A device that allows you to find metal objects located in a neutral environment, for example, soil, due to their conductivity, is called a metal detector (metal detector). This device allows you to find metal objects in various environments, including the human body.
Largely due to the development of microelectronics, metal detectors, which are produced by many enterprises around the world, have high reliability and small overall and weight characteristics.
Not so long ago, such devices could most often be seen at sappers, but now they are used by rescuers, treasure hunters, utility workers when searching for pipes, cables, etc. Moreover, many "treasure hunters" use metal detectors that they collect with their own hands ...
Design and principle of operation of the device
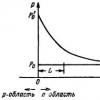
The metal detectors on the market work on different principles. Many believe that they use the principle of pulsed echo or radar. Their difference from locators lies in the fact that the transmitted and received signals operate constantly and simultaneously, in addition to everything else, they work at coinciding frequencies.
Devices operating on the "reception-transmission" principle register the reflected (re-emitted) signal from a metal object. This signal appears due to the effect on a metal object of an alternating magnetic field, which is generated by the metal detector coils. That is, the design of devices of this type provides for the presence of two coils, the first is transmitting, the second is receiving.
Devices of this class have the following advantages:
- simplicity of design;
- great opportunities for the detection of metallic materials.
At the same time, metal detectors of this class have certain disadvantages:
- metal detectors can be sensitive to the composition of the ground in which they are searching for metal objects.
- technological difficulties in the manufacture of the product.
In other words, devices of this type must be configured by hand before work.
Other devices are sometimes referred to as a beat detector. This name came from the distant past, more precisely from the time when superheterodyne receivers were widely used. Beating is a phenomenon that becomes noticeable when two signals with similar frequencies and equal amplitudes are added together. The beating consists in the pulsation of the amplitude of the summed signal.
The signal ripple frequency is equal to the frequency difference of the summed signals. Passing such a signal through a rectifier, it is also called a detector, the so-called difference frequency is isolated.
This scheme has been used for a long time, but nowadays, it is not used. They were replaced by synchronous detectors, but the term remained in use.
A beating metal detector works using the following principle - it registers the frequency difference from two transmitter coils. One frequency is stable, the other contains an inductor.
The device is tuned by hand so that the generated frequencies coincide or at least be close. As soon as the metal enters the zone of action, the set parameters change and the frequency changes. The frequency difference can be recorded in a variety of ways, ranging from headphones to digital methods.
Devices of this class are distinguished by a simple sensor design, low sensitivity to the mineral composition of the soil.
But besides this, during their operation, it is necessary to take into account the fact that they have high energy consumption.
Typical design
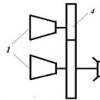
The metal detector includes the following components:
- The coil is a box-type construction that houses the receiver and transmitter of the signal. Most often, the coil has an elliptical shape and polymers are used for its manufacture. A wire is connected to it, connecting it to the control unit. This wire carries the signal from the receiver to the control unit. The transmitter generates a signal when metal is detected, which is broadcast to the receiver. The coil is mounted on the lower shaft.
- The metal part on which the coil is fixed and the angle of its inclination is adjusted is called the lower shaft. Thanks to this solution, a more thorough examination of the surface occurs. There are models in which the lower part can adjust the height of the metal detector and provides a telescopic connection to the rod, which is called the middle one.
- The middle boom is the node located between the lower and upper boom. Devices are fixed on it, allowing you to adjust the dimensions of the device. on the market you can find models that consist of two rods.
- The top bar is usually curved. It resembles the letter S. This shape is considered optimal for fixing it on the hand. An armrest, a control unit and a handle are installed on it. The armrest and handle are made of polymer materials.
- The metal detector control unit is required to process the data received from the coil. After the signal has been converted, it is sent to headphones or other display devices. In addition, the control unit is designed to adjust the operating mode of the device. The wire from the coil is connected using a quick-release device.
All devices included in the metal detector are waterproof.
It is this relative simplicity of the design that allows you to make metal detectors with your own hands.
Varieties of metal detectors
There is a wide range of metal detectors on the market that are used in many areas. Below is a list showing some of the variations of these devices:
Most modern metal detectors can find metal objects at a depth of 2.5 m, special deep products can detect a product at a depth of 6 meters.
Frequency of work
The second parameter is the frequency of operation. The thing is that low frequencies allow a metal detector to see at a rather large depth, but they are not able to see small details. High frequencies allow you to see small objects, but do not allow viewing the ground at great depths.
The simplest (budget) models operate at one frequency, models that belong to the average price level use 2 or more frequencies in their work. There are models that use 28 frequencies when searching.
Modern metal detectors are equipped with such a function as metal discrimination. It allows you to distinguish the type of material located at depth. In this case, when a ferrous metal is found in the search engine's headphones, one sound will sound, and when a colored metal is found, another.
Such devices are referred to as pulse-balanced. They use frequencies from 8 to 15 kHz in their work. Batteries of 9 - 12 V are used as a source.
Devices of this class are capable of detecting a gold object at a depth of several tens of centimeters, and items made of ferrous metals at a depth of about 1 meter or more.
But, of course, these parameters depend on the device model.
How to assemble a homemade metal detector with your own hands
There are many models of devices on the market for searching for metal in the ground, walls, etc. Despite its external complexity, making a metal detector with your own hands is not so difficult and almost anyone can do it. As noted above, any metal detector consists of the following key components - a coil, a decoder and a power supply signaling device.
To assemble such a metal detector with your own hands, you need the following set of elements:
- controller;
- resonator;
- capacitors of various types, including film;
- resistors;
- sound emitter;
- Voltage regulator.
Do-it-yourself simplest metal detector
The metal detector circuit is not complicated, but you can find it either in the vastness of the world network, or in specialized literature. Above is a list of radio elements that are useful for assembling a metal detector with your own hands at home. A simple metal detector can be assembled by hand using a soldering iron or other available method. The main thing in this case, the details should not touch the body of the device. To ensure the operation of the assembled metal detector, power supplies of 9 - 12 volts are used.
For winding the coil, a wire with a cross-sectional diameter within 0.3 mm is used, of course, this will depend on the chosen scheme. By the way, the wound coil must be protected from the effects of extraneous radiation. To do this, they shield it with their own hands using ordinary food foil.
For the firmware of the controller, special programs are used, which can also be found on the Internet.
Metal detector without microcircuits
If a novice "treasure hunter" has no desire to get involved with microcircuits, there are circuits without them.
There are simpler circuits based on the use of traditional transistors. Such a device can find metal at a depth of several tens of centimeters.
Deep metal detectors are used to find metals at great depths. But it is worth noting that they are not cheap and therefore it is quite possible to assemble it with your own hands. But before you start making it, you need to understand how a typical scheme works.
The circuit of a deep metal detector is not the simplest one and there are several options for its execution. Before assembling it, you must prepare the following set of parts and elements:
- capacitors of various types - film, ceramic, etc.;
- resistors of different ratings;
- semiconductors - transistors and diodes.
Nominal parameters, quantity depend on the selected circuit diagram of the device. To assemble the above elements, you will need a soldering iron, a set of tools (screwdriver, pliers, wire cutters, etc.), material for making a board.
The assembly process for a deep metal detector looks like this. First, a control unit is assembled, the basis of which is a printed circuit board. It is made of PCB. Then the assembly scheme is transferred directly to the surface of the finished board. After the drawing is transferred, the board must be etched. For this, a solution is used, which includes hydrogen peroxide, salt, electrolyte.
After the board is etched, holes must be made in it to install the circuit components. After the board has been tinned. The most important stage is coming. Do-it-yourself installation and soldering of parts to the prepared board.
To wind the coil with your own hands, use a PEV brand wire with a diameter of 0.5 mm. The number of turns and the diameter of the coil depend on the chosen scheme of the deep metal detector.
A little about smartphones
There is an opinion that it is quite possible to make a metal detector from a smartphone. This is not true! Yes, there are applications that are installed under the Android OS.
But in fact, after installing such an application, he will actually be able to find metal objects, but only pre-magnetized ones. He will not be able to search and even more to discriminate against metals.
It's almost like looking for treasures. Some are stopped by the fact that they live far from mountains or rivers in order to search for nuggets by washing the sand. Others do not understand radio components in order to know how to get gold from them. Still others prefer to search for precious metal with a metal detector, but do not have the means to buy it. Fortunately, the device is quite simple, and even without being a radio amateur, you can make it yourself.
Operating principle
What is a metal detector? This is a device that, using certain radiation, finds the metal located underground, without direct contact with it. The response data that comes in helps to identify the find and informs about it using an audio or visual signal.
The principle of operation of a metal detector
The electromagnetic field that the device emits is in contact with metals, in this case with gold, which provokes the appearance of eddy currents on their surface. By measuring the conductivity, metals are identified and this is signaled.
Metal detectors can have different waveform parameters, signal return processing techniques, additional functions, and much more. Therefore, before you start making the device, you need to decide what exactly you want to get at the output.
The standard frequency for metal detectors is 6-20 kHz, but for gold it should be slightly higher, 14-20 kHz or more. This is because gold is often found in the form of tiny nuggets, so a higher sensitivity is needed. If there is such an opportunity, then it is good to have a device with a multifrequency custom search, then it will be possible to increase the number of objects that it recognizes.
Among all the metal detector circuits on the Internet, experts advise choosing devices with balanced induction, which have two coils in the head and a powerful electronic circuit. Of great interest are also circuits with the principle of operation of a receiver-transmitter, operating at high frequencies, about 20 kHz, which makes it possible to distinguish non-ferrous from ferrous metals.
Common parameters
Various technical methods can be used to design a metal detector. Much depends on the conditions in which it will be used. Therefore, the idea of what requirements the device must meet must be determined as clearly as possible. The following device parameters are distinguished:
- sensitivity - a characteristic that determines how small objects the detector can detect;
- selectivity - the ability to identify metals and respond to specific ones;
- resistance to interference - the ability not to react to extraneous radio signals from radio stations, cars, lightning strikes and others;
- power consumption - how much the device consumes and how long the built-in rechargeable battery or batteries are;
- penetration - the depth at which the instrument can detect metals;
- dimensions of the device;
- search area size - the area covered by the device without changing its location.
Resolution is the main parameter, in turn, it is also a composite one. The device outputs one or two signals, and there are more properties that determine the object and its location. For example, if you lower the frequency of the generator, you can achieve an increase in the search and penetration zone, but lose in sensitivity and mobility due to an increase in the size of the coil.
 Simple metal detector circuit
Simple metal detector circuit The design feature of the metal detector is that all of the above parameters in combination or separately depend on the frequency of the coil. Thus, this characteristic is decisive in the design of the device. By frequency, metal detectors are divided into the following:
- ultra-low-frequency: frequency up to several hundred hertz, low mobility, high power consumption, complex in design and signal processing;
- low-frequency: hundreds, thousands of Hz, the sensitivity is small, the noise immunity is large, the design is simple, the permeability depends on the power - from 1 to 4 m, mobile;
- high frequency: tens of kHz, the design is simple, the permeability is up to 1.5 m, the noise immunity is poor, the discrimination is so-so, the sensitivity is good;
- high-frequency: radio frequencies, typical for gold, excellent discrimination, low permeability, up to 80 cm, low consumption, other parameters are poor.
Device design
The device, which does not require absolutely any knowledge in radio engineering, can be assembled with your own hands, having: a calculator, a radio receiver, a box with a hinged lid made of plastic or cardboard, double-sided tape. The calculator should be as cheap as possible in order to serve as the basis for radio interference, and the receiver should not have noise immunity.
DIY metal detector, instructions:
- We unfold the box, forming a book out of it.
- We fix the calculator and receiver in the box, the last one in the lid.
- Turn on the receiver and look for a free area at the top of the AM range.
- We turn on the calculator: the receiver should emit a sound, set it to maximum volume.
- If there is no tone, adjust until it appears.
- We fold the lid so that the tone disappears. In this position, the magnetic vector of the primary pulses will be perpendicular to the axis of the magnetic antenna rod.
- We fix the cover.
Thus, it is quite simple to assemble a primitive device, but in order to get more data, you need to already have some knowledge and skills in radio electronics. On the Internet, you can find a suitable one from a variety of schemes.
Metal detector circuit
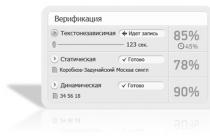
Today I would like to present to your attention a diagram of a metal detector, and everything that concerns it, what you see in the photo. After all, it is sometimes so difficult to find an answer to a question in a search engine - Diagram of a good metal detector
In other words, the metal detector has a name Tesoro eldorado
The metal detector can work in both the search for all metals and background discrimination.
Technical characteristics of the metal detector.
The principle of operation is inductively balanced
-Working frequency, kHz 8-10kHz
-Mode of work is dynamic
-Mode of accurate detection (Pin-Point) is in statics
-Power supply, 12
-Sensitivity level regulator is
-Threshold tone control is
-Ground balance is (manual)
Detection depth in the air with a DD-250mm sensor In the ground, the device sees targets almost the same as in the air.
-coins 25mm - about 30cm
- gold ring - 25cm
- helmet 100-120cm
-maximum depth 150cm
-Consumption current:
-Without sound about 30 ma
And the most important and intriguing is the scheme of the device itself.

The picture enlarges easily when you click on it
To assemble a metal detector, you need the following parts:
 So that you do not have to spend a long time setting up the device, do the assembly and soldering carefully, the board should not contain any clamps.
So that you do not have to spend a long time setting up the device, do the assembly and soldering carefully, the board should not contain any clamps.
For tinning boards, it is best to use rosin in alcohol, after tinning the tracks, do not forget to wipe the tracks with alcohol
Part side PCB


We start assembling from soldering jumpers, then resistors, further sockets for microcircuits and everything else. Another small recommendation, now with regard to the manufacture of the device board. It is highly desirable to have a tester that can measure the capacitance of capacitors. The fact is that the device that is, two identical amplification channels, therefore, the amplification along them should go as much as possible the same, and for this it is advisable to select those parts that are repeated on each amplification stage so that they have the most identical parameters as measured by the tester (that is, what are the readings in a particular stage on one channel - the same readings on the same cascade and in the other channel)
Making a coil for a metal detector
 Today I would like to talk about the manufacture of a sensor in a finished case, so the photo is more than words.
Today I would like to talk about the manufacture of a sensor in a finished case, so the photo is more than words.
We take the case, fix the sealed conductor in the right place and install the cable, ring the cable and mark the ends.
Next, we wind the coils. The DD-sensor is manufactured according to the same principle as for all balancers, therefore I will focus only on the required parameters.
TX - transmitting coil 100 turns 0.27 RX - receiving coil 106 turns 0.27 enameled winding wire.
After winding, the spools are tightly wound with threads, soaked in varnish.

After drying, they are tightly wrapped with electrical tape around the entire circumference. From above it is shielded with foil, between the end and the beginning of the foil there should be a gap of 1 cm uncovered by it, in order to avoid a short-circuited loop.
The coil can be shielded with graphite, for this we mix graphite with nitro varnish 1: 1 and cover it with a uniform layer on top of a tinned copper 0.4 wire wound on a coil (without gaps), connect the wire to the cable screen.
We put it in the case, connect and approximately bring the coils into balance, there should be a double beep on the ferrite, a single beep on the coin, if, on the contrary, we swap the terminals of the receiving winding. Each of the coils is tuned in frequency separately, there should not be any metal objects nearby !!! The coils are tuned with an attachment for measuring resonance. We connect the attachment to the Eldorado board in parallel with the transmitting coil and measure the frequency, then with the RX coil and the selected capacitor we achieve a frequency 600 Hz higher than that in TX.
After selecting the resonance, we put the coil together and check whether the device sees the entire VDI scale from aluminum foil to copper, if the device does not see the entire scale, then we select the capacity of the resonant capacitor in the RX circuit with a step of 0.5-1nf in one direction or another, and then the moment when the device sees foil and copper at the minimum of discrimination, and when the discrimination is turned on, the entire scale will be cut out in turn.

Finally, we reduce the coils to zero, fixing everything with hot melt glue. Then, to facilitate the coil, glue the voids with pieces of foam, the foam sits on the hot melt glue, otherwise it will float up after pouring the coil.
Fill in the first layer of epoxy without adding 2-3mm to the top

We fill in the second layer of resin with a color scheme. Aniline dye is well suited for dyeing fabrics, the powder comes in different colors and costs a penny. The dye must first be mixed with the hardener, then add the hardener to the resin, the dye will not dissolve immediately in the resin.
Begin the correct assembly of the board by checking the correct power supply to all nodes.
Take the circuit and the tester, turn on the power on the board, and referring to the diagram, walk the tester through all the points of the nodes where power should be supplied.
When the discrim knob is at minimum, the device should see all non-ferrous metals.
, when winding the discrim, they should be cut
all metals in order to copper should not be cut if the deviceThis is how it works, so it is configured correctly. The discrimination scale must be selected in such a way that it completely fits into a full turn of the discrimination knob, this is done by selecting c10. When the capacity decreases, the scale is stretched and vice versa.
I can say without a doubt that this is the simplest metal detector I have ever seen. It is based on only one TDA0161 microcircuit. You will not need to program anything - just build and that's it. Also, its huge difference is that it does not emit any sounds during operation, unlike the metal detector on the NE555 microcircuit, which initially squeaks unpleasantly and you need to guess about the found metal by its tonality.
In this circuit, the buzzer only starts beeping when it detects metal. The TDA0161 microcircuit is a specialized industrial version for inductive sensors. And on it, metal detectors are mainly built for production, which give a signal when the metal approaches the induction sensor.
You can buy such a microcircuit at -
It is not expensive and is quite affordable for everyone.
Here is a diagram of a simple metal detector

Metal detector characteristics
- Microcircuit supply voltage: from 3.5 to 15V
- Generator frequency: 8-10 kHz
- Current consumption: 8-12 mA in alarm mode. In the search state, approximately 1 mA.
- Working temperature: -55 to +100 degrees Celsius
A battery from an old cell phone works well for power.
Coil: 140-150 turns. The diameter of the coil is 5-6 cm. Can be converted to a coil with a larger diameter.

The sensitivity will depend directly on the size of the search coil.
In the circuit, I use both light and sound alarms. You can choose one if you like. Buzzer with internal generator.
Thanks to this simple scheme, you can make a pocket metal detector or a large metal detector, whichever is more necessary for you.
After assembly, the metal detector works immediately and does not need adjustments, with the exception of setting the response threshold with a variable resistor. Well this is standard procedure for a metal detector.
So friends, collect the thing you need and, as they say, fit in the household. For example, to search for electrical wiring in the wall, even nails in a log ...
Everyone can assemble such an apparatus, even those who are completely far from electronics, you just need to solder all the parts as in the diagram. The metal detector consists of two microcircuits. They do not require any firmware or programming.
Power supply 12 volts, it is possible from finger-type batteries, but better than a 12V battery (small)
The coil is wound on a 190mm mandrel and contains 25 turns of PEV 0.5 wire
Specifications:
- Current consumption 30-40 mA
- Reacts to all metals no discrimination
- Sensitivity 25 mm coin - 20 cm
- Large metal objects - 150 cm
- All parts are not expensive and readily available.
List of required parts:
1) Soldering iron
2) Textolite
3) Wires
4) Drill 1mm
Here is a list of the parts you need.

Diagram of the metal detector itself

The circuit uses 2 microcircuits (NE555 and K157UD2). They are quite common. K157UD2 - can be wiped out from old equipment, which I successfully did




Capacitors 100nF be sure to take film, these are the ones, we take the voltage as little as possible

We print a sketch of the board on plain paper

Cut out a piece of PCB for its size.

Apply tightly and with a sharp object push through the places of future holes

This is how it should work out.

Next, we take any drill or drilling machine and drill holes


After drilling, you need to draw the tracks. You can do it through, or just paint them with Nitro varnish with a simple brush. The tracks should look exactly the same as on the paper template. And we poison the board.

In the places marked in red, put jumpers:


Next, we just solder all the components into place.
For K157UD2, it is better to put an adapter socket.



To wind the search coil, you need a copper wire with a diameter of 0.5-0.7 mm

If there is none, you can use another. I didn’t have enough lacquered copper wire. I took an old network cable.

He took off the shell. There were enough wires. Two veins were enough for me, they also wound the coil.


According to the scheme, the coil is 19 cm in diameter and contains 25 turns. Immediately, I note that the coil needs to be made of this diameter based on what you will be looking for. The larger the coil, the deeper the search, but the larger coil does not see fine details well. The small coil sees fine details well, but the depth is not great. I immediately wound myself three coils of 23cm (25 turns), 15cm (17 turns) and 10cm (13-15 turns). If you need to dig up scrap metal, then put a large one, if you look for small things on the beach, then the coil is smaller, well, you will figure it out yourself.
We wind the coil on anything of a suitable diameter and wrap it tightly with electrical tape so that the turns are tightly next to each other.


The coil should be as flat as possible. The speaker took the first one that came across.
Now we connect everything and try the circuit for performance.
After turning on the power, you need to wait 15-20 seconds for the circuit to warm up. We put the coil away from any metal, it is best to hang it in the air. Then we begin to twist the variable resistor 100K until clicks appear. As soon as the clicks appear, we twist in the opposite direction, as soon as the clicks disappear, that's enough. After that, we also adjust the 10K resistor.
At the expense of the K157UD2 microcircuit. In addition to the one that I picked out, I asked a neighbor for 1 more and bought two on the radio market. I inserted the purchased microcircuits, turned on the device, and he refused to work. I racked my brains for a long time until I just put another microcircuit (the one that I dropped out). And everything worked right away. So that's what a transitional socket is for, to pick up a live microcircuit and not suffer with desoldering and soldering.
Purchased microcircuits