, soft switches and routers.
Virtual machine — analog of a physical computer, implemented in a virtual environment. The concepts of "virtual machine" and "virtual server" differ only in their final purpose, but in fact they are one and the same.
Cloud services
Separately, it is worth describing the main services provided on the basis of virtual technologies. A large group of such services are united under the abbreviation XaaS, which stands for "anything as a service." All these services are based on the main three: PaaS, SaaS, IaaS.
PaaS ( Platform as a Service - platform as a service) — this kind of cloud computing, which is provided to the customer in the form of a ready-made software platform, which includes various tools, and allows you to customize them. Basically, this platform can be anything: a testing environment, a database management system, or automation of management processes. Moreover, such a platform is managed and maintained by a service provider.
SaaS ( Software as a Service - software as a service) — this is probably the most common type of cloud-based service. It consists in providing the customer for use of any programs that are located in the cloud of the service provider. A prime example is a Google email inbox or, for example, the Microsoft Office 365 suite.
IaaS (InfrastructureasaService - infrastructure as a service) — a type of cloud service that involves a customer leasing a pool of computing resources from a service provider as a virtual infrastructure. These can be virtual servers, storage systems, various network elements, or any combination of these components.
But besides the basic ones, there are many other cloud services. Let's take a closer look at them:
DRaaS (DisasterRecoveryasaService - disaster recovery as a service) — a service for providing the customer with the possibility of restoring the operability of his own virtual structure in the cloud of a service provider in the event of an accident or disaster. Services of this type help to eliminate the impact of serious disruptions on the business, which means that they are most in demand by companies for which the operation of applications and services is a critical parameter.
BaaS (BackupasaService - backup as a service) — a service for providing the customer with a platform and tools for organizing the procedure for backing up data to the cloud. The implementation of this service depends on many factors, such as the amount of data to be backed up, the bandwidth of communication channels, as well as the backup scheme and the depth of the archive. This is convenient for companies that have a large amount of critical data, but organizing their own reliable backup system is not cost-effective.
BaaS (BackendasaService - backend as a service)- a set of ready-made server functionality that allows you to simplify and speed up application development. In other words, it is a full-fledged development environment hosted in the cloud, which means that it allows you to use all the advantages of the technology, such as, for example, unlimited scalability.
MaaS ( Monitoring as a Service - monitoring as a service) — a relatively new type of cloud service, which consists in organizing monitoring of its own infrastructure using software located in the cloud of a service provider. As in many other cases, this solution allows you to use the most advanced software tools without buying them or organizing administration.
DBaaS ( Data Base as a Service - database as a service) — a service that allows clients to connect to a database located in the cloud. In this case, the cost of the solution is calculated based on the volume of the base and the number of client connections. The main advantages of such a solution, of course, will be scaling and the absence of the need to ensure data security.
HaaS ( Hardware as a Service - equipment as a service) - a service for the provision of computing power from the cloud. In fact, instead of buying an iron server, the client can rent it, while it will be located at the service provider's site, which will provide power redundancy and timely maintenance.
NaaS ( Network as a Service - network as a service) - a service for the provision of network infrastructure as an alternative to your own network. NaaS capabilities allow you to use routing tools, as well as increase or decrease the bandwidth of the channel.
STaaS ( Storage as a Service - storage as a service) — it is a service for providing disk space in the cloud. For the user, such a solution looks like an additional logical drive or just a network folder. The advantage of STaaS is the availability of redundancy as a prerequisite for any service provider.
DaaS (DesktopasaService - desktop as a service)- a service that provides the user with a remote desktop. Unlike local, remote desktop can have really powerful technical characteristics, this allows you to use applications of different levels without being tied to the capabilities of your desktop PC.
CaaS ( Communications as a Service - communication as a service) - a service for the provision of communication tools in the cloud. In other words, this service allows you to organize telephony, instant messaging or, for example, the ability to conduct video conferencing by a service provider.
CaaS ( Container as a Service - container as a service) - a type of service that has recently become more and more popular. It consists in providing the client with the ability to organize, start or stop the container using the web interface or API tools.
Conclusion
In this article, we reviewed the basic concepts that allow you to better navigate the world of cloud technologies, and also disassembled most of the services provided on their basis. We hope that this information will be useful to you.
Research stages
Set a work goal.
Find a source of information.
Process information.
Give definitions, reveal concepts.
Analyze the results.
Draw conclusions.
Research Objectives
Study the basic information about "Cloud" technologies, about the varieties and applications of these technologies.
Consider "cloud" technologies, in particular, in education, and more about MICROSOFT technologies.
General Provisions
The term " cloud computing"(English - cloud computing) is applicable for any services that are provided via the Internet. The essence of cloud technologies is to provide users with remote access to services, computing resources and applications (including operating systems and infrastructure) over the Internet. The development of this sphere of hosting (a hosting service for placing the client's equipment on the territory of the provider with ensuring its connection to communication channels with high bandwidth) was due to the emerging need for software and digital services that could be controlled from the inside, but which would be this is more economical and efficient. These Internet services, also known as "cloud services", can be divided into three main categories:
infrastructure as a service
platform as a service
software as a service
Compared to the traditional approach, cloud services allow you to manage larger infrastructures, serve different groups of users within the same cloud, and also mean complete dependence on the cloud service provider. When providing a cloud service, a pay-per-use payment type is used. Usually, the unit of measurement of the working time is taken as a minute or hour of resource use. When assessing the amount of data, the unit of measurement is taken as a megabyte of stored information. In this case, the user pays for exactly the amount of resources that he actually used during a certain time. In addition, the cloud infrastructure provides the user with the ability, if necessary, to "raise" or "lower" the maximum limits of allocated resources, thereby taking advantage of the elasticity of the service provided. The user of cloud services does not need to worry about the infrastructure that ensures the performance of the services provided to him. All tasks related to configuration, troubleshooting, infrastructure expansion, etc. are undertaken by the service provider.
Types of clouds
Clouds can be public or private.
A private cloud is an infrastructure designed to be used by a single organization that includes multiple consumers (for example, divisions of the same organization). A private cloud can be owned, managed and operated by the organization itself or by a third party (or some combination of these), and it can physically exist both inside and outside the owner's jurisdiction.
A public cloud is an infrastructure designed for free use by the general public. The public cloud can be owned, operated and operated by commercial, academic, and government organizations (or any combination of these). The public cloud physically exists in the jurisdiction of the owner - the service provider.
A hybrid cloud is a combination of two or more different cloud infrastructures (private, public) that remain unique objects, but are interconnected by standardized or private technologies for transferring data and applications (for example, short-term use of public cloud resources for balancing loads between clouds).
A public cloud is a type of infrastructure designed for use by a specific community of consumers from organizations with common tasks. A public cloud can be co-owned, operated and operated by one or more of the community organizations or a third party (or any combination of these), and it can physically exist both within and outside the owner's jurisdiction
In practice, the boundaries between all these types of computation are blurry.
Three layers of cloud services

Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure for rent. The user is provided with a "clean" instance of a virtual server with a unique IP address or set of addresses and part of the storage system. To control the parameters, start and stop this instance, the provider provides the user with a programming interface (API).
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS can be thought of as a turnkey virtual platform consisting of one or more virtual servers with operating systems and specialized applications installed. Most cloud providers offer the user a choice of a variety of ready-to-use cloud environments.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
The SaaS concept provides the ability to use software as a service and do it remotely over the Internet. This approach allows you not to buy a software product, but simply temporarily use it when a need arises.
Benefits of cloud computing
The user pays for the service only when he needs it, and most importantly, he pays only for what he uses.
Cloud technologies allow you to save money on purchasing, maintaining, upgrading software and equipment.
Scalability, fault tolerance and security - automatic allocation and release of the necessary resources depending on the needs of the application. Maintenance, software updates are performed by the service provider.
Remote access to data in the cloud - you can work from anywhere on the planet where you have access to the Internet.
Disadvantages of cloud computing
The user is not the owner and does not have access to the internal cloud infrastructure. The safety of user data is highly dependent on the provider company.
A disadvantage that is relevant for Russian users: in order to receive high-quality services, the user must have reliable and fast access to the Internet.
Not all data can be entrusted to an Internet provider not only for storage, but even for processing
There is a risk that the online service provider will one day fail to back up the data and it will be lost in a server crash.
Trusting your data to an online service, you lose control over them and limit your freedom (the User will not be able to change some of his information, it will be stored in conditions beyond his control).
Application of cloud technologies
As an example of the use of cloud technologies in education, one can name electronic diaries and journals, personal accounts for students and teachers, an interactive reception room, and more. These are thematic forums where students can exchange information. This is also a search for information, where students can solve certain educational problems even in the absence of a teacher or under his guidance. To do this, you can use:
computer programs
electronic textbooks
simulators
diagnostic, test and training systems
applied and instrumental software
laboratory complexes
systems based on multimedia technology
telecommunication systems (e.g. e-mail, teleconferencing
electronic libraries and more.


Microsof cloud technology for educational institutions
Microsoft Cloud: Office 365, Azure Education
Microsoft Office 365 for Educational Institutions allows you to take full advantage of cloud services, helping to save time and money, and also increases the productivity of students and employees. Basic functionality that includes cloud versions of Exchange Online, SharePoint Online and Office Web Apps, and Lync Online with video conferencing will be available free of charge. You can find detailed information about new prices and tariffs at the link: [email protected].Office 365 Education combines the capabilities of familiar Office desktop applications with online versions of the next generation of Microsoft communications and collaboration services. Office 365 is easy to use and administer, with the robust security and reliability of a leading global service provider.
More information can be found at the link: http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/office365/education/school-services.aspx#fbid=RAc3tEIrx3K.
With the Windows Azure in education offering, educators have the opportunity to incorporate one of the most innovative and rapidly evolving technologies into their learning experience, both in theory and practice. It's no secret that in a few years the demand in the labor market for specialists in the field of cloud computing will increase significantly; with the help of Windows Azure in education, universities are able to train such specialists.
Cloud computing involves running applications or storing data on servers located in distributed data centers that are accessible over the Internet. A dedicated cloud platform is required to develop and run such applications. Such a platform is Windows Azure, the "cloud" counterpart of the Windows Server operating system. However, if Windows Server is software that you purchased and deployed on servers in your local data center, then Windows Azure is hosted in Microsoft data centers and is available to you remotely as an environment for developing and executing applications. You do not need to buy and install software, you only pay for the rent of computing resources and capacities of the Microsoft data center platform.
How does Windows Azure work?
Windows Azure is based on running a virtual machine for each instance of an application. The developer determines the required amount of data storage and the required computing power (number of virtual machines), after which the platform provides the appropriate resources. When the initial resource requirements change, in accordance with the new customer request, the platform allocates additional or reduces unused data center resources for the application.
A feature of the PaaS model ("platform-as-a-service") is the separation of the application and infrastructure: the developer only needs to determine the amount of resources required for the application, and all actions to provide the requested resources, manage them, dynamic distribution, monitoring, scaling, etc. are performed provider.
For students wishing to study cloud technologies on their own or working on projects in the cloud computing industry, Microsoft also provides free access to Windows Azure, allowing them to immerse themselves in the educational process without any restrictions.
Teachers:
5 months of access
2 small compute nodes
3GB storage
2 connections to service bus
2 SQL Asure Web Edition (1GB)
Students:
Work completed.
The term "cloud technology" is on everyone's lips now. An active discussion of the possible nuances of working with such technologies is being conducted both on the forums of large Internet companies and among novice users. And there really is something to discuss.
Every day in search engines, computer owners are increasingly asking the question "what is cloud technology." This is not surprising, because more and more users are learning about this innovation. Antivirus programs are a prime example. New versions of Norton Internet Security, Kaspersky and many others in the settings offer to activate the option of protection from the cloud. Since curiosity is inherent in human nature itself, it is quite logical that people become interested in cloud technologies.
Alas, something revolutionary should not be expected. In part, these technologies have existed on the Web for a long time, they just lacked an accurate and capacious definition, systematization and understanding of potential opportunities. Cloud computing is a way of processing digital data outside of the host computer environment. Since many people are familiar with the term thanks to anti-virus applications, we will consider the work of "clouds" using this group of programs as an example.
Let's imagine that an anti-virus application encounters suspicious program code, which is not described in the virus databases. If the user does not know what cloud technologies are and has not allowed their use (checkmark in the settings), then the antivirus will try to localize the suspicious file until the databases are updated. Everything is completely different if cloud technologies are activated. In this case, information about the strange code is automatically transmitted to the server of the anti-virus program developer, where it is promptly checked by specialists for potential danger. If the threat is confirmed to all computers connected to this resource, instructions are sent on how to neutralize the danger. The result is an unprecedented speed of response to the emergence of new viruses. What is cloud technology in this example? The answer lies in executing the processing of suspicious code on the facilities of the developer's servers, outside the computers of ordinary users. This is the key feature.
Cloud computing gives a second life to low-power computing devices. Suppose we have a calculator that has Internet access and is connected to a specialized "cloud" consisting of clusters of high-performance computers. We can perform elementary operations on our own, but what if we need complex calculations? In this case, the calculator sends the task data to the cloud service, and in response it receives a ready-made solution. For the user, the actions that took place between the set of commands and the receipt of the response went unnoticed. After all, the main thing is the result, and it has been achieved. Of course, a calculator is an extreme, but on the other hand, it's easier to understand how it works.
In addition to such unobvious clouds, there are special services that largely replace full-fledged applications on the local computer. For example, a user needs to edit a text file in the Word program. To do this, you will need to purchase the program itself (and the licensed version is not cheap), allocate free disk space on the media, connect the necessary modules. Of course, all this can be solved, but what if there are a lot of computers (enterprise)? Spend money on a purchase It is much easier to use a cloud service that provides access to certain programs hosted on its sites. The user needs to go to the desired site through the browser, remotely launch Word and open his file for editing. By the way, convenient interfaces are usually implemented in this way.
The advantages of cloud technologies can be enumerated for a long time. There are fewer cons, but they are significant: reduced privacy and dependence on the work of a third-party resource.