The concept of computer networks; local and global networks; network topology; network operating systems.
The purpose of the lecture:
- study hardware and software of local and global networks.
The advent of personal computers required a new approach to organizing a data processing system, to creating new information technologies. There was a need to move from using separate computers in centralized data processing systems to distributed processing is givenof those v computer network. Subscribers networks can be individual computers, computer complexes, terminals, industrial robots, machine tools with numerical control, etc. Depending on the territorial location of subscribers, computer networks are divided into global, regional and local... Combining global, regional and local computer networks allows you to create multihomed hierarchies providing powerful means of processing huge information arrays and access to unlimited information resources.
In the general case, a computer network is represented by a set of three subsystems nested within each other: workstation networks, server networks and basic data network.
The basic requirements that determine the architecture of computer networks are as follows: openness, vitality, adaptability, security information . These requirements are provided by the modular organization of process control in the network, implemented according to a multi-level scheme. The number of layers and the distribution of functions between them significantly affects the complexity of the software of the computers included in the network, and the efficiency of the network. There is no formal procedure for choosing the number of levels.
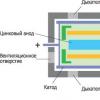
The reference model is seven-level scheme: level 1 - physical, u level 2 - channel, y level 3 - network, level 4 - transport, 5 - session, 6 - representative, 7 - applied... Layers 1-3 organize the core data network as a system that provides reliable data transfer between network subscribers. At level 5, at the request of processes, ports are created for receiving and transmitting messages and connections are organized - logical channels.
The procedure for the implementation of connections in the network is regulated protocols.
The basic principles of organizing a computer network determine its main characteristics: operational capabilities, performance, message delivery time and the cost of the services provided.
Information systems based on local computer networks, provide the solution to the following tasks: data storage, data processing, organization of user access to data, transfer of data and the results of their processing to users.
Computer networks implement distributed data processing. Here, data processing is split between two entities: client and server... The server provides storage of public data and organizes access to this data. In the process of data processing, the client generates a request to the server to perform complex procedures. The server executes the request and sends the results to the client. A similar model of a computer network was called archiclient-server textures.
Another model of a computer network is file server that launches the operating system and controls the flow of data transmitted over the network. Selected workstations and any shared peripherals (printers, scanners, modems, etc.) are connected to the file server. Each workstation runs its own disk operating system, but unlike a stand-alone personal computer, it contains a network interface card and is physically connected by cables to a file server. Workstation launches the shell of the network, which allows you to use files and programs stored on a file server as easily as those on its own disks. To add a workstation to the network, the shell network operating system is loaded at the beginning of the computer's operating system. The shell retains most of the commands and functions of the operating system and adds more functionality to the local system, which makes it flexible.
Based on the distribution of functions, local computer networks are divided into peer-to-peer and double rank(hierarchical networks or networks with a dedicated server). In a peer-to-peer network, a computer acts as both a client and a server. Peer-to-peer resource sharing is perfectly acceptable for small offices with 5-10 users, combining them into a workgroup. A two-rank network is organized on the basis of a server on which network users are registered. For modern computer networks, it is typical mixed a network that unites workstations and servers, with part of the workstations forming peer-to-peer networks, and the other part belonging to dual-peer networks.
The geometric connection diagram (physical connection configuration) of the network nodes is called network topology... There are a large number of options for network topologies, the basic of which are tire, ring, star... The local network can use one of the listed topologies. It depends on the number of combined computers, their relative position and other conditions.
Bus topology problems arise in the following cases: when a break occurs at any point on the bus; in case of failure of the network adapter of one of the computers and transmission of signals with interference to the bus; if you need to connect a new computer to the network. The disadvantages of a ring organization are breaks anywhere in the ring, stopping the entire network; dependence of the message transmission time by the time of successive operation of each node located between the sender and the receiver; the possibility of unintentional distortion of information due to the passage of data through each node. The combination of basic topologies (hybrid) provides a wide range of solutions that accumulate the advantages and disadvantages of the basic ones.
Different networks have different procedures describing methods of accessing network channels ( data transfer protocols). The most common are specific implementations of access methods: Ethernet, Arcnet and Token- Ring.
Access method Ethernet developed by the firm Xerox in 1975, is most popular, as it provides a high data transfer rate and does not exclude the possibility of simultaneous transmission of messages by two or more stations. This access method uses a shared bus topology.
Access method Arcnet developed by the firm DatapointCorp... became widespread due to the fact that the equipment Arcnet cheaper than hardware Ethernet or Token- Ring. Arcnet used in LANs with star topology.
Access method Token- Ring was developed by the company IBM and is designed for ring network topology.
In addition to the problems of creating local computer networks, there is also the problem of expanding (combining) computer networks. A computing network created at a certain stage in the development of an information system may eventually cease to meet the needs of all users. At the same time, the physical properties of signals, data transmission channels and design features of network components impose severe restrictions on the number of nodes and the geometric dimensions of the network. The following devices are used to combine local networks: repeater, bridge, router,Gateway.
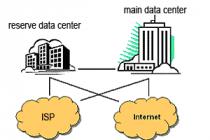
Large local networks are united into global ones. The operation of global networks is supported by control centers (special computers), which serve only for administrative purposes, keep records, provide users with information on network resources, and check the operation of the network. Users communicate with other network subscribers through special communication software. Currently, the largest global network, covering almost all countries in the world, is considered Internet.
Internet ensures the exchange of information between all computers that are part of the network, connected to it, and provides its users with a variety of resources. The type of computer and the operating system it uses are irrelevant.
In order for information to be transmitted between computers, regardless of the communication lines used, the type of computer and software, special data transfer protocols. They work on the principle of dividing data into blocks of a certain size (packets), which are sequentially sent to the addressee. There are two main protocols used on the Internet : internet protocol IP and transmission control protocol TCP... Since these protocols are interconnected, we usually talk about the protocol TCP/ IP.
Main cells Internet are local area networks. If some local network is connected to Internet, then each workstation on this network can also connect to Internet... Computers that self-connect to Internet are called host computers.
Each computer connected to the network has its own address. There are special requirements for station addresses. The address must be in a format that allows it to be processed automatically, and must carry information about its owner. For this purpose, two addresses are set for each computer: digital IP-address and domain address... The first of them is more understandable for a computer, the second for a person. Both of these addresses are equal.
To simplify the communication of network subscribers, its entire address space is divided into separate areas - domains which in the address system Internet are represented by geographic regions and have a two-letter name. There are domains, divided according to thematic criteria, with a three-letter abbreviated name. A computer name includes at least two levels of domains, which are separated from each other by a period. The top-level domain is indicated on the right, and subdomains of the general domain on the left.
To handle the search path in domains, there are special name servers.
The use of Internet technologies is not necessarily implemented within the framework of the worldwide information network. The technologies used in the global network are also suitable for creating powerful corporate information systems and systems for ensuring teamwork ( IntraNet).
Components (protocols, programs, server computers) assembled together to provide one of the services Internet are called services(services, services) network. One of the most important services is Email... Local e-mail systems are characterized by secrecy, low cost, and high functionality. There are two main types of local systems: centralizedbathroom systems and systems based on local area networks... There are many email software packages available. These include MicrosoftOutlookExpress, MicrosoftMail, NovellGroupWise other. Email capabilities can be used in Internet... In this case, an address system is used based on the domain address of the computer connected to Internet.
Additional information on the topic can be obtained at.
The goal of teaching students the basics of computer networks is to provide knowledge of the theoretical and practical foundations in the field of LAN and WAN, network applications and applications for creating web pages and sites, in the field of organizing computer security and information protection in networks, as well as in the field of doing business in Internet.
A computer network is a collection of computers that can communicate with each other using communication equipment and software.
Telecommunications is the transmission and reception of information such as sound, image, data and text over long distances through electromagnetic systems: cable channels; fiber optic channels; radio channels and other communication channels. A telecommunication network is a set of hardware and software through which telecommunications are carried out. Telecommunication networks include: 1. Computer networks (for data transmission) 2. Telephone networks (transmission of voice information) 3. Radio networks (transmission of voice information - broadcast services) 4. Television networks (transmission of voice and images - broadcast services)
Why do we need computing or computer networks? Computer networks are created with the aim of accessing system-wide resources (information, software and hardware), distributed (decentralized) in this network. On a territorial basis, local and territorial (regional and global) networks are distinguished.
A distinction should be made between computer and terminal networks. Computer networks connect computers, each of which can work autonomously. Terminal networks typically link powerful computers (mainframes) to terminals (input / output devices). An example of terminal devices and networks is a network of ATMs or ticket offices.
The main difference between LAN and WAN is in the quality of the communication lines used and in the fact that in a LAN there is only one way of transferring data between computers, and in a WAN there are many of them (there is redundancy of communication channels). Since the communication lines in the LAN are of better quality, the data transfer rate in the LAN is much higher than in the WAN. But there is a constant penetration of LAN technologies into the WAN and vice versa, which significantly improves the quality of networks and expands the range of services provided. In this way, the differences between LAN and WAN are gradually being smoothed out. The trend of convergence (convergence) is typical not only for LAN and WAN, but also for telecommunication networks of other types, which include radio networks, telephone and television networks. Telecommunication networks consist of the following components: access networks, highways, information centers. A computer network can be represented by a multilayer model consisting of layers:
computers;
communication equipment;
Operating systems;
network applications. Various types and classes of computers are used in computer networks. Computers and their characteristics determine the capabilities of computer networks. Communication equipment includes: modems, network cards, network cables and intermediate network equipment. Intermediate equipment includes: transceivers or transceivers (traceivers), repeaters or repeaters (repeaters), hubs (hubs), bridges (bridges), switches, routers (routers), gateways (gateways).
To ensure the interaction of software and hardware systems in computer networks, uniform rules or a standard were adopted that determines the algorithm for transmitting information in networks. Network protocols were adopted as a standard, which determine the interaction of equipment in networks. Since the interaction of equipment in a network cannot be described by a single network protocol, a multi-layered approach was applied to the development of networking tools. As a result, a seven-level model of open systems interaction - OSI - was developed. This model divides the means of interaction into seven functional levels: application, representative (presentation layer), session, transport, network, channel and physical. A set of protocols sufficient for organizing the interaction of equipment in a network is called a communication protocol stack. The most popular is the TCP / IP stack. This stack is used to connect computers on the Internet and in corporate networks.
The protocols are implemented by autonomous and network operating systems (communication means that are included in the OS), as well as by telecommunication equipment devices (bridges, switches, routers, gateways). Network applications include various email applications (Outlook Express, The Bat, Eudora and others) and browsers - programs for viewing web pages (Internet Explorer, Opera, Mozzila Firefox, and others). Website creation applications include Macromedia HomeSite Plus, WebCoder, Macromedia Dreamweaver, Microsoft FrontPage, and other applications. The global information network Internet is of great interest. The Internet is an association of transnational computer networks with various types and classes of computers and network equipment, operating under various protocols and transmitting information through various communication channels. The Internet is a powerful means of telecommunication, storage and provision of information, e-business and distance (interactive or online) learning.
1. Types of computer networks. Types, main components of lvs.
Types of computer networks:
Computer network (computer network, data transmission network)- a communication system between two or more computers. Various physical phenomena can be used to transmit information, as a rule, various types of electrical signals or electromagnetic radiation. Types of computer networks: Personal network is a network built “around” a person. These networks are designed to unite all personal electronic devices of the user (telephones, PDAs, smartphones, laptops, headsets, etc.). The standards for such networks are currently referred to as Bluetooth. LAN- serves to unite computers located at a small distance from each other. Such a network usually does not extend beyond one room. City computer network(English MAN - Metropolitan Area Network) covers several buildings within one city or the whole city. Corporate network- a set of LANs, powerful computers and terminal systems using a common information highway for exchange. National Network- a network that unites computers within one state (National LambdaRail, GEANT) Glob-I will calculate-I network- a data transmission network designed to serve a significant territory using publicly available communication lines.
Types: By type of functional interaction: Peer-to-peer - the most basic and intended for small work groups. With their help, users of several computers can use shared disks, printers and other devices, transmit messages to each other and perform other collective operations. Here, any computer can perform both the role of a server and a client. Such a network is cheap and easy to maintain, but it cannot provide information protection for a large network). Multi-rank (they use dedicated computers - servers for storing shared data and programs for using shared resources. Such a network has good expandability, high performance and reliability, but requires constant qualified maintenance). By type of network topology: Tire, Star, Ring, Lattice. Mixed topology. By network OS: Windows, UNIX, Mixed.
Types, main components of a LAN:
Slave station- a computer designed for a local network. The network adapter is a special board that allows the computer to interact with other devices on this network. It implements physical communication with m / u network devices via a network cable. Server- some service device, a cat in the LAN plays the role of a control center and data concentrator. It is a combination of hardware and software that is used to manage shared network resources.
3. Network topology. Network standards (types of networks) Data transmission medium (network cable).
Network topology(from the Greek. τόπος, place) - a description of the network configuration, a diagram of the location and connection of network devices.
The network topology can be:
physical- describes the actual location and connections between network nodes.
logical- describes the path of the signal within the physical topology.
There are many ways to connect network devices, of which five basic topologies can be distinguished: bus, ring, star, mesh, and lattice. The rest of the methods are combinations of the basic ones. In general, these topologies are called mixed or hybrid, but some of them have their own names, such as "Tree".
Ring- the basic topology of a computer network, in which workstations are connected in series to each other, forming a closed network. The ring does not use a concurrent method of sending data; a computer on the network receives data from a neighbor and redirects it further if it is not addressed to him. To determine who can transmit data, a marker is usually used. The data goes in a circle, in one direction only.
Advantages: Easy to install; Almost complete absence of additional equipment; Possibility of stable operation without a significant drop in the data transfer rate under intensive network load, since the use of the token eliminates the possibility of collisions.
Disadvantages: Failure of one workstation, and other problems (cable break), affect the performance of the entire network; Complexity of configuration and configuration; Complexity of troubleshooting;
Tire, is a common cable (called a bus or backbone) to which all workstations are connected. There are terminators at the ends of the cable to prevent signal reflection.
A message sent by a workstation is distributed to all computers on the network. Each machine checks - to whom the message is addressed and if it is, then processes it. In order to exclude the simultaneous sending of data, either the "carrier" signal is used, or one of the computers is the main one and "gives the word" to the rest of the stations. Advantages Short network setup time; Cheap (less cable and network devices required); Easy to set up; Failure of a workstation does not affect network performance;
Disadvantages Any problems in the network, such as a cable break, failure of the terminator, completely destroy the operation of the entire network; Complex localization of faults; With the addition of new workstations, network performance decreases.
Star- the basic topology of a computer network, in which all computers on the network are connected to a central node (usually a network hub), forming a physical network segment. Such a network segment can function both separately and as part of a complex network topology (usually a "tree").
The workstation to which the data needs to be sent sends it to the hub, which determines the addressee and gives him the information. At a certain point in time, only one machine on the network can send data, if two packets arrive at the hub at the same time, both parcels are not received and the senders will need to wait a random period of time to resume data transmission.
Advantages: failure of one workstation does not affect the operation of the entire network as a whole; good network scalability; easy troubleshooting and network breaks; high network performance (subject to correct design); flexible administration options.
Disadvantages failure of the central hub will result in the inoperability of the network (or network segment) as a whole; more cabling is often required to lay the network than most other topologies; the finite number of workstations on the network (or network segment) is limited by the number of ports in the central hub.
Mesh topology(in English mesh) - connects each workstation on the network with all other workstations on the same network. Topology refers to fully connected, unlike others - not fully connected.
The sender of the message connects in turn with the network nodes until he finds the one he needs, which will receive the data packets from him.
Comparison with other topologies
Advantages Reliability, if the cable breaks, the computer has enough connection paths in the network.
Disadvantages high installation cost; the complexity of setup and operation;
In wired networks, this topology is rarely used, because excessive cable consumption becomes too expensive. However, in wireless technology, mesh-based networks are becoming more common as network media costs do not increase and network reliability comes to the fore.
Lattice- a concept from the theory of the organization of computer networks. This is a topology in which the nodes form a regular multidimensional lattice. Moreover, each edge of the lattice is parallel to its axis and connects two adjacent nodes along this axis. A one-dimensional "lattice" is a chain connecting two external nodes (having only one neighbor) through a certain number of internal ones (which have two neighbors - left and right). By connecting both external nodes, a ring topology is obtained. 2D and 3D lattices are used in supercomputer architecture.
Advantages: high reliability. Disadvantages: Complexity of implementation.
As a physical medium for signal transmission, the computer acts
Network cable.Coaxial- comp. of copper core, insulation, surrounding copper braid and outer sheath. May have an additional layer of foil. The thin coax cable is flexible, approximately 0.5 cm in diameter, capable of transmitting signals up to 185 m away without noticeable distortion. Capable of transmitting data at a speed of 10 Mbit / s, it allows to implement the bus and ring topology. Thick coax cable - about 1 cm in diameter, the copper core is thicker than that of the thin one. It transmits signals over a distance of 500 m. To connect it to a special device - a transceiver, the cat is equipped with a special connector. Twisted pair- two insulated copper wires twisted around each other. Twisting wires allows you to get rid of electrical noise induced by neighboring pairs and other sources. STP (shielded twisted pair) and UTP (unshielded twisted pair) - allows you to transmit a signal up to 100 m. There are 5 categories of UTP: 1) traditional telephone cable for analog transmission signals 2) cable of 4 twisted pairs, capable of transmitting signals at a speed of 4 Mbit / s 3) cable of 4 twisted pairs, capable of transmitting signals at a rate of 10 Mbit / s 4) 16 Mbit / s 5) 100-1000 Mbit / s c (The higher the pair category, the shorter the twist steps). To connect the twisted pair to the network, an RJ-45 connector is used. Used in star topology. Fiber optic- data is transmitted through optical fibers in the form of modulated light pulses. It is a reliable and secure transmission method, since electrical signals are not transmitted, therefore, the fiber-optic cable cannot be opened and data intercepted. Fiber optic lines are designed to move large amounts of data at high speeds. The signal in them practically does not fade away and is not distorted. It consists of a thin glass cylinder, called a core, covered with a layer of glass (shell) with a distortion coefficient different from that of the core. Sometimes fiber is made of plastic. Each fiber transmits signals in one direction, so the cable consists of 2 fibers with separate connectors (for transmission and for reception). Singlemode and multimode- for communication over short distances, because it is easier to install. Fiber optic is used for laying information highways, corporate networks, for transmitting data over significant distances. (2 kilometers full duplex over multimode fiber and up to 32 kilometers over single mode).
Wireless LAN (WLAN) is a wireless local area network. Wi-Fi is one of the Wireless LAN options. Allows you to deploy a network without laying a cable, can reduce the cost of deploying and expanding the network. Standards 802.11a / b / g speeds from 11 to 53 Mbps. WiMAX is a Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access protocol developed by the WiMAX Forum. ... Unlike WiFi (IEEE 802.11x) networks, where access to the access point is provided to clients in a random manner, in WiMAX, each client is given a well-defined amount of time. In addition, WiMAX supports mesh topology.
Mouse
Keyboard
Keyboard – keyboard control device for a personal computer. For entering alphanumeric data and control commands. The combination of monitor and keyboard provides the simplest user interface.
Keyboard functions do not need to be supported by special system programs (drivers). The software you need to get started with your computer is already in the read-only memory (ROM) chip in the basic I / O system, and therefore the computer responds to keystrokes immediately after being turned on.
The standard keyboard has over 100 keys, functionally divided into several groups.
The group of alphanumeric keys is intended for entering character information and commands typed by letters. Each key can operate in several modes (registers) and, accordingly, can be used to enter several characters.
The function key group includes twelve keys located at the top of the keyboard. The functions assigned to these keys depend on the properties of the specific program currently running, and in some cases, on the properties of the operating system. A common convention for most programs is that the F1 key invokes the help system, where you can find help on the operation of other keys.
Service keys are located next to the keys of the alphanumeric group. Due to the fact that they have to be used often, they are oversized. These include SHIFT, ENTER, ALT, CTRL, TAB, ESC, BACKSPACE, and more.
Two groups of cursor keys are located to the right of the alphanumeric pad.
The group of keys of the additional panel duplicates the action of the numeric and some symbolic keys of the main panel. The appearance of the additional keyboard dates back to the early 80s. At the time, keyboards were relatively expensive devices. The original purpose of the additional panel was to reduce wear on the main panel when carrying out cash and settlement calculations, as well as when managing computer games. Nowadays, keyboards are classified as low-value quick-wear devices and devices, and there is no significant need to protect them from wear and tear.
Mouse - manipulator type control device... It is a flat box with two or three buttons. The movement of the mouse on a flat surface is synchronized with the movement of the graphic object (mouse pointer) on the monitor screen.
Unlike a keyboard, a mouse is not a standard control, and a personal computer does not have a dedicated port for it. Nor is there a permanent dedicated interrupt for the mouse, and basic input and output does not include software for handling mouse interrupts. In this regard, at the first moment after turning on the computer, the mouse does not work. It needs the support of a special system program - the mouse driver. The mouse driver is designed to interpret signals from the port. In addition, it provides a mechanism for communicating information about the position and state of the mouse to the operating system and running programs.
The computer is controlled by moving the mouse along the plane and by short pressing of the right and left buttons (clicks). Unlike the keyboard, the mouse cannot be used directly to enter character information - the principle of control is event-driven. The movements of the mouse and its button clicks are events from the point of view of its driver program. By analyzing these events, the driver determines when the event occurred and where on the screen the pointer was at that moment. This data is passed to the application that the user is currently working with. From them, the program can determine the command that the user had in mind and start executing it.
The combination of monitor and mouse provides the most modern type of user interface called graphical. The user observes graphic objects and controls on the screen. Using the mouse, it changes the properties of objects and activates the controls of the computer system, and using the monitor, it receives a graphical response.
Adjustable mouse parameters include: sensitivity (expresses the amount of movement of the pointer on the screen for a given linear movement of the mouse), functions of the right and left buttons, and sensitivity to double clicking (the maximum time interval at which two clicks of a mouse button are regarded as one double click ).
Computer network (CS) – a set of computers and terminals connected using communication channels into a single system that meets the requirements of distributed data processing.
In general, under telecommunication network (TS ) understand a system consisting of objects that perform the functions of generating, transforming, storing and consuming a product, called points (nodes) of the network, and transmission lines (communications, communications, connections) that transfer the product between points.
Depending on the type of product - information, energy, mass - one distinguishes, respectively, information, energy and material networks.
Information network (IS)– a communication network in which information is the product of the generation, processing, storage and use of information. Traditionally, telephone networks are used to transmit sound information, images - television, text - telegraph (teletype). Nowadays, information integrated service networks, allowing to transmit sound, image and data in a single communication channel.
Computing network (ВС) - information network, which includes computing equipment. Computing network components can be computers and peripheral devices that are sources and receivers of data transmitted over the network.
The sun is classified according to a number of characteristics.
1. Depending on the distance between the nodes of the network, the aircraft can be divided into three classes:
· local(LAN, LAN - Local Area Network) - covering a limited area (usually within the distance of stations no more than a few tens or hundreds of meters from each other, less often by 1 ... 2 km);
· corporate (enterprise scale ) - a set of interconnected LANs covering the territory on which one enterprise or institution is located in one or more closely located buildings;
· territorial- covering significant geographic space; among territorial networks, regional (MAN - Metropolitan Area Network) and global (WAN - Wide Area Network) networks can be distinguished, having regional or global scales, respectively.
Computer telecommunications is one of the most dynamically developing areas of information technology. Compared to other sections of information technology, its technological component significantly exceeds the theoretical one. Therefore, the effectiveness of studying this topic strongly depends on the ability to organize practical work of students with computer networks.
Within the framework of this section of the basic course, the following list of pedagogical goals is implemented: to give an idea of the purpose and structure of local and global networks; to acquaint students with the basic information services of networks, with the possibilities of the Internet; teach how to exchange files in a local network of a computer class; to acquaint with the methods of searching for information on the Internet (if technical capabilities are available).
local area networks;
global networks.
The topic of computer networks is extensive in terms of the number of concepts and can be presented with varying degrees of detail. The disclosure of this topic in school textbooks is usually brief. Therefore, along with a discussion of methodological issues, this subsection of the manual includes additional information on the topic that will be useful to the teacher.
Issues under study:
¦ Local area network (LAN), organization and purpose.
¦ Local networks of school KUVT.
¦ Organization of global networks (WAN).
¦ Information services of the HS.
¦ Hardware of networks.
¦ What is the Internet.
¦ Internet and World Wide Web information services.
If the computers in the computer science classroom are united into a local network, then this circumstance greatly facilitates the study of this topic. It is the school computer class that should become the starting point in the conversation about the transfer of information in computer networks. Having defined a computer network as a system of computers connected by information transmission channels, the teacher demonstrates such a system on the equipment of a computer class and reports that such a network is called a local network.
Local computer networks are small in scale and operate within the same premises, buildings, enterprises. It is possible that the school has a local network that unites computers installed in different rooms: in classrooms, the office of the director, accounting, etc. In the same way, various departments of enterprises, firms, institutions are often combined into a local network.
Local networks, depending on the purpose and technical solutions, can have different structures for combining computers. They are also called configurations, architecture, network topology.
There are situations in LANs when the topology does not have some kind of regular structure. For example, computers can be connected on an "one-to-one" basis.
The use of local area networks serves two main purposes:
1) file exchange between network users;
2) the use of public resources: large disk space, printers, centralized database, software, etc.
Users of a shared local area network are usually called a workgroup, and the computers they work at are called workstations. If all computers on the network are equal, i.e. the network consists only of user workstations, it is called a peer-to-peer network. Peer-to-peer networks are used for the first of the noted purposes: file exchange. Each computer on such a network has its own name. Working group members can use these names to access the disk memory of their colleagues' PCs and copy files to their own computer or copy their files to other computers. The possibility of such exchange is provided by a special network operating system. Network OS tools can protect information from unauthorized access. Thus, the local network eliminates the need to use floppy disks to transfer information from one computer to another.
Another way of organizing a local network is a network with a dedicated (host) computer. It is called a file server. This organization is most often used in school computer labs. The teacher has access to the file server, and the students work at their workstations. All workstations are connected to the host machine (star connection). Therefore, a direct exchange of information occurs between the server and each workstation. Of course, in such a system, students can also exchange files, but "in transit" through the server. Usually a server is a more powerful machine than workstations, with a large hard disk, with additional external devices (for example, a CD-ROM drive, printer, modem). With such an organization of the local network, the second of the above goals is realized: user access to the common hardware and information resources of the server. In particular, programs stored on the server disk can be loaded into the workstation's RAM and run for execution, just as it is done from a PC's own disk. From his workplace, the user can create and save files on the server hard disk.
The network operating system manages the operation of the network. The operating system supports the standards (protocols) of information exchange in the network, sets the priority when different users access the same resources, etc. The main purpose of the network operating system is to enable users to work in a local network without interfering with each other. Peer-to-peer networking is supported by the Windows 95/98 operating system. The most common OS for networks with a dedicated server: Novell NetWare, Windows NT.
Global computer networks interconnect computers located at large distances (in the scale of the region, country, world). If students can see the local network with their own eyes, then acquaintance with global networks will be more descriptive. Here, as in many other topics, the analogy method comes to the rescue. The device of the global network can be compared to the device of the telephone system - the telephone network. The subscribers' phones are connected to the switch nodes. In turn, all city switches are interconnected so that communication can be established between any two subscribers' phones. This whole system forms the city's telephone network. Urban (regional) networks are interconnected by intercity lines. Access to telephone networks of other countries takes place via international communication lines. Thus, the whole world is "entangled" in telephone networks. Two subscribers in any part of the world connected to this network can communicate with each other.
Having told about this, invite the students to imagine that the subscribers have personal computers instead of telephones; instead of switches, there are powerful computer nodes, and a wide variety of information circulates over such a network: from text to video and sound. This is the modern world system of global computer networks.
The first global computer network began operating in 1969 in the United States, it was called ARPANET and united only 4 remote computers. An example of a modern network for scientific and educational purposes is BITNET. It covers 35 countries of Europe, Asia and America, unites more than 800 universities, colleges, research centers. The largest Russian network is RELCOM, created in 1990. RELCOM is part of the European network of EUNET networks, which, in turn, is a member of the giant world INTERNET community. This hierarchy is typical for the organization of global networks.
The network consists of nodal host computers, PCs of network subscribers, communication lines. Typically, a network node contains not one, but many computers. The server functions of different network services can be performed by different computers.
Host computers are constantly on, constantly ready to receive and transmit information. In this case, they say that they work on-line. Subscribers' computers communicate with the network (in on-line mode) only for a certain time - a communication session. Having sent and received the necessary information, the subscriber can disconnect from the network and then work with the received information autonomously - in off-line mode. The route of information transmission is usually unknown to the user. He can only be sure that the information passes through the connection node and reaches its destination. The routing of the transmitted data is handled by the system facilities of the network. In different sessions, communication with the same correspondent can take different routes.
A gateway is a computer that organizes the connection of a given network with other global networks.
Information services of global networks. Email. In the history of global networks, electronic mail (e-mail) appeared as the very first information service. This service remains the main and most important in computer telecommunications. We can say that there is a process of replacing traditional paper mail with e-mail. The advantages of the latter are obvious: first of all, it is a high speed of delivery of correspondence (minutes, rarely - hours), comparative cheapness. Already now, huge volumes of business and personal correspondence go through e-mail. E-mail, combined with facsimile communication, provides the vast majority of the needs for the transmission of letters and documents.
In order for a subscriber to use e-mail services, he must:
* have a hardware connection of your personal computer to the mail server of the computer network node;
* have your own mailbox and password on this server to access it;
* have a personal email address;
* have an e-mail client (mailer) on your computer.
Along with e-mail in global networks, there are other types of information services for users.
Telnet. This service allows the user to work in the terminal mode of a remote computer, that is, to use the programs installed on it in the same way as programs on their own computer.
FTP. This is the name of the network protocol and the programs that handle the work with the directories and files of the remote machine. The FTP client has the ability to browse the directories of FTP servers, copy files of interest.
Archie. This is the name of the special servers that act as search programs in the FTP server system. They help you quickly find the files you need.
Gopher. A system for searching and extracting information from the network with advanced tools for multi-level menus, reference books, index links, etc.
WAIS. Networked information retrieval system based on distributed databases and libraries.
Usenet. Teleconferencing system. Another name is newsgroups. Serves subscribers of certain thematic conferences by sending them materials by e-mail. mailboxes and, having found outgoing mail there, organizes its poisoning. Network hardware. Host computers (servers). The host computer has its own unique address in the network and acts as a node machine serving subscribers. Various types of machines are used as host computers: from powerful PCs to minicomputers and even mainframes (mainframes). The main requirements are a high-speed processor and a large amount of disk memory (hundreds of GB). Host computers on the Internet use the Unix operating system. All server programs serving applications run on Unix.
From what has already been said above, it follows that the concept of "server" has a software and hardware meaning. For example, a host computer that is currently running an e-mail server acts as a mail server. If a WWW server program starts running on the same machine, it becomes a Web server. Often the functions of the servers of different services are divided on a network node between different computers.
Communication lines. The main types of communication lines between computers on a network are telephone lines, electrical cables, fiber optic cables, and wireless communication. The main parameters of communication lines are bandwidth (maximum information transfer rate), noise immunity, and cost. In terms of cost, the most expensive are fiber-optic lines, the cheapest are telephone lines. However, as the price decreases, the quality of the line also decreases. Table 12.1 gives comparative characteristics of lines in terms of speed and noise immunity parameters.
Table 1. Characteristics of communication lines
Most often, dedicated telephone lines or radio links are used for communication between host computers. If the nodes of the network are located relatively close to each other (within the city), then the connection between them can be organized via cable lines - electric or fiber-optic. Recently, satellite radio communication has been actively used on the Internet.
Typically, subscribers (clients) connect to the site of their provider through a telephone line. Increasingly, wireless communication is beginning to be used for these purposes.
From the user's point of view, the Internet is a certain set of information services that he can receive from the network. Services include: e-mail, teleconferences (mailing lists), file archives, directories and databases, the World Wide Web - WWW, etc. The Internet is unlimited information resources. The impact that the Internet will have on the development of human society is not yet fully understood.
Internet information services. Along with the information services listed above (e-mail, teleconferences, etc.) provided to users of global networks, there are services, the emergence and development of which is associated exclusively with the development of the global Internet. The most notable of these is the WWW.
WWW - World Wide Web - World Wide Web. It is a hypertext information system on the Internet. Recently, the WWW and its software has become a universal means of information services on the Internet.
Basic concepts related to WWW:
Web page - the main information unit in the WWW, which has its own address;
Web server - a computer that stores Web pages and the corresponding software for working with them;
Web browser - a client program that allows you to retrieve and view Web pages;
Web site - A section of data on a Web server owned by an organization or person. In this section, the owner places his information in the form of many interconnected Web pages. Usually the site has a title - the home page, from which you can move through the pages of the site using hyperlinks or "back and forth" signs. The most popular Web browsers are Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator. The main task of a browser is to access the Web server for the page you are looking for and display the page on the screen. The easiest way to get the information you need from the Internet is to specify the address of the resource you are looking for. For storing and searching information on the Internet, a universal addressing is used, which is called URL - Uniform Resource Locator. A number of special search programs operate to help the user on the Internet. They are also called search engines, search engines, search engines. The search engine gives the user a list of document addresses in which the keywords specified by the user are found. Below are the addresses of the most popular Russian search engines:
http://mssia.agama.com/Aport/
http://www.rambler.ru/
http://yandex.ru/
http://www.altavista.telia.com/
In addition to the WWW, among the relatively new services on the Internet, there are the following:
IRC. Internet Relay Chat - real-time chat. Allows you to conduct a written dialogue with remote interlocutors on-line;
Internet telephony. A service that supports on-line voice communication of network clients.
If it is possible to access the Internet, the practical work of students can be organized in the following areas:
* preparation, sending and receiving e-mail;
* work with a Web browser, viewing Web pages;
* contacting FTP - servers, extracting files;
* search for information in the WWW system using search programs.
Acquaintance with each new type of application software serving the corresponding information service (mail program, Web browser, search program) should be carried out according to the standard methodological scheme: data, environment, operating modes, command system.