Page 2 of 2
V article considered principle actions and device contemporary laser printers. She opens series articles, dedicated principles and problems laser fees.
The image obtained with the help of modern laser printers (as well as matrix and inkjet) consists of dots (dots). The smaller these dots and the more frequently they are located, the higher the image quality. The maximum number of dots that the printer can separately print on a segment of 1 inch (25.4 mm) is called resolution and is characterized in dots per inch, while the resolution can be 1200 dpi or more. The quality of the text printed on a laser printer with a resolution of 300 dpi is approximately the same as a typographic one. However, if the page contains graphics containing grayscale, then a resolution of at least 600 dpi is required to obtain a high-quality graphic image. With a printer resolution of 1200 dpi, the print is almost photographic quality. If you need to print a large number of documents (for example, more than 40 sheets per day), a laser printer seems to be the only reasonable choice, since 600 dpi resolution and a print speed of 8 ... 1 2 pages per minute are standard parameters for modern personal laser printers.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF A LASER PRINTER
The first laser printer was introduced by Hewlett Packard. It used the electrographic principle of creating images - the same as in copiers. The difference was in the method of exposure: in copiers it occurs with the help of a lamp, and in laser printers, the light of the lamp has replaced the laser beam.
The heart of a laser printer is a photoconductive cylinder (Organic Photo Conductor), which is often called a print drum or simply a drum. It is used to transfer the image to paper. The photoconductor is a metal cylinder covered with a thin film of a photosensitive semiconductor. The surface of such a cylinder can be provided with a positive or negative charge, which is maintained as long as the drum is not illuminated. If any part of the drum is exposed, the coating becomes conductive and the charge flows from the illuminated area, forming an uncharged zone. This is a key point in understanding how a laser printer works.
Another important part of the printer is the laser and the optical-mechanical system of mirrors and lenses that moves the laser beam along the surface of the drum. The small-sized laser generates a very thin light beam. Reflected from rotating mirrors (usually tetrahedral or hexagonal in shape), this beam illuminates the surface of the photoconductor, removing its charge at the exposure point.

To obtain a dot image, the laser is turned on and off using a control microcontroller. The rotating mirror unfolds the beam as a line of latent image on the surface of the photoconductor.
After the formation of the line, a special stepper motor turns the drum to form the next one. This offset corresponds to the vertical resolution of the printer and is usually 1/300 or 1/600 of an inch. The process of formation of the latent image on the drum resembles the formation of a raster on the screen of a television monitor.
Two main methods of preliminary (primary) charge of the photocylinder surface are used:
Ø using a thin wire or mesh called "corona wire". A high voltage applied to the wire causes a glowing ionized area around it, called the corona, and gives the drum the necessary static charge;
Ø using a pre-charged rubber roller (PCR).
So, an invisible image is formed on the drum in the form of statically discharged dots. What's next?
DEVICECARTRIDGE
Before we talk about the process of transferring and fixing an image on paper, let's consider the design of a cartridge for a Hewlett Packard Laser Jet 5L printer. There are two main compartments in this typical cartridge: the waste toner compartment and the toner compartment.
The main structural elements of the waste toner compartment:
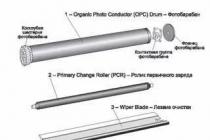
1 - photoconductor(Organic Photo Conductor (OPC) Drum). It is an aluminum cylinder coated with an organic light-sensitive and photoconductive material (usually zinc oxide), which is able to preserve the image applied by the laser beam;
2 - Shaft primary charge(Primary Charge Roller (PCR)). Provides uniform negative drum charge. It is made of a conductive rubber or foam base applied to a metal shaft;
3 - « Viper» , squeegee, cleaning blade(Wiper Blade, Cleaning Blade). Cleans the drum of toner residue that has not been transferred to the paper. Structurally made in the form of a metal frame (stamping) with a polyurethane plate (blade) at the end;
4 - Blade cleaning (Recovery Blade). Covers the area between the drum and the waste toner box. The Recovery Blade lets the toner left on the drum into the hopper and prevents it from spilling out in the opposite direction (from the hopper to the paper).

The main structural elements of the toner compartment:
1 - Magnetic shaft(Magnetic Developer Roller, Mag Roller, Developer Roller). It is a metal tube with a non-moving magnetic core inside. Toner is attracted to the magnetic shaft, which, before being fed to the drum, acquires a negative charge under the action of a constant or alternating voltage;
2 - « Doctor» (Doctor Blade, Metering Blade). Provides even distribution of a thin layer of toner on the magnetic roller. Structurally made in the form of a metal frame (stamping) with a flexible plate (blade) at the end;
3 - Sealing blade magnetic shaft(Mag Roller Sealing Blade). A thin plate similar in function to the Recovery Blade. Covers the area between the magnetic roller and the toner supply compartment. Mag Roller Sealing Blade allows toner remaining on the magnetic roller to enter the compartment, preventing toner from leaking in the opposite direction;
4 - Bunker for toner (toner Reservoir). Inside it is the "working" toner, which will be transferred to the paper during the printing process. Besides, the activator of a toner (Toner Agitator Bar) - the wire frame intended for hashing of a toner is built in the bunker;
5 - Seal, check (Seal). In a new (or regenerated) cartridge, the toner hopper is sealed with a special seal that prevents toner from spilling during transportation of the cartridge. This seal is removed prior to use.

PRINCIPLE OF LASER PRINTING
The figure shows the cartridge in section. When the printer is turned on, all components of the cartridge begin to move: the cartridge is being prepared for printing. This process is similar to the printing process, but the laser beam does not turn on. Then the movement of the cartridge components stops - the printer enters the ready-to-print state.
After sending a document for printing, the following processes take place in the laser printer cartridge:

Charger drum. The primary charge roller (PCR) evenly transfers negative charge to the surface of the rotating drum.

Exposure. The negatively charged surface of the drum is only exposed to the laser beam where the toner will be applied. Under the action of light, the photosensitive surface of the drum partially loses its negative charge. Thus, the laser exposes the latent image to the drum in the form of dots with a weakened negative charge.

Application toner. At this stage, the latent image on the drum is converted by toner into a visible image that will be transferred to paper. The toner located near the magnetic roller is attracted to its surface under the influence of the field of a permanent magnet, from which the core of the roller is made. When the magnetic shaft rotates, the toner passes through a narrow slot formed by the "doctor" and the shaft. As a result, it acquires a negative charge and sticks to those parts of the drum that have been exposed. "Doctor" ensures uniform application of toner on the magnetic roller.

Transfer toner on the paper. Continuing to rotate, the drum with the developed image comes into contact with the paper. On the reverse side, the paper is pressed against the Transfer Roller, which carries a positive charge. As a result, the negatively charged toner particles are attracted to the paper, which produces an image "poured" with toner.

Anchoring Images. A sheet of paper with an unfixed image moves to the fixing mechanism, which consists of two contiguous shafts, between which the paper is pulled. The lower shaft (Lower Pressure Roller) presses it against the upper shaft (Upper Fuser Roller). The top roller is heated, and upon contact with it, the toner particles are melted and fixed on the paper.

cleaning drum. Some of the toner does not transfer to the paper and remains on the drum, so it needs to be cleaned. This function is performed by the viper. Any toner remaining on the drum is wiped off by the wiper into the waste toner box. At the same time, the Recovery Blade closes the area between the drum and the hopper, preventing toner from spilling onto the paper.

"Erasing" Images. At this stage, the latent image applied by the laser beam is "erased" from the surface of the drum. With the help of the primary charge roller, the surface of the photoconductor is evenly "covered" with a negative charge, which is restored in those places where it was partially removed under the influence of light.
Today I want to talk about device and principle of operation of a laser printer. Everyone is familiar with this device, but few people know about the principle of its operation and the causes of its malfunctions. In this article I will try to clearly talk about the principle of operation of "laser printers", and in subsequent articles about malfunctions of laser printers, about the reason for their appearance, and about how to eliminate them.
Laser printer device
At the heart of any modern laser printer is a photoelectricprinciple xerography. Based on this method, all laser printers structurally consist of three main parts (assemblies):
- Laser sanitizing unit.
- Image transfer unit.
- Node for fixing the image.
The image transfer unit usually refers to the laser printer cartridge and charge transfer roller (Transferroller) in the printer itself. We will talk about the device of the “laser” cartridge later in more detail, and in this article we will consider only the principle of operation. It should also be noted that instead of laser scanning in some printers (mainly from OKІ» ) LED scanning is applied. It performs the functionseHowever, only the role of the laser is performed by LEDs.
For example, consider laser printer HP LaserJet 1200 (Fig. 1.). The model is quite successful and well-proven for its long service life, convenience and reliability.
We print on any material (mainly paper), and the paper feed unit is responsible for sending it to the “mouth” of the printer. As a rule, it is divided into two types that are structurally different from each other. Lower Tray Feeder, is called - Tray 1, and feeding mechanism from the top(bypass) - Tray 2. Despite the structural differences in their composition, they have (see Fig. 3):
- Pickup Roller- needed to pull paper into the printer,
- Block brake pad and separator needed to separate and pick up only one sheet of paper.
Directly involved in the formation of the image printer cartridge(Fig. 4) and laser scanning unit.
The cartridge for laser printers consists of three main elements (see Fig. 4):
Photocylinder,
precharge shaft,
magnetic shaft.
photo cylinder
photo cylinder(ORS- organicphotoconductivedrum), or also photoconductor, is an aluminum shaft coated with a thin layer of photosensitive material, which is additionally covered with a protective layer. Previously, photocylinders were made on the basis of selenium, so they were also called selenium shafts, are now made from photosensitive organic compounds, but their old name is still widely used.
Main property photocylinder– change the conductivity under the influence of light. What does it mean? If the photocylinder is given some kind of charge, it will remain charged for quite a long time, however, if its surface is illuminated, then in places of illumination the conductivity of the photocoating increases sharply (resistance decreases), the charge "flows" from the surface of the photocylinder through the conductive inner layer in this place a neutrally charged region will appear.
Rice. 2 HP 1200 Laser Printer with cover removed.
The numbers indicate: 1 - Cartridge; 2 - Image transfer unit; 3 - Node for fixing the image (stove).

Rice. 3 Paper feed unitTray 2 , rear view s.
1 - Paper pickup roller; 2 - Braking pad (blue stripe) with a separator (not visible in the photo); 3 - Charge transfer roller (transferroller), transmitting paper static charge.

Rice. 4 Disassembled laser printer cartridge.
1- Photocylinder; 2- Precharge shaft; 3- Magnetic shaft.
Image overlay process.
Photo cylinder with pre-charge shaft (PCR) receives an initial charge (positive or negative). The amount of charge itself is determined by the print settings of the printer. After the photocylinder is charged, the laser beam passes over the surface of the rotating photocylinder, and the places where the photocylinder is illuminated become neutrally charged. These neutral areas correspond to the desired image.
The laser scanning unit consists of:
semiconductor laser with focusing lens,
- Rotating mirror on the motor,
- Forming lens groups,
- Mirrors.

Rice. 5 Laser scanning unit with cover removed.
1,2 - Semiconductor laser with focusing lens; 3- rotating mirror; 4- Forming lens group; 5- Mirror.
The drum has direct contact magnetic shaft m (Magneticroller), which supplies toner from the cartridge hopper to the photo cylinder.
The magnetic shaft is a hollow cylinder with a conductive coating, inside which a permanent magnet rod is inserted. The toner located in the hopper in the hopper is attracted to the magnetic shaft under the influence of the magnetic field of the core and an additionally applied charge, the value of which is also determined by the print settings of the printer. This determines the density of future printing. From the magnetic shaft, under the action of electrostatics, the toner is transferred to the image formed by the laser on the surface of the photocylinder, since it has an initial charge, it is attracted to the neutral areas of the photocylinder and repelled from equally charged ones. This is the image we need.
There are two main mechanisms for creating an image. Most printers (HP,Canon, Xerox) a toner with a positive charge is used, remaining only on the neutral surfaces of the photocylinder, that is, the laser illuminates only those areas where the image should be. The photo cylinder in this case is negatively charged. The second mechanism (used in printersEpson, Kyocera, Brother) is to use a negatively charged tuner, and the laser discharges areas of the photocylinder that should not have toner. The photo cylinder initially receives a positive charge and the negatively charged toner is attracted to the positively charged areas of the photo cylinder. Thus, in the first case, a finer transfer of details is obtained, and in the second, a denser and more uniform fill. Knowing these features, you can more accurately select a printer for solving your problems (printing text or printing sketches).
Before contact with the photo cylinder, the paper also receives a static charge (positive or negative), via the charge transfer roller (Transferroller). Under the influence of this static charge, the toner transfers from the photo of the cylinder to the paper during contact. Immediately after this, the static charge remover removes this charge from the paper, which eliminates the attraction of the paper to the photo cylinder.
Toner
Now we need to say a few words about the toner. Toner is a finely dispersed powder consisting of polymer balls coated with a layer of magnetic material. The composition of the color tuner also includes dyes. Each company in its models of printers, MFPs and copiers uses original toners that differ in dispersion, a magnetnawn and physical properties. Therefore, in no case should you refill cartridges with random toners, otherwise you can ruin your printer or MFP very quickly (verified by experience).
If, after passing the paper through the laser scanning unit, remove the paper from the printer, we will see an image that has already been formed, which can be easily destroyed by touch.
Image fixation unit or "stove"
In order for an image to become durable, it must be fix. Image freeze occurs with the help of additives that are part of the toner, having a certain melting point. The third main element of the laser printer is responsible for fixing the image (Fig. 6) - image fixation unit or "stove". From a physical point of view, fixation is carried out by pressing the molten toner into the paper structure and its subsequent solidification, which gives the image durability and good resistance to external influences.

Rice. 6 Image fixation unit or stove. Top view assembled, bottom with paper separator bar removed.
1 - Thermal film; 2 - Pressure shaft; 3 - Paper separator bar.

Rice. 7 Heating element and thermal film.
Structurally, the “stove” can consist of two shafts: the upper one, inside which there is a heating element, and the lower shaft, which is necessary for pressing the molten toner into the paper. In the HP 1200 printer under consideration, the “stove” consists of thermal films(Fig. 7) - a special flexible, heat-resistant material, inside of which there is a heating element, and a lower pressure roller, which presses the paper due to the support spring. Monitors the temperature of the thermal film temperature sensor(thermistor). Passing between the thermal film and the pressure roller, the paper heats up to approximately 200 ° C at the points of contact with the thermal film.˚ . At this temperature, the toner melts and in liquid form is pressed into the texture of the paper. So that the paper does not stick to the thermal film, there are paper separators at the exit from the oven.
Here's what we've looked at - How does a printer work. This knowledge will help us in the future to find out the causes of breakdowns and eliminate them. But in no case should you climb into the printer yourself if you are not sure that you can fix it, this will only make it worse. It is better not to save money, but to entrust this matter to professionals, because buying a new printer will cost you much more.
In a printer based on laser printing technology, everything works by using static electricity. How it works? A laser beam hits the photoconductor in the cartridge and forms an image. At the next stage of image formation, the photoconductor comes into contact with the toner and at the point of contact, where the laser shone and changed the charge, the toner sticks. By the same principle, toner sticks to the paper from the photodrum, and then it is baked in the so-called “stove”. The paper comes out warm from the stove. Don't worry, it's already a little cold.
Learn more about the laser printer printing process
When the photosensitive drum rotates, a positive charge is formed on its surface, which is applied to the photo roller using a laser beam. The positive charge attracts the toner particles, which are negatively charged, and they adhere to the surface of the drum.
The sheet of paper is positively charged and passes under the rotating photo roller during the printing process. Negatively charged toner particles are transferred from the drum to the sheet of paper, thus the image is transferred to the paper. Further, the toner, which is on the paper, is fixed under the influence of heat.
Unlike printing on dot-matrix and inkjet printers, where the image is transferred to paper line by line, with laser printing, the text on an A4 sheet is formed in just 3 turns of the drum unit.
Laser printers are based on the printing system used in copiers. In copiers, a special lamp transfers the image from the copied sheet to the photosensitive surface of the drum in the form of an electrostatic charge. The photoconductor converts the optical image created by the light reflected from the copied image into its electrostatic equivalent, which attracts toner particles with the opposite charge to the surface of the drum.

However, the laser printer does not have the original image; instead, it has a matrix of 1s and 0s in its memory that transmits the image. In the case of black and white printing, 1 sends a signal to the microprocessor and a laser beam is directed to the photoconductor. When the beam touches the surface of the drum, a positive charge is formed in this place, and negatively charged toner particles will adhere to the drum in this very place. Accordingly, 0 does not transmit a signal and no charge appears on the surface of the drum, and later these areas will remain white on paper. How to get rid of white stripes when printing, read the article -
It is difficult to imagine modern life without a printer. Scripts are printed in schools, abstracts are printed at the university, contracts are printed at work, and even at home it is extremely necessary for us to transfer this or that information to paper. There are several types of printers, they are classified by type of printing, by format, by size, and even by type of printed materials. Consider the principle of printing inkjet and laser printers.
How an inkjet printer works
We will try to highlight the principle of printing an inkjet printer briefly. Its print quality is slightly worse than that of a laser. However, their cost is much lower than that of laser ones. An inkjet printer is ideal for home use. It is easy to operate and easy to maintain. The principle of printing inkjet and laser printers are markedly different. This is manifested both in the ink supply technology and in the design of the equipment. Therefore, let's first talk about how an inkjet printer prints.
Its principle of operation is as follows: an image is formed in a special matrix, and then this matrix prints the image on the canvas using liquid dyes. Another type of inkjet printer is equipped with cartridges that are installed in a special unit. In this case, with the help of the print head, ink is supplied to the print matrix, and it transfers the image to paper.
Methods for storing ink and applying it to paper

There are three ways to apply ink to a canvas:
Piezoelectric method;
. gas bubble method;
. drop-on-demand method.
The first method, when printed, leaves an ink dot on the canvas, due to the piezoelectric element. With its help, the tube is compressed and unclenched, preventing excess ink from getting onto the paper.
Gas bubbles, also known as injected bubbles, leave an imprint on the web due to high temperatures. Each nozzle of the printing matrix is equipped with which heats up in a fraction of a second. The resulting gas bubbles are pushed through the nozzle and transferred to the consumable.
The drop-on-demand method also uses gas bubbles in the process. But it is a more streamlined technology that greatly increases the speed and quality of modern printing.
An inkjet printer stores ink in two ways. There is a separate removable tank from which ink is supplied to the print head. The second way to store ink uses a special cartridge, which is also located in the print head. To replace the cartridge, you must also replace the head itself.
Let's talk about inkjet printers

Inkjet printers have gained particular popularity due to the possibility When printing, the image is formed by superimposing the main tones on each other of different saturation. The set of primary colors bears the abbreviation CMYK. It includes: yellow, magenta, cyan and black.
Initially, a three-color set was offered, which included all of the above tones, except for the black shade. But when overlaying yellow, cyan and magenta, at 100% saturation, it was not possible to achieve black. The result was a brown or gray color. Therefore, it was decided to add black ink.
Features of the inkjet printer

The main indicators of the quality of the printer include noise, print speed, print quality and durability.
Operational properties of the printer:
- Printing principle - inkjet. The ink is fed through special nozzles and printed on the canvas. Unlike needle printers, where applying ink is a shock-mechanical process, inkjet printers are very quiet. How the printer prints is not audible, you can only distinguish the noise of the engine that moves the print heads. does not exceed 40 dB.
- The print speed of an inkjet printer is much faster than that of a needle printer. The print quality also depends on this indicator. Printer printing principle: the higher the speed, the worse the print. If you choose high quality printing, the process slows down and the ink is applied more thoroughly. The average of such a printer is approximately 3-5 pages per minute. More modern models have increased this figure to 9 pages per minute. Color printing takes a little longer.
- The font is one of the main advantages of an inkjet printer. The quality of font display can only be compared with a laser printer. You can improve print quality by using good quality paper. It should have fast absorbing properties. A good image is obtained on paper with a density of 60-135g / m². Copier paper with a density of 80 g / m² also showed itself well. For fast drying of ink use function of heating of paper. Despite the fact that the principle of printing an inkjet and a laser printer is completely different, high-quality equipment allows you to achieve a similar effect.
- Paper. Unfortunately, the inkjet printer is not designed to print on roll media. And to get multiple copies, you will have to use multiple printing.
Disadvantages of Inkjet Printing
As it turned out above, inkjet printers print with liquid dyes using a matrix. The image is formed from dots. The most expensive part in a printer is the print head, some companies have integrated the print head of the printer into the cartridge to reduce the overall dimensions of the device. The principle of printing inkjet and laser printers are significantly different from each other.
The disadvantages of such a printer include:
- Low print speed.
- If the printer has not been used for a long time, the ink may dry out.
- Consumables have a high cost and a small resource.
Benefits of Inkjet Printing
- Attractive price, perfect price-performance ratio.
- The printer has very modest dimensions, which allows it to be placed in a small office without creating inconvenience to the user.
- Cartridges are easy to refill yourself, just buy ink and read the instructions.
- Connectivity With large print volumes, this will significantly reduce costs.
- High quality photo printing.
- Wide range of print media.
A little about the laser printer

A laser printer is a type of equipment designed to print text or images on paper. The history of this type of equipment is very unusual. And it has a marketing approach, unlike an inkjet printer, during the creation of which hundreds of scientific concepts were developed.
It was not until 1969 that Xerox began to develop the principle of printing a laser printer. For several years, scientific work was carried out, many methods were used to improve the existing apparatus. In 1978, the first copier appeared in the world, which used a laser beam to create a print. The printer turned out to be huge, and the price did not allow anyone to purchase this unit. After some time, Canon became interested in the development, and in 1979 the first desktop laser printer was released. After a lot of companies started optimizing copiers and releasing new models, however, the principle of printing a laser printer has not changed.
How a laser printer prints

Prints obtained in this way have high performance characteristics. Moisture is not terrible for them, they are not afraid of erasing and fading. Images obtained in this way are very high quality and durable.
Printing principle of laser printer briefly:
- The laser printer applies the image to the canvas in several stages. The toner (special powder) melts and sticks to the paper under the influence of temperature.
- A squeegee (special scraper) removes unused toner from the drum into the waste accumulator.
- The caronator polarizes the surface of the drum, and by means of electrostatic forces assigns a positive or negative charge to it.
- The image is formed on the surface of the drum using a rotating mirror that directs it to the right place.
- The drum moves along the surface of the magnetic shaft. There is toner on the shaft, which sticks to those places on the drum where there is no charge.
- After the drum rolls over the paper, leaving the toner on the canvas.
- At the final stage, the paper with the toner sprayed on it is rolled through the oven, where the substance melts under the influence of high temperatures and reliably adheres to the paper.
The printing principle of a laser printer has much in common with the technology used in copiers.
Color laser printers and their main differences

The process of printing on a color printer differs from black and white by the presence of several shades, which, when mixed in a certain proportion, are able to recreate all the colors known to us. Color laser printers use four separate compartments for each ink color. This is their main difference.
Printing on a color printer consists of the following steps: image analysis, its raster image, the arrangement of colors and their corresponding toners. Then the charge distribution is formed. After the procedure is the same as for black and white printing. The ink sheet passes through an oven where the toners are melted and firmly bonded to the paper.
Their advantage lies in the fact that the principle of printing a laser printer allows you to achieve very thin beams that discharge the desired areas. As a result, we get a very high-quality high-resolution image.
Advantages of modern laser printers
The benefits of laser printers include:
- High print speed.
- Persistence, clarity and endurance of prints (they are not afraid of a humid microclimate).
- High resolution image.
- Low printing cost.
Disadvantages of laser printer printing

The main disadvantages of laser printers:
- During operation of the equipment, ozone is released. So, you need to work with him in a well-ventilated area.
- High power consumption.
- Bulky.
- High cost of equipment
Based on all the pros and cons, we can conclude that inkjet printers are great for home use. They have an affordable price and small dimensions, which is important for many users.
A laser printer is suitable for offices and other institutions where there are a lot of black and white printouts and document processing speed is important.
The history of laser printers began in 1938 with the development of dry ink printing technology. Chester Carlson, while working on inventing a new way to transfer images to paper, used static electricity. The method was called electrography and was first used by the Xerox Corporation, which released the Model A copier in 1949. However, for this mechanism to work, some operations had to be done manually. 10 years later, the fully automatic Xerox 914 was created, which is considered the prototype of modern laser printers.
The idea to "draw" what should be printed later directly on the copy drum with a laser beam belongs to Gary Starkweather. Since 1969, the company has been developing and in 1977 released the Xerox 9700 serial laser printer, which printed at a speed of 120 pages per minute.
The device was very large, expensive, intended exclusively for enterprises and institutions. And the first desktop printer was developed by Canon in 1982, a year later - a new model LBP-CX. HP partnered with Canon to launch the Laser Jet series in 1984 and immediately took the lead in the home laser printer market.
Currently, monochrome and color printers are produced by many corporations. Each of them uses its own technologies, which can vary significantly, but the general principle of operation of a laser printer is typical for all devices, and the printing process can be divided into five main stages.
Photoconductor charge
The print drum (Optical Photoconductor, OPC) is a metal cylinder coated with a photosensitive semiconductor on which an image is formed for subsequent printing. Initially, the OPC is supplied with a charge (positive or negative). You can do this in one of two ways using:
- coronator (Corona Wire), or coronator;
- charge roller (Primary Charge Roller, PCR), or charging shaft.
Corotron is a block of wire and a metal frame around it.
The corona wire is a tungsten filament with a carbon, gold or platinum coating. Under the action of high voltage between the wire and the frame, a discharge occurs, a luminous ionized area (crown), an electric field is created that transfers a static charge to the photoconductor.
Usually, a wire cleaning mechanism is built into the unit, since its contamination greatly degrades print quality. Using a corotron has certain disadvantages: scratches, accumulation of dust, toner particles on the filament or bending of the filament can lead to an increase in the electric field in this place, a sharp decrease in the quality of printouts, and possibly damage to the surface of the drum.
In the second version, the supporting structure with the heating element inside is wrapped by a flexible film made of a special heat-resistant plastic. The technology is considered less reliable, used in printers for small businesses and home use, where heavy equipment loads are not expected. To prevent the sheet from sticking to the oven and twisting it around the shaft, a bar with paper separators is provided.
Color print
Four primary colors are used to form a color image:
- black,
- yellow,
- purple,
- blue.
Printing is carried out according to the same principle as black and white, but first the printer breaks the picture to be obtained into monochrome images for each of the colors. In the process of work, color cartridges transfer their drawings to paper, and their imposition on each other gives the final result. There are two color printing technologies.
Multipass
With this method, an intermediate carrier is used - a shaft or a toner transfer belt. In one revolution, one of the colors is applied to the tape, then another cartridge is fed into the right place and the second image is superimposed on top of the first image. In four passes, a complete image is formed on the intermediate carrier, which is transferred to paper. The print speed of a color image in printers using this technology is four times slower than a monochrome one.
single pass
The printer includes a complex of four separate printing mechanisms under common control. The color and black cartridges are lined up, each with a separate laser unit and transfer roller, and the paper passes under the photoconductors, sequentially collecting all four monochrome images. Only after that the sheet enters the oven, where the toner is fixed on the paper.

Print with pleasure.